Fibrosis can occur in a variety of organs. Several
tissues and organs have been found to be affected by fibrosis in
clinical practice, including the liver, kidney, lung, heart and
skin (1,2). The global annual incidence of
fibrosis-related diseases is ~1 in 20, affecting nearly a quarter
of the world's population and causing a substantial disease burden
(3). Human health is seriously
threatened by fibrotic diseases. The diverse structural
characteristics and microenvironments of different organs and
tissues in the human body contribute to discrepancies in the
fibrosis process (4). Despite
the growing research on fibrosis, the portrayal of the mechanisms
of fibrosis remains incomplete. There are still many questions that
need to be continuously discussed, so developing targeted therapies
for fibrotic diseases remains challenging.
Autophagy, also known as type II programmed cell
death, is a dynamic biological process in which cells utilize
lysosomes to selectively remove damaged, aged or excess
biomolecules and organelles, thereby releasing free small molecules
for cellular recycling and utilization. It is regarded as an
essential mechanism for the body's self-protection (5). Almost all eukaryotic cells
demonstrate a basal level of autophagy.
Recent research confirms that autophagy is critical
to fibrotic disease progression (6,7).
Autophagy can affect fibrosis through various pathways. For
instance, macrophage autophagy could inhibit fibrosis progression,
while endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) may promote fibrosis
progression by impacting autophagy (8-10). Furthermore, autophagy has a
crucial role in the progression of fibrotic diseases by mediating
endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) (11). Autophagy can also have an impact
on fibrotic disease development by prompting cells to produce
secretory phenotypes and regulating the secretion of inflammatory
factors. Increasing evidence suggests that autophagy-related
processes can affect the initiation and progression of fibrosis,
which can assist in driving the development of antifibrotic
medicines based on inhibiting or promoting autophagy. In this
review, the different roles of autophagy during fibrosis
progression and the potential of autophagy and autophagy-related
processes as therapeutic targets for fibrosis were dissected and
discussed.
Microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA)
and macroautophagy are the three forms of autophagy in mammalian
cells. In spite of the differences among the three types of
autophagy, the basic functions and features are merging with cargo
at the lysosome for degradation and recycling (12,13). Microautophagy involves lysosomes
directly engulfing cytoplasmic components, mainly smaller
organelles within the cell. Microautophagy can be either selective
or non-selective, is capable of degrading entire organelles and can
be activated by signals such as environmental stress. The main
function of microautophagy is to remove dysfunctional intracellular
proteins and organelles (13-15). CMA utilizes heat shock proteins
and transporter proteins on the lysosomal membrane to degrade
proteins expressing targeting motifs. Molecular chaperones such as
heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 8/HCS70 recognize the
targeting motif and transfer the protein to the lysosomal membrane.
At the lysosomal membrane, the target binds to lysosomal-associated
membrane protein (LAMP)-2A on the lysosome and is subsequently
transferred to the lysosomal lumen for degradation (13,16). Macroautophagy is the most common
form of autophagy. Macroautophagy primarily targets larger
organelles, removing intracellular waste and damaged organelles.
The central process of macroautophagy involves the formation of
autophagosomes by the encapsulation of lipid membrane structures
around the substrates designated for degradation. Autophagosomes
fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes after the phagocytosis of
cytoplasmic material. Thus, the substrate undergoes degradation
(13,17).
Autophagy is a dynamic and complex process (if not
specified, the form of autophagy discussed in this paper refers to
macroautophagy). The macroautophagy process can be summarized in
four steps: Initiation, autophagosome formation, autophagolysosome
formation and autophagolysosomal degradation (18). i) Autophagy initiation: This
stage comprises the generation and expansion of phagocytic
vesicles. This step involves two protein complexes: The vacuolar
protein sorting 34 (VPS34) complex [VPS34, BECLIN1,
autophagy-related 14 (ATG14) and VPS15] and the Unc51-like kinase 1
(ULK1) complex (19). ii)
Autophagosome formation: During this process, phagocytic vesicle
expansion occurs, and two ubiquitin-like binding systems regulate
the expansion and completion of autophagosomes: The
ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L system and the ATG8/microtubule-associated
protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) system (18). Ubiquitin-like system
ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L: ATG16L interacts with ATG5-ATG12 to form
ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L, which adheres to autophagosomes and participates
in the extension of autophagic precursor membranes (20,21). ATG8/LC3 ubiquitin-like system:
LC3 is ATG8's mammalian homologue, and ATG4 cleaves it into
cytoplasmic LC3-I (the cytosolic form of LC3). During the formation
of autophagosomes, cytosolic LC3-I participates in ubiquitin-like
reactions through interactions with ATG7 and ATG3 and then couples
with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to generate lipidated LC3-II
(the conjugate form of LC3-I with PE). As an autophagosome
structural protein, LC3-II is attached to the membrane of
autophagosomes. Subsequently, ATG4 excises LC3-II from the outer
membrane of autophagic lysosomes during the autophagic degradation
process, and the generated product, LC3-I, can be recycled. In
autophagic lysosomes, LC3-II on the inner membrane, along with
encapsulated content, is degraded by lysosomes (22). Unlike ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L, LC3B-II
is distributed on both the outer and inner surfaces of
autophagosomes. LC3B-II is essential for the extension and
completion of autophagic membranes. After autophagosome membrane
closure, the ATG16-ATG5-ATG12 complex detaches from the vesicle,
but part of LC3B-II still covalently binds to the membrane. Thus,
LC3B-II is currently the most widely recognized molecular marker
(21,23). iii) Autophagy lysosome formation:
After autophagosome formation, LC3-II on the outer membrane is
removed from the PE by ATG4 and liberated back into the cytoplasm
(24). LAMP, the lysosomal
membrane protein, and RAB7, a small GTPase, are crucial in the
fusion processes of autophagosomes and lysosomes. This process is
characterized by the formation of isolated membrane structures
containing cytoplasmic constituents (25). Furthermore, acetylation plays a
significant role in autophagic lysosome biogenesis (26). iv) Autophagolysosomal
degradation: The inner membrane of the autophagosome is degraded by
lysosomal enzymes during autophagic lysosome formation so that the
contents of the two are well mixed. As the contents continue to
degrade, raw materials necessary for cellular life activities, such
as amino acids, are continuously produced, which are conveyed to
the cytosol to be re-utilized by the cell, whereas residues that
cannot be recycled may be expelled from the cell or retained in the
cytosol (27).
Several forms of cellular stress can activate
autophagy [including, but not limited to, DNA damage, protein
aggregates, intracellular pathogens, reactive oxygen species (ROS),
hypoxia, damaged organelles and nutrient or growth factor
deficiencies]. This process involves the promotion or inhibition of
multiple signaling pathways to coordinate the various stages of
autophagy (28). Autophagy is
regulated by three major nutrient-sensing pathways: The mammalian
target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway, the adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway and the
oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent histone
deacetylase sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) pathway (29).
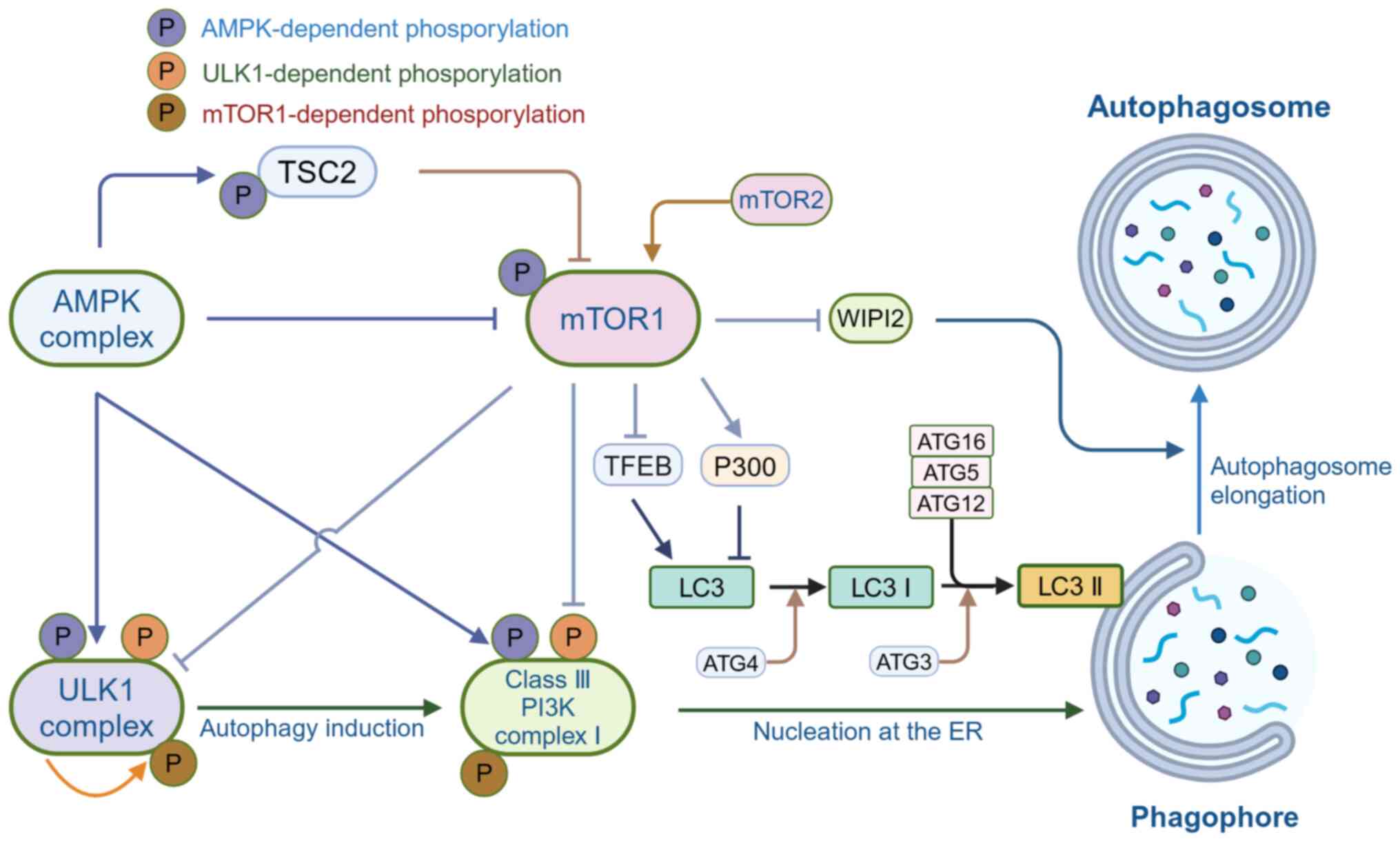
The mammalian target of rapamycin 1 (mTOR1), a
serine/threonine protein kinase, is a member of the PI3K-associated
kinase family and is sensitive to rapamycin (30). mTORC1 phosphorylates ULK1 and
ATG13 to inactivate the autophagy regulatory complex composed of
ULK1, ATG13, FAK family interacting protein of 200 kDa (FIP200) and
ATG101, which affects autophagy vesicle formation. Under
nutrient-rich conditions, mTORC1 inhibits autophagy-promoting
kinase activity of the ULK1 complex by mediating site-specific
phosphorylation of ULK1 and ATG13. However, there are adaptive
changes in how the organism is regulated during starvation and
cellular stress, such as mTORC1 inhibition and ULK1 dissociation
from mTORC1. Consequently, site-specific phosphorylation of ULK1
and ATG13 is deregulated (19).
Meanwhile, the autophosphorylation of threonine located at site 180
activates the ULK1 complex, and in this state, ULK1 phosphorylates
ATG13, FIP200 and ATG101 in the ULK1 complex. After that, the
active ULK1 complexes are transferred to the isolation membrane of
the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby initiating autophagy (31,32). Furthermore, AMPK affects mTORC1
as well. In the presence of sufficient glucose, active mTORC1
inhibits ULK1 activation in two mechanisms: Phosphorylating the
ULK1-specific site (serine 757) and disrupting the ULK1 and AMPK
interaction. After ULK1 activation is inhibited, autophagy
initiation is also impaired. In the presence of glucose
insufficiency, AMPK activity inhibits the phosphorylation of
mTORC1, then ULK1 interacts with AMPK and is phosphorylated,
resulting in ULK1 activation and autophagy initiation (31). In the class III
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex I, the phosphorylation of
ATG14, autophagy and beclin 1 regulator 1 (AMBRA1) and nuclear
receptor binding factor 2 (NRBF2) inhibits the nucleation step of
autophagy. However, mTORC1 regulates autophagy by phosphorylating
ATG14, AMBRA1 and NRBF2 (25). A
study showed that mTORC1 regulates the elongation process in
autophagosome formation and influences LC3 binding to the
autophagosome membrane through targeting WD repeat domain,
phosphoinositide interacting 2 (WIPI2) and P300 acetyltransferases,
respectively. For instance, activating P300 by inhibiting its
intramolecular autoinhibition promotes the acetylation of LC3,
depriving it of the ability to be lapidated (33). By binding to ATG16L, WIPI2
promotes the binding of ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L complexes to phagophores,
therefore enhancing lipidation of LC3 by PE (34). In addition to directly inhibiting
autophagy, mTORC1 can also indirectly inhibit it by regulating the
transcription of genes associated with lysosomal biogenesis. For
instance, recent research on transcription factor EB (TFEB) has
found that TFEB regulates the expression of genes involved in
lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy, including those associated with
autophagosome formation, fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes,
and lysosomal biogenesis (35).
In addition, overexpression of TFEB increased the expression of UV
radiation resistance associated, WIPI, microtubule-associated
protein 1 light chain 3B, sequestosome 1, VPS11, VPS19 and ATG9B,
which are involved in various steps of autophagy (36). Furthermore, mTORC2 can also play
multiple roles as an important regulator in autophagy regulation,
including the indirect inhibition of autophagy through the
activation of mTORC1 (37). In
summary, mTOR inhibits autophagy induction. Therefore, the
development of novel mTOR inhibitors that can precisely regulate
autophagy provides new avenues for the treatment of clinically
difficult diseases (Fig. 1).
In the cell, AMPK acts as an energy sensor, actively
upregulating catabolism and inhibiting anabolism (38). By specifically phosphorylating
different autophagy-associated protein complexes or different
components of the same protein, AMPK can affect different phases of
autophagy and thus promote autophagy (39). AMPK antagonizes mTORC1 to
regulate the activity of the ULK complex. Two distinct mechanisms
induce autophagy when AMPK is activated: Inhibition of mTOR and
direct phosphorylation of ULK1 (40). Most regulatory factors can affect
mTORC1 by interfering with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and ras
homolog enriched in brain (RHEB). RHEB binds to GTP to form
RHEB-GTP, which then binds and activates mTORC1. The TSC complex,
however, has GTPase activity that hydrolyzes GTP to inactivate
RHEB-GDP. Therefore, the TSC complex can inhibit mTORC1 activity by
modulating RHEB (41). AMPK is
phosphorylated and activated under low-energy conditions or
starvation situations, and it inhibits mTOR activity in two ways.
i) AMPK directly phosphorylates TSC2, promoting GTPase-activating
protein (GAP) activity in the TSC complex. GTP dephosphorylation of
RHEB-GTP results in its conversion to the inactive RHEB-GDP, which
interrupts RHEB-mediated mTORC1 activation. ii) AMPK inhibits the
mTOR signaling pathway by directly phosphorylating regulatory
associated protein of mTOR complex 1 (RAPTOR), stopping RAPTOR from
binding to mTOR or its substrates (35,37). The inactivation of mTOR leads to
decreased ULK1 phosphorylation and increased ULK1 binding to AMPK,
thereby exhibiting a unique role in autophagy regulation. AMPK
promotes the activity of ULK1, which induces autophagy during
glucose deprivation. AMPK interacts with the serine/proline-rich
region of ULK1 and directly phosphorylates ULK1 at several sites,
resulting in changes in the conformation of ULK1. The
conformational changes in ULK1 enhance interactions between ULK1
and the other components of the ULK1 complex, increasing its
activity and stability. mTORC1 regulates the interactions between
AMPK and ULK1 through various mechanisms. In the nutrient-rich
environment, ULK1 is phosphorylated by mTORC1, inhibiting its
interaction with AMPK (42,43). In addition to this, mTORC1 can
also phosphorylate ATG13, which decreases ULK1 complex activity. In
contrast, under starvation conditions, mTORC1 activity is
inhibited, leading to the rapid dephosphorylation of ULK1 and
ATG13, which activates ULK1 kinase and initiates autophagy.
Accompanying this change is that AMPK and ULK1 interact more
effectively, increasing ULK1 activity and promoting
ULK1-ATG13-FIP200 complex formation (30). Thus, AMPK and mTORC1 coordinately
regulate ULK1 to induce autophagy in response to cellular nutrient
levels. AMPK, ULK1 and mTORC1 form a signaling triad that
constitutes a transient feedback mechanism to maintain the dynamic
homeostasis of autophagy (44).
AMPK also affects autophagy by regulating the activity of the
PI3KC-3/VPS34 complex and the transcriptional regulation of
autophagy (45) (Fig. 1).
During the process of growth and development,
autophagy is an essential catabolic process for basic biological
activities (71). According to
current research findings, the functions of autophagy include the
following: i) Immune Response: Autophagy removes intracellular
pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria, through a process called
heterophagy. It also regulates inflammation and antigen
presentation, contributing to the normal function of the immune
system (72). ii) Nutrient
recycling: In times of nutrient deprivation or starvation, the
autophagic process recycles cellular components and provides
nutrients to cells. In degrading and recycling cytoplasmic
material, autophagy provides cells with vital components, such as
amino acids, for survival and energy production (56). iii) Energy homeostasis: During
periods of metabolic stress, such as fasting or exercise, autophagy
is upregulated to provide a source of energy by breaking down
cellular components. As a result, cells adapt to changing nutrient
supplies and maintain a balance of energy (56). iv) Development and
differentiation: Autophagy participates in various differentiation
and developmental processes, including cellular differentiation,
tissue remodeling and embryonic development. It helps to remove
unnecessary or excessive cellular components, shape tissues and
organs, and promote normal cell development and differentiation
(73,74). v) Cellular quality control:
Autophagy sustains cellular homeostasis by cleaning out damaged or
dysfunctional cellular components (e.g., misfolded proteins,
damaged organelles and excess or aggregated proteins). By
eliminating these components, autophagy contributes to preventing
the accumulation of toxic substances and maintaining cellular
homeostasis (75).
Fibrosis is defined as the over-accumulation of
extracellular matrix (ECM) components in organs or tissues, which
is a normal and necessary stage in the process of organ or tissue
repair (76). However, continual
or severe injury causes the accumulation of ECM components, which
can disrupt tissue structural integrity, lead to organ dysfunction
and ultimately cause various organ failures (76). Fibrosis affects almost every
tissue in an organism, including the skin, lungs, liver, kidneys
and ligamentum flavum (77,78).
Numerous different triggers can contribute to the
ongoing aggravation of progressive fibrosis disease. However,
regardless of the initiating event, all fibrotic diseases are
characterized by the activation of ECM-producing myofibroblasts,
which are the primary mediators of fibrotic tissue remodeling
(76,78). When tissues are injured,
myofibroblasts from various sources remodel the extracellular
environment to initiate healing responses, which restore tissue
integrity and promote the replacement of parenchymal cells
(79). Typically, the deposition
of ECM proteins in the initial stages of tissue healing contributes
to the tissue repair process. In mild injuries, the fibrotic matrix
is taken up during the tissue repair process (80). However, sustained injury can lead
to dysregulation of this process, resulting in excessive deposition
of ECM proteins, myofibroblast activity and the gradual development
of a chronic inflammatory environment infiltrated by macrophages
and immune cells (81). In such
a microenvironment, cells are exposed to a significant release of
cytokines and growth factors by myofibroblasts, such as TGF-β and
WNT1, which are significant players in the fibrotic process
(82). TGF-β and WNT1 bind to
their stem cell surface receptors and initiate downstream
signaling, ultimately leading to nuclear translocation of SMAD2/3
and CREB binding protein/β-catenin transcriptional regulators. This
leads to the upregulation of target gene expression, further
enhancing myofibroblast differentiation and the production and
secretion of ECM proteins, such as collagen, laminin and
fibronectin (83,84). As excess ECM deposition proceeds,
the matrix undergoes structural changes and hardens (76). Cells sense ECM tension through
mechanotransduction of cell surface integrin receptors, which
activate the Hippo signaling pathway and its major downstream
effectors Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional
co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) (85). In addition, activated YAP and TAZ
translocate to the nucleus and promote the upregulation of
pro-growth genes, such as connective tissue growth factor and
platelet-derived growth factor, which promote myofibroblast
proliferation and activation through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
(85).
In clinical practice, biomarkers of fibrotic
diseases are crucial for early diagnosis, disease progression
tracking, prognostic evaluation and treatment efficacy assessment
(86). The following are generic
fibrosis markers in fibrotic diseases. i) Collagen: The main
component of fibrosis, as well as its degradation products in
serum, can be used as markers (87,88). ii) Fibronectin: An important
component of the ECM, upregulated during fibrosis (89). iii) Matrix metalloproteinases and
their inhibitors: They reflect matrix remodeling processes,
balancing the disintegration and accumulation of the ECM, and serve
a crucial role in regulating fibrosis (90-92). iv) MicroRNAs: MicroRNAs regulate
the expression of fibrosis-related genes in a variety of fibrotic
diseases and have potential diagnostic and therapeutic value
(93-95).
Biomarkers of fibrotic disease exhibit considerable
variability across different tissues and organs. Liver fibrosis
markers include the following: i) The aspartate aminotransferase
(AST) to alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ratio, which is often
elevated in liver fibrosis (96); ii) fibrosis indices: AST to
platelet ratio index (based on AST level and platelet count) and
FIB-4 (based on age, AST, ALT and platelet count) (97); iii) FibroTest: A score is
calculated in combination with various serum markers (e.g.,
α2-microglobulin, apolipoprotein-A1, transferrin, total bilirubin,
γ-glutamyltransferase, etc.) and is used to assess the degree of
liver fibrosis (98); iv)
hyaluronic acid: Serum levels of hyaluronic acid are significantly
elevated during liver fibrosis (99). Pulmonary fibrosis markers include
the following: i) Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6): KL-6, released
after damage to alveolar epithelial cells, is commonly used in the
monitoring of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (100-102); and ii) surfactant protein D,
which reflects lung tissue damage and the inflammatory state
(102-104). Renal fibrosis markers include
i) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, which is elevated in
acute kidney injury and renal fibrosis (105); and ii) urinary collagen
degradation products, which reflect collagen metabolism and
fibrotic activity (106,107).
Cardiac fibrosis markers include i) Galectin-3, which is involved
in the fibrotic process and it is an important marker of cardiac
fibrosis (108-110); ii) ST2 protein, which reflects
cardiac stress and fibrotic activity with significant prognostic
value (109,110); and iii) collagen degradation
products, reflecting cardiac collagen metabolism (111).
The mechanism of fibrosis varies among organs, so
the selection of appropriate markers needs to be tailored to the
specific type of disease.
Macrophages are immune cells found in almost all
tissues. Macrophages participate in non-specific immunoregulation
by phagocytosis of bacteria and other pathogens, while also
transmitting signals to lymphocytes to participate in specific
immunoregulation, thus contributing to immunity, repair and
homeostasis of the body (112).
Macrophages may be categorized into two subpopulations, M1 and M2,
which secrete pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors,
respectively (113). Continued
research has indicated that macrophages play a critical role in
regulating organ fibrosis (114). When an organ or tissue is
infected or injured, macrophages polarize into the pro-inflammatory
M1 phenotype, secreting proinflammatory cytokines to remove
antigens and necrotic cells (115). Pro-inflammatory macrophages are
categorized as M1-type macrophages, while anti-inflammatory
macrophages are categorized as M2-type macrophages (115). During the organ or tissue
repair phase, M2 macrophages secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines
that suppress inflammation as well as contribute to tissue repair
and remodeling (116). In a
pathological situation, persistent pro-inflammatory macrophages
produce pro-inflammatory factors continuously, resulting in chronic
inflammation, which ultimately accelerates the progression of organ
fibrosis significantly (117).
It has been confirmed that autophagy regulates macrophage
polarization (118). By
inhibiting M1 proinflammatory macrophage polarization, macrophage
autophagy ameliorates organ fibrosis and attenuates chronic
inflammation (9).
After chronic or severe organ damage, fibrous
connective tissue accumulates and parenchymal cells decrease,
resulting in fibrosis. Continuous progression may result in severe
damage to organ structure and function, or even death, posing a
serious threat to human health and life (119). Pathologically, organ fibrosis
is characterized by an imbalance in ECM homeostasis, resulting in
excessive accumulation of collagen, fibronectin and other ECM
components (120). Thus,
fibrosis can also be seen as the result of abnormal tissue
repair.
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a common pathological
feature and the ultimate outcome of numerous lung diseases. The
main feature of PF is the excessive accumulation of ECM in the
lungs, leading to the thickening of the alveolar walls, which
ultimately causes the destruction of the alveolar structure and
respiratory failure (121,122). Type II alveolar epithelial cell
dysfunction or disorder is considered to be the initiating factor
for PF. In addition, the contribution of macrophages in the
evolution and progression of fibrotic diseases should not be
overlooked (121,123). Depending on their location,
macrophages in the lung are classified as alveolar macrophages
(AMs) or interstitial macrophages (124). Normally, AMs reside in the
alveolar cavity and are the most important component of the
alveoli. AMs play a crucial role in preventing inflammation and
fibrosis in the lungs.
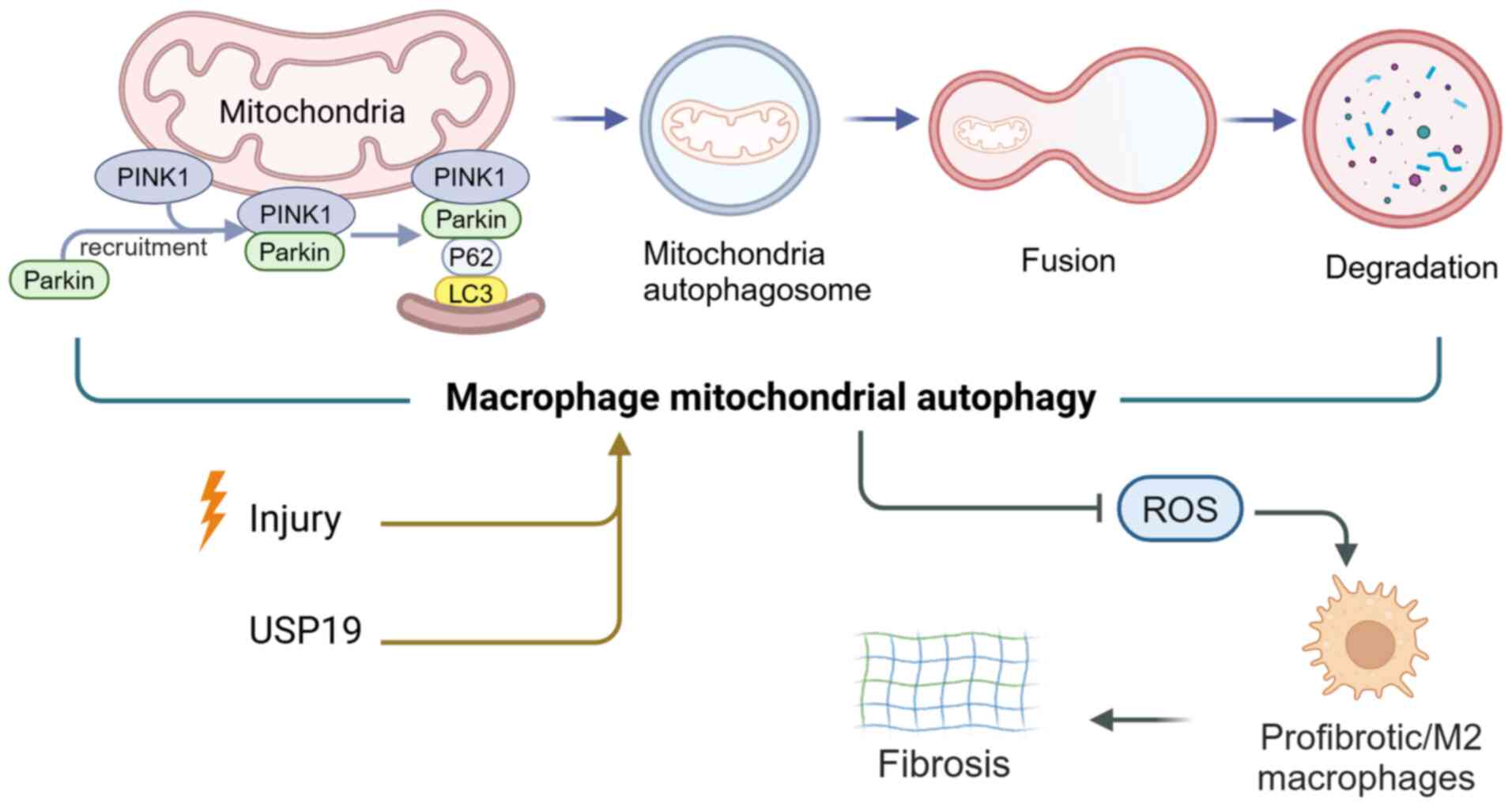
In silicosis, autophagy inhibits inflammation and AM
apoptosis and plays a protective role in the progression of
silicosis. Du et al (125) found that crystalline silica
(CS) triggered autophagy activity in AMs, thereby protecting AMs
from CS-induced apoptosis. In AMs, diosgenin promoted autophagy and
therefore attenuated CS-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Mechanistically, diosgenin can exert antifibrotic effects by
enhancing macrophage autophagy activity. Diosgenin leads to
mitochondrial dysfunction through silica inhalation and activates
beclin1, which increases the expression of two key proteins of
mitochondrial autophagy, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and
parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (PARKIN), in AMs in mice.
Diosgenin-mediated AMs mitochondrial autophagy eliminated damaged
mitochondria and further ameliorated silicosis fibrosis. In ATG5
knockout mice, the protective effect of diosgenin was lost, and
macrophages in these mice lacked autophagy function (126,127). In addition, microRNA-205-5p
promotes macrophage autophagy by inhibiting S-phase
kinase-associated protein 2-mediated ubiquitination of Beclin1,
thereby suppressing lung fibrosis in silicosis mice (128). These experimental results
suggest that tissue-resident macrophage autophagy can inhibit PF
during silicosis progression. In addition, the lung has some
macrophages of monocyte origin. The origin of these macrophages is
different from that of tissue-resident macrophages. A study by
Jessop et al (129)
showed that in mouse monocyte-derived macrophages, exposure to CS
can enhance autophagic activity. ATG5 gene knockout in mice
resulted in impaired macrophage autophagy derived from monocytes,
and more fibrosis was observed in ATG5 knockout mice exposed to
silica compared to littermate control mice (129). These experimental results show
that, similar to tissue-resident macrophages, monocyte-derived
macrophages are also able to protect against CS-induced PF. In
conclusion, macrophage autophagy has been shown to inhibit chronic
inflammation, therefore inhibiting PF. However, there are different
views among scientists, e.g., it has been suggested that autophagy
may exacerbate lung injury and PF under certain circumstances, such
as when autophagy levels are excessive or uncontrolled (130).
Renal fibrosis is the ultimate pathway leading to
end-stage renal failure in almost all chronic progressive kidney
diseases. In the kidney, macrophages play a crucial role in the
generation and evolution of renal fibrosis (131). A study confirmed that
macrophage autophagy suppresses the pro-inflammatory response of
macrophages. Loss of macrophage autophagy leads to abnormal
macrophage polarization, increased M1 and decreased M2, which
causes worsening inflammation (132). Therefore, macrophage autophagy
plays a crucial role in both macrophage polarization and
suppressing inflammation. Liu et al (133) experimentally demonstrated that
ubiquitin-specific peptidase 19 (USP19) can regulate NLR family
pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) function by affecting autophagy
and thereby significantly influencing inflammation and macrophage
polarization. In terms of mechanisms, USP19 increases autophagic
flux and reduces mitochondrial ROS production, thus inhibiting
inflammation and promoting macrophage polarization in M2 (133) (Fig. 3). In a study using two mouse
models of experimental renal fibrosis, Bhatia et al
(134) found that macrophage
mitochondrial autophagy regulates the PINK1/mitofusin 2/PARKIN
pathway, which could protect mice's kidneys from fibrosis (Fig. 3). Based on a renal fibrosis
model, Zhang et al (135) found that fibrosis and
macrophage infiltration were positively correlated with
lymphangiogenesis. The activation of the VEGF-C/VEGFR3 signaling
pathway inhibited macrophage autophagy, consequently facilitating
macrophage M1 polarization, which then increased the
transdifferentiation of M1 macrophages into lymphatic endothelial
cells (LECs). By contrast, rapamycin-induced macrophage autophagy
decreased M1 macrophage polarization and transdifferentiation to
LECs. Thus, macrophage autophagy reduces LEC production, thereby
inhibiting renal fibrosis (135). In summary, when the kidney is
severely injured or repetitively injured, a large number of
macrophages infiltrate into the damaged area and persist at the
infiltration site, leading to chronic inflammation and renal
fibrosis. Macrophage autophagy inhibits macrophage polarization to
M1, thereby suppressing inflammation and renal fibrosis.
In liver disease, macrophage autophagy similarly
influences the progression of liver fibrosis. Lodder et al
(136) demonstrated that the
autophagic pathway in macrophages exerts a protective effect
against hepatic fibrosis by limiting the release of inflammatory
cytokines such as IL-1A and IL-1B from macrophages, which are key
mediators of liver fibrosis. By contrast, rapamycin-induced
autophagy activation limits the production of IL-1A and IL-1B in
macrophages. These results reveal macrophage autophagy as a
paracrine pathway that regulates IL-1-dependent activation of
hepatic myofibroblasts.
In conclusion, macrophage autophagy protects against
organ fibrosis.
The endoplasmic reticulum, a complex and closed
intracellular tubular endomembrane system interwoven into a
three-dimensional network structure, is the central organelle
responsible for the production of secreted and transmembrane
proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum has the function of folding,
assembling and modifying proteins (137). The biological functions of the
endoplasmic reticulum are tightly regulated. Cellular homeostasis
is disrupted when cells encounter various strong stimuli, such as
nutritional deficiencies and oxidative stress stimuli, initiating a
series of self-protective mechanisms, such as ERS (138). It has been indicated that ERS
is activated when the folding capacity of the endoplasmic reticulum
breaks down, resulting in accumulation of misfolded and unfolded
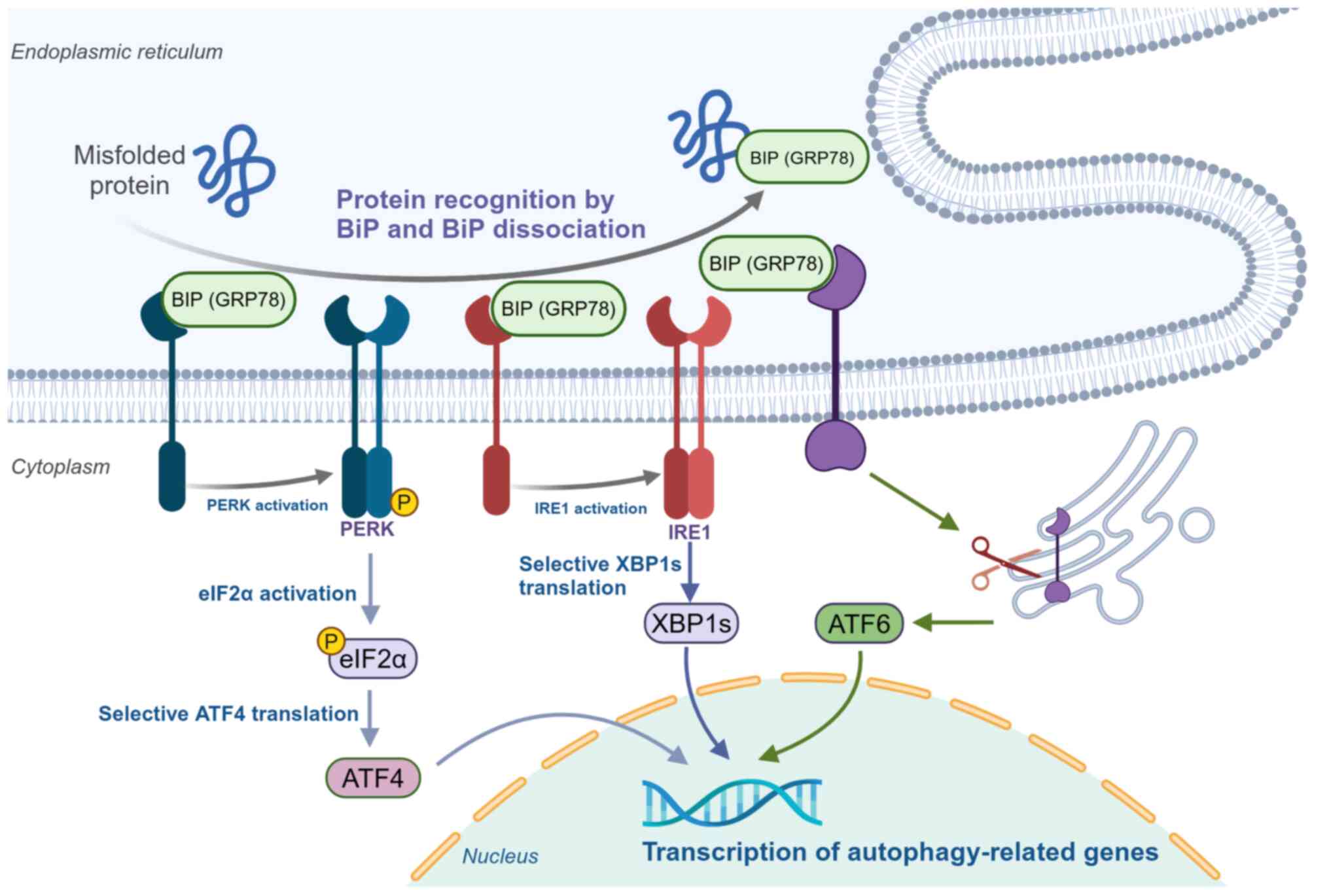
proteins and disrupted protein homeostasis (139). In mammalian cells, three
endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane proteins act as ERS sensors:
Activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), inositol-requiring enzyme
1 (IRE1)α and protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
(PERK) (140,141) (Fig. 4). Under conditions of protein
homeostasis, BIP (a molecular chaperone located in the endoplasmic
reticulum membrane that facilitates degradation and refolding of
unfolded and misfolded proteins accumulated in the endoplasmic
reticulum to restore homeostasis) binds to these sensors, rendering
them inactive (140,142). During ERS, BIP dissociates from
the sensor (at this time, the affinity of BIP for unfolded and
misfolded proteins increases), triggering the unfolded protein
response (UPR), which is one of the adaptive responses to stress
(141,143). Through activation of PERK, IRE1
and ATF6, the UPR promotes protein expression and restores the
normal protein structure of misfolded or unfolded proteins. When
the ERS-activated UPR is insufficient or does not completely
eliminate the accumulated misfolded and unfolded proteins, as a
complementary form, the ubiquitin-proteasome system collaborates
with the UPR to degrade the misfolded and unfolded proteins, thus
restoring the normal morphology of the endoplasmic reticulum
(144). If the stimulus to the
cell is persistent or excessively severe so that the synergistic
action of the UPR and the ubiquitin-proteasome still does not fully
restore the endoplasmic reticulum to its normal state, autophagy
appears to be the last resort for restoring endoplasmic reticulum
homeostasis. Persistence of ERS activates autophagy (145). Autophagy and ERS exhibit tight
reciprocal regulation, both of which are crucial for maintaining
cellular homeostasis and responding to environmental stimuli
(146,147). The specific relationship
includes the following four aspects: i) ERS induces autophagy: ERS
is triggered when unfolded or misfolded proteins accumulate in the
endoplasmic reticulum. In response to this stress, cells initiate
the UPR, and by activating sensors such as IRE1, PERK and ATF6,
these UPR signaling pathways can facilitate the initiation of
autophagy (146,148). ii) Autophagy to alleviate ERS:
Autophagy can selectively degrade damaged endoplasmic reticulum
regions, remove accumulated unfolded proteins and restore
endoplasmic reticulum function (149). iii) Feedback regulation and
homeostasis: A feedback regulatory mechanism exists between ERS and
autophagy to ensure that cells balance survival and apoptotic
signaling in response to stress (150,151). iv) Disease association:
Dysregulated autophagy and ERS response are closely associated with
the development of multiple diseases, e.g., PF (152), inflammatory bowel disease
(147) and cardiovascular
disease (153).
An association between ERS-induced autophagy and
fibrotic disease has been identified. During fibrosis, autophagy
regulates ERS to influence disease progression primarily through
the following mechanisms: i) Reducing ERS load and modulating UPR:
Autophagy reduces the endoplasmic reticulum burden and relieves ERS
by breaking down aberrant proteins and damaged endoplasmic
reticulum and activating the UPR, preventing further fibrosis
development (154). ii)
Modulation of inflammatory response: ERS is often accompanied by an
inflammatory response, and autophagy can reduce tissue damage and
the fibrosis process by removing inflammatory signaling molecules
and inhibiting the excessive release of inflammatory mediators
(147,155). iii) Maintaining cell survival
and function: By regulating autophagy, cells can more effectively
respond to protein folding stress, avoid apoptosis or necrosis, and
protect the tissue structure (156,157). iv) Involvement in ECM
metabolism: Autophagy indirectly affects fibrosis progression by
regulating collagen degradation (154). Shu et al (158) demonstrated that ERS in renal
proximal tubular cells can induce renal fibrosis. Furthermore, the
PERK-mediated UPR signaling pathway links ERS to autophagy
activation. Autophagy activation contributes, at least in part, to
fibrosis associated with ERS (158). Xiong et al (159) found that cardiac
Ca2+ concentrations increased and endoplasmic reticulum
markers were upregulated during tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate
(TCEP)-induced cardiac fibrosis. However, Ca2+ overload
and subsequent cardiac fibrosis were attenuated with the use of
CDN1163, an inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ ATPase, which also suppressed the upregulation of
endoplasmic reticulum markers. Furthermore, CDN1163 supplementation
inhibited TCEP-induced excessive autophagy in the heart. Thus, by
inhibiting sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+
ATPase expression, TCEP can lead to Ca2+ overload, which
triggers ERS and excessive autophagy, ultimately leading to cardiac
fibrosis (159). Ren et
al (160) found that milk
fat globule-egf factor 8 (MFG-E8) gene defects exacerbated
pancreatic fibrosis. By contrast, pancreatic fibrosis was
attenuated in cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis mice treated
with injections of exogenous MFG-E8. Meanwhile, ERS and CMA levels
were reduced in cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis mice after
the administration of exogenous MFG-E8. Further experiments
revealed that MFG-E8 inhibited the ERS-induced CMA pathway by
targeting the specific CMA activator QX77, which reversed the
effects of MFG-E8. This suggests that MFG-E8 inhibits pancreatic
fibrosis by suppressing the ERS-induced CMA pathway. Recombinant
MFG-E8 is likely to be developed as a novel medication for
pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis (160). Zheng et al (161) found that tunicamycin-induced
ERS was associated with family with sequence similarity 172, member
A (FAM172A)-mediated calcium flux. The autophagic process was
observed in both normal fibrous tissue and epidural scar tissue
cell lines after tunicamycin treatment. Further experimentation
revealed that overexpression of FAM172A inhibited the autophagic
process in normal fibrous tissue and epidural scar tissue. However,
when the expression of FAM172A was inhibited, the autophagic
process was increased in both cell lines. In a mouse model, FAM172A
inhibited epidural fibrosis. Thus, ERS-associated calcium currents
mediate the downregulation of FAM172A expression, which promotes
autophagy in fibroblasts, a critical pathogenic factor in epidural
fibrosis (161).
In summary, ERS-mediated autophagy exhibits a
promoting effect on fibrosis development.
EndMT, a special type of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT), refers to the process in which endothelial cells
lose their original characteristics and transform into mesenchymal
cells under the action of multiple stimuli. During the
transformation process, endothelial cells gradually lose their
morphology and function and acquire mesenchymal cell phenotypic
characteristics such as proliferation, migration and collagen
synthesis (162). In the
process of acquiring the mesenchymal phenotype, endothelial cells
(ECs) lose endothelial-specific markers such as vascular
endothelial cadherin, platelet and endothelial cell adhesion
molecule 1 and vonWillebrand factor. Instead, they start to express
mesenchymal markers, such as vimentin, α-smooth muscle actin and
type I collagen (163,164). At the same time, the cell
morphology changes from compact cobblestone-like to elongated
spindle-like. Cells acquire an impaired antiplatelet-generating
capacity and loss of cell-to-cell connectivity and polarity, but
enhanced mesenchymal cell properties, such as invasion and
migration. Partial EndMT is a process in which ECs remain in an
intermediate stage of transdifferentiation for an extended period
rather than permanently acquiring a mesenchymal phenotype (165). This is the stage at which cells
gain a mesenchymal phenotype, while retaining endothelial markers
and exhibiting progenitor-like characteristics. This intermediate
stage of phenotypic transformation is unstable and can be reversed
under certain conditions, making it a potential target for therapy
(166,167).
EndMT has been shown to promote the formation of
heart valves and septa during embryonic development and has also
been indicated to contribute to certain pathological conditions,
such as cardiac and renal fibrosis and PF, tumor progression, and
wound healing processes (168).
ECs, however, are not fully understood regarding their regulatory
role in cellular metabolism to drive EndMT. Currently, it has been
found that autophagy regulates the EndMT, which contributes to the
development of fibrotic diseases (Fig. 5). Zhang et al (169) showed that advanced
glycosylation end-products (AGEs)/AGE receptor (RAGE) regulates
autophagy in heart failure, which results in EndMT-induced cardiac
fibrosis. RAGE knockdown inhibited autophagy-regulated EndMT,
attenuated cardiac fibrosis and improved cardiac function.
Therefore, mechanistic studies focusing on the
AGEs/RAGE-autophagy-EndMT axis may provide novel therapeutic
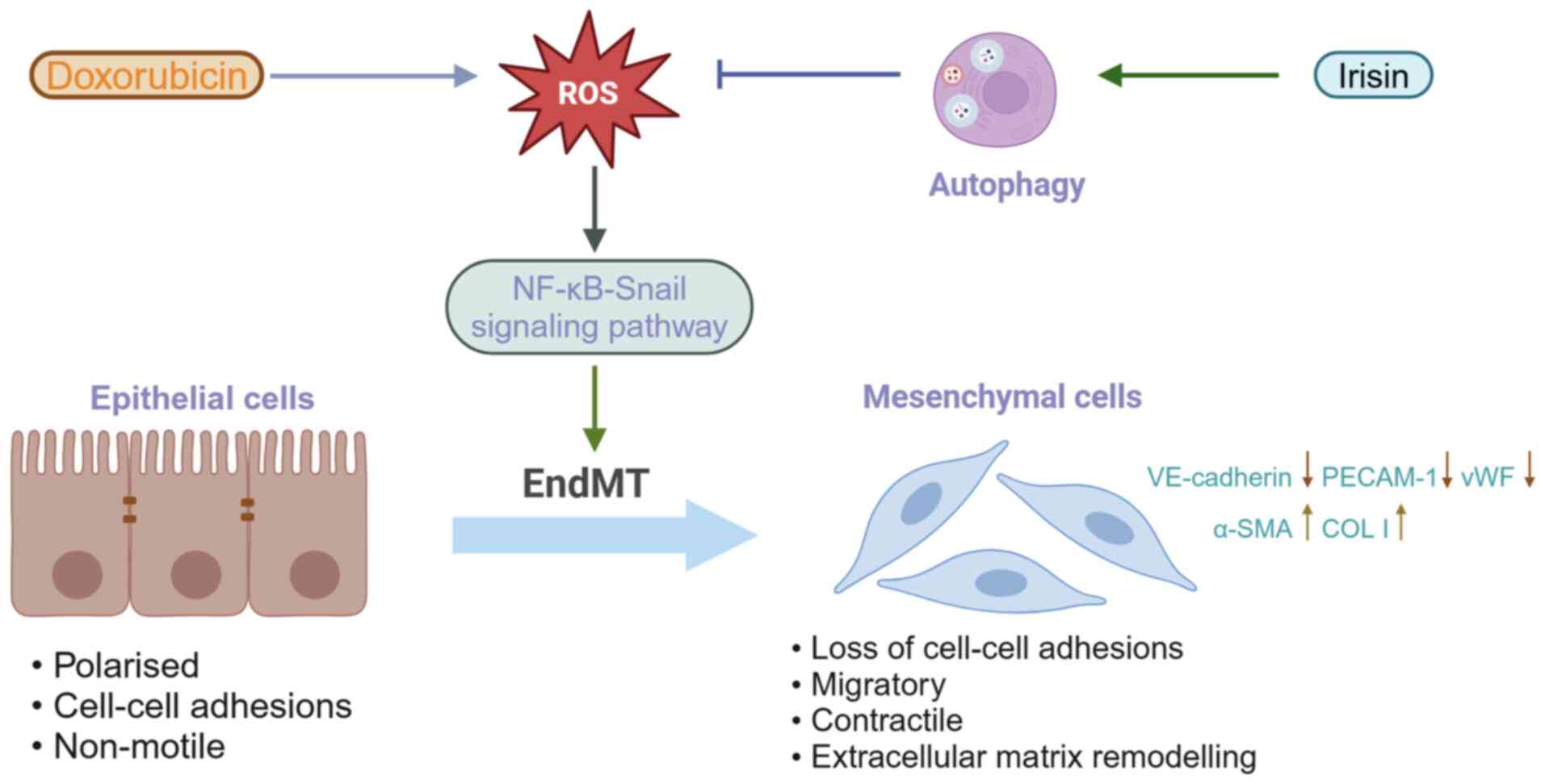
targets for the treatment of heart failure (169). Pan et al (170) found that early perivascular
fibrosis induced by doxorubicin was associated with the EndMT
program. Disturbed autophagy leads to ROS accumulation, and ROS can
trigger NF-κB-Snail activation, which could be the basis for
doxorubicin involvement in EndMT induction. In an animal model of
disseminated intravascular coagulation, irisin attenuated
perivascular fibrosis and EndMT. Irisin can improve autophagy
disorders, eliminate ROS and reverse EndMT by modulating uncoupling
protein 2, irisin's proven target. ROS accumulation and autophagy
disorders are identified as the factors contributing to EndMT in
CMEC, which is involved in the initiation and development of
perivascular fibrosis in disseminated intravascular coagulation
(170) (Fig. 5). Zhou et al (171) analyzed the late proliferative
endometrium of both normal patients and those with severe
intrauterine adhesions (IUA), confirming that the endometrial
tissue in patients with IUA exhibited autophagy deficiencies, which
promoted EMT and fibrosis. Further analysis of the sequencing
results of autophagy-related gene expression revealed that the most
significant differential gene, iodothyronine deiodinase 2, triggers
autophagy defects in endometrial epithelial cells through the
MAPK/ERK-mTOR pathway, leading to EMT. Meanwhile, in vivo
experiments also confirmed that targeting autophagy could inhibit
EMT and alleviate fibrosis (171). Singh et al (172) found that the deletion of ATG7,
an essential autophagy gene in ECs, resulted in disrupted
autophagic flux, an increase in mesenchymal markers, loss of ECs
and significant changes in the structure of the ECs. In in
vitro experiments, deletion of ATG7 led to upregulation of key
pro-fibrotic genes and TGF-β signaling. In in vivo
experiments, mice with specific knockout of ATG7 in the ECs
exhibited a reduction in endothelial-specific markers. Higher
sensitivity to collagen accumulation and bleomycin-induced PF was
also observed. The study provided novel evidence indicating that
the loss of in vivo endothelial autophagy exacerbates the
fibrotic response in mice. This occurs through a regulatory effect
of autophagy to restrain TGF-β-dependent EndMT. These findings
suggest that it is possible that autophagy regulates the crosstalk
between EndMT and organ fibrosis. The autophagy gene ATG7 has been
demonstrated to regulate organ fibrosis by modulating shifts in
EndMT (172).
Autophagy is able to change the secretory phenotype
of tissue cells. For example, autophagy leads to a secretory
phenotype that facilitates the production of profibrotic cytokines,
which results in the secretion of the corresponding pro-fibrotic
cytokines, leading to fibrotic disease progression. Livingston
et al (173) found that
autophagy was sustained at high levels in renal tubular cells after
ischemic acute kidney injury, leading to the expression and
secretion of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)2. FGF2 is a key
paracrine factor produced by renal tubular cells of the secretory
phenotype that promotes fibroblast activation and interstitial
fibrosis during maladaptive renal repair (173). Zhou et al (154) demonstrated that ERS in
fibroblasts triggers the upregulation of autophagy, which promotes
the phenotypic transformation of fibroblasts and the synthesis and
secretion of collagen. The study also found that autophagy
regulates the secretion of inflammatory factors, which contribute
to the development of fibrotic diseases. In a study by Nam et
al (174), after unilateral
ureteral obstruction, autophagy induced in distal renal tubular
epithelial cells was demonstrated to confer protection against
renal tubular interstitial fibrosis by modulating the TGF-β/SMAD4
signaling pathway and the NLRP3 inflammatory
vesicle/caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway.
There is a great deal of scientific evidence that
the development of fibrotic diseases is profoundly influenced by
autophagy. Autophagy can promote or inhibit fibrosis in organs and
tissues in several mechanisms. Over the past years, numerous
researchers have contributed to the discovery of autophagy's role
in fibrosis as well as its potential as a therapeutic target.
Significant breakthroughs have been made in the development of
targeted antifibrotic medicines against autophagic mechanisms. Liu
et al (175) found that,
through regulation of the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and RAB27A,
arrestin beta 1 enhances the release of MBL-associated serine
protease 1 (MASP1)-enriched extracellular vesicles from
hepatocytes. Their follow-up experiments revealed that activation
of hepatic stellate cells through P38 MAPK/ATF2 signaling promotes
liver fibrosis, with hepatocyte-derived MASP1 being a crucial
factor. Therefore, MASP1 may have high potential to be developed as
a critical therapeutic target for liver fibrosis (175). Wang et al (11) found that lycopene slows
aristolochic acid 1-induced renal fibrosis by activating
mitochondrial autophagy and inhibiting renal cell EMT. Therefore,
the targeted modulation of mitochondrial autophagy represents a
promising new approach to treat chronic kidney disease. Lycopene is
promising as a novel medicine with unexpected effects for treating
renal fibrosis (11). Also,
according to Li et al (176), excessive apoptosis and
insufficient autophagy in AMs coexisted during the evolution of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Zukamu, a traditional Chinese
medicine, regulates the 'autophagy-apoptosis' balance in AMs, thus
inhibiting the fibrosis process to a certain extent. This
demonstrated that it may be possible to treat IPF by inhibiting
apoptosis of AMs and promoting the autophagic activity of AMs,
which is another novel perspective for treating fibrotic diseases
and provides valuable insights for future mechanistic studies and
targeted new medicine development (176). Therefore, the treatment of
fibrosis by promoting or inhibiting autophagy has great potential
for the future.
The exploration of the relationship between
autophagy and fibrosis provides an important reference for academic
research and clinical practice. i) Elucidation of disease
mechanisms: In-depth study of the mechanism of autophagy in
fibrosis contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the
pathological process of the disease (11,177). ii) Guiding future research
directions: The present review provides new perspectives on
research in autophagy, facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration
and advancing medical development (178). iii) Potential therapeutic
targets: The development of medicines targeting autophagy-related
molecules offers a novel direction for fibrosis treatment (11,175). iv) Disease course prediction:
The alteration of autophagy-related protein expression levels in
fibrotic tissues may serve as a biomarker for disease progression
and treatment efficacy (87-95). This serves as a crucial reference
for early diagnosis, prognosis assessment and individualized
treatment planning in the clinic. Clarifying various autophagy
regulatory pathways would facilitate the identification of
particular autophagy regulatory mechanisms in distinct organs
during fibrosis, hence advancing precision medicine and improving
therapeutic efficacy.
However, the relationship between autophagy and
fibrosis remains largely unexplored. Although there are various
types of autophagy, current research on autophagy and fibrosis
predominantly focuses on macroautophagy and the role of other types
of autophagy, such as CMA, various selective autophagies and
microautophagy, in fibrosis remains to be elucidated. Further, the
interactions between autophagy and other physiological or
pathological responses, such as ferroptosis, pyroptosis, apoptosis
and inflammatory responses, require thorough examination. This will
contribute to a more comprehensive, integrated and in-depth
understanding of the function of autophagy in cellular
physiological and pathological responses. In addition, the
assessment of autophagic activity is mainly based on the amount of
LC3-II detected, but it does not provide any accurate feedback on
the dynamic autophagic process. In addition, suitable monitoring
indicators are required to accurately reflect autophagic flux or
autophagic degradation. Finally, from a clinical perspective, there
is a necessity for more efficacious and targeted
autophagy-targeting medicines. While the majority of the current
evidence of the role of autophagy in fibrosis was obtained from
animal models and in vitro cultured cells, it is still
unknown whether these findings derived from in vitro cells
and animals can be translated to humans. A method to monitor human
autophagic activity is required to assess the effect of autophagy
on human fibrotic diseases and the therapeutic progress. Although
significant advancements have been achieved in understanding the
effect of autophagy on fibrosis, it is essential to address these
challenges so that existing and forthcoming new strategies can be
better utilized to modulate autophagy for the benefit of patients
with fibrotic diseases.
Not applicable.
YC was primarily responsible for the writing,
review and revision of the article. ZW participated in the
literature review and provided feedback for this review. QM and CS
provided guidance throughout the preparation of this manuscript and
made significant revisions to the text. Data authentication is not
applicable. All authors read and approved the final version of the
manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant no. 81802198) and the Natural Science
Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant no. BK20221176).
|
1
|
Miguel V, Alcalde-Estévez E, Sirera B,
Rodríguez-Pascual F and Lamas S: Metabolism and bioenergetics in
the pathophysiology of organ fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
222:85–105. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan Z, El Sharkway R, Bayoumi A, Metwally
M, Gloss BS, Brink R, Lu DB, Liddle C, Alqahtani SA, Yu J, et al:
Inhibition of MERTK reduces organ fibrosis in mouse models of
fibrotic disease. Sci Transl Med. 16:eadj01332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao X, Kwan JYY, Yip K, Liu PP and Liu
FF: Targeting metabolic dysregulation for fibrosis therapy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 19:57–75. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Antar SA, Ashour NA, Marawan ME and
Al-Karmalawy AA: Fibrosis: Types, effects, markers, mechanisms for
disease progression, and its relation with oxidative stress,
immunity, and inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 24:40042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palmer JE, Wilson N, Son SM, Obrocki P,
Wrobel L, Rob M, Takla M, Korolchuk VI and Rubinsztein DC:
Autophagy, aging, and age-related neurodegeneration. Neuron.
113:29–48. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liang S, Wu YS, Li DY, Tang JX and Liu HF:
Autophagy and renal fibrosis. Aging Dis. 13:712–731. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo D, Lu X, Li H, Li Y, Wang Y, Jiang S,
Li G, Xu Y, Wu K, Dou X, et al: The spermine oxidase/spermine axis
coordinates ATG5-Mediated autophagy to orchestrate renal senescence
and fibrosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23069122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Wu X, Wang Y and Guo Y: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and autophagy are involved in adipocyte-induced
fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
476:2527–2538. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wen JH, Li DY, Liang S, Yang C, Tang JX
and Liu HF: Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization,
chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front Immunol.
13:9468322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, Tan J, Wang Y, Gong Y, Zhang X,
Yuan Z, Lu X, Tang H, Zhang Z, Jiang X, et al: Atg5 deficiency in
macrophages protects against kidney fibrosis via the CCR6-CCL20
axis. Cell Commun Signal. 22:2232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Ping Z, Gao H, Liu Z, Xv Q, Jiang
X and Yu W: LYC inhibits the AKT signaling pathway to activate
autophagy and ameliorate TGFB-induced renal fibrosis. Autophagy.
20:1114–1133. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamamoto H and Matsui T: Molecular
mechanisms of macroautophagy, microautophagy, and
chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Nippon Med Sch. 91:2–9. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li WW, Li J and Bao JK: Microautophagy:
Lesser-known self-eating. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:1125–1136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xu Y, Qian C, Wang Q, Song L, He Z, Liu W
and Wan W: Deacetylation of ATG7 drives the induction of
macroautophagy and LC3-associated microautophagy. Autophagy.
20:1134–1146. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tukaj C: The significance of
macroautophagy in health and disease. Folia Morphol (Warsz).
72:87–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakahira K, Pabon Porras MA and Choi AM:
Autophagy in pulmonary diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
194:1196–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zachari M and Ganley IG: The mammalian
ULK1 complex and autophagy initiation. Essays Biochem. 61:585–596.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuma A, Mizushima N, Ishihara N and Ohsumi
Y: Formation of the approximately 350-kDa Apg12-Apg5.Apg16
multimeric complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential
for autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem. 277:18619–18625. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Silva VR, Neves SP, Santos LS, Dias RB and
Bezerra DP: Challenges and therapeutic opportunities of autophagy
in cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:34612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barth S, Glick D and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Assays and artifacts. J Pathol. 221:117–124. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pugsley HR: Quantifying autophagy:
Measuring LC3 puncta and autolysosome formation in cells using
multispectral imaging flow cytometry. Methods. 112:147–156. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Agrotis A, Pengo N, Burden JJ and Ketteler
R: Redundancy of human ATG4 protease isoforms in autophagy and
LC3/GABARAP processing revealed in cells. Autophagy. 15:976–997.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saftig P, Beertsen W and Eskelinen EL:
LAMP-2: A control step for phagosome and autophagosome maturation.
Autophagy. 4:510–512. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kroemer G, Mariño G and Levine B:
Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 40:280–293.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy as a
cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene. 23:2891–2906.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao XC, Livingston MJ, Liang XL and Dong
Z: Cell apoptosis and autophagy in renal fibrosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1165:557–584. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim YC and Guan KL: mTOR: A pharmacologic
target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 125:25–32. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hosokawa N, Hara T, Kaizuka T, Kishi C,
Takamura A, Miura Y, Iemura S, Natsume T, Takehana K, Yamada N, et
al: Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the
ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell.
20:1981–1991. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y and Zhang H: Regulation of
autophagy by mTOR signaling pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1206:67–83.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wan W, You Z, Xu Y, Zhou L, Guan Z, Peng
C, Wong CCL, Su H, Zhou T, Xia H and Liu W: mTORC1 Phosphorylates
Acetyltransferase p300 to regulate autophagy and lipogenesis. Mol
Cell. 68:323–335.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dooley HC, Razi M, Polson HE, Girardin SE,
Wilson MI and Tooze SA: WIPI2 links LC3 conjugation with PI3P,
autophagosome formation, and pathogen clearance by recruiting
Atg12-5-16L1. Mol Cell. 55:238–252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roczniak-Ferguson A, Petit CS, Froehlich
F, Qian S, Ky J, Angarola B, Walther TC and Ferguson SM: The
transcription factor TFEB links mTORC1 signaling to transcriptional
control of lysosome homeostasis. Sci Signal. 5:ra422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Settembre C, Di Malta C, Polito VA, Garcia
Arencibia M, Vetrini F, Erdin S, Erdin SU, Huynh T, Medina D,
Colella P, et al: TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis.
Science. 332:1429–1433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun Y, Wang H, Qu T, Luo J, An P, Ren F,
Luo Y and Li Y: mTORC2: A multifaceted regulator of autophagy. Cell
Commun Signal. 21:42023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Herzig S and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Guardian of
metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
19:121–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Tamargo-Gómez I and Mariño G: AMPK:
Regulation of metabolic dynamics in the context of autophagy. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:38122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang H, Yu Z, Chen X, Li J, Li N, Cheng J,
Gao N, Yuan HX, Ye D, Guan KL and Xu Y: Structural insights into
TSC complex assembly and GAP activity on Rheb. Nat Commun.
12:3392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang NC: Autophagy and stem cells:
Self-eating for self-renewal. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:1382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang S, Li H, Yuan M, Fan H and Cai Z:
Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front Physiol. 13:10155002022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S and
Stork B: Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy:
cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Kim J, Kim YC, Fang C, Russell RC, Kim JH,
Fan W, Liu R, Zhong Q and Guan KL: Differential regulation of
distinct Vps34 complexes by AMPK in nutrient stress and autophagy.
Cell. 152:290–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carafa V, Rotili D, Forgione M, Cuomo F,
Serretiello E, Hailu GS, Jarho E, Lahtela-Kakkonen M, Mai A and
Altucci L: Sirtuin functions and modulation: from chemistry to the
clinic. Clin Epigenetics. 8:612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Begum MK, Konja D, Singh S, Chlopicki S
and Wang Y: Endothelial SIRT1 as a target for the prevention of
arterial aging: Promises and challenges. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
78(Suppl 6): S63–S77. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Joo SY, Aung JM, Shin M, Moon EK, Kong HH,
Goo YK, Chung DI and Hong Y: The role of the Acanthamoeba
castellanii Sir2-like protein in the growth and encystation of
Acanthamoeba. Parasit Vectors. 13:3682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ding X, Zhu C, Wang W, Li M, Ma C and Gao
B: SIRT1 is a regulator of autophagy: Implications for the
progression and treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.
Pharmacol Res. 199:1069572024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang Q, Wang SY, Fleuriel C, Leprince D,
Rocheleau JV, Piston DW and Goodman RH: Metabolic regulation of
SIRT1 transcription via a HIC1:CtBP corepressor complex. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:829–833. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yu H, Gan D, Luo Z, Yang Q, An D, Zhang H,
Hu Y, Ma Z, Zeng Q, Xu D and Ren H: α-Ketoglutarate improves
cardiac insufficiency through NAD(+)-SIRT1 signaling-mediated
mitophagy and ferroptosis in pressure overload-induced mice. Mol
Med. 30:152024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Gao Y, Kim K, Vitrac H, Salazar RL, Gould
BD, Soedkamp D, Spivia W, Raedschelders K, Dinh AQ, Guzman AG, et
al: Autophagic signaling promotes systems-wide remodeling in
skeletal muscle upon oncometabolic stress by D2-HG. Mol Metab.
86:1019692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang J, Wang H, Li B, Liu J, Zhang X, Wang
Y, Peng J, Gao L, Wang X, Hu S, et al: Inhibition of ACSS2 triggers
glycolysis inhibition and nuclear translocation to activate
SIRT1/ATG5/ATG2B deacetylation axis, promoting autophagy and
reducing malignancy and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer.
Metabolism. 162:1560412025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li X, Zhao C, Mao C, Sun G, Yang F, Wang L
and Wang X: Oleic and linoleic acids promote chondrocyte apoptosis
by inhibiting autophagy via downregulation of SIRT1/FOXO1
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1870:1670902024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang Q, Sun K, Gao T, Gao Y, Yang Y, Li Z
and Zuo D: SIRT1 silencing promotes EMT and Crizotinib resistance
by regulating autophagy through AMPK/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway in
EML4-ALK L1196M and EML4-ALK G1202R mutant non-small cell lung
cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 63:2133–2144. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
He C: Balancing nutrient and energy demand
and supply via autophagy. Curr Biol. 32:R684–r696. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Baeken MW: Sirtuins and their influence on
autophagy. J Cell Biochem. 125:e303772024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim JY, Mondaca-Ruff D, Singh S and Wang
Y: SIRT1 and autophagy: Implications in endocrine disorders. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9309192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ghosh HS, McBurney M and Robbins PD: SIRT1
negatively regulates the mammalian target of rapamycin. PLoS One.
5:e91992010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li Y, Corradetti MN, Inoki K and Guan KL:
TSC2: filling the GAP in the mTOR signaling pathway. Trends Biochem
Sci. 29:32–38. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kume S, Uzu T, Horiike K, Chin-Kanasaki M,
Isshiki K, Araki S, Sugimoto T, Haneda M, Kashiwagi A and Koya D:
Calorie restriction enhances cell adaptation to hypoxia through
Sirt1-dependent mitochondrial autophagy in mouse aged kidney. J
Clin Invest. 120:1043–1055. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yang X, Jiang T, Wang Y and Guo L: The
role and mechanism of SIRT1 in resveratrol-regulated osteoblast
autophagy in osteoporosis rats. Sci Rep. 9:184242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bánréti A, Sass M and Graba Y: The
emerging role of acetylation in the regulation of autophagy.
Autophagy. 9:819–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB,
Liu J, Bruns NE, Tsokos M, Alt FW and Finkel T: A role for the
NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3374–3379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Huang R, Xu Y, Wan W, Shou X, Qian J, You
Z, Liu B, Chang C, Zhou T, Lippincott-Schwartz J and Liu W:
Deacetylation of nuclear LC3 drives autophagy initiation under
starvation. Mol Cell. 57:456–466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hyttinen JM, Niittykoski M, Salminen A and
Kaarniranta K: Maturation of autophagosomes and endosomes: A key
role for Rab7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:503–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lee J, Kim J, Lee JH, Choi YM, Choi H, Cho
HD, Cha GH, Lee YH, Jo EK, Park BH and Yuk JM: SIRT1 promotes host
protective immunity against toxoplasma gondii by controlling the
FoxO-autophagy axis via the AMPK and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:135782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xu C, Wang L, Fozouni P, Evjen G, Chandra
V, Jiang J, Lu C, Nicastri M, Bretz C, Winkler JD, et al: SIRT1 is
downregulated by autophagy in senescence and ageing. Nat Cell Biol.
22:1170–1179. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wei F, Wang Y, Yao J, Mei L, Huang X, Kong
H, Chen J, Chen X, Liu L, Wang Z, et al: ZDHHC7-mediated
S-palmitoylation of ATG16L1 facilitates LC3 lipidation and
autophagosome formation. Autophagy. 20:2719–2737. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Valdor R and Macian F: Autophagy and the
regulation of the immune response. Pharmacol Res. 66:475–483. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hu YX, Han XS and Jing Q: Autophagy in
Development and Differentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1206:469–487.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Adelipour M, Saleth LR, Ghavami S,
Alagarsamy KN, Dhingra S and Allameh A: The role of autophagy in
the metabolism and differentiation of stem cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1868:1664122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pohl C and Dikic I: Cellular quality
control by the ubiquitinproteasome system and autophagy. Science.
366:818–822. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Henderson NC, Rieder F and Wynn TA:
Fibrosis: From mechanisms to medicines. Nature. 587:555–566. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sun C, Zhang H, Wang X and Liu X:
Ligamentum flavum fibrosis and hypertrophy: Molecular pathways,
cellular mechanisms, and future directions. FASEB J. 34:9854–9868.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wynn TA and Ramalingam TR: Mechanisms of
fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med.
18:1028–1040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Schuster R, Younesi F, Ezzo M and Hinz B:
The role of myofibroblasts in physiological and pathological tissue
repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 15:a0412312023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Humphreys BD: Mechanisms of renal
fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 80:309–326. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Weiskirchen R, Weiskirchen S and Tacke F:
Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms
and translational implications. Mol Aspects Med. 65:2–15. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Piersma B, Bank RA and Boersema M:
Signaling in fibrosis: TGF-β, WNT, and YAP/TAZ converge. Front Med
(Lausanne). 2:592015.
|
|
83
|
Burgy O and Königshoff M: The WNT
signaling pathways in wound healing and fibrosis. Matrix Biol.
68-69:67–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:325–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Noguchi S, Saito A and Nagase T: YAP/TAZ
signaling as a molecular link between fibrosis and cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:36742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Habibie H, Adhyatmika A, Schaafsma D and
Melgert BN: The role of osteoprotegerin (OPG) in fibrosis: Its
potential as a biomarker and/or biological target for the treatment
of fibrotic diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 228:1079412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Williams L, Layton T, Yang N, Feldmann M
and Nanchahal J: Collagen VI as a driver and disease biomarker in
human fibrosis. FEBS J. 289:3603–3629. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Bai L, Li A, Gong C, Ning X and Wang Z:
Protective effect of rutin against bleomycin induced lung fibrosis:
Involvement of TGF-β1/α-SMA/Col I and III pathway. BioFactors.
46:637–644. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ge M, Zou H, Chen J, Zhang Q, Li C, Yang
J, Wu J, Xie X, Liu J, Lei L, et al: Cellular fibronectin-targeted
fluorescent aptamer probes for early detection and staging of liver
fibrosis. Acta Biomater. 190:579–592. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Biel C, Faber KN, Bank RA and Olinga P:
Matrix metalloproteinases in intestinal fibrosis. J Crohns Colitis.
18:462–478. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Liu H, Yan W, Ma C, Zhang K, Li K, Jin R,
Xu H, Xu R, Tong J, Yang Z and Guo Y: Early detection of cardiac
fibrosis in diabetic mice by targeting myocardiopathy and matrix
metalloproteinase 2. Acta Biomater. 176:367–378. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhou D, Tian Y, Sun L, Zhou L, Xiao L, Tan
RJ, Tian J, Fu H, Hou FF and Liu Y: Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is a
urinary biomarker and pathogenic mediator of kidney fibrosis. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 28:598–611. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Patel V and Noureddine L: MicroRNAs and
fibrosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 21:410–416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Duan ZY, Bu R, Liang S, Chen XZ, Zhang C,
Zhang QY, Li JJ, Chen XM and Cai GY: Urinary miR-185-5p is a
biomarker of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy.
Front Immunol. 15:13260262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhao X, Xue X, Cui Z, Kwame Amevor F, Wan
Y, Fu K, Wang C, Peng C and Li Y: microRNAs-based diagnostic and
therapeutic applications in liver fibrosis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
RNA. 14:e17732023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Xuan Y, Wu D, Zhang Q, Yu Z, Yu J and Zhou
D: Elevated ALT/AST ratio as a marker for NAFLD risk and severity:
insights from a cross-sectional analysis in the United States.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 15:14575982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Amernia B, Moosavy SH, Banookh F and Zoghi
G: FIB-4, APRI, and AST/ALT ratio compared to FibroScan for the
assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in Bandar Abbas, Iran. BMC Gastroenterol. 21:4532021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cylwik B, Bauer A, Gruszewska E, Gan K,
Kazberuk M and Chrostek L: The diagnostic value of fibrotest and
hepascore as non-invasive markers of liver fibrosis in primary
sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). J Clin Med. 12:75522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Dzudzor B, Hammond H, Tachi K, Alisi A,
Vento S, Gyasi RK and Aheto JMK: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and
hyaluronic acid levels as markers of fibrosis in patients with
chronic liver disease at the main tertiary referral hospital in
Ghana: A case-control study design. Health Sci Rep. 6:e11012023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Soccio P, Moriondo G, d'Alessandro M,
Scioscia G, Bergantini L, Gangi S, Tondo P, Foschino Barbaro MP,
Cameli P, Bargagli E and Lacedonia D: Role of BAL and Serum Krebs
von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) in patients with pulmonary fibrosis.
Biomedicines. 12:2692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jehn LB, Costabel U, Boerner E, Wälscher
J, Theegarten D, Taube C and Bonella F: Serum KL-6 as a biomarker
of progression at any time in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. J
Clin Med. 12:11732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chiba S, Ohta H, Abe K, Hisata S, Ohkouchi
S, Hoshikawa Y, Kondo T and Ebina M: The diagnostic value of the
interstitial biomarkers KL-6 and SP-D for the degree of fibrosis in
combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Pulm Med.
2012:4929602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
White ES, Xia M, Murray S, Dyal R,
Flaherty CM, Flaherty KR, Moore BB, Cheng L, Doyle TJ, Villalba J,
et al: Plasma surfactant protein-D, matrix metalloproteinase-7, and
osteopontin index distinguishes idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from
other idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 194:1242–1251. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ikeda K, Chiba H, Nishikiori H, Azuma A,
Kondoh Y, Ogura T, Taguchi Y, Ebina M, Sakaguchi H, Miyazawa S, et
al: Serum surfactant protein D as a predictive biomarker for the
efficacy of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: A post-hoc analysis of the phase 3 trial in Japan. Respir
Res. 21:3162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Saito H, Tanaka T, Tanaka S, Higashijima
Y, Yamaguchi J, Sugahara M, Ito M, Uchida L, Hasegawa S, Wakashima
T, et al: Persistent expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated
lipocalin and M2 macrophage markers and chronic fibrosis after
acute kidney injury. Physiol Rep. 6:e137072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Hijmans RS, Rasmussen DG, Yazdani S, Navis
G, van Goor H, Karsdal MA, Genovese F and van den Born J: Urinary
collagen degradation products as early markers of progressive renal
fibrosis. J Transl Med. 15:632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Papasotiriou M, Genovese F, Klinkhammer
BM, Kunter U, Nielsen SH, Karsdal MA, Floege J and Boor P: Serum
and urine markers of collagen degradation reflect renal fibrosis in
experimental kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
30:1112–1121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Karabinowska-Małocha A, Dziewięcka E,
Szymańska M, Banyś P, Urbańczyk-Zawadzka M, Krupiński M, Mielnik M,
Wiśniowska-Śmiałek S, Podolec P, Budkiewicz A, et al: Link between
fibrosis-specific biomarkers and interstitial fibrosis in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Kardiol Pol. 81:692–699. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Scisciola L, Paolisso P, Belmonte M,
Gallinoro E, Delrue L, Taktaz F, Fontanella RA, Degrieck I,
Pesapane A, Casselman F, et al: Myocardial sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2 expression and cardiac remodelling in patients with
severe aortic stenosis: The BIO-AS study. Eur J Heart Fail.
26:471–482. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Al Ali L, Meijers WC, Beldhuis IE, Groot
HE, Lipsic E, van Veldhuisen DJ, Voors AA, van der Horst ICC, de
Boer RA and van der Harst P: Association of fibrotic markers with
diastolic function after STEMI. Sci Rep. 14:191222024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
de Jong S, van Veen TA, de Bakker JM, Vos
MA and van Rijen HV: Biomarkers of myocardial fibrosis. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 57:522–535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yan L, Wang J, Cai X, Liou YC, Shen HM,
Hao J, Huang C, Luo G and He W: Macrophage plasticity: Signaling
pathways, tissue repair, and regeneration. MedComm (2020).
5:e6582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Luo M, Zhao F, Cheng H, Su M and Wang Y:
Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory
diseases. Front Immunol. 15:13529462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ge Z, Chen Y, Ma L, Hu F and Xie L:
Macrophage polarization and its impact on idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Front Immunol. 15:14449642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N and Gordon S:
Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor
activity: A marker of alternative immunologic macrophage
activation. J Exp Med. 176:287–292. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wang C, Ma C, Gong L, Guo Y, Fu K, Zhang
Y, Zhou H and Li Y: Macrophage polarization and its role in liver
disease. Front Immunol. 12:8030372021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
118
|
Wu MY and Lu JH: Autophagy and macrophage
functions: Inflammatory response and phagocytosis. Cells. 9:702019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Rockey DC, Bell PD and Hill JA: Fibrosis-a
common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med.
372:1138–1149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wang Y, Jiao L, Qiang C, Chen C, Shen Z,
Ding F, Lv L, Zhu T, Lu Y and Cui X: The role of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 in fibrosis diseases and its molecular
mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 171:1161162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ogawa T, Shichino S, Ueha S and Matsushima
K: Macrophages in lung fibrosis. Int Immunol. 33:665–671. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Huang WJ and Tang XX: Virus infection
induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Transl Med. 19:4962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tian Y, Lv J, Su Z, Wu T, Li X, Hu X,
Zhang J and Wu L: LRRK2 plays essential roles in maintaining lung
homeostasis and preventing the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21066851182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mornex JF, Cordier G and Revillard JP:
Markers of lymphocyte activation in interstitial pulmonary disease.
Rev Fr Mal Respir. 11:293–300. 1983.In Frence.
|
|
125
|
Du S, Li C, Lu Y, Lei X, Zhang Y, Li S,
Liu F, Chen Y, Weng D and Chen J: Dioscin alleviates crystalline
silica-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through
promoting alveolar macrophage autophagy. Theranostics. 9:1878–1892.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Li C, Lu Y, Du S, Li S, Zhang Y, Liu F,
Chen Y, Weng D and Chen J: Dioscin exerts protective effects
against crystalline silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
Theranostics. 7:4255–4275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhong Y, Jin R, Luo R, Liu J, Ren L, Zhang
Y, Shan Z and Peng X: Diosgenin targets CaMKK2 to alleviate type II
diabetic nephropathy through improving autophagy, mitophagy and
mitochondrial dynamics. Nutrients. 15:35542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Qian Q, Ma Q, Wang B, Qian Q, Zhao C, Feng
F and Dong X: MicroRNA-205-5p targets E2F1 to promote autophagy and
inhibit pulmonary fibrosis in silicosis through impairing
SKP2-mediated Beclin1 ubiquitination. J Cell Mol Med. 25:9214–9227.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Jessop F, Hamilton RF, Rhoderick JF, Shaw
PK and Holian A: Autophagy deficiency in macrophages enhances NLRP3
inflammasome activity and chronic lung disease following silica
exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 309:101–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Tan S and Chen S: Macrophage autophagy and
silicosis: Current perspective and latest insights. Int J Mol Sci.
22:4532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Tang PM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
Macrophages: Versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 15:144–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Liu K, Zhao E, Ilyas G, Lalazar G, Lin Y,
Haseeb M, Tanaka KE and Czaja MJ: Impaired macrophage autophagy
increases the immune response in obese mice by promoting
proinflammatory macrophage polarization. Autophagy. 11:271–284.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liu T, Wang L, Liang P, Wang X, Liu Y, Cai
J, She Y, Wang D, Wang Z, Guo Z, et al: USP19 suppresses
inflammation and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by
manipulating NLRP3 function via autophagy. Cell Mol Immunol.
18:2431–2442. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
134
|
Bhatia D, Chung KP, Nakahira K, Patino E,
Rice MC, Torres LK, Muthukumar T, Choi AM, Akchurin OM and Choi ME:
Mitophagy-dependent macrophage reprogramming protects against
kidney fibrosis. JCI Insight. 4:e1328262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Li L, Liang X, Cheng P,
Li Q, Chang X, Wang K, Huang S, Li Y, et al: Lymphangiogenesis in
renal fibrosis arises from macrophages via VEGF-C/VEGFR3-dependent
autophagy and polarization. Cell Death Dis. 12:1092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Lodder J, Denaës T, Chobert MN, Wan J,
El-Benna J, Pawlotsky JM, Lotersztajn S and Teixeira-Clerc F:
Macrophage autophagy protects against liver fibrosis in mice.
Autophagy. 11:1280–1292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Oakes SA and Papa FR: The role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol.
10:173–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Senft D and Ronai ZA: UPR, autophagy, and
mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response. Trends
Biochem Sci. 40:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C,
Kroemer G, Kaufman RJ, Malhi H and Ren J: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress in liver diseases. Hepatology. 77:619–639. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 54:795–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Chen X, Shi C, He M, Xiong S and Xia X:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic
targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Ernst R, Renne MF, Jain A and von der
Malsburg A: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane homeostasis and the
unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
16:a0414002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Gong J, Wang XZ, Wang T, Chen JJ, Xie XY,
Hu H, Yu F, Liu HL, Jiang XY and Fan HD: Molecular signal networks
and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 18:1–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Xia SW, Wang ZM, Sun SM, Su Y, Li ZH, Shao
JJ, Tan SZ, Chen AP, Wang SJ, Zhang ZL, et al: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and protein degradation in chronic liver disease.
Pharmacol Res. 161:1052182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Benedetti R, Romeo MA, Arena A, Gilardini
Montani MS, D'Orazi G and Cirone M: ATF6 supports lysosomal
function in tumor cells to enable ER stress-activated
macroautophagy and CMA: Impact on mutant TP53 expression.
Autophagy. 20:1854–1867. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Chen L, Wei M, Zhou B, Wang K, Zhu E and
Cheng Z: The roles and mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated autophagy in animal viral infections. Vet Res.
55:1072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Shi Y, Jiang B and Zhao J: Induction
mechanisms of autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury, inflammatory bowel disease,
and colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 170:1159842024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Feng S, Ji J, Li H and Zhang X:
H2S alleviates renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by
suppressing ERS-induced autophagy. Transpl Immunol. 83:1020062024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
He L, Li H, Li C, Liu ZK, Lu M, Zhang RY,
Wu D, Wei D, Shao J, Liu M, et al: HMMR alleviates endoplasmic
reticulum stress by promoting autophagolysosomal activity during
endoplasmic reticulum stress-driven hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Cancer Commun (Lond). 43:981–1002. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Habshi T, Shelke V, Kale A, Anders HJ and
Gaikwad AB: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in
the transition from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease.
J Cell Physiol. 238:82–93. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Liao H, Liu S, Ma Q, Huang H, Goel A,
Torabian P, Mohan CD and Duan C: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
induced autophagy in cancer and its potential interactions with
apoptosis and ferroptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1872:1198692025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Baek AR, Hong J, Song KS, Jang AS, Kim DJ,
Chin SS and Park SW: Spermidine attenuates bleomycin-induced lung
fibrosis by inducing autophagy and inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress (ERS)-induced cell death in mice. Exp Mol Med. 52:2034–2045.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Ma C, Liu Y and Fu Z: Implications of
endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in aging and
cardiovascular diseases. Front Pharmacol. 15:14138532024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zhou L, Liu Z, Chen S, Qiu J, Li Q, Wang
S, Zhou W, Chen D, Yang G and Guo L: Transcription factor
EB-mediated autophagy promotes dermal fibroblast differentiation
and collagen production by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress
and autophagy-dependent secretion. Int J Mol Med. 47:547–560. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Wu W, Zhao Y, Hu T, Long Y, Zeng Y, Li M,
Peng S, Hu J and Shen Y: Endoplasmic reticulum stress is
upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease and contributed TLR2
pathway-mediated inflammatory response. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 46:192–198. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Shi Y, Gao Z, Xu B, Mao J, Wang Y, Liu Z
and Wang J: Protective effect of naringenin on cadmium
chloride-induced renal injury via alleviating oxidative stress,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy in chickens. Front
Pharmacol. 15:14408772024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Feng J, Chen Y, Lu B and Sun X, Zhu H and
Sun X: Autophagy activated via GRP78 to alleviate endoplasmic
reticulum stress for cell survival in blue light-mediated damage of
A2E-laden RPEs. BMC Ophthalmol. 19:2492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Shu S, Wang H, Zhu J, Liu Z, Yang D, Wu W,
Cai J, Chen A, Tang C and Dong Z: Reciprocal regulation between ER
stress and autophagy in renal tubular fibrosis and apoptosis. Cell
Death Dis. 12:10162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Xiong X, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xie J, Bian Y,
Yin Q, Tong R, Yu D and Pan L: Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)
ATPase (SERCA)-mediated ER stress crosstalk with autophagy is
involved in tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate stress-induced cardiac
fibrosis. J Inorg Biochem. 236:1119722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Ren Y, Cui Q, Zhang J, Liu W, Xu M, Lv Y,
Wu Z, Zhang Y and Wu R: Milk fat globule-egf factor 8 alleviates
pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting ER stress-induced
chaperone-mediated autophagy in mice. Front Pharmacol.
12:7072592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Zheng Y, Zhang D, Su L, Wen Y and Wang Y:
FAM172A supervises ER (endoplasmic reticulum) stress-triggered
autophagy in the epidural fibrosis process. JOR Spine. 5:e12032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Singh A, Bhatt KS, Nguyen HC, Frisbee JC
and Singh KK: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
cardiovascular pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. 25:61802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Jimenez SA and Piera-Velazquez S:
Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the pathogenesis
of Systemic Sclerosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Myth or reality? Matrix Biol. 51:26–36.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Piera-Velazquez S, Li Z and Jimenez SA:
Role of endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the
pathogenesis of fibrotic disorders. Am J Pathol. 179:1074–1080.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Singh B, Cui K, Eisa-Beygi S, Zhu B, Cowan
DB, Shi J, Wang DZ, Liu Z, Bischoff J and Chen H: Elucidating the
crosstalk between endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT)
and endothelial autophagy in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
Vascul Pharmacol. 155:1073682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Jackson AO, Zhang J, Jiang Z and Yin K:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: A novel therapeutic target
for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 27:383–393.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Lu X, Gong J, Dennery PA and Yao H:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: Pathogenesis and therapeutic
targets for chronic pulmonary and vascular diseases. Biochem
Pharmacol. 168:100–107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Bischoff J: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Circ Res. 124:1163–1165. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Zhang L, He J, Wang J, Liu J, Chen Z, Deng
B, Wei L, Wu H, Liang B, Li H, et al: Knockout RAGE alleviates
cardiac fibrosis through repressing endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition (EndMT) mediated by autophagy. Cell Death Dis.
12:4702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Pan JA, Zhang H, Lin H, Gao L, Zhang HL,
Zhang JF, Wang CQ and Gu J: Irisin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced
cardiac perivascular fibrosis through inhibiting
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by regulating ROS
accumulation and autophagy disorder in endothelial cells. Redox
Biol. 46:1021202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Zhou Z, Wang H, Zhang X, Song M, Yao S,
Jiang P, Liu D, Wang Z, Lv H, Li R, et al: Defective autophagy
contributes to endometrial epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
intrauterine adhesions. Autophagy. 18:2427–2442. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Singh KK, Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Ramadan
A, Matkar PN, Ehsan M, Sandhu P, Mantella LE, Gupta N, et al: The
essential autophagy gene ATG7 modulates organ fibrosis via
regulation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
290:2547–2559. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
173
|
Livingston MJ, Shu S, Fan Y, Li Z, Jiao Q,
Yin XM, Venkatachalam MA and Dong Z: Tubular cells produce FGF2 via
autophagy after acute kidney injury leading to fibroblast
activation and renal fibrosis. Autophagy. 19:256–277. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
174
|
Nam SA, Kim WY, Kim JW, Park SH, Kim HL,
Lee MS, Komatsu M, Ha H, Lim JH, Park CW, et al: Autophagy
attenuates tubulointerstital fibrosis through regulating
transforming growth factor-β and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 10:782019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Liu X, Tan S, Liu H, Jiang J, Wang X, Li L
and Wu B: Hepatocyte-derived MASP1-enriched small extracellular
vesicles activate HSCs to promote liver fibrosis. Hepatology.
77:1181–1197. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Li S, Liu G, Gu M, Li Y, Li Y, Ji Z, Li K
and Wang Y, Zhai H and Wang Y: A novel therapeutic approach for
IPF: Based on the 'Autophagy-Apoptosis' balance regulation of
Zukamu Granules in alveolar macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol.
297:1155682022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Chen M, Menon MC, Wang W, Fu J, Yi Z, Sun
Z, Liu J, Li Z, Mou L, Banu K, et al: HCK induces macrophage
activation to promote renal inflammation and fibrosis via
suppression of autophagy. Nat Commun. 14:42972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Liu XY, Zhang W, Ma BF, Sun MM and Shang
QH: Advances in research on the effectiveness and mechanism of
active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine in regulating
hepatic stellate cells autophagy against hepatic fibrosis. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 18:2715–2727. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|