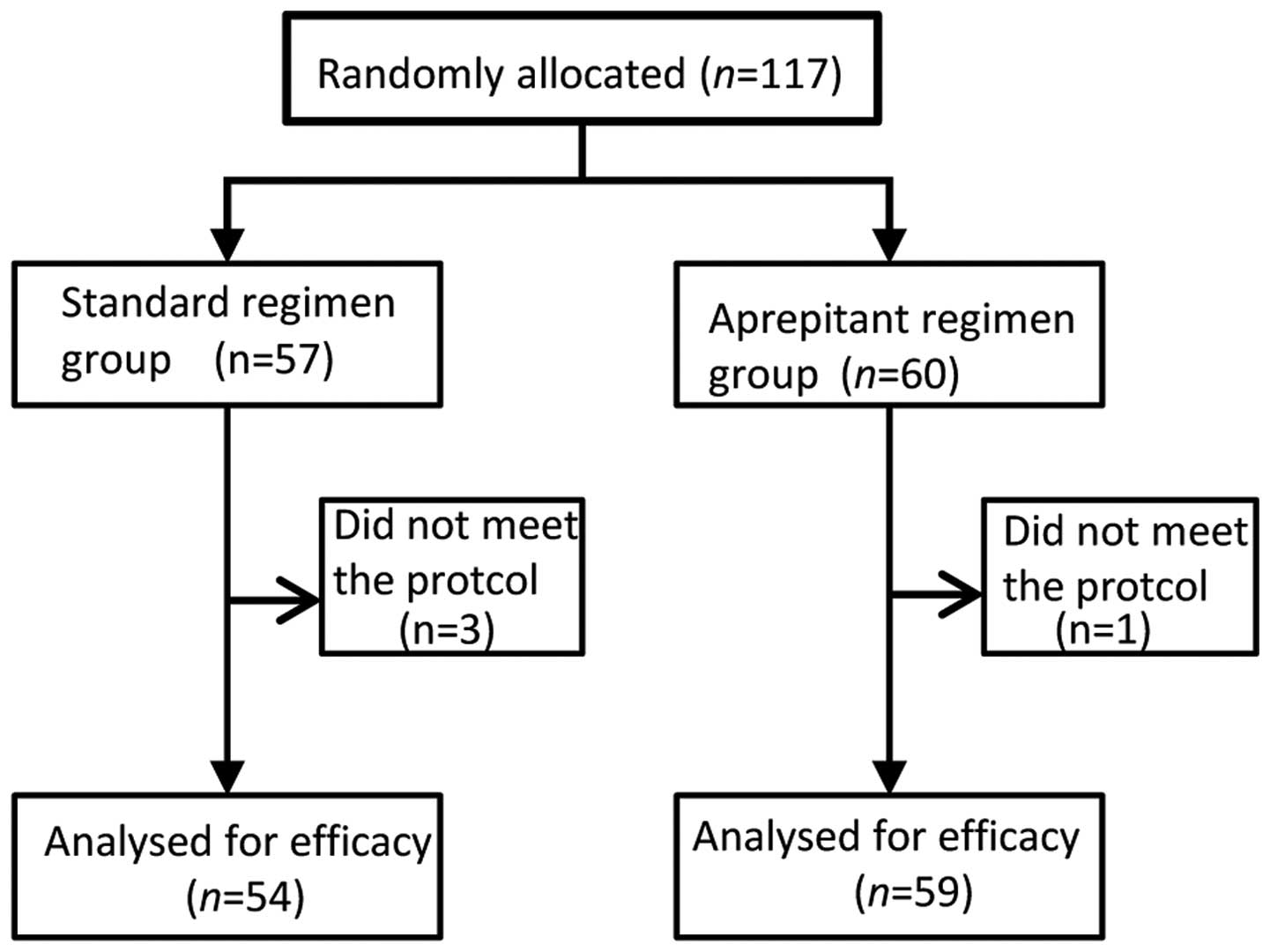
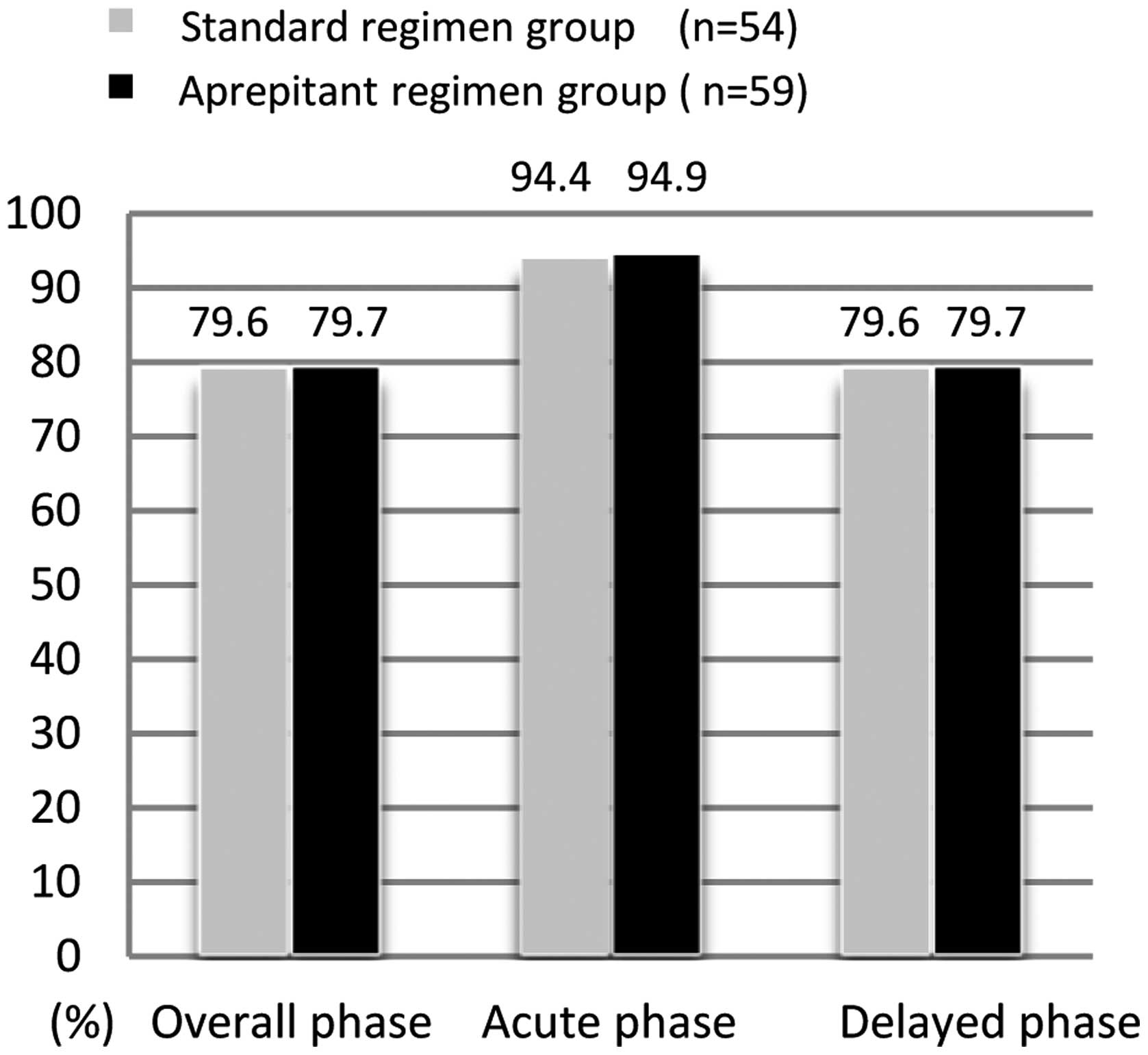
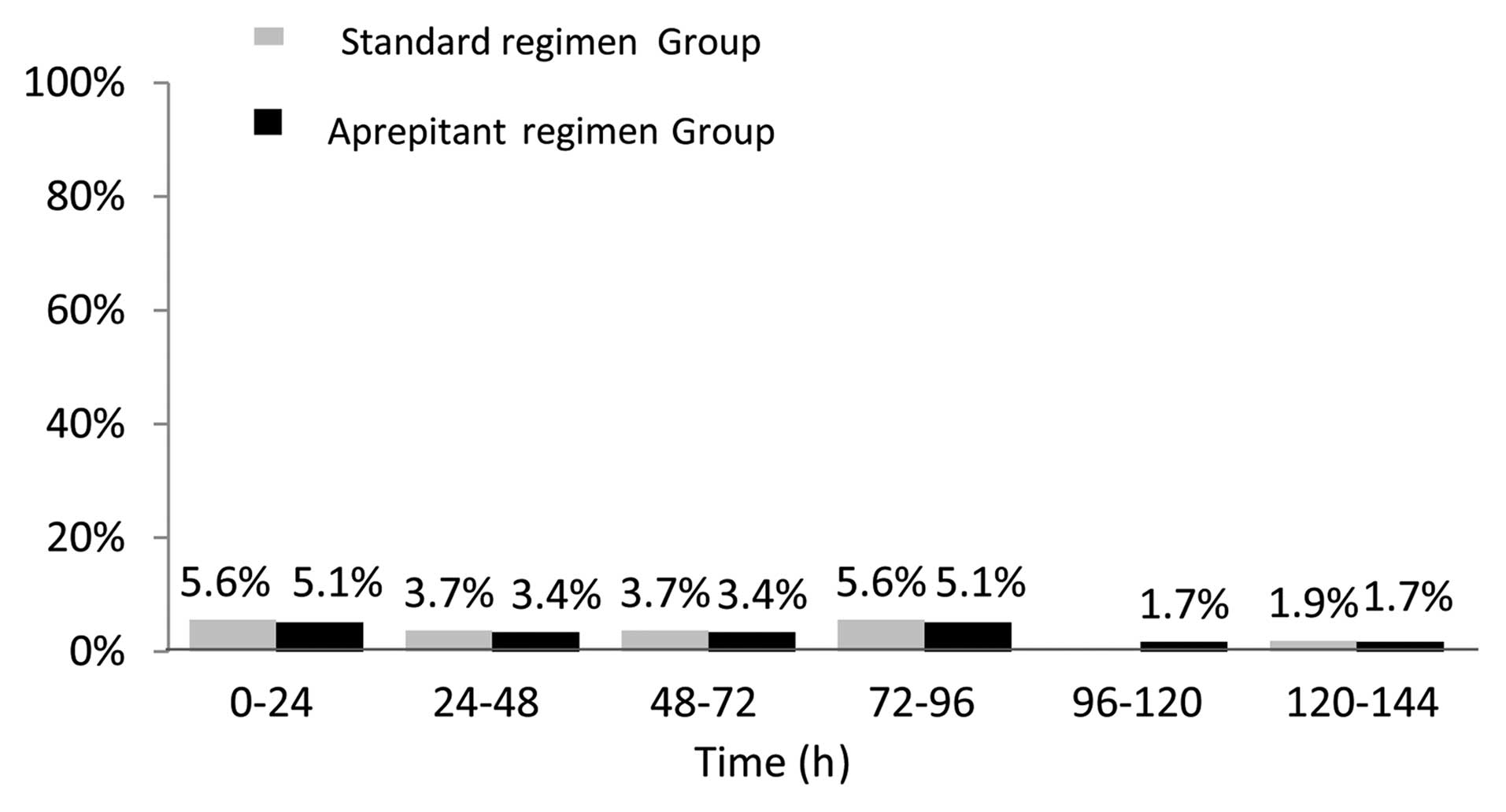
|
1
|
Oo TH and Hesketh PJ: Drug insight: New
anti-emetics in the management of chemotherapy-induced nausea and
vomiting. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2:196–201. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soukop M, McQuade B, Hunter E, Stewart A,
Kaye S, Cassidy J, Kerr D, Khanna S, Smyth J and Coleman R:
Ondansetron compared with metoclopramide in the control of emesis
and quality of life during repeated chemotherapy for breast cancer.
Oncology. 49:295–304. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sigsgaard T, Herrstedt J, Andersen LJ,
Havsteen H, Langer SW, Kjaerbøl AG, Lund H, Kjaer M and
Dombernowsky P: Granisetron compared with predonisolone plus
metopimazine as anti-emetic prophylaxis during multiple cycles of
moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 80:412–418. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sigsgaard T, Herrstedt J, Handberg J,
Kjaer M and Dombernowsky P: Ondansetron plus metopimazine compared
with ondansetron plus metopimazine plus prednisolone as anti-emetic
prophylaxis in patients receiving multiple cycles of moderately
emetogenic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 19:2091–2097.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Kris MG, Hesketh PJ, Somerfield MR, Feyer P, Clark-Snow R, Koeller
JM, Morrow GR, Chinnery LW, Chesney MJ, Gralla RJ and Grunberg SM:
American society of clinical oncology guideline for anti-emetics in
oncology: Update 2006. J Clin Oncol. 24:2932–2947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warr DG, Hesketh PJ, Gralla RJ, Muss HB,
Herrstedt J, Eisenberg PD, Raftopoulos H, Grunberg SM, Gabriel M,
Rodgers A, et al: Efficacy and tolerability of aprepitant for the
prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients
with breast cancer after moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2822–2830. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rapoport BL, Jordan K, Boice JA, Taylor A,
Brown C, Hardwick JS, Carides A, Webb T and Schmoll HJ: Aprepitant
for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
associated with a broad range of moderately emetogenic
chemotherapies and tumor types: A randomized, double-blind study.
Support Care Cancer. 18:423–431. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roila F, Warr D, Aapro M, Clark-Snow RA,
Einhorn L, Gralla RJ, Herrstedt J, Saito M and Tonato M: Delayed
emesis: Moderately emetogenic chemotherapy (single-day chemotherapy
regimens only). Support Care Cancer. 19(Suppl 1): S57–S62. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer
in. 2008 GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Van Cutsem E and Oliveira J: ESMO
Guidelines Working Group: Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical
recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol.
20(Suppl 4): S61–S63. 2009.
|
|
11
|
Yoo PS, Lopez-Soler RI, Longo WE and Cha
CH: Liver resection for metastatic colorectal cancer in the age of
neoadjuvant chemotherapy and bevacizumab. Clin Colorectal Cancer.
6:202–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin
M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer
G, et al: Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin
as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 18:2938–2947. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saltz LB, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E,
Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS,
Rivera F, et al: Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based
chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer:
A randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 26:2013–2019. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Twelves C, Brunet
R, Butts C, Conroy T, Debraud F, Figer A, Grossmann J, Sawada N, et
al: XELOX (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin): Active first-line
therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 22:2084–2091. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L,
Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan
P, Bridgewater J, et al: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin
as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2343–2351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
André T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J,
Hickish T, Topham C, Bonetti A, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Rivera F
and de Gramont A: Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin,
fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or
III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:3109–3116.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haller DG, Tabernero J, Maroun J, de Braud
F, Price T, Van Cutsem E, Hill M, Gilberg F, Rittweger K and
Schmoll HJ: Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with
fluorouracil and folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III
colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:1465–1471. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Prevention of chemotherapy- and
radiotherapy-induced emesis: Results of the perugia consensus
conference. Antiemetic subcommittee of the multinational
association of supportive care in cancer (MASCC). Ann Oncol.
9:811–819. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gralla RJ, Osoba D, Kris MG, Kirkbride P,
Hesketh PJ, Chinnery LW, Clark-Snow R, Gill DP, Groshen S, Grunberg
S, et al: Recommendations for the use of anti-emetics:
Evidence-based, clinical practice guidelines. American society of
clinical oncology. J Clin Oncol. 17:2971–2994. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Herrstedt J, Aapro MS, Roila F and Kataja
VV: ESMO, Guidelines Task Force: ESMO minimum clinical
recommendations for prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced nausea and
vomiting (NV). Ann Oncol. 16(Suppl 1): i77–i79. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perez EA, Hesketh P, Sandbach J, Reeves J,
Chawla S, Markman M, Hainsworth J, Bushnell W and Friedman C:
Comparison of single-dose oral granisetron versus intravenous
ondansetron in the prevention of nausea and vomiting induced by
moderately emetogenic chemotherapy: A multicenter, double-blind,
randomized parallel study. J Clin Oncol. 16:754–760.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jordan K, Hinke A, Grothey A, Voigt W,
Arnold D, Wolf HH and Schmoll HJ: A meta-analysis comparing the
efficacy of four 5-HT3-receptor antagonists for acute
chemotherapy-induced emesis. Support Care Cancer. 15:1023–1033.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roila F, Herrstedt J, Aapro M, Gralla RJ,
Einhorn LH, Ballatori E, Bria E, Clark-Snow RA, Espersen BT, Feyer
P, et al: Guideline update for MASCC and ESMO in the prevention of
chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: Results
of the Perugia consensus conference. Ann Oncol. 21(Suppl 5):
v232–v243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Basch E, Prestrud AA, Hesketh PJ, Kris MG,
Feyer PC, Somerfield MR, Chesney M, et al: Antiemetics: American
society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J
Clin Oncol. 29:4189–4198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roscoe JA, Heckler CE, Morrow GR, Mohile
SG, Dakhil SR, Wade JL and Kuebler JP: Prevention of delayed
nausea: A University of Rochester cancer center community clinical
oncology program study of patients receiving chemotherapy. J Clin
Oncol. 30:3389–3395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Double-blind, dose-finding study of four
intravenous doses of dexamethasone in the prevention of
cisplatin-induced acute emesis. Italian group for anti-emetic
research. J Clin Oncol. 16:2937–2942. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gralla RJ, Navari RM, Hesketh PJ, Popovic
W, Strupp J, Noy J, Einhorn L, Ettinger D, Bushnell W and Friedman
C: Single-dose oral granisetron has equivalent anti-emetic efficacy
to intravenous ondansetron for highly emetogenic cisplatin-based
chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 16:1568–1573. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vardy J, Chiew KS, Galica J, Pond GR and
Tannock IF: Side effects associated with the use of dexamethasone
for prophylaxis of delayed emesis after moderately emetogenic
chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 94:1011–1015. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hesketh PJ, Grunberg SM, Gralla RJ, Warr
DG, Roila F, de Wit R, Chawla SP, Carides AD, Ianus J, Elmer ME, et
al: The oral neurokinin-l antagonist aprepitant for the prevention
of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: A multinational,
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients
receiving high-dose cisplatin-the aprepitant protocol 052 study
group. J Clin Oncol. 21:4112–4119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|