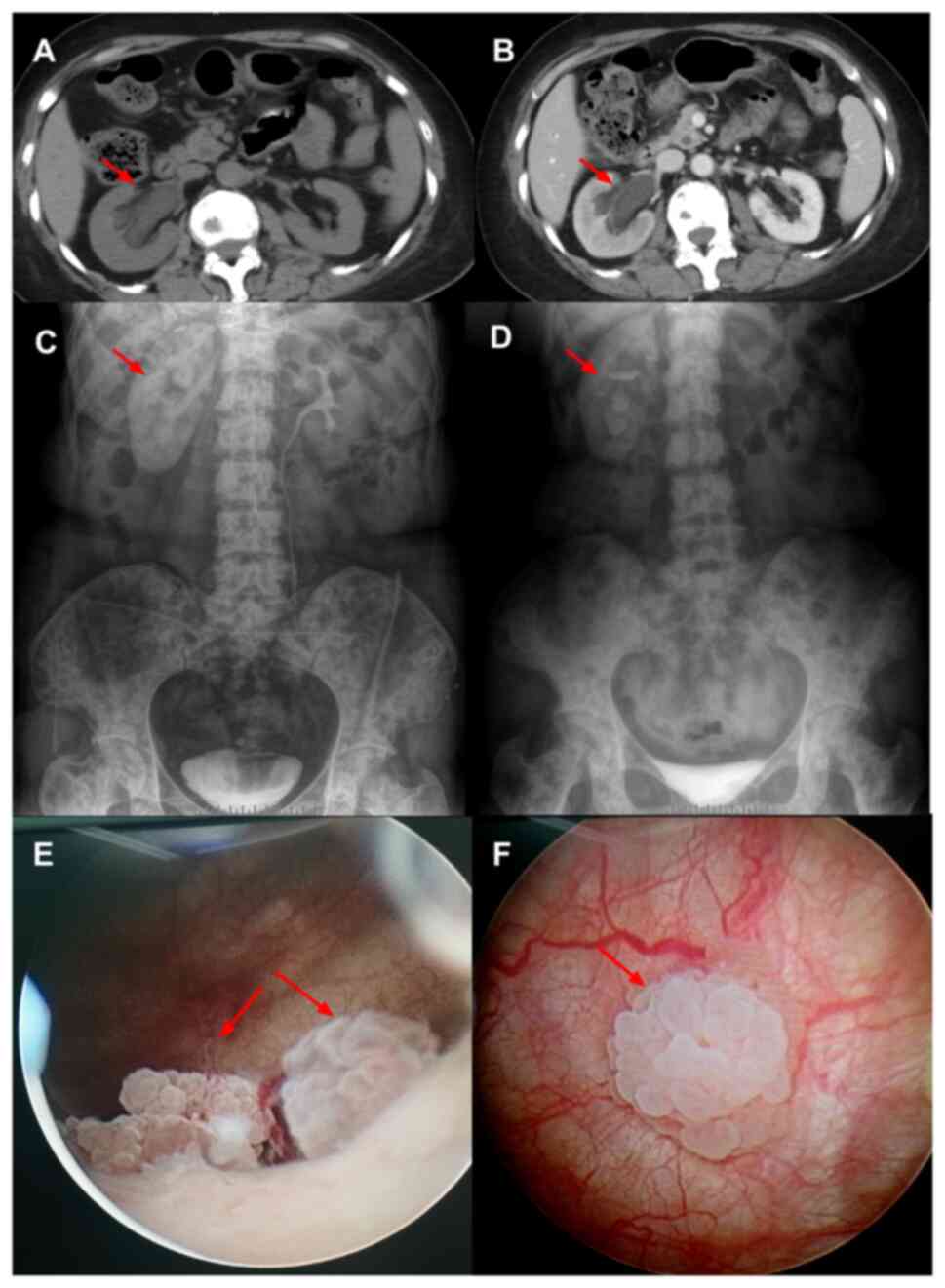
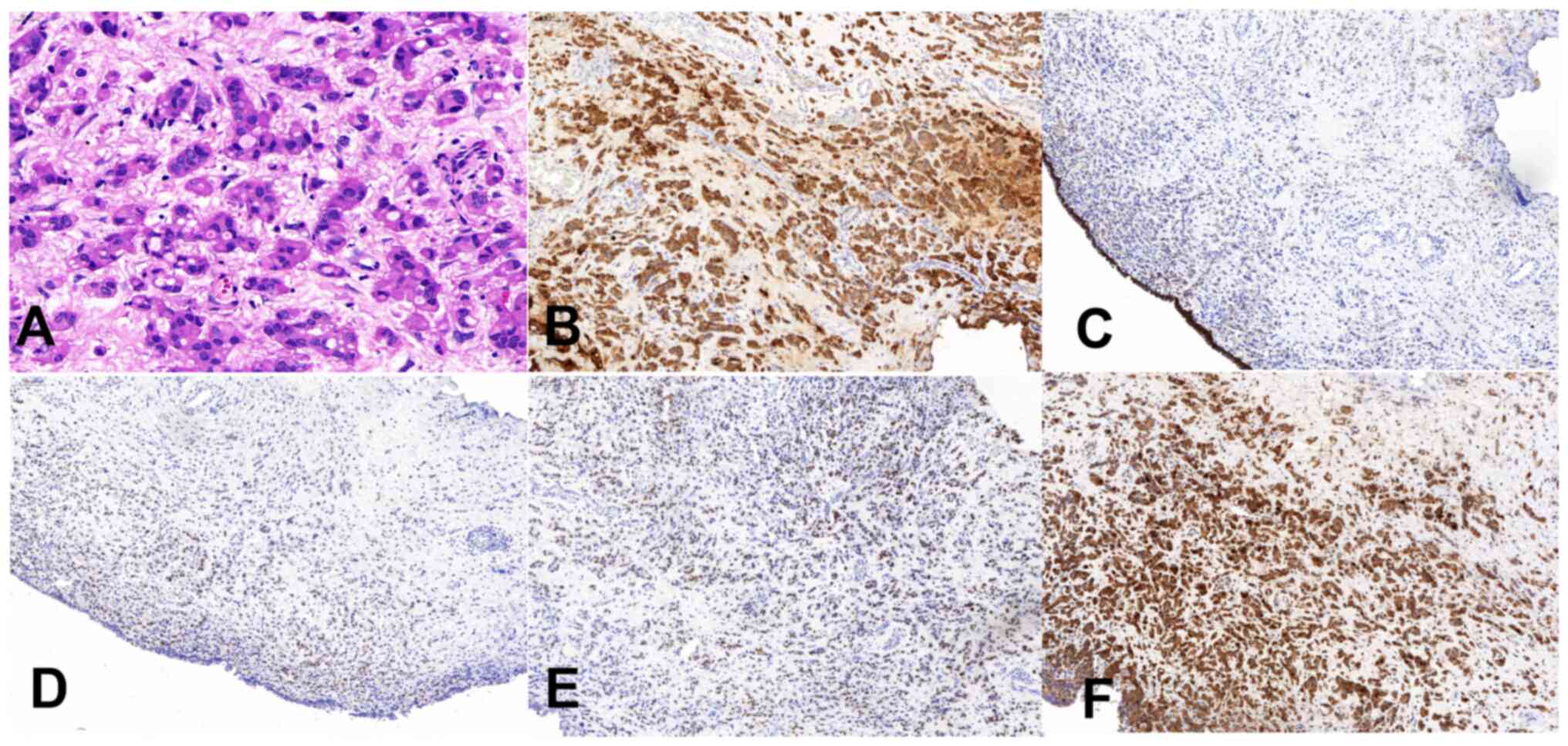
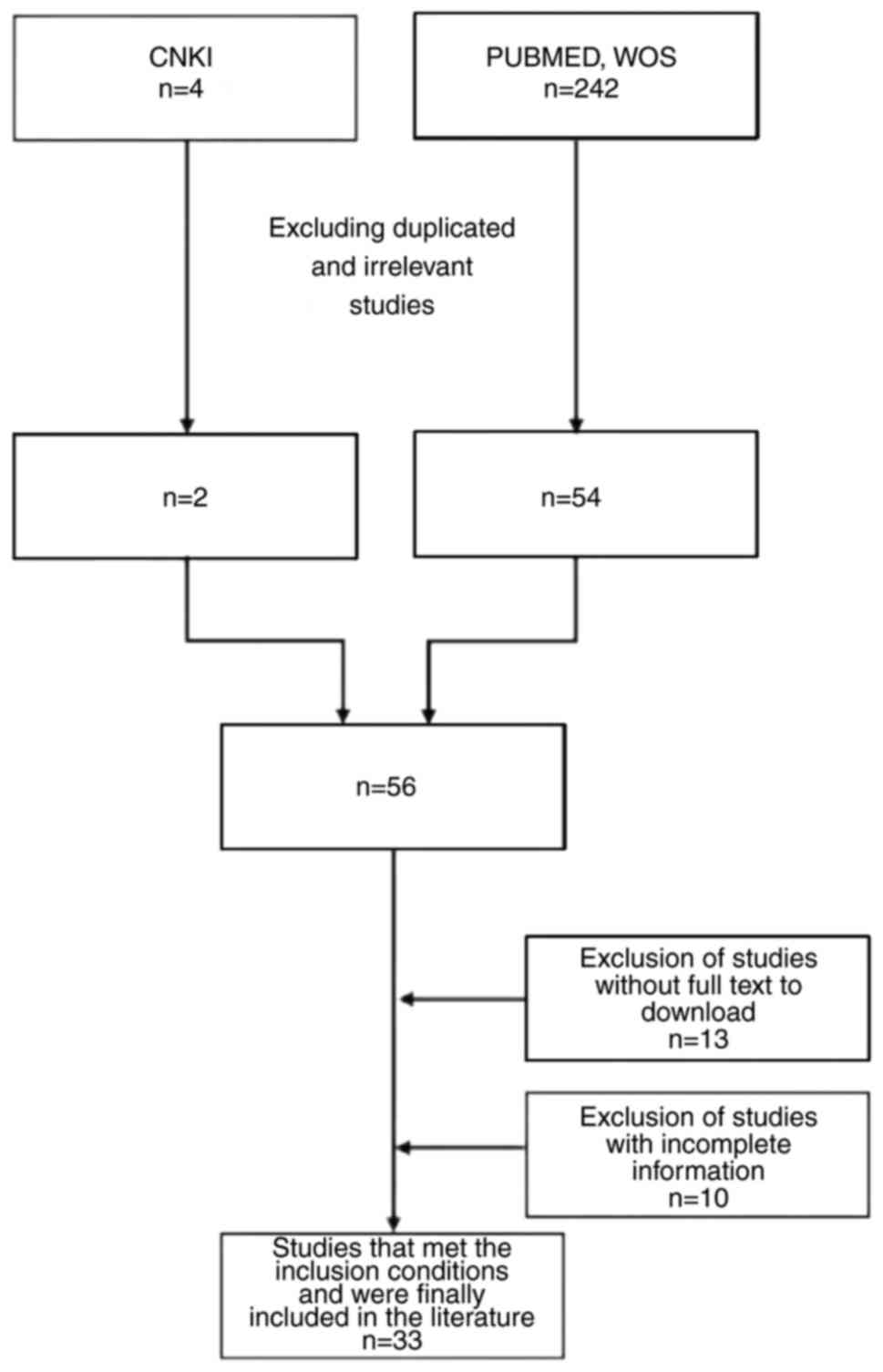
|
1
|
Katsura C, Ogunmwonyi I, Kankam HK and
Saha S: Breast cancer: Presentation, investigation and management.
Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 83:1–7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arnold M, Morgan E, Rumgay H, Mafra A,
Singh D, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Gralow JR, Cardoso F, Siesling S
and Soerjomataram I: Current and future burden of breast cancer:
Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast. 66:15–23. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peng Z, Wei J, Lu X, Zheng H, Zhong X, Gao
W, Chen Y and Jing J: Treatment and survival patterns of Chinese
patients diagnosed with breast cancer between 2005 and 2009 in
Southwest China: An observational, population-based cohort study.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e38652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lou Z, Fei X, Christakos G, Yan J and Wu
J: Improving spatiotemporal breast cancer assessment and prediction
in Hangzhou City, China. Sci Rep. 7:31882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Trayes KP and Cokenakes S: Breast cancer
treatment. Am Fam Physician. 104:171–178. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Malinaric R, Balzarini F, Granelli G,
Ferrari A, Trani G, Ambrosini F, Mantica G, Panarello D, De Rose AF
and Terrone C: From women to women-hematuria during therapy for
metastatic breast cancer, what to suspect and when to be alarmed;
Bladder metastasis from breast cancer-our experience and a
systematic literature review. Front Oncol. 12:9769472022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei S and Siegal GP: Metastatic
organotropism: An intrinsic property of breast cancer molecular
subtypes. Adv Anat Pathol. 24:78–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanguedolce F, Landriscina M, Ambrosi A,
Tartaglia N, Cianci P, Di Millo M, Carrieri G, Bufo P and Cormio L:
Bladder metastases from breast cancer: Managing the unexpected. a
systematic review. Urol Int. 101:125–131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ashley S, Choudhury A, Hoskin P, Song Y
and Maitre P: Radiotherapy in metastatic bladder cancer. World J
Urol. 42:472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Q, Li J, Zhu S, Wu J, Chen C, Liu Q,
Wei W, Zhang Y and Sun S: Breast cancer subtypes predict the
preferential site of distant metastases: A SEER based study.
Oncotarget. 8:27990–27996. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bates AW and Baithun SI: Secondary
neoplasms of the bladder are histological mimics of nontransitional
cell primary tumours: Clinicopathological and histological features
of 282 cases. Histopathology. 36:32–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan NAJ, Abdallah M and Tirona MT:
Hormone Receptor Positive/HER2 negative breast cancer with isolated
bladder metastasis: A rare case. J Investig Med High Impact Case
Rep. 9:232470962110221862021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu H and Doğan BE: American Joint
Committee on Cancer's Staging System for Breast Cancer, Eighth
Edition: Summary for Clinicians. Eur J Breast Health. 17:234–238.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhai ZX SJJ and Wang ZP: Invasive lobular
carcinoma of breast with metastatic tumor of bladder and bone: A
case report and literature review. J Contemp Urol Reprod Oncol.
5:308–309. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Nieder C and Pawinski A: A case of
recurrent breast cancer with solitary metastasis to the urinary
bladder. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2014:9315462014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang G, Zhou C, Conklin C, Hayes MM,
Villamil CF, Ostry A and Jones EC: Metastatic breast carcinoma to
the urinary bladder-a report of 11 cases including a tumor to tumor
metastasis. Virchows Arch. 474:333–339. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shah KG, Modi PR and Rizvi J: Breast
carcinoma metastasizing to the urinary bladder and retroperitoneum
presenting as acute renal failure. Indian J Urol. 27:135–136. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gatti G, Zurrida S, Gilardi D, Bassani G,
dos Santos GR and Luini A: Urinary bladder metastases from breast
carcinoma: Review of the literature starting from a clinical case.
Tumori. 91:283–286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ghaida RA, Ayoub H, Nasr R, Issa G and
Bulbul M: Bladder metastasis from primary breast cancer: A case
report and literature review. Cent European J Urol. 66:177–184.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zagha RM and Hamawy KJ: Solitary breast
cancer metastasis to the bladder: An unusual occurrence. Urol
Oncol. 25:236–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elia G, Stewart S, Makhuli ZN, Krenzer BE,
Mathur S, Simon HM and Mehdi S: Metastatic breast cancer diagnosed
during a work-up for urinary incontinence: A case report. Int
Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 10:39–42. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Poulakis V, Witzsch U, de Vries R and
Becht E: Metastatic breast carcinoma to the bladder: 5-year
followup. J Urol. 165:9052001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kleinmann N, Mor Y, Laufer M, Duvdevani M,
Fridman E and Ramon J: A solitary metastasis of breast cancer to
the urinary bladder. Breast J. 11:4972005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin WC and Chen JH: Urinary bladder
metastasis from breast cancer with heterogeneic expression of
estrogen and progesterone receptors. J Clin Oncol. 25:4308–4310.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao GQ, Chow J and Unger PD: Metastatic
tumors to the urinary bladder: Clinicopathologic study of 11 cases.
Int J Surg Pathol. 20:342–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cormio L, Sanguedolce F, Di Fino G,
Massenio P, Liuzzi G, Ruocco N, Bufo P and Carrieri G: Asymptomatic
bladder metastasis from breast cancer. Case Rep Urol.
2014:6725912014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al Ibraheemi AA: Case report of metastatic
invasive breast lobular carcinoma to the urinary bladder. Int J
Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 10:51–55. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoneyama K, Nakagawa M and Hara A: Bladder
metastasis from primary breast cancer: A case report. Surg Case
Rep. 4:732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mohammed S and Bua AA: Metastatic breast
cancer to the urinary bladder in the caribbean. Case Rep Oncol.
14:1586–1590. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Haid M, Ignatoff J, Khandekar JD, Graham J
and Holland J: Urinary bladder metastases from breast carcinoma.
Cancer. 46:229–232. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Berger Y, Nissenblatt M, Salwitz J and
Lega B: Bladder involvement in metastatic breast carcinoma. J Urol.
147:137–139. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soon PS, Lynch W and Schwartz P: Breast
cancer presenting initially with urinary incontinence: A case of
bladder metastasis from breast cancer. Breast. 13:69–71. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lawrentschuk N, Chan Y and Bolton DM:
Metastatic breast cancer to the bladder. Breast J. 11:1432005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feldman PA, Madeb R, Naroditsky I,
Halachmi S and Nativ O: Metastatic breast cancer to the bladder: A
diagnostic challenge and review of the literature. Urology.
59:1382002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang D, Jing T, Hui X and Yue W: A case
report for Postoperative bladder metastasis of breast cancer. Chin
J of Endourology. 16:89–90. 2022.
|
|
36
|
De Rose AF, Balzarini F, Mantica G,
Toncini C and Terrone C: Late urinary bladder metastasis from
breast cancer. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 91:60–62. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gitau SN, Njau A and Mwanzi S: Urinary
bladder metastasis from breast cancer: A rare cause of hematuria.
BJR Case Rep. 6:201900482020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pontes JE and Oldford JR: Metastatic
breast carcinoma to the bladder. J Urol. 104:839–842. 1970.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rigatti P, Broglia L, Montorsi F,
Maffezzini M, Sironi M, Radice F, Abelli P, Pace M, Diamantini S,
Veronesi AM, et al: Breast cancer metastases of the urinary
bladder. Int J Tissue React. 13:159–163. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Silverstein LI, Plaine L, Davis JE and
Kabakow B: Breast carcinoma metastatic to bladder. Urology.
29:544–547. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ryan PD, Harisinghani M, Lerwill MF and
Kaufman DS: Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital.
Case 6-2006. A 71-year-old woman with urinary incontinence and a
mass in the bladder. N Engl J Med. 354:850–856. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Williams JR, Stott MA and Moisey CU:
Bilateral hydronephrosis secondary to breast carcinoma
metastasising to the bladder. Br J Urol. 69:97–98. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schneidau T, Stroumbakis N, Choudhury M,
Eshgi M and Mallouh C: Metastatic breast cancer to the bladder: A
case report. Int Urol Nephrol. 27:297–300. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Luczyńska E, Pawlik T, Chwalibóg A, Anioł
J and Ryś J: Metastatic breast cancer to the bladder case report
and review of literature. J Radiol Case Rep. 4:19–26.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Reichman G, Michielsen DP and De Grève J:
Tamoxifen to treat urge-incontinence from an isolated bladder
metastasis of a primary breast cancer. Cent European J Urol.
65:36–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang R, Zhu Y, Liu X, Liao X, He J and Niu
L: The Clinicopathological features and survival outcomes of
patients with different metastatic sites in stage IV breast cancer.
BMC Cancer. 19:10912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner
SP, Malmström PU, Choi W, Guo CC, Lotan Y and Kassouf W: Bladder
cancer. Lancet. 388:2796–2810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Alfred Witjes J, Max Bruins H, Carrión A,
Cathomas R, Compérat E, Efstathiou JA, Fietkau R, Gakis G, Lorch A,
Martini A, et al: European Association of Urology guidelines on
muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2023
Guidelines. Eur Urol. 85:17–31. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Karaosmanoglu AD, Onur MR, Karcaaltincaba
M, Akata D and Ozmen MN: Secondary tumors of the urinary system: An
imaging conundrum. Korean J Radiol. 19:742–751. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lodh B, Sinam RS and Singh KA:
Adenocarcinoma of urinary bladder in patient with primary gastric
cancer: An unusual synchronous distant metastasis. Indian J Cancer.
53:53–55. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Klinger ME: Secondary tumors of the
genito-urinary tract. J Urol. 65:144–153. 1951. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Goldstein AG: Metastatic carcinoma to the
bladder. J Urol. 98:209–215. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Barroso-Sousa R and Metzger-Filho O:
Differences between invasive lobular and invasive ductal carcinoma
of the breast: Results and therapeutic implications. Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 8:261–266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rakha EA and Ellis IO: Lobular breast
carcinoma and its variants. Semin Diagn Pathol. 27:49–61. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Makki J: Diversity of breast carcinoma:
Histological subtypes and clinical relevance. Clin Med Insights
Pathol. 8:23–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Roulot A, Héquet D, Guinebretière JM,
Vincent-Salomon A, Lerebours F, Dubot C and Rouzier R: Tumoral
heterogeneity of breast cancer. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 74:653–660.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bevers TB, Niell BL, Baker JL, Bennett DL,
Bonaccio E, Camp MS, Chikarmane S, Conant EF, Eghtedari M, Flanagan
MR, et al: NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Breast cancer
screening and diagnosis, version 1.2023. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
21:900–909. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Santinelli A, Pisa E, Stramazzotti D and
Fabris G: HER-2 status discrepancy between primary breast cancer
and metastatic sites. Impact on target therapy. Int J Cancer.
122:999–1004. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mao QZ, Rong S, Xia MD, Li HZ and Zang MF:
Bladder secondary carcinoma in female. Beijing Medicine.
26:312–314. 2004.
|
|
61
|
Karjol U, Jonnada P, Cherukuru S and
Chandranath A: Bladder metastasis from breast cancer: A systematic
review. Cureus. 12:e74082020.PubMed/NCBI
|