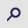
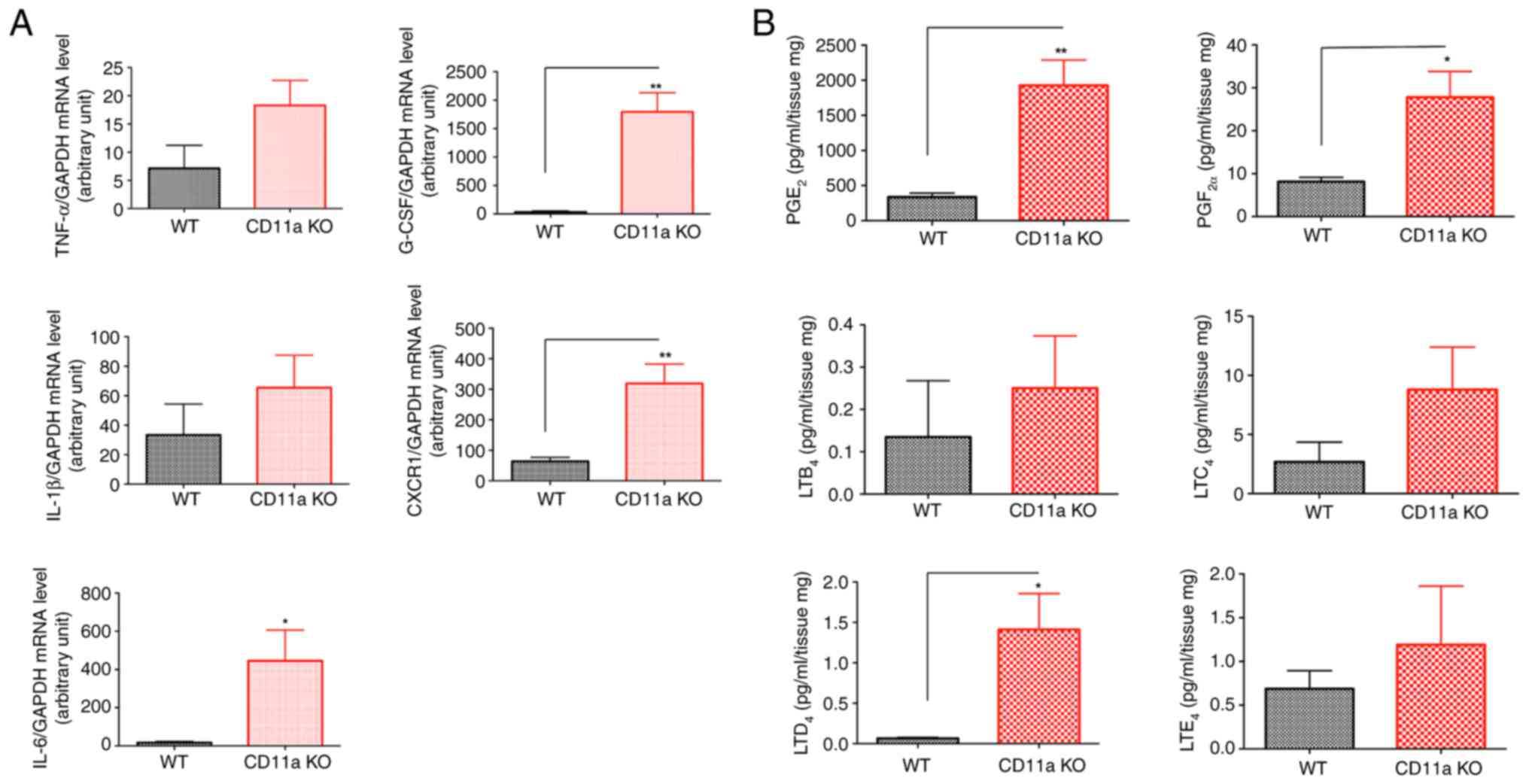
|
1
|
Wigmore TJ, Mohammed K and Jhanji S:
Long-term survival for patients undergoing volatile versus IV
anesthesia for cancer surgery: A retrospective analysis.
Anesthesiology. 124:69–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jun IJ, Jo JY, Kim JI, Chin JH, Kim WJ,
Kim HR, Lee EH and Choi IC: Impact of anesthetic agents on overall
and recurrence-free survival in patients undergoing esophageal
cancer surgery: A retrospective observational study. Sci Rep.
7:140202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu ZF, Lee MS, Wong CS, Lu CH, Huang YS,
Lin KT, Lou YS, Lin C, Chang YC and Lai HC: Propofol-based total
intravenous anesthesia is associated with better survival than
desflurane anesthesia in colon cancer surgery. Anesthesiology.
129:932–941. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I,
Mathers C, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A and Bray F: Estimating the
global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and
methods. Int J Cancer. 144:1941–1953. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakamoto K, Schmidt JW and Wagner KU:
Mouse models of breast cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 1267:47–71. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Casey AE, Laster WR Jr and Ross GL:
Sustained enhanced growth of carcinoma EO771 in C57 black mice.
Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 77:358–362. 1951. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnstone CN, Smith YE, Cao Y, Burrows AD,
Cross RS, Ling X, Redvers RP, Doherty JP, Eckhardt BL, Natoli AL,
et al: Functional and molecular characterisation of EO771.LMB
tumours, a new C57BL/6-mouse-derived model of spontaneously
metastatic mammary cancer. Dis Model Mech. 8:237–251.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stollings LM, Jia LJ, Tang P, Dou H, Lu B
and Xu Y: Immune modulation by volatile anesthetics.
Anesthesiology. 125:399–411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yuki K and Eckenhoff RG: Mechanisms of the
immunological effects of volatile anesthetics: A review. Anesth
Analg. 123:326–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuki K, Astrof NS, Bracken C, Soriano SG
and Shimaoka M: Sevoflurane binds and allosterically blocks
integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1. Anesthesiology.
113:600–609. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuki K, Astrof NS, Bracken C, Yoo R,
Silkworth W, Soriano SG and Shimaoka M: The volatile anesthetic
isoflurane perturbs conformational activation of integrin LFA-1 by
binding to the allosteric regulatory cavity. FASEB J. 22:4109–4116.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuki K, Bu W, Xi J, Sen M, Shimaoka M and
Eckenhoff RG: Isoflurane binds and stabilizes a closed conformation
of the leukocyte function-associated antigen-1. FASEB J.
26:4408–4417. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung S and Yuki K: Differential effects of
volatile anesthetics on leukocyte integrin macrophage-1 antigen. J
Immunotoxicol. 13:148–156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimaoka M and Springer TA: Therapeutic
antagonists and conformational regulation of integrin function. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 2:703–716. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ho MK and Springer TA: Mac-1 antigen:
quantitative expression in macrophage populations and tissues, and
immunofluorescent localization in spleen. J Immunol. 128:2281–2286.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding ZM, Babensee JE, Simon SI, Lu H,
Perrard JL, Bullard DC, Dai XY, Bromley SK, Dustin ML, Entman ML,
et al: Relative contribution of LFA-1 and Mac-1 to neutrophil
adhesion and migration. J Immunol. 163:5029–5038. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Coxon A, Rieu P, Barkalow FJ, Askari S,
Sharpe AH, von Andrian UH, Arnaout MA and Mayadas TN: A novel role
for the beta 2 integrin CD11b/CD18 in neutrophil apoptosis: A
homeostatic mechanism in inflammation. Immunity. 5:653–666. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Berrueta L, Bergholz J, Munoz D, Muskaj I,
Badger GJ, Shukla A, Kim HJ, Zhao JJ and Langevin HM: Stretching
reduces tumor growth in a mouse breast cancer model. Sci Rep.
8:78642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tomayko MM and Reynolds CP: Determination
of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 24:148–154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sonner JM, Gong D, Li J, Eger EI II and
Laster MJ: Mouse strain modestly influences minimum alveolar
anesthetic concentration and convulsivity of inhaled compounds.
Anesth Analg. 89:1030–1034. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dahan A, Sarton E, Teppema L, Olievier C,
Nieuwenhuijs D, Matthes HW and Kieffer BL: Anesthetic potency and
influence of morphine and sevoflurane on respiration in mu-opioid
receptor knockout mice. Anesthesiology. 94:824–832. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okuno T, Koutsogiannaki S, Hou L, Bu W,
Ohto U, Eckenhoff RG, Yokomizo T and Yuki K: Volatile anesthetics
isoflurane and sevoflurane directly target and attenuate Toll-like
receptor 4 system. FASEB J. 33:14528–14541. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zha H, Matsunami E, Blazon-Brown N,
Koutsogiannaki S, Hou L, Bu W, Babazada H, Odegard KC, Liu R,
Eckenhoff RG and Yuki K: Volatile anesthetics affect macrophage
phagocytosis. PLoS One. 14:e02161632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuki K, Bu W, Shimaoka M and Eckenhoff R:
Volatile anesthetics, not intravenous anesthetic propofol bind to
and attenuate the activation of platelet receptor integrin αIIbβ3.
PLoS One. 8:e604152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Walker OL, Dahn ML, Power Coombs MR and
Marcato P: The prostaglandin E2 pathway and breast cancer stem
cells: Evidence of increased signaling and potential targeting.
Front Oncol. 11:7916962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akaydin S, Ramazanoğlu S, Salihoğlu EM,
Karanlik H and Demokan S: Leukotriene D4 levels in patients with
breast cancer. FABAD J Pharm Sci. 47:331–338. 2022.
|
|
28
|
Yuki K: The role of general anesthetic
drug selection in cancer outcome. Biomed Res Int. 2021:25630932021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koutsogiannaki S, Schaefers MM, Okuno T,
Ohba M, Yokomizo T, Priebe GP, DiNardo JA, Sulpicio SG and Yuki K:
From the cover: Prolonged exposure to volatile anesthetic
isoflurane worsens the outcome of polymicrobial abdominal sepsis.
Toxicol Sci. 156:402–411. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tazawa K, Koutsogiannaki S, Chamberlain M
and Yuki K: The effect of different anesthetics on tumor
cytotoxicity by natural killer cells. Toxicol Lett. 266:23–31.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barber DF, Faure M and Long EO: LFA-1
contributes an early signal for NK cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol.
173:3653–3659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao N, Wang C, Yu Y, Xie L, Xing Y, Zhang
Y, Wang Y, Wu J and Cai Y: LFA-1/ICAM-1 promotes NK cell
cytotoxicity associated with the pathogenesis of ocular
toxoplasmosis in murine model. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 16:e00108482022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hickman A, Koetsier J, Kurtanich T,
Nielsen MC, Winn G, Wang Y, Bentebibel SE, Shi L, Punt S, Williams
L, et al: LFA-1 activation enriches tumor-specific T cells in a
cold tumor model and synergizes with CTLA-4 blockade. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1541522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hedrick CC and Malanchi I: Neutrophils in
cancer: Heterogeneous and multifaceted. Nat Rev Immunol.
22:173–187. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
DeNardo DG and Ruffell B: Macrophages as
regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol.
19:369–382. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tai LH, Tanese de Souza C, Sahi S, Zhang
J, Alkayyal AA, Ananth AA and Auer RA: A mouse tumor model of
surgical stress to explore the mechanisms of postoperative
immunosuppression and evaluate novel perioperative immunotherapies.
J Vis Exp. 512532014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guo P, Huang J, Wang L, Jia D, Yang J,
Dillon DA, Zurakowski D, Mao H, Moses MA and Auguste DT: ICAM-1 as
a molecular target for triple negative breast cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:14710–14715. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|