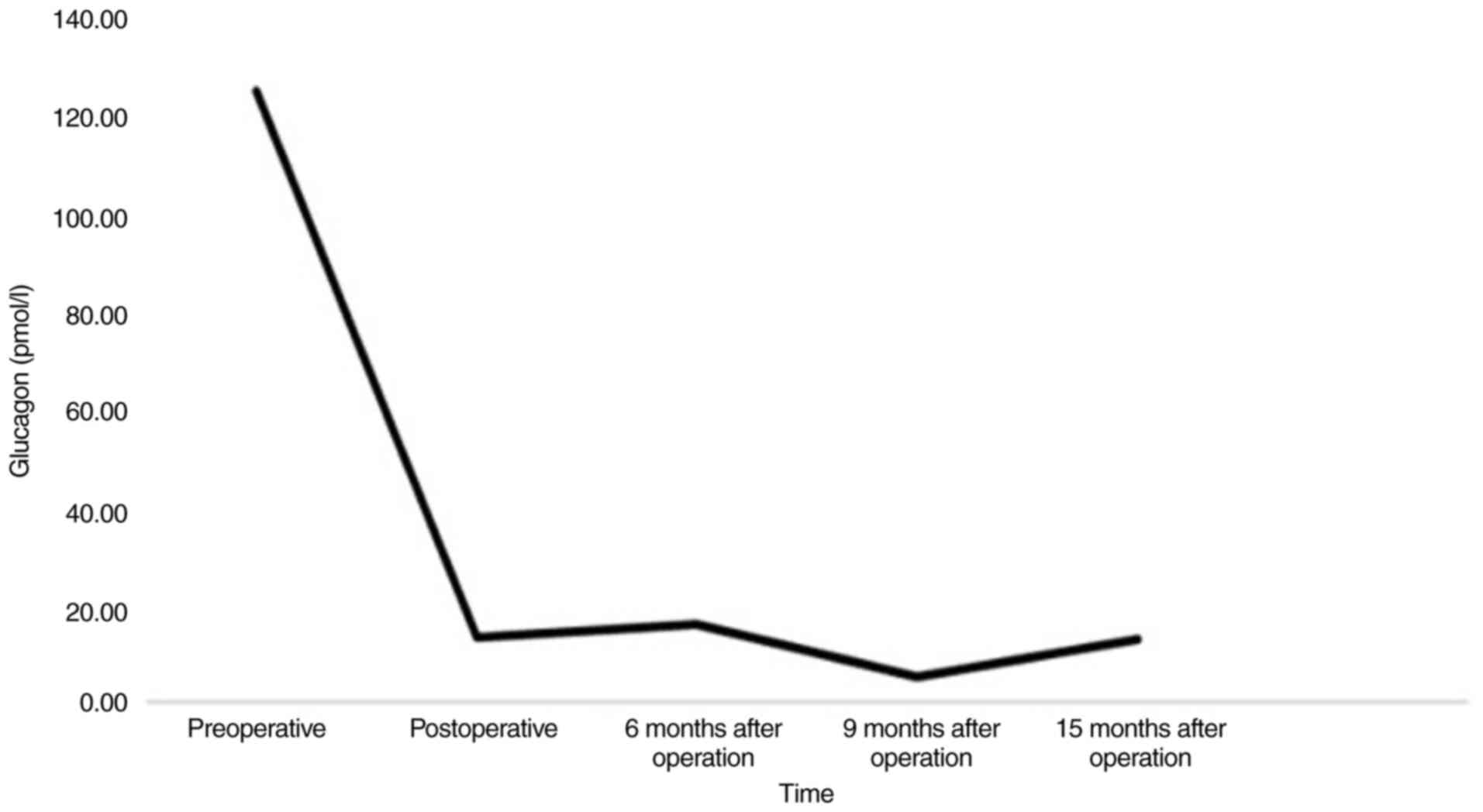
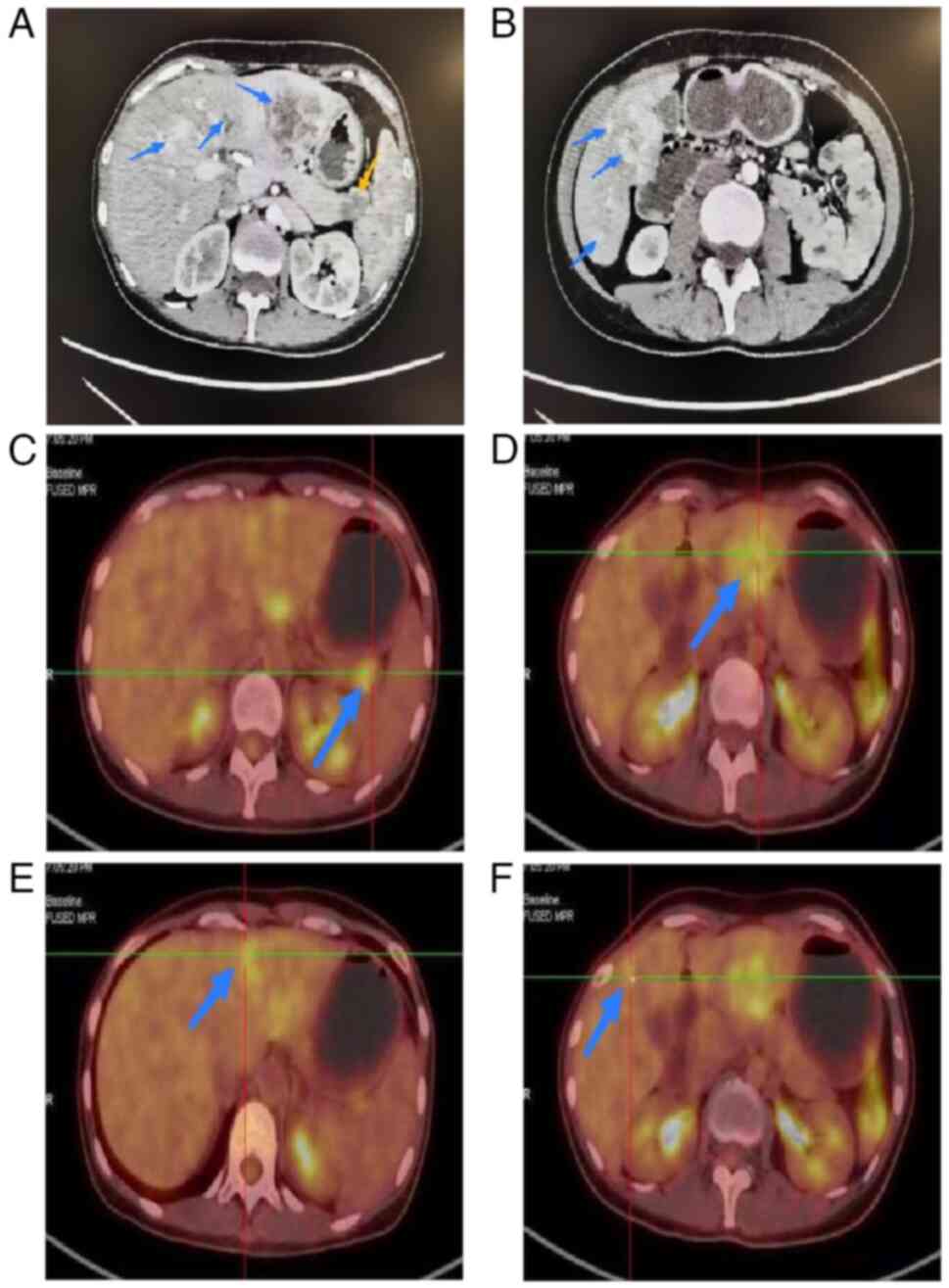
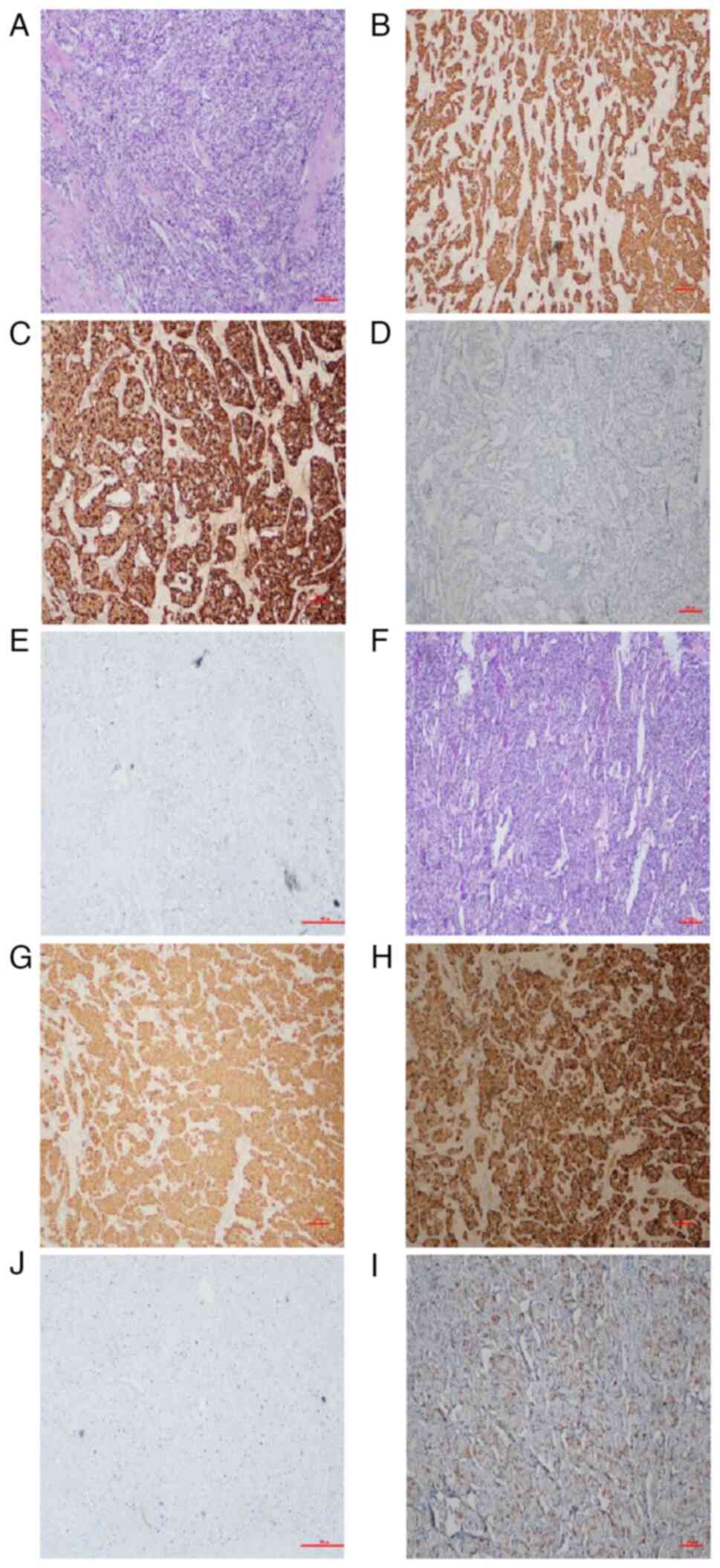
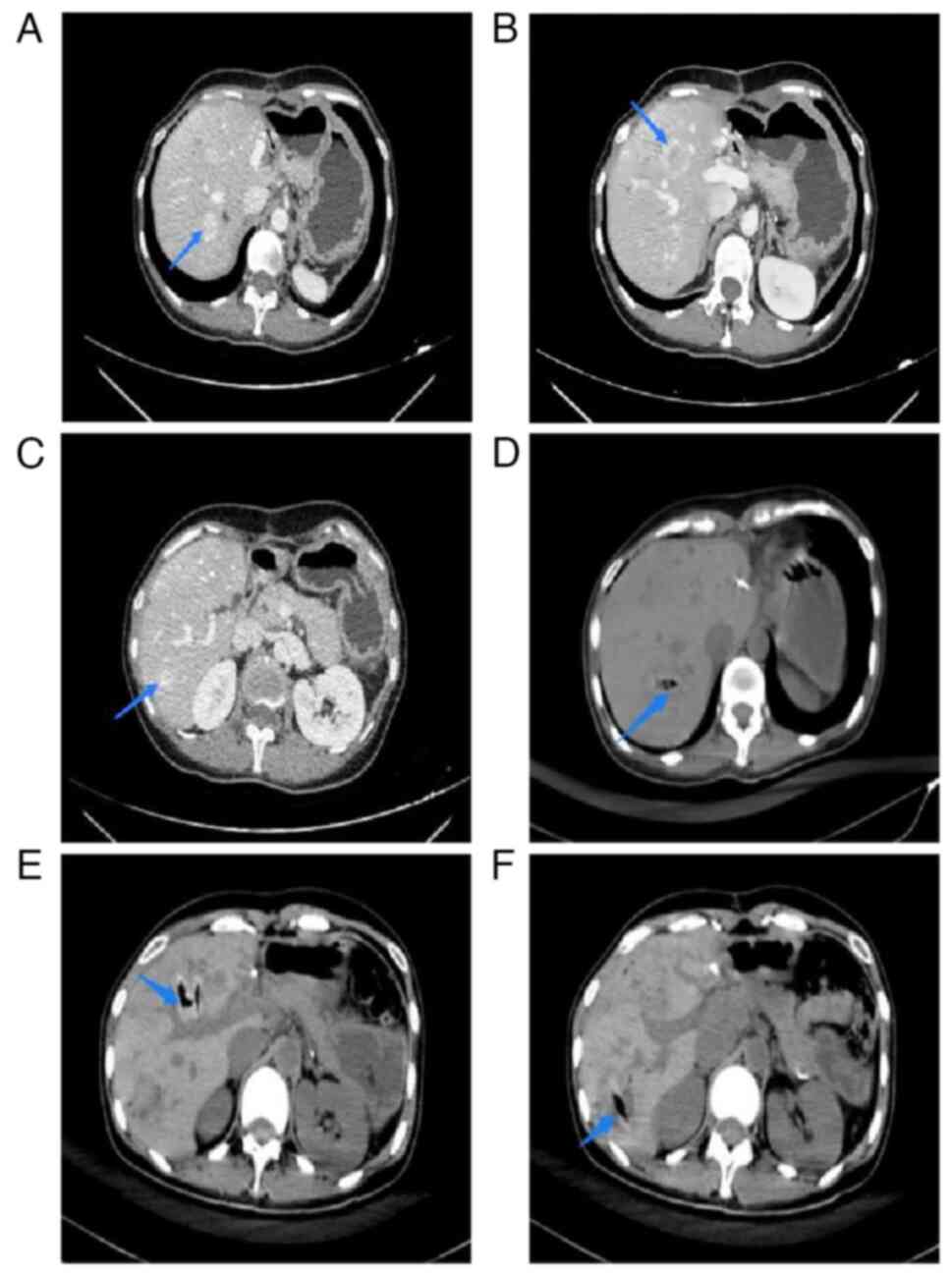
|
1
|
Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, Paradis
V, Rugge M, Schirmacher P, Washington KM, Carneiro F and Cree IA;
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, : The 2019 WHO
classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology.
76:182–188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schwartz RA: Glucagonoma and
pseudoglucagonoma syndromes. Int J Dermatol. 36:81–89. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stacpoole PW: The glucagonoma syndrome:
Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment. Endocr Rev. 2:347–361.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yusuf MA, Mehmood S, Iftikhar J, Saqib M,
Siddique MZ and Imtiaz W: Glucagonoma syndrome: A Rare
paraneoplastic disorder due to neuroendocrine tumor of the
pancreas. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 32 (Suppl):S147–S149. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eldor R, Glaser B, Fraenkel M, Doviner V,
Salmon A and Gross DJ: Glucagonoma and the glucagonoma
syndrome-cumulative experience with an elusive endocrine tumour.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 74:593–598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Metz DC and Jensen RT: Gastrointestinal
neuroendocrine tumors: Pancreatic endocrine tumors.
Gastroenterology. 135:1469–1492. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Toberer F, Hartschuh W and Wiedemeyer K:
Glucagonoma-Associated necrolytic migratory erythema: The broad
spectrum of the clinical and histopathological findings and clues
to the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 41:e29–e32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li W, Yang X, Deng Y, Jiang Y, Xu G, Li E,
Wu Y, Ren J, Ma Z, Dong S, et al: Necrolytic migratory erythema is
an important visual cutaneous clue of glucagonoma. Sci Rep.
12:90532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doi R: Surgical management of pancreatic
endocrine tumors. Nihon Rinsho. 69 (Suppl 2):S611–S666, (In
Japanese).
|
|
10
|
John AM and Schwartz RA: Glucagonoma
syndrome: A review and update on treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol
Venereol. 30:2016–2022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cui M, Wang R and Liao Q: Necrolytic
migratory erythema: An important sign of glucagonoma. Postgrad Med
J. 97:1992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wermers RA, Fatourechi V, Wynne AG, Kvols
LK and Lloyd RV: The glucagonoma syndrome. Clinical and pathologic
features in 21 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 75:53–63. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chastain MA: The glucagonoma syndrome: A
review of its features and discussion of new perspectives. Am J Med
Sci. 321:306–320. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tolliver S, Graham J and Kaffenberger BH:
A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome:
Necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 57:642–645. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song X, Zheng S, Yang G, Xiong G, Cao Z,
Feng M, Zhang T and Zhao Y: Glucagonoma and the glucagonoma
syndrome. Oncol Lett. 15:2749–2755. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He S, Zeng W, Geng S and Jia J:
Glucagonoma syndrome with atypical necrolytic migratory erythema.
Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 87:49–53. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang ZX, Wang F and Zhao JG: Glucagonoma
syndrome with severe erythematous rash: A rare case report.
Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e171582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sarmiento JM and Que FG: Hepatic surgery
for metastases from neuroendocrine tumors. Surg Oncol Clin N Am.
12:231–242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Madoff DC, Gupta S, Ahrar K, Murthy R and
Yao JC: Update on the management of neuroendocrine hepatic
metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 17:1235–1250. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ito T, Igarashi H and Jensen RT: Therapy
of metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs): Recent
insights and advances. J Gastroenterol. 47:941–960. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saeed A, Buell JF and Kandil E: Surgical
treatment of liver metastases in patients with neuroendocrine
tumors. Ann Transl Med. 1:62013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vaghaiwalla T and Keutgen XM: Surgical
management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Surg Oncol Clin N
Am. 29:243–252. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kvols LK, Moertel CG, O'Connell MJ, Schutt
AJ, Rubin J and Hahn RG: Treatment of the malignant carcinoid
syndrome. Evaluation of a long-acting somatostatin analogue. N Engl
J Med. 315:663–666. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ruszniewski P, Ish-Shalom S, Wymenga M,
O'Toole D, Arnold R, Tomassetti P, Bax N, Caplin M, Eriksson B,
Glaser B, et al: Rapid and sustained relief from the symptoms of
carcinoid syndrome: Results from an open 6-month study of the
28-day prolonged-release formulation of lanreotide.
Neuroendocrinology. 80:244–251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Farley HA and Pommier RF: Treatment of
neuroendocrine liver metastases. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 25:217–225.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kose E, Kahramangil B, Aydin H, Donmez M,
Takahashi H, Aucejo F, Siperstein A and Berber E: Outcomes of
laparoscopic tumor ablation for neuroendocrine liver metastases: A
20-year experience. Surg Endosc. 34:249–256. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mohan H, Nicholson P, Winter DC, O'Shea D,
O'Toole D, Geoghegan J, Maguire D, Hoti E, Traynor O and Cantwell
CP: Radiofrequency ablation for neuroendocrine liver metastases: A
systematic review. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 26:935–942.e1. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dasari A, Shen C, Halperin D, Zhao B, Zhou
S, Xu Y, Shih T and Yao JC: Trends in the incidence, prevalence,
and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the
United States. JAMA Oncol. 3:1335–1342. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chan JA and Kulke MH: Medical management
of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Current and future therapy.
Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 25:423–437. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saltz L, Trochanowski B, Buckley M,
Heffernan B, Niedzwiecki D, Tao Y and Kelsen D: Octreotide as an
antineoplastic agent in the treatment of functional and
nonfunctional neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer. 72:244–248. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lo CH, Ho CL and Shih YL: Glucagonoma with
necrolytic migratory erythema exhibiting responsiveness to
subcutaneous octreotide injections. QJM. 107:157–158. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kimbara S, Fujiwara Y, Toyoda M, Chayahara
N, Imamura Y, Kiyota N, Mukohara T, Fukunaga A, Oka M, Nishigori C
and Minami H: Rapid improvement of glucagonoma-related necrolytic
migratory erythema with octreotide. Clin J Gastroenterol.
7:255–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|