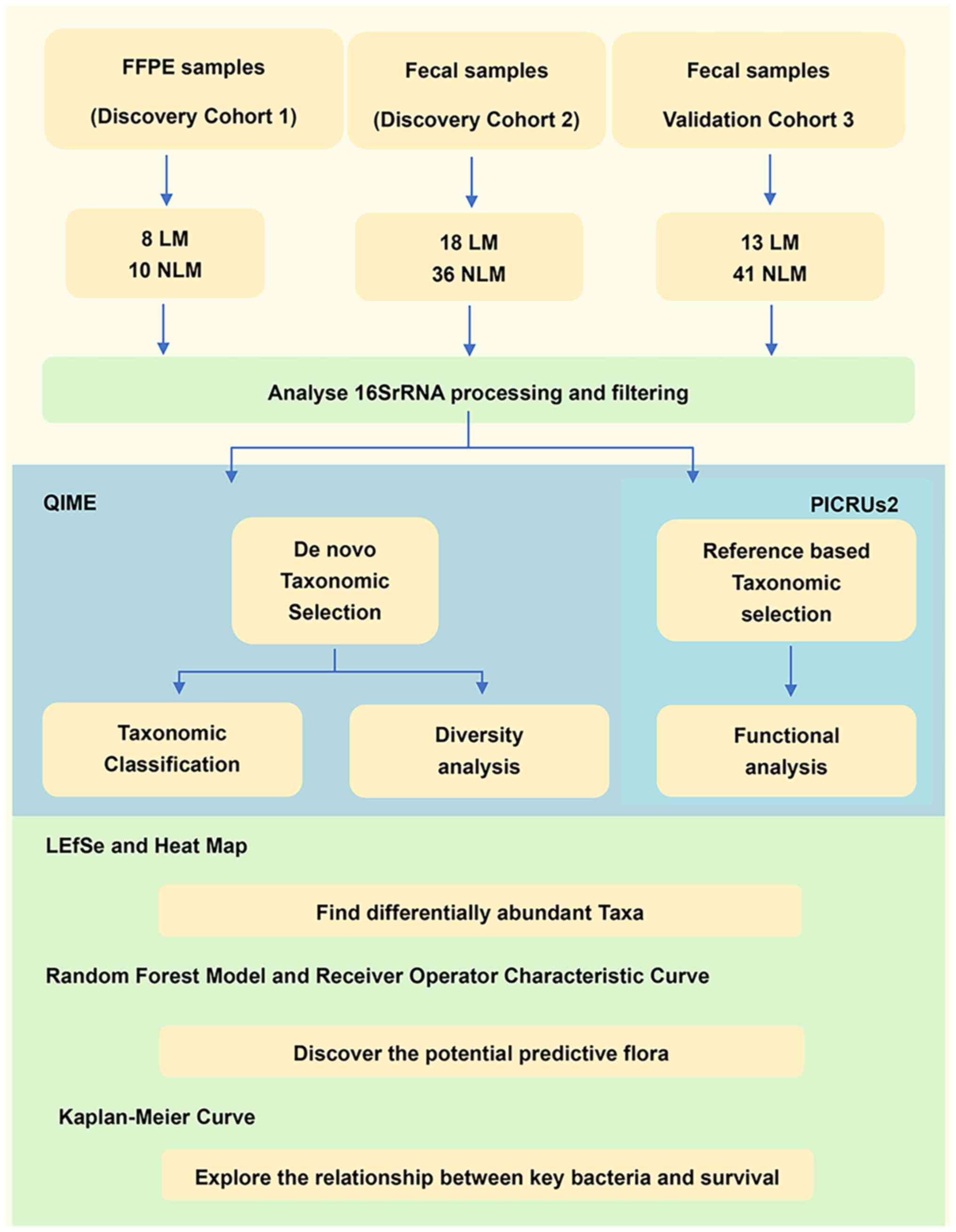
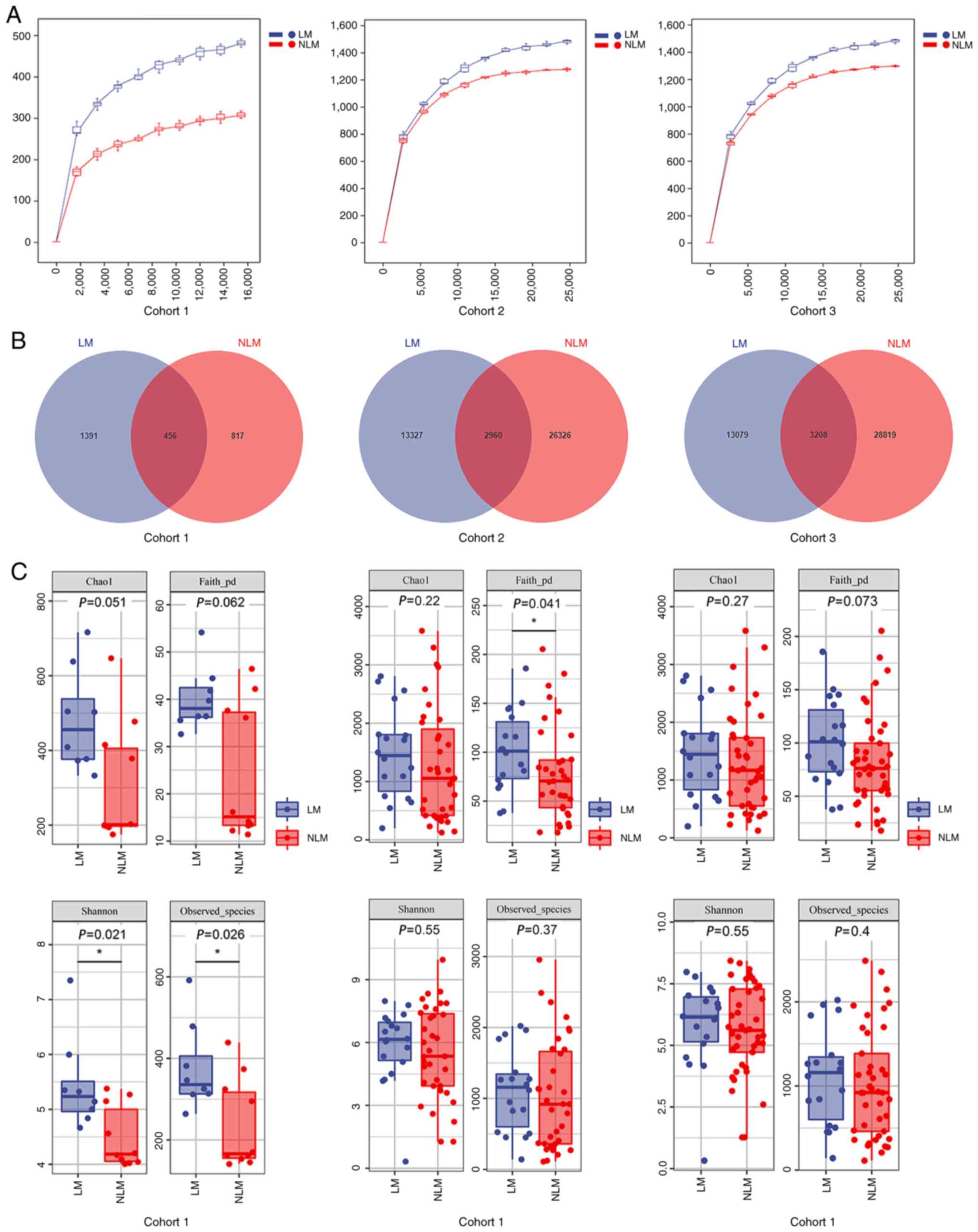
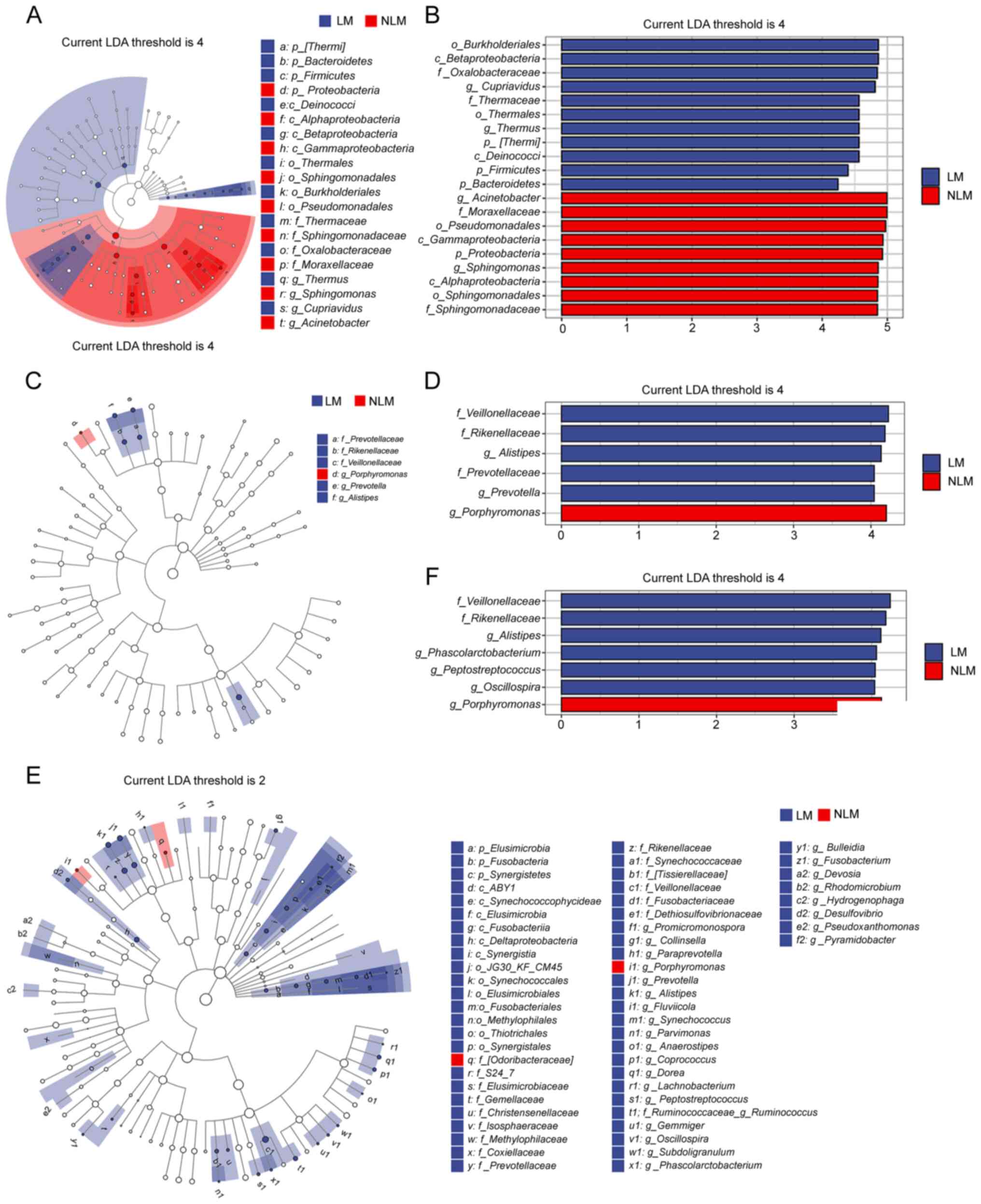
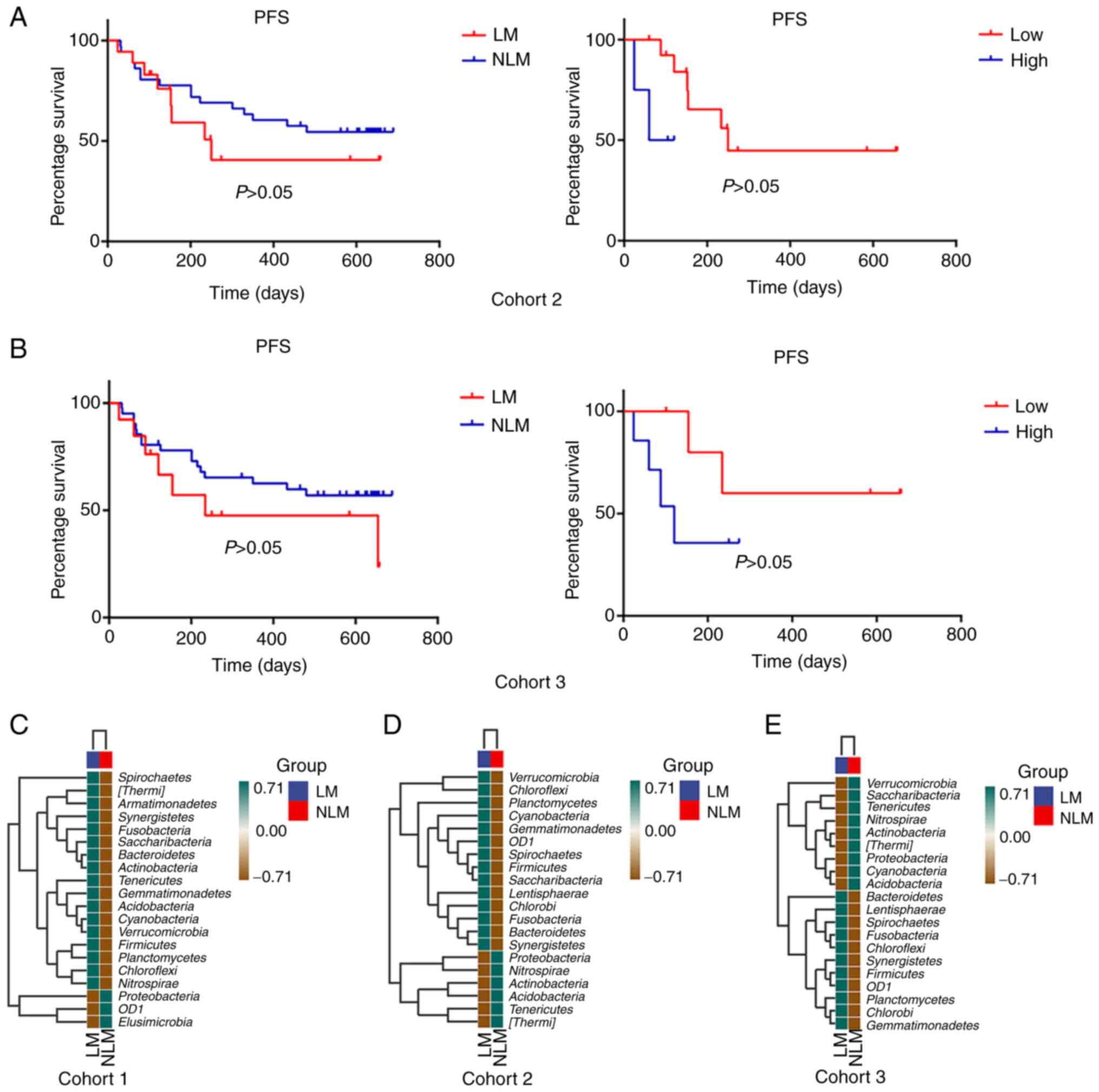
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abdalla EK, Adam R, Bilchik AJ, Jaeck D,
Vauthey JN and Mahvi D: Improving resectability of hepatic
colorectal metastases: Expert consensus statement. Ann Surg Oncol.
13:1271–1280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martin J, Petrillo A, Smyth EC, Shaida N,
Khwaja S, Cheow HK, Duckworth A, Heister P, Praseedom R, Jah A, et
al: Colorectal liver metastases: Current management and future
perspectives. World J Clin Oncol. 11:761–808. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Engstrand J, Nilsson H, Stromberg C, Jonas
E and Freedman J: Colorectal cancer liver metastases-a
population-based study on incidence, management and survival. BMC
Cancer. 18:782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ursell LK, Metcalf JL, Parfrey LW and
Knight R: Defining the human microbiome. Nutr Rev. 70 (Suppl
1):S38–S44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan X, Jin Y, Chen G, Ma X and Zhang L:
Gut microbiota dysbiosis drives the development of colorectal
cancer. Digestion. 102:508–515. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jobin C: Colorectal cancer: Looking for
answers in the microbiota. Cancer Discov. 3:384–387. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Uchino Y, Goto Y, Konishi Y, Tanabe K,
Toda H, Wada M, Kita Y, Beppu M, Mori S, Hijioka H, et al:
Colorectal cancer patients have four specific bacterial species in
oral and gut microbiota in common-a metagenomic comparison with
healthy subjects. Cancers (Basel). 13:33322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu J, Feng Q, Wong SH, Zhang D, Liang QY,
Qin Y, Tang L, Zhao H, Stenvang J, Li Y, et al: Metagenomic
analysis of faecal microbiome as a tool towards targeted
non-invasive biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Gut. 66:70–78. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sheng Q, Du H, Cheng X, Cheng X, Tang Y,
Pan L, Wang Q and Lin J: Characteristics of fecal gut microbiota in
patients with colorectal cancer at different stages and different
sites. Oncol Lett. 18:4834–4844. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Cao P, Su W, Deng
Y, Zhan N, Fu X, Huang Y and Dong W: Fusobacterium nucleatum
promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer by activating autophagy
signaling via the upregulation of CARD3 expression. Theranostics.
10:323–339. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin M, Shang F, Wu J, Fan Q, Chen C, Fan
J, Liu L, Nie X, Zhang T, Cai K, et al: Tumor-associated microbiota
in proximal and distal colorectal cancer and their relationships
with clinical outcomes. Front Microbiol. 12:7279372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Torres Moral T, Sanchez-Niubo A,
Monistrol-Mula A, Gerardi C, Banzi R, Garcia P, Demotes-Mainard J
and Haro JM; The Permit Group, : Methods for stratification and
validation cohorts: A scoping review. J Pers Med. 12:6882022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Himbert C, Stephens WZ, Gigic B, Hardikar
S, Holowatyj AN, Lin T, Ose J, Swanson E, Ashworth A, Warby CA, et
al: Differences in the gut microbiome by physical activity and BMI
among colorectal cancer patients. Am J Cancer Res. 12:4789–4801.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han S, Zhuang J, Pan Y, Wu W and Ding K:
Different characteristics in gut microbiome between advanced
adenoma patients and colorectal cancer patients by metagenomic
analysis. Microbiol Spectr. 10:e01593222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marchesi JR, Dutilh BE, Hall N, Peters WH,
Roelofs R, Boleij A and Tjalsma H: Towards the human colorectal
cancer microbiome. PLoS One. 6:e204472011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen W, Liu F, Ling Z, Tong X and Xiang C:
Human intestinal lumen and mucosa-associated microbiota in patients
with colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 7:e397432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zeller G, Tap J, Voigt AY, Sunagawa S,
Kultima JR, Costea PI, Amiot A, Böhm J, Brunetti F, Habermann N, et
al: Potential of fecal microbiota for early-stage detection of
colorectal cancer. Mol Syst Biol. 10:7662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kalasabail S, Engelman J, Zhang LY,
El-Omar E and Yim HCH: A perspective on the role of microbiome for
colorectal cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel). 13:46232021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rossi T, Vergara D, Fanini F, Maffia M,
Bravaccini S and Pirini F: Microbiota-derived metabolites in tumor
progression and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:57862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoshimoto S, Loo TM, Atarashi K, Kanda H,
Sato S, Oyadomari S, Iwakura Y, Oshima K, Morita H, Hattori M, et
al: Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer
through senescence secretome. Nature. 499:97–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bullman S, Pedamallu CS, Sicinska E,
Clancy TE, Zhang X, Cai D, Neuberg D, Huang K, Guevara F, Nelson T,
et al: Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic
response in colorectal cancer. Science. 358:1443–1448. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Debesa-Tur G, Pérez-Brocal V, Ruiz-Ruiz S,
Castillejo A, Latorre A, Soto JL and Moya A: Metagenomic analysis
of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor and normal mucosa reveals
differences in the microbiome of colorectal cancer patients. Sci
Rep. 11:3912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kostic AD, Gevers D, Pedamallu CS, Michaud
M, Duke F, Earl AM, Ojesina AI, Jung J, Bass AJ, Tabernero J, et
al: Genomic analysis identifies association of Fusobacterium
with colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 22:292–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Castellarin M, Warren RL, Freeman JD,
Dreolini L, Krzywinski M, Strauss J, Barnes R, Watson P,
Allen-Vercoe E, Moore RA and Holt RA: Fusobacterium
nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma.
Genome Res. 22:299–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Weng W, Peng J, Hong L, Yang L,
Toiyama Y, Gao R, Liu M, Yin M, Pan C, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum increases proliferation of colorectal cancer cells
and tumor development in mice by activating Toll-like receptor 4
signaling to nuclear factor-κB, and up-regulating expression of
MicroRNA-21. Gastroenterology. 152:851–866.e24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rubinstein MR, Wang X, Liu W, Hao Y, Cai G
and Han YW: Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal
carcinogenesis by modulating E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling via its
FadA adhesin. Cell Host Microbe. 14:195–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abed J, Emgård JE, Zamir G, Faroja M,
Almogy G, Grenov A, Sol A, Naor R, Pikarsky E, Atlan KA, et al:
Fap2 Mediates Fusobacterium nucleatum colorectal
adenocarcinoma enrichment by binding to tumor-expressed Gal-GalNAc.
Cell Host Microbe. 20:215–225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sakamoto Y, Mima K, Ishimoto T, Ogata Y,
Imai K, Miyamoto Y, Akiyama T, Daitoku N, Hiyoshi Y, Iwatsuki M, et
al: Relationship between Fusobacterium nucleatum and
antitumor immunity in colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Cancer
Sci. 112:4470–4477. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nosho K, Sukawa Y, Adachi Y, Ito M,
Mitsuhashi K, Kurihara H, Kanno S, Yamamoto I, Ishigami K, Igarashi
H, et al: Association of Fusobacterium nucleatum with
immunity and molecular alterations in colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:557–566. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mima K, Sukawa Y, Nishihara R, Qian ZR,
Yamauchi M, Inamura K, Kim SA, Masuda A, Nowak JA, Nosho K, et al:
Fusobacterium nucleatum and T cells in colorectal carcinoma.
JAMA Oncol. 1:653–661. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Su T, Zhang Y, Lee A, He J, Ge Q
and Wang L, Si J, Zhuo W and Wang L: Fusobacterium nucleatum
promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by modulating KRT7-AS/KRT7.
Gut Microbes. 11:511–525. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mima K, Nishihara R, Qian ZR, Cao Y,
Sukawa Y, Nowak JA, Yang J, Dou R, Masugi Y, Song M, et al:
Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal carcinoma tis sue and
patient prognosis. Gut. 65:1973–1980. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yin H, Miao Z, Wang L, Su B, Liu C, Jin Y,
Wu B, Han H and Yuan X: Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes
liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating the hepatic
immune niche and altering gut microbiota. Aging (Albany NY).
14:1941–1958. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu C, Fan L, Lin Y, Shen W, Qi Y, Zhang Y,
Chen Z, Wang L, Long Y, Hou T, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through
miR-1322/CCL20 axis and M2 polarization. Gut Microbes.
13:19803472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu X, Xu Q, Tong Y, Zhang Z, Dun G, Feng
Y, Tang J, Han D, Mao Y, Deng L, et al: Long non-coding RNA EVADR
induced by Fusobacterium nucleatum infection promotes
colorectal cancer metastasis. Cell Rep. 40:1111272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rezasoltani S, Dabiri H, Asadzadeh-Aghdaei
H, Sepahi AA, Modarressi MH and Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E: The gut
microflora assay in patients with colorectal cancer: In feces or
tissue samples? Iran J Microbiol. 11:1–6. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ringel Y, Maharshak N, Ringel-Kulka T,
Wolber EA, Sartor RB and Carroll IM: High throughput sequencing
reveals distinct microbial populations within the mucosal and
luminal niches in healthy individuals. Gut Microbes. 6:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Imrit K, Goldfischer M, Wang J, Green J,
Levine J, Lombardo J and Hong T: Identification of bacteria in
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded heart valve tissue via 16S rRNA
gene nucleotide sequencing. J Clin Microbiol. 44:2609–2611. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim S, Park C, Ji Y, Kim DG, Bae H, van
Vrancken M, Kim DH and Kim KM: Deamination effects in
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples in the era of
precision medicine. J Mol Diagn. 19:137–146. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Riquelme E, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Montiel M,
Zoltan M, Dong W, Quesada P, Sahin I, Chandra V, San Lucas A, et
al: Tumor microbiome diversity and composition influence pancreatic
cancer outcomes. Cell. 178:795–806.e12. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carrick DM, Mehaffey MG, Sachs MC,
Altekruse S, Camalier C, Chuaqui R, Cozen W, Das B, Hernandez BY,
Lih CJ, et al: Robustness of next generation sequencing on older
formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. PLoS One. 10:e01273532015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Oh E, Choi YL, Kwon MJ, Kim RN, Kim YJ,
Song JY, Jung KS and Shin YK: Comparison of accuracy of whole-exome
sequencing with formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded and fresh frozen
tissue samples. PLoS One. 10:e01441622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|