Introduction
Antimicrobials are commonly prescribed in Obstetrics
and Gynaecology prophylactically for pre-operative and
post-operative procedures (1)
(caesarean section, episiotomy, medical termination of pregnancy,
total vaginal or abdominal hysterectomy, laparoscopic procedures,
tubal ligation, dilatation and curettage, and myomectomy) or to
treat ongoing infection (vaginitis, pelvic inflammatory disease,
endometriosis, sexually transmitted diseases and urinary tract
infections).
The rational use of antimicrobials in women of the
child-bearing age group is important because it affects this
population as well as their offspring. Indiscriminate use of
antibiotics may result in the appearance of drug-resistant
organisms (2).
Drug utilization is defined by the WHO as ‘The
marketing, distribution, prescription, and use of drugs in society,
with special emphasis on the resulting medical, social, and
economic consequences’. A drug utilization study is therefore one
designed to describe quantitatively and qualitatively the use of a
given drug, i.e., class of drugs, indications, duration of
treatment, dosage, previous or associated treatments and compliance
(3,4).
Surgical site infections are a common complication
of obstetric and gynaecological procedures. The use of
antimicrobial prophylaxis for caesarean section has been shown to
be effective in reducing postoperative morbidity, cost and duration
of hospitalization (5–8).
Antimicrobial usage in the above setting becomes
inevitable but should be restricted. The judicious use of these
drugs can prevent post-partum infection of the mother and neonate
and reduce incidence of adverse drug reactions.
The present study was performed to assess the usage
of antimicrobials in 100 women undergoing caesarean section
Materials and methods
A prospective study of 100 prescriptions of women
attending the inpatient and outpatient Department of Obstetrics and
Gynaecology, People's Hospital of Linyi (Shandong, China), a
Tertiary Care Hospital during the period of February 2013 to August
2013 was conducted. Prior to start of the study Institutional
Ethics Committee approval was obtained. The prescriptions were
analyzed using WHO core drug use indicators including average
number of drugs per encounter, percentage of drugs prescribed by
generic name, percentage of drugs prescribed from the essential
drug list, patient care and availability of drugs (4).
The data collected were analyzed for the following
para-meters: i) age of patient; ii) gravidity; iii) type of
caesarean section - (elective/emergency); iv) number of drugs per
prescription; v) class of antimicrobials; vi) duration of
antimicrobial treatment; vii) average number of antimicrobials
prescribed; viii) polypharmacy; ix) number of fixed-dose
combinations prescribed; x) generic/brand name prescribed; and xi)
failure of prophylaxis.
Results
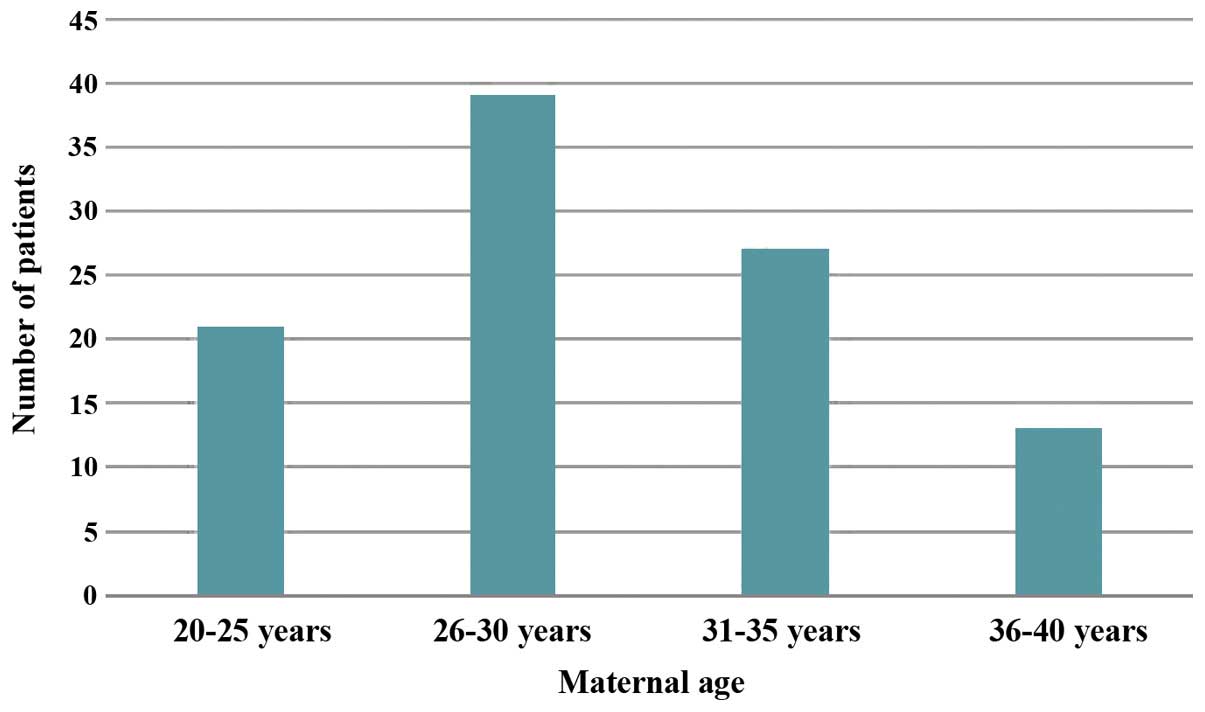
Of 100 patients, 87% were in the age group of 20–35
years, 21% were in the age group of 20–25 years, 39% were in the
age group of 26–30 years, 27% were in the age group of 31–35 years
and the remaining 13% were in the age group of 36–39 years
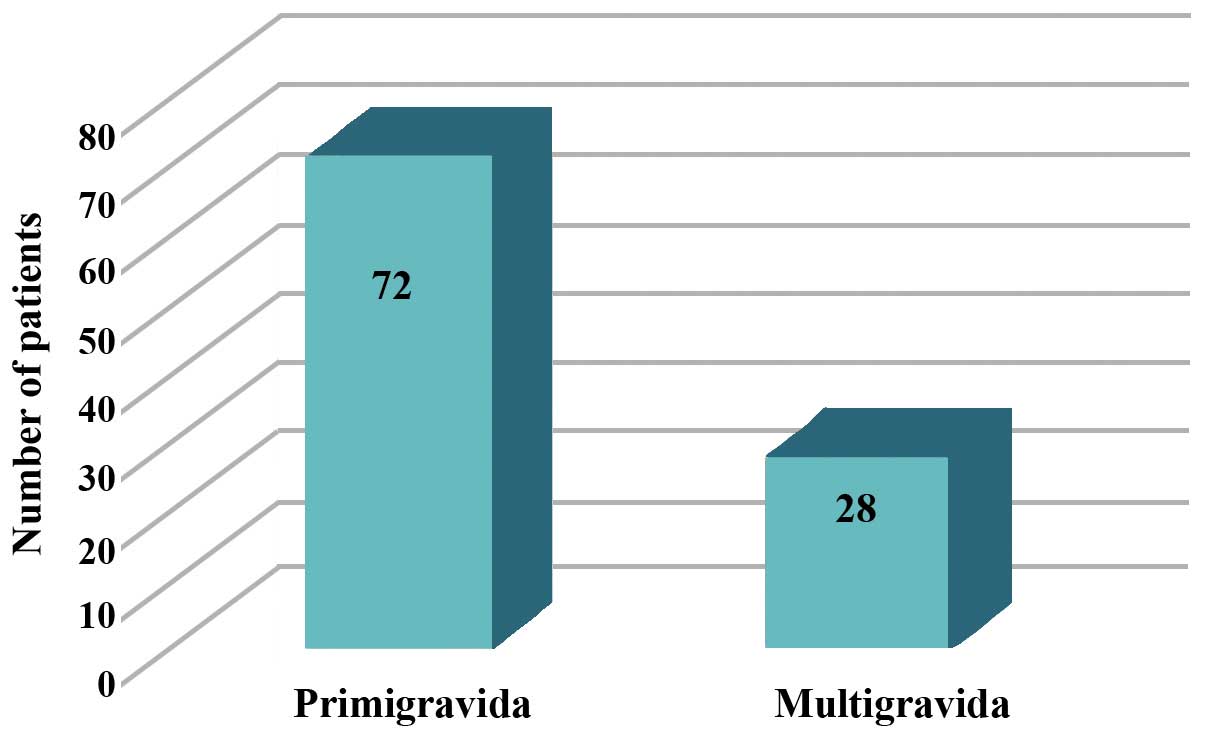
(Fig. 1). The highest proportion of
patients was primigravida (72%) (Fig.
2). Elective C-sections were carried out in 38% of cases and
the remaining were emergency C-section in whom intra- and
post-operative antimicrobial prophylaxis was received for a
duration of 7 days (Fig. 3).
Antimicrobial prophylaxis was given to all the patients, while the
most commonly prescribed antimicrobial was a combination of
ceftriaxone and sulbactam (Fig. 4).
Patients who were reported with infection even after antimicrobial
prophylaxis were 27% (Fig. 5).
Post-partum endometritis develops usually in
patients undergoing caesarean section, after labour or rupture of
membranes despite the use of prophylactic antibiotics (9). Therapeutic use of antimicrobials was
‘empirical’. Patients who were reported with infection even after
antimicrobial prophylaxis were 17% of which 2% were diagnosed with
post-partum endometritis, 8% with wound infection and 7% with
urinary tract infection (10,11). The
patients with failure of antimicrobial prophylaxis were shifted to
other regimens following empiric treatment (Tables I and II).
 | Table I.Number of antimicrobials prescribed
per patient. |
Table I.
Number of antimicrobials prescribed
per patient.
| No. of
antimicrobials | Percentage of
use |
|---|
| 4 | 6 |
| 5 | 22 |
| 6 | 28 |
| 7 | 13 |
| 8 | 16 |
| 9 or more | 15 |
 | Table II.Antepartum complications. |
Table II.
Antepartum complications.
| Antepartum
complications | No. of patients |
|---|
| Antepartum
infections | 17 |
| Gestational
diabetes | 5 |
| Antepartum
anemia | 44 |
Discussion
The largest number of patients in the present study
was in the age group of 26–30 years. The age distribution is a
reflection of the demographic status of the community as the
majority of women tend to complete their families during this
period. The emergency lower segment caesarean section (LSCS) group
formed over 50% of the study participants. It is important to opt
for elective procedures, where feasible, as it provides the
opportunity to have a clean operative field (12,13).
LSCS were performed under antimicrobial prophylaxis to avoid
post-operative morbidity. This reflects that, in general, the
practice in the audit setting is evidence-based.
Regardless of the antibiotic regimen used, the
protective effect of prophylactic antibiotics was homogeneous
across all the patients undergoing caesarean section. This effect
of significant reduction in postoperative infectious morbidity (by
around two thirds) led the reviewers to recommend that antibiotic
prophylaxis be provided to all the women undergoing caesarean
section. All the patients received antimicrobial prophylaxis, which
is good clinical practice and comparable to international standards
of evidence-based practice worldwide. The reduction in
post-operative infection-related morbidity, in turn, is cost
effective as it reduces the number of days the patient has to stay
in hospital. Additionally, it reduces the incidence of
hospital-acquired infections and infection with more resistant
microorganisms.
The most frequent microbes isolated from endometrial
cultures of women with post-caesarean wound infections are
staphylococci, enterococci, anaerobes and ureaplasmas (14–17).
Furthermore, when specifically identified, ureaplasma (or
Mycoplasma genus) is the most common organism isolated from the
amniotic fluid and chorioamnion at caesarean delivery, and is
associated with a 3- to 8-fold increased risk of post-caesarean
endometritis or wound infection (18,19).
Bacterial vaginosis is also associated with an increased risk of
post-caesarean endometritis. Therefore, the recommended regimen of
ceftriaxone alone does not cover frequent isolates or risk factors
of such infection. Thus, use of an extended spectrum regimen
involving a second antibiotic metronidazole was used (9,20,21).
In conclusion, antimicrobial prophylaxis was given
routinely to all 100 patients undergoing caesarean section
pre-operatively, intra-operatively and post-operatively. Use of
prophylactic antibiotics for patients undergoing caesarean section
has significantly reduced post-operative maternal infection,
morbidity and hospital stay (22,23).
Pre-operative prophylaxis was given in the early rupture of
membranes. Fixed-dose combinations were used, the most common being
ceftriaxone and sulbactam combination. Incidence of infection even
after antimicrobial prophylaxis was reported due to pre-existing
infection, debilitating disease or prolonged rupture of membranes.
Patients with recurrent infection were shifted to a regime that
included amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, ciprofloxacin and
tinidazole combination and the duration of treatment was prolonged
(24). Patients with failure of
antimicrobial prophylaxis were treated following the change in
antimicrobial regimen, prolonging the duration of treatment and
dilatation and curettage in 2% of the patients who reported with
post-partum endometritis. Drugs were prescribed only by brand names
which is of concern, generic drug prescribing is recommended and
would enhance cost-effectiveness. Use of certain antimicrobials
(fluoroquinolones and nitro-imidazole) not recommended in lactating
mothers could have been avoided.
Since the patients with failure of antimicrobial
prophylaxis received ‘empiric’ treatment, antibiotic culture
sensitivity testing is recommended prior to introducing a change in
the antimicrobial treatment regimen, to exclude antibiotic
resistance.
References
|
1
|
Warnecke HH, Graeff H, Selbmann HK,
Preac-Mursic V, Adam D, Gloning KP, Jänicke F and Zander J:
Perioperative short-term prophylaxis with antibiotics in caesarean
section. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 42:654–661. 1982.(In German).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smaill FM and Grivell RM: Antibiotic
prophylaxis versus no prophylaxis for preventing infection after
cesarean section. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
10:CD0074822014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Jonge L, Bos HJ, van Langen IM, de
Jong-van den Berg LT and Bakker MK: Antibiotics prescribed before,
during and after pregnancy in the Netherlands: a drug utilization
study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 23:60–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee F, Wong P, Hill F, Burgner D and
Taylor R: Evidence behind the WHO guidelines: hospital care for
children: what is the role of prophylactic antibiotics in the
management of burns? J Trop Pediatr. 55:73–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clifford V and Daley A: Antibiotic
prophylaxis in obstetric and gynaecological procedures: a review.
Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 52:412–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Schalkwyk J, Van Eyk N, Yudin MH,
Boucher M, Cormier B, Gruslin A, Money DM, Ogilvie G, Castillo E,
Paquet C, et al: Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of
Canada Infectious Diseases Committee: Antibiotic prophylaxis in
obstetric procedures. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 32:878–892. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Janisch H, Philipp K and Riss P: The
effect of antibiotic prophylaxis in vaginal obstetric procedures
(author's transl). Wien Klin Wochenschr. 91:227–230. 1979.(In
German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tita AT, Rouse DJ, Blackwell S, Saade GR,
Spong CY and Andrews WW: Emerging concepts in antibiotic
prophylaxis for cesarean delivery: a systematic review. Obstet
Gynecol. 113:675–682. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watts DH, Krohn MA, Hillier SL and
Eschenbach DA: Bacterial vaginosis as a risk factor for
post-cesarean endometritis. Obstet Gynecol. 75:52–58.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mara JE and Baker JL: Hypertension and
haematomas: prophylaxis with apresoline. Br J Plast Surg.
30:169–170. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lamont RF, Sobel JD, Kusanovic JP,
Vaisbuch E, Mazaki-Tovi S, Kim SK, Uldbjerg N and Romero R: Current
debate on the use of antibiotic prophylaxis for caesarean section.
BJOG. 118:193–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dlamini LD, Sekikubo M, Tumukunde J, Kojjo
C, Ocen D, Wabule A and Kwizera A: Antibiotic prophylaxis for
caesarean section at a Ugandan hospital: a randomised clinical
trial evaluating the effect of administration time on the incidence
of postoperative infections. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 15:912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liabsuetrakul T, Lumbiganon P and
Chongsuvivatwong V: Prophylactic antibiotic prescription for
cesarean section. Int J Qual Health Care. 14:503–508. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Newton ER and Wallace PA: Effects of
prophylactic antibiotics on endometrial flora in women with
postcesarean endometritis. Obstet Gynecol. 92:262–268. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sherman D, Lurie S, Betzer M, Pinhasi Y,
Arieli S and Boldur I: Uterine flora at cesarean and its
relationship to postpartum endometritis. Obstet Gynecol.
94:787–791. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Watts DH, Eschenbach DA and Kenny GE:
Early postpartum endometritis: the role of bacteria, genital
mycoplasmas, and Chlamydia trachomatis. Obstet Gynecol. 73:52–60.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Emmons SL, Krohn M, Jackson M and
Eschenbach DA: Development of wound infections among women
undergoing cesarean section. Obstet Gynecol. 72:559–564.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Roberts S, Maccato M, Faro S and Pinell P:
The microbiology of post-cesarean wound morbidity. Obstet Gynecol.
81:383–386. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Andrews WW, Shah SR, Goldenberg RL, Cliver
SP, Hauth JC and Cassell GH: Association of post-cesarean delivery
endometritis with colonization of the chorioamnion by Ureaplasma
urealyticum. Obstet Gynecol. 85:509–514. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Keski-Nisula L, Kirkinen P, Katila ML,
Ollikainen M, Suonio S and Saarikoski S: Amniotic fluid U.
urealyticum colonization: significance for maternal peripartal
infections at term. Am J Perinatol. 14:151–156. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoon BH, Romero R, Park JS, Chang JW, Kim
YA, Kim JC and Kim KS: Microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity
with Ureaplasma urealyticum is associated with a robust host
response in fetal, amniotic, and maternal compartments. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 179:1254–1260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gordon HR, Phelps D and Blanchard K:
Prophylactic cesarean section antibiotics: maternal and neonatal
morbidity before or after cord clamping. Obstet Gynecol.
53:151–156. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Itskovitz J, Paldi E and Katz M: The
effect of prophylactic antibiotics on febrile morbidity following
cesarean section. Obstet Gynecol. 53:162–165. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ledger WJ: Prophylactic antibiotics in
cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 194:15002006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|