Introduction
Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) refers to a
group of symptoms related to lower urinary tract diseases that are
characterized by increased urinary frequency, urinary urgency,
nocturia and dysuria. LUTS can be categorized according to storage,
voiding and postmicturition symptoms. Storage LUTS includes urinary
urgency, urinary frequency, nocturi and urinary incontinence
(1). Overactive bladder (OAB) is
classed as one of the representative diseases of storage LUTS
(2). The International Continence
Society defines the symptoms of OAB as an urgent urination need,
with or without urinary incontinence, and increased daytime and
nocturnal urination, exclusion of organic bladder pathology is
required prior to OAB diagnosis (3). OAB is reported to have a high
prevalence of 20.8% in the Asia-Pacific region and a high
recurrence rate of symptoms after remission. Existing available OAB
treatment options include behavioral training, drug intervention,
detrusor injection and electrical stimulation of sacral or tibial
nerves, but the curative effect of these options is limited
(4,5).
The impact of diet and lifestyle habits on the
occurrence of LUTS has been reported in a previous study (6). A high salt intake is a characteristic
element of the Western diet, however, it has been demonstrated that
a high salt intake can lead to urinary frequency and nocturia in
various animal models (7,8). Although epidemiologic studies have
suggested that a high salt diet (HSD) is associated with the
development of OAB, current in vivo and in vitro
studies on the association of a HSD with development of OAB are
limited (7,9).
Although the etiology and pathogenesis of OAB is
currently unclear, it has been suggested that the bladder
epithelium might be involved in neural signaling as a receptor for
tension, chemical or temperature stimuli, termed the epithelial
origin theory (10,11). Damage to the epithelium has been
suggested to increase the excitability of local afferent nerves,
which in turn leads to unstable contraction of the detrusor and the
development of OAB (12). Studies
have reported that decreased expression levels of cell
junction-associated proteins increases the permeability of the
bladder epithelial layer in cystitis-related OAB (13,14).
Increased permeability has been shown to promote the diffusion of
urinary solutes across the urinary epithelial barrier, which
increases bladder afferent nerve sensitivity and facilitates
voiding at low filling volumes (15). A HSD has been reported to increase
the permeability of barriers such as the intestinal barrier or
blood brain barrier to trigger colitis or cerebral apoptosis
(16,17). The excessive sodium load that
enters the circulatory system following a HSD must be eliminated
through the urine, which keeps the bladder in a state of high
sodium urinary load (8). However,
it is currently unclear whether a high salt environment affects the
bladder epithelium barrier to induce OAD symptoms.
NLRP3 detects pathogens and cell damage, activating
the NLRP3 inflammasome, which in turn activates caspase-1, leading
to cytokine activation and pyroptosis. The inflammasome includes
NLRP3, caspase-1 and ASC, connecting NLRP3 and caspase-1(18). NF-κB regulates immune responses,
inflammation, and cell survival, activation and differentiation.
Dysregulated NF-κB activation is linked to inflammatory diseases,
such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple
sclerosis and asthma (19).
Elevated sodium intake in mice with hypertension increased NLRP3
signaling activation and IL-1β secretion, while NF-κB signaling
induced the transcriptional expression of NLRP3 (19-21).
The link between OAB, NLRP3 and NF-κB involves inflammatory
pathways (22). NLRP3, a key
component of the inflammasome, is elevated in OAB, promoting the
secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β. NF-κB, a
transcription factor, regulates NLRP3 expression, exacerbating
inflammation and contributing to bladder detrusor overactivity in
OAB (23). In a Sprague Dawley
rats animal model of neurogenic bladder, inhibition of NF-κB
signaling attenuated uroepithelial cell pyroptosis, thereby serving
an important role in bladder epithelial barrier homeostasis
(24). Tight junction proteins,
including Claudins, Occludins, and Zonula occludens proteins, seal
the space between adjacent cells in the bladder epithelial barrier,
preventing pathogen entry and collectively maintaining barrier
integrity and functionality (25).
Therefore, it could be suggested that HSD-induced OAB may be
associated with the activation of NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling
pathways and bladder epithelial damage.
TRPV4 was localized to the epithelial and muscular
layers of the bladder where it has been reported to sense various
stimuli. TRPV4 is suggested to increase the sensitivity of the
detrusor and excitation of the voiding reflex, as reported in
previous OAB models (26,27).
The present study aimed to investigate the effects
of HSD on bladder barrier function and the development of OAB. In
order to investigate the underlying mechanisms of HSD-induced OAB
and bladder epithelium damage, in vivo experiments to
examine the voiding characteristics and bladder epithelial
integrity of a HSD murine model were performed, followed by in
vitro investigations of the effect of high salt on bladder
epithelium damage.
Materials and methods
Murine model
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance
with the National Institute of Health guidelines and were approved
by the Institutional Animal Ethical Care Committee of Southern
Medical University (approval no. NFYY-2021-0572; Guangzhou, China).
Pathogen-free male C57BL/6 mice (age, 6-8 weeks; weight, 20-24 g)
were purchased from SPF Biotechnology Co., Ltd. All mice were
housed in a temperature- and humidity-controlled environment
(22±1˚C; 50±5%) with a 12 h light/dark cycle and free access to
food and water. Currently available literature suggests 0.49% NaCl
(w/v) in drinking water as the normal salt diet for mice (28). HSD mice (HSD group, n=6) were
provided with drinking water containing 2% (w/v) NaCl (1.7 g
NaCl/mouse/week) for 8 weeks, in accordance with a previously
published HSD murine model (29).
Control mice (CON group, n=6) received normal drinking water during
the experiment. In addition, CON and HSD groups were both provided
with 0.3% (w/w) salt concentration feed, which is the normal
concentration of NaCl in mice feed, according to the manufacturer's
guidelines (SPF Biotechnology Co., Ltd). Urine was collected every
week for further examination. After 8 weeks, the necks of the
animals were severed under complete anesthesia achieved through an
intraperitoneal injection of 1.5% (w/v) sodium pentobarbital (40
mg/kg). Death was confirmed by cardiac arrest, a drop in body
temperature and a lack of response to strong stimuli. The tissue
harvest time was ~10-15 min/mouse. Tissue was snap frozen with a
freezing temperature of -80˚C. After euthanasia, serum was
collected and bladder tissue harvested in a sterile manner for
further analysis. Blood collection was performed by open laparotomy
through the abdominal aorta using a fine needle to collect ~0.5-0.8
ml of blood. Each day, mice were weighed at a regular time, the
cage bedding was changed and their health assessed. If mice were
found unable to feed or drink, did not respond to gentle
stimulation or experienced body weight loss >20% compared with
their starting weight, they were considered to be unsuitable for
further experimentation and were to be euthanized by cervical
dislocation under general anesthesia using the aforementioned
method. However, no animal in this experiment reached these humane
endpoints.
SV40 virus transformed human
uroepithelium cells (SV-HUC-1s)
Human SV-HUC-1s (cat. no. CRL-9520; American Type
Culture Collection) were cultured in Ham's F-12K medium (Gibco;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine
serum (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 0.5%
penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
under standard cell culture conditions (temperature, 37˚C;
CO2, 5%). SV-HUC-1s were seeded into 6-well plates at a
density of 6x104 cells/well (n=6 well/treatment group)
in culture media for 24 h for use in the reactive oxygen species
(ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) assays and
reverse-transcriptase quantitative (RT-q) PCR. The concentration of
NaCl in Ham's F-12K medium was 150 mM. During the logarithmic
growth period, additional NaCl was added to the HSD group to reach
a concentration of 190 mM for 24 h (21). CON cells were simultaneously
maintained in standard Ham's F-12K media (150 mM) for 24 h.
Urinary frequency measurement
Urgency is a subjective sensation that cannot
intuitively be assessed in mice. Measurement of non-urinary
contractions in urodynamic experiments was utilized as an indicator
of urgency, which previous studies have reported to be an objective
method of measuring a response to the sensation of urgency
(30-32).
Urinary frequency was measured as previously described (33). Briefly, individual mice were placed
in a metabolic cage and abstained from water for 4 h. A sheet of
copper sulfate paper was placed at the bottom of each cage. Urinary
frequency was determined by the number of voiding spots on the
filter paper. Overlapping urine spots with defined edges were
considered to be separate urinations. Urination frequency was
recorded for 3 consecutive days and the average of the three days'
values were calculated.
Cystometry
Mice were anesthetized using 3.0-4.0% isoflurane by
inhalation for induction of anesthesia and anesthesia maintained
using 1.0-1.5% isoflurane while the mouse was placed in the supine
position. The lower abdomen was excised to fully to expose the
bladder. An intravenous needle (0.6x15 mm) was gently inserted into
the bladder and secured and a 1.0 ml syringe was used to withdraw
residual urine. The BL-420N BioSignal Acquisition System (Chengdu
Techman software Co., Ltd.) was used as a pressure measurement
device. Sterile saline at 0.9% (w/v) was continuously pumped into
the bladder at a flow rate of 1 ml/h. When a consistent and stable,
the non-interfering cluttered waveform of micturition was
established, digital intravesical pressure signals were
continuously recorded for 30 min or for at least five void cycles.
During the bladder filling period, it was observed if urine flowed
out of the external urethra of the mice. When the bladder of mice
contracts, there is a noticeable increase in pressure on the
urodynamic chart, and urination occurring simultaneously is termed
micturition contraction. When the bladder of mice contracts without
urination, it is defined as non-micturition contraction (34). When the bladder contracts and
urination occurs, the pressure recorded on the urodynamic chart
represents the peak pressure and the maximum bladder capacity was
calculated (maximum bladder capacity=perfusion time x perfusion
rate).
Gene expression analysis
Total RNA was extracted from whole bladder tissue or
SV-HUC-1s using either the Animal Total RNA Isolation Kit or the
Cell Total RNA Isolation Kit, respectively (cat. no.
RE-03011/03014; Foregene Co., Ltd.) according to the manufacturer's
instructions. A reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme, HiScript III RT
SuperMix for qPCR + gDNA wiper (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd.; cat. no.
R323-01), was used to obtain cDNA from total RNA (temperature and
duration: 50˚C for 15 min; 85˚C for 5 sec). The RT-qPCR reactions
(initial denaturation: 95˚C for 30 sec; 40 cycles of amplification
at 95˚C for 10 sec and 60˚C for 30 sec; followed by melting curve
analysis at 95˚C for 15 sec, 60˚C for 1 min and 95˚C for 15 sec)
were performed using the ChamQ SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme Biotech
Co., Ltd.), using the LightCycler480 (Roche Diagnostics). GAPDH was
used as the internal reference gene. Relative quantification of
target genes were calculated using the 2-∆∆Cq method
(35). All sequences of primers
utilized are listed in Table
I.
 | Table IPrimer sequences for reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR. |
Table I
Primer sequences for reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR.
| Gene | | Sequence
(5'-3') |
|---|
| Mouse | Claudin1 | F:
GCCATCTACGAGGGACTGTG |
| | | R:
CCCCAGCAGGATGCCAATTA |
| | TJP1 | F:
AGAGACAAGATGTCCGCCAG |
| | | R:
TGCAATTCCAAATCCAAACC |
| | IL-1β | F:
CAGGCAGGCAGTATCACTCA |
| | | R:
TGCAATTCCAAATCCAAACC |
| | TNF-α | F:
AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACT |
| | | R:
CCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCTAC |
| | TRPV4 | F:
CGGACCACAGTGGACTACCT |
| | | R:
GAGACAACCACCAGCACAGA |
| | GAPDH | F:
AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG |
| | | R:
TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGG |
| | | TCA |
| Human | TNF-α | F:
TCCTTCAGACACCCTCAACC |
| | | R:
AGGCCCCAGTTTGAATTCTT |
| | IL-1β | F:
GGGCCTCAAGGAAAAGAATC |
| | | R:
TTCTGCTTGAGAGGTGCTGA |
| | TJP-1 | F:
TGAGGCAGCTCACATAATGC |
| | | R:
GGTCTCTGCTGGCTTGTTTC |
| | CLAUDIN-1 | F:
CCGTTGGCATGAAGTGTATG |
| | | R:
CCAGTGAAGAGAGCCTGACC |
| | TRPV4 | F:
GCGAGGTCATTACGCTCTTC |
| | | R:
TAGAGGGCTGCTGAGACGAT |
| | NCF-1 | F:
AGTCCTGACGAGACGGAAGA |
| | | R:
TACATGGACGGGAAGTAGCC |
| | CYBA | F:
CGCTTCACCCAGTGGTACTT |
| | | R:
GAGAGCAGGAGATGCAGGAC |
| | CASP1 | F:
GCTTTCTGCTCTTCCACACC |
| | | R:
CATCTGGCTGCTCAAATGAA |
| | ASC | F:
TGACGGATGAGCAGTACCAG |
| | | R:
TCCTCCACCAGGTAGGACTG |
| | NLRP3 | F:
CTTCTCTGATGAGGCCCAAG |
| | | R:
GCAGCAAACTGGAAAGGAAG |
| | GSDMD | F:
GGTTCTGGAAACCCCGTTAT |
| | | R:
CCAGGTGTTAGGGTCCACAC |
| | NF-κB1 | F:
CCTGGATGACTCTTGGGAAA |
| | | R:
TCAGCCAGCTGTTTCATGTC |
| | GAPDH | F:
ACAGTCAGCCGCATCTTCTT |
| | | R:
GACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCAG |
Histological staining and
analysis
The bladder tissue samples of mice were collected,
sliced horizontally and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 3 days at
room temperature. The samples were embedded in paraffin, sectioned
at 4-µm thick and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E;
hematoxylin for 4 min and eosin for 20 sec) at room temperature.
The method of histologic scoring was as previously described
(36). Briefly, the histologic
score was determined by the degree of bladder edema, inflammatory
cell infiltration, bleeding and ulcer formation and depth of
mucosal injury (absent, 0; mild, 1; moderate, 2; severe, 3).
Measurements of the thickness of mucous layer and lamina propria
was obtained from three randomly selected regions of a tissue
section from each sample and the mean thickness was calculated.
Immunohistochemistry was performed as follows: Antigen retrieval
was performed with 0.01 M, pH 6.0 sodium citrate solution for 10
min in a microwave at 98˚C and then allowed to cool down at room
temperature. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked with 0.3%
hydrogen peroxide at room temperature for 10 min, followed by
incubation with 5% goat serum (cat. no. BL210A; Biosharp Life
Sciences) for 30 min at room temperature. The samples were then
incubated at 4˚C overnight with the following primary antibodies:
Rabbit anti-TJP-1 antibody (1:250; cat. no. ab276131; Abcam),
rabbit anti-CLAUDIN-1 antibody (1:200; cat. no. YT0942; ImmunoWay
Biotechnology Company), rabbit anti-TRPV4 antibody (1:200; cat. no.
YT5833; ImmunoWay Biotechnology Company), rabbit anti-CASP1
antibody (1:200; cat. no. YP0749; ImmunoWay Biotechnology Company)
and rabbit anti-NF-κB antibody (1:200; cat. no. YM8001; ImmunoWay
Biotechnology Company). Subsequently, the samples were incubated
with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary
antibody at 37˚C for 30 min (1:200; cat. no. LF102; Shanghai
Epizyme Biotech Co., Ltd.). DAB solution (cat. no. BL732A; Biosharp
Life Sciences) was added and the samples were incubated 3 min.
Counterstain sections were immersed in hematoxylin and 0.1% HCl-
ethanol for 1-10 sec, and washed with distilled water. Samples were
dehydrated through 95% ethanol for 1 min, 100% ethanol for 2 min,
xylene for 2 min, and then immersed with the coverslip with
mounting medium. All images were scanned by a NanoZoomer Digital
slide scanner and captured with an NDP View2 Plus Image viewing
software (version U12388-01; Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.).
Quantification of the average optical density was performed using
the Image-Pro Plus software (version 6.0; Media Cybernetics, Inc.)
in three randomly chosen fields of view, at x10 magnification, from
each sample.
Biochemical and oxidative stress
marker analysis
Serum and urine Na+, K+,
Ca2+ and Cl- concentrations were determined
using an automatic biomedical analyzer (Roche Diagnostics). Mice
urinary proteins were detected using an ELISA kit, according to the
manufacturer's protocol (cat. no. MM-44286M2; Shanghai MEIMIAN
Biotechnology, Co., Ltd.). MDA levels were detected using an ELISA
kit, according to the manufacturer's protocol (cat. no. E-EL-0060;
Wuhan Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). MPO levels were
detected using the MPO Activity Assay kit, according to the
manufacturer's protocol (cat. no. E-BC-K074-M; Wuhan Elabscience
Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). MPO and MDA levels were evaluated using
the homogenate of the cell culture, whereby cells were digested for
2 mins, centrifuged at 20˚C and 200 x g for 3 min and resuspended
for use).
Intracellular ROS generation
determination
Intracellular ROS was detected using a ROS assay kit
(cat. no. S0033S; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). Briefly,
SV-HUC-1 cells were cultured in 6-well plates and incubated with
fluorescent 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology) for 20 min at 37˚C. The fluorescent ROS signals
were detected in darkness and images captured using an excitation
wavelength of 488 nm and an emission wavelength of 525 nm using an
inverted fluorescence microscope (ECLIPSE Ti2; Nikon Corporation).
The ROS levels of each group were calculated using the Image-Pro
Plus software. The average fluorescence intensity of each sample
was calculated in relation to a reference value obtained from the
average fluorescence intensity of the CON group.
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as mean ± SD or median with
interquartile range and were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software
(version 8.0; Dotmatics). Statistical analyses were performed using
a two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test
for non-normal distributions, as indicated in the figure legends.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference. Correlation between variables was calculated using
Spearman correlation analysis. Consideration was only given to
correlation values ρ>0.6 and P<0.05. Correlation network
graphs were plotted using Wekemo Bioincloud software (www.bioincloud.tech).
Results
A HSD in mice altered micturition
characteristics
In the present study, mice were placed on either a
standard salt intake diet or a HSD for 8 weeks, following which
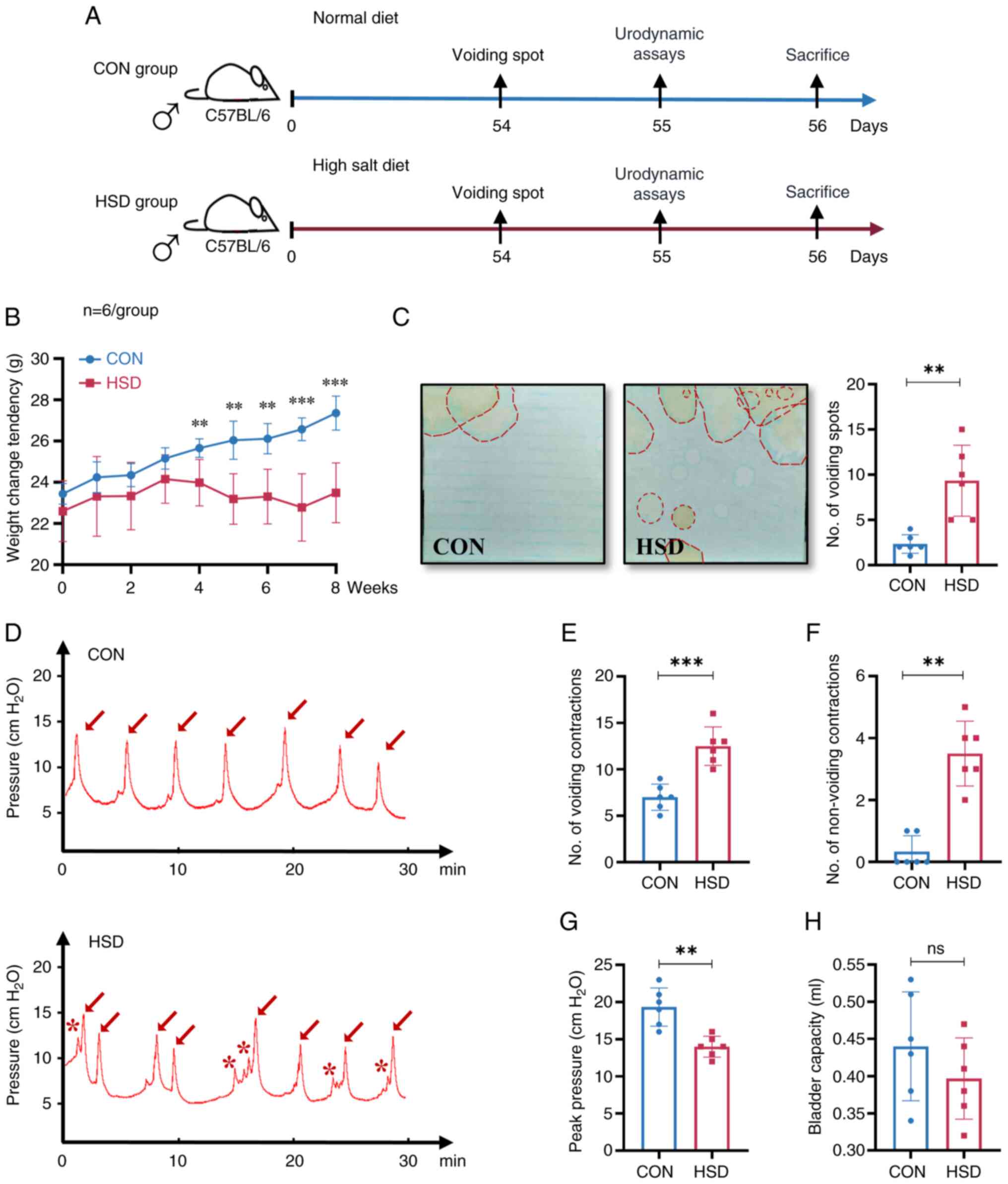
changes in bladder and voiding behavior were assessed (Fig. 1A). An 8 week HSD significantly
decreased the rate of weight gain of the HSD group compared with
CON group (Fig. 1B; Table II). There were no significant
differences in serum Na+ and Cl-
concentrations in the HSD group compared with the CON group
(Table II). The concentration of
Na+ and Cl- in the urine of the HSD group was
4-fold higher compared with the CON group. Furthermore, a HSD did
not significantly change the urine concentrations of K+
and Ca2+, however, urine protein expression levels were
significantly increased in the HSD group compared with the CON
group. Measurement of the number of voiding spots indicated that
the HSD group urinated significantly more often compared with the
CON group and the location of voiding tended to be in the middle of
the cage in the HSD group compared with the CON group (Fig. 1C). Previous behavioral studies have
reported that mice are more inclined to urinate in corners
(37). In the present study, the
HSD group tended to urinate more in the middle of the cage, which
suggested that they were potentially more likely to experience
frequent micturition compared with the CON group. Furthermore, the
cystometry curve demonstrated that the number of voiding
contractions and the number of non-voiding contractions were
significantly increased in the HSD group compared with the CON
group (Fig. 1D-F). A significant
decrease in the maximum bladder pressure in the HSD group compared
with the CON group was observed (Fig.
1G). There was no significant difference in bladder capacity of
the HSD group compared with the CON group (Fig. 1H). The aforementioned results
indicated that an 8 week HSD altered micturition characteristics
and resulted in OAB-like symptoms in mice.
 | Table IIBaseline characteristics and
biochemical indicators of serum and urine samples. |
Table II
Baseline characteristics and
biochemical indicators of serum and urine samples.
| Characteristic | Control group | High salt diet
group | P-value |
|---|
| Weight at week 8,
g | 27.35±0.75 | 23.48±1.33 | <0.001 |
| Water consumption,
ml/week | 35.54±4.60 | 82.97±7.92 | <0.001 |
| Serum biochemistry,
mmol/l | | | |
|
Na+ | 149.40±1.50 | 146.80±2.04 | 0.074 |
|
Cl- | 103.68±0.95 | 107.25±14.36 | 0.592 |
| Urinary
biochemistry | | | |
|
Na+,
mmol/l | 75.20±40.29 | 396.67±98.49 | <0.001 |
|
Cl-,
mmol/l | 87.08±39.22 | 455.17±146.12 | <0.001 |
|
K+,
mmol/l | 166.18±19.03 | 121.07±50.55 | 0.122 |
|
Ca2+,
mmol/l | 0.83±0.21 | 0.84±0.40 | 0.962 |
|
Urine
protein, µg/l | 47.07±3.47 | 73.61±9.68 | <0.001 |
A HSD in mice promoted an inflammatory
response and impaired barrier integrity of the bladder
Histological scores of the bladder and the bladder
weight/body weight ratio showed no significant differences between
the HSD and CON groups (Fig. 2A
and B), which was consistent with
the clinicopathologic features of patients with OAB (3). However, the histological scores of
the bladder in the HSD group were markedly higher compared with the
CON group; therefore, the thickness of the mucosal layer and lamina
propria of the bladder were separately measured. No significant
difference in the thickness of the lamina propria was observed;
however, the bladder mucosa layer of the HSD group was
significantly thinner compared with that of the CON group (Fig. 2C). The mRNA expression levels of
the pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α in the bladder were
significantly higher in the HSD group compared with the CON group
(Fig. 2D). The mRNA and protein
expression levels of TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1 in the bladder epithelium
were significantly lower, while the levels of TRPV4 were
significantly increased in the HSD group compared with the CON
group (Fig. 2E-G). These results
suggested that a HSD in mice impaired the integrity of the bladder
epithelial barrier and potentially caused an inflammatory
response.
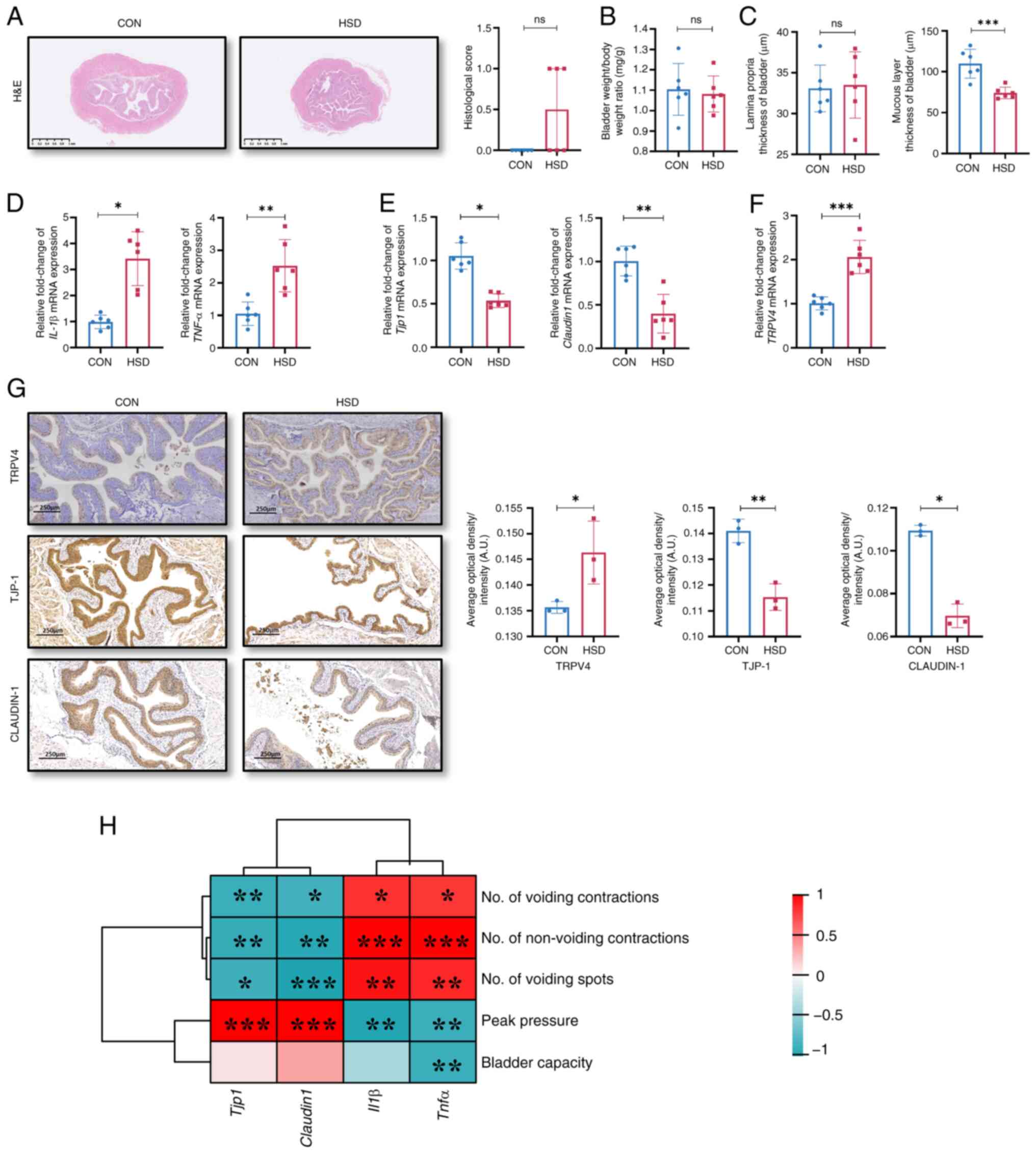 | Figure 2A HSD in vivo impaired barrier
function of bladder. (A) H&E staining and histological score of
bladder tissues (scale bar, 1 mm). Data were presented as the
median with interquartile range. (B) Bladder weight/body weight
ratio. (C) Thickness of lamina propria and mucosal layer of the
bladder. Relative mRNA expression levels of (D) inflammatory
response markers, IL-1β and TNF-α, (E) tight junction proteins,
TJP-1 and Claudin-1 and (F) TRPV4. (G) Representative images of
histological staining and quantification of protein expression of
TRPV4, TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1 in bladder tissues sections from CON and
HSD mice. Scale bar, 250 µm (n=3). (H) Correlation analysis between
the mRNA expression levels of tight junction proteins and
inflammation factors in the bladder and urination characteristics
in CON and HSD mice. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n=6).
P-values were calculated using a two-tailed unpaired Student's t
test; ***P<0.001, **P<0.01 and
*P<0.05. HSD, high salt diet; CON, control; TJP-1,
tight junction protein 1; TRPV4, transient receptor potential
vanilloid 4; ns, non-significant; A.U., arbitrary units. |
A HSD increased uroepithelial
oxidative stress and affected NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling
pathways
The mRNA and protein expression levels of tight
junction proteins, TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1 in the bladder was
significantly negatively correlated with the number of voiding
contractions, non-voiding contractions and voiding spots, and was
significantly positively correlated with peak pressure (Fig. 2H). However, the mRNA expression
levels of inflammatory factors, IL-1β and TNF-α, in the bladder
were significantly positively correlated with OAB-like voiding
behaviors, moreover, TNF-α level was significantly negatively
correlated with bladder capacity.
Previous studies have reported that oxidative stress
and the NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling pathways are important for the
maintenance of bladder epithelial cell homeostasis both in animals
and in vitro models of bladder cancer and interstitial
cystitis (24,38,39).
However, to the best of our knowledge, whether the aforementioned
pathways are altered in a HSD-triggered OAB model has not been
reported to date. Therefore the present study undertook a series of
in vitro experiments to examine the role of oxidative
stress, NLRP3 and the NF-κB signaling pathways in HSD-induced OAB.
The mRNA expression levels of TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1 were
significantly reduced, whereas the TRPV4 expression level was
significantly increased in the HSD group compared with the CON
group (Fig. 3A and B), which were consistent with the
aforementioned results of the in vivo HSD model in the
present study. The mRNA expression levels of IL-1β and TNF-α, as
well as the relative expression levels of MPO, were significantly
increased in the HSD group compared with the CON group (Fig. 3C and D). The fluorescence intensity of ROS was
significantly higher in the HSD group compared with the CON group
(Fig. 3E). The mRNA expression
levels of neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 and cytochrome B-245 alpha
chain, which are structural protein components of NADPH oxidase,
were significantly higher in the HSD group compared with the CON
group (Fig. 3F). MDA, an indicator
of lipid peroxidation, was significantly increased in the HSD group
compared with the CON group (Fig.
3G). This suggested a that high salt culture environment led to
a higher level of oxidative stress in vitro.
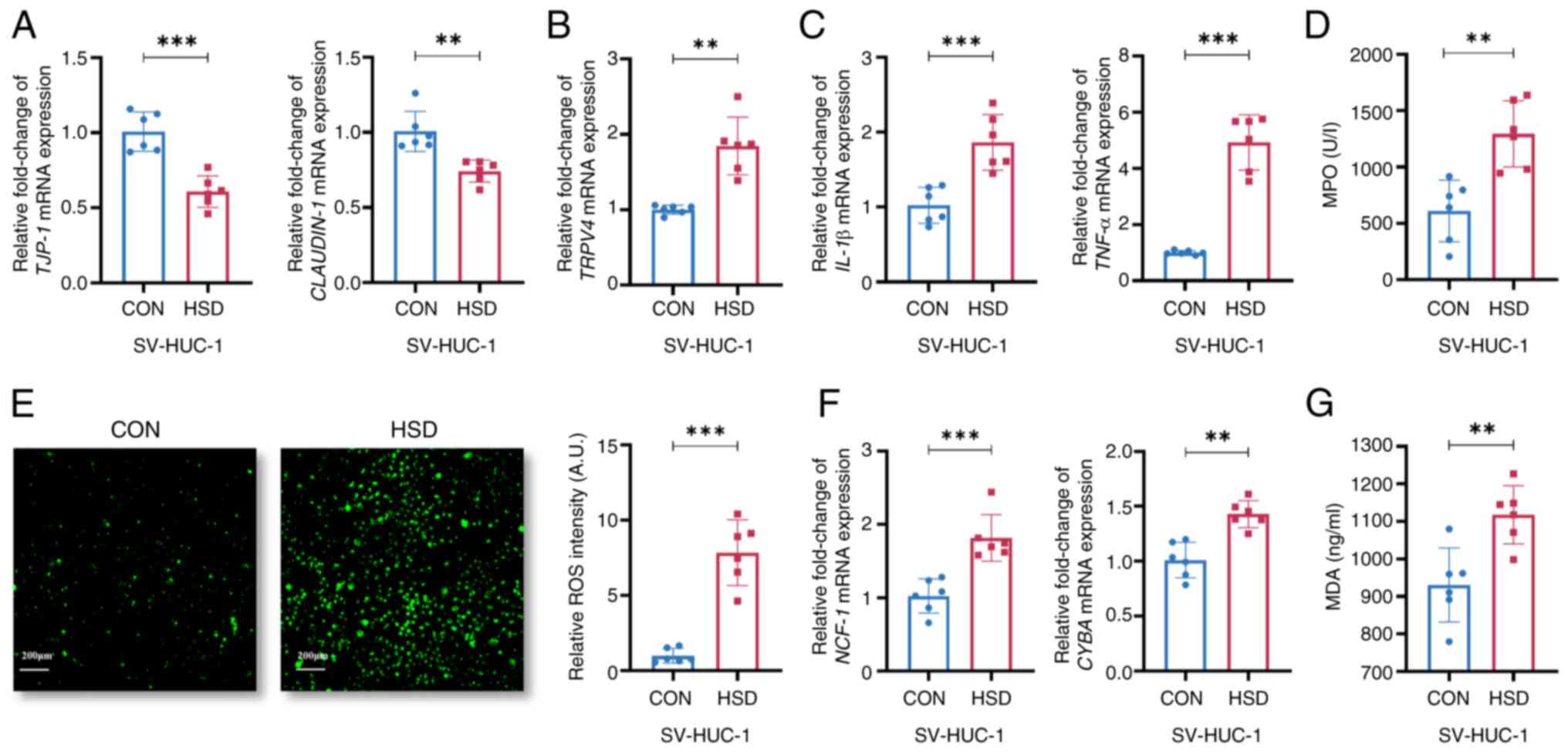 | Figure 3A HSD increased uroepithelial
oxidative stress in SV-HUC-1 cells. Relative mRNA expression levels
of (A) TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1, (B) TRPV4 and (C) IL-1β and TNF-α in
HSD-treated and CON cells. (D) Relative MPO expression levels in
CON and HSD groups. (E) Representative images and quantification of
intracellular ROS levels (scale bar, 200 µm). (F) Relative mRNA
expression levels of NCF-1 and CYBA. (G) Relative MDA expression
levels in CON and HSD groups. Data are presented as mean ± SD
(n=6). P-values were calculated using a two-tailed unpaired
Student's t-test; ***P<0.001 and
**P<0.01. HSD, high salt diet; CON, control;
SV-HUC-1, SV40 virus transformed human uroepithelium cells; TJP-1,
tight junction protein 1; TRPV4, transient receptor potential
vanilloid 4; MPO, myeloperoxidase; ROS, reactive oxygen species;
NCF-1, neutrophil cytosolic factor 1; CYBA, cytochrome B-245 alpha
chain; MDA, malondialdehyde. |
The protein expression level of CASP1 and the mRNA
expression levels of CASP1, NLRP3, apoptosis-associated speck-like
protein containing a caspase recruitment domain and gasdermin D
were significantly increased in the HSD group compared with the CON
group (Fig. 4A and B). The protein and mRNA expression levels
of NF-κB and NF-κB1, respectively, were significantly increased in
the HSD group compared with the CON group (Fig. 4C and D), which suggested that high salt
treatment affected NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in the
urinary epithelium in vitro and in vivo.
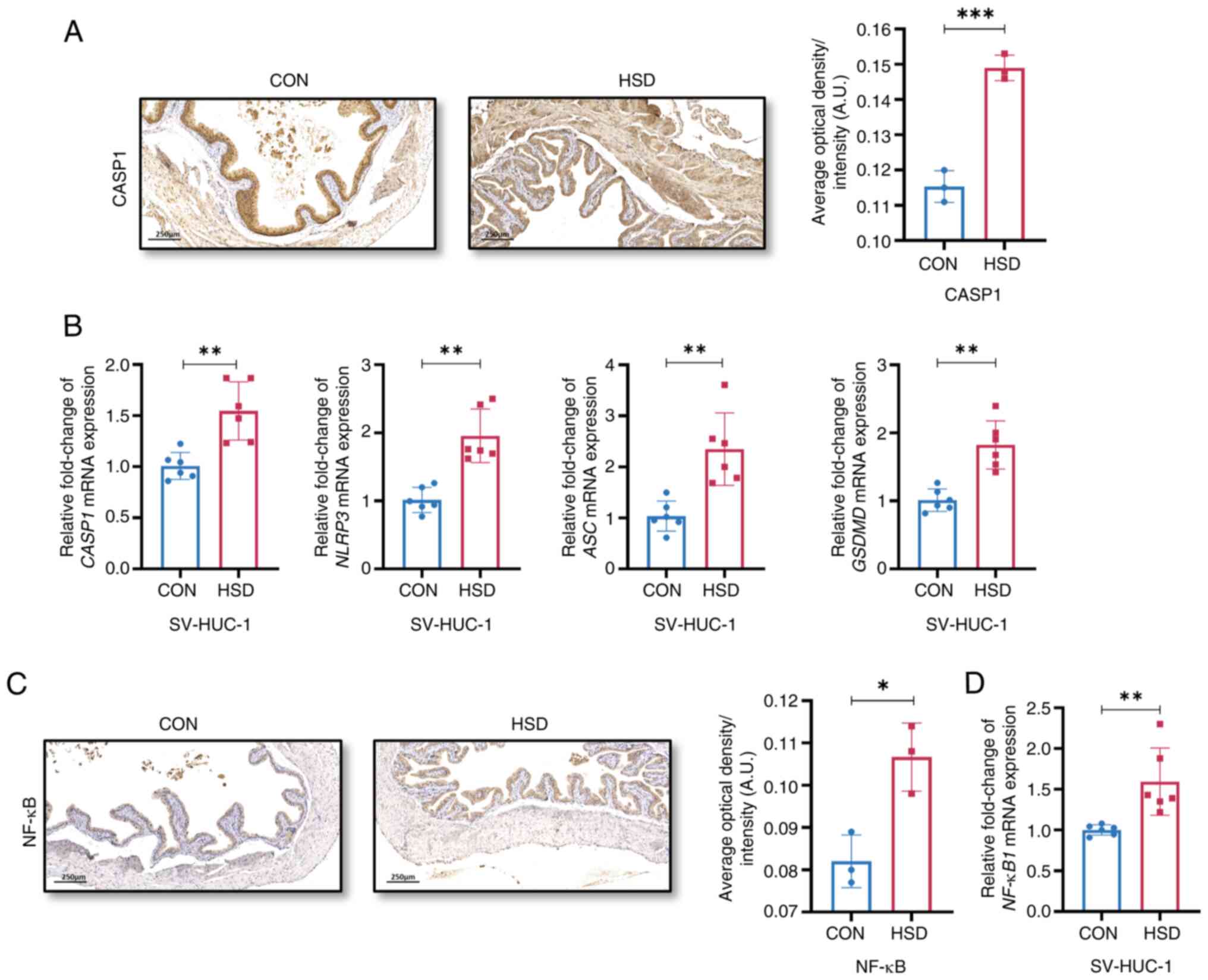 | Figure 4A HSD activated NLRP3 and NF-κB
signaling pathways. (A) Representative histological images and
quantification of NLRP3 signaling component, CASP-1 expression
in vivo (n=3). (B) Relative mRNA expression levels of CASP1,
NLRP3, ASC and GSDMD in CON and HSD treated SV-HUC-1 cells (n=6).
(C) Representative histological images and quantification of NF-κB
expression in vivo (n=3). (D) Relative mRNA expression
levels of NF-κB1 in CON and HSD treated SV-HUC-1 cells (n=6). Data
are presented as the mean ± SD. P-values were calculated using a
two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test; ***P<0.001,
**P<0.01 and *P<0.05. HSD, high salt
diet; CON, control; SV-HUC-1, SV40 virus transformed human
uroepithelium cells; CASP1, caspase-1; ASC, apoptosis-associated
speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; NLRP3,
nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and
pyrin domain containing 3; GSDMD, gasdermin D. |
Discussion
The present study demonstrated that an 8 week HSD
in vivo mouse model induced the increased expression of
inflammatory state markers in the bladder, reduced gene and protein
expression levels of bladder epithelial tight junction proteins,
TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1, and increased both protein and mRNA expression
levels of TRPV4, which were associated with the development of
OAB-like symptoms. In addition, the present study utilized a human
cell line and demonstrated that high salt intervention increased
oxidative stress level and elevated gene and protein expression
levels of the NF-κB and NLRP3 pathway in vitro. To the best
of our knowledge, the present study is the first to report that a
HSD-induced inflammatory response of the bladder and OAB-like
symptoms in vivo may be associated with activation of
oxidative stress, NLRP3 and NF-κB signaling.
The ability of the body to maintain urine within the
healthy concentration range relies upon the selective regulation of
molecules according to molecular size and charge by tight junctions
strands between bladder epithelial cells (40). The function of the bladder
epithelial barrier is to monitor the mechanical and chemical
environment of the bladder and transmit environmental alternations
to the underlying tissues, such as afferent nerve fibers and smooth
muscle (41). In the present
study, changes in the ion concentration and albumin of urine in the
HSD group indicated potential impairment of the bladder epithelial
barrier function. Previous studies have shown that defects of
proteins expression in uroepithelial tight junction formation, in
particular tight junction proteins CLAUDIN-1 and occludin, led to
sensory afferent nerve activation and caused pelvic pain, urinary
frequency and urinary urgency (42,43).
The present study demonstrated that gene and protein expression
levels of tight junction proteins TJP-1 and CLAUDIN-1 in the
bladder epithelium of mice were significantly reduced in an in
vivo model of HSD and were significantly negatively correlated
with OAB-like symptoms. The aforementioned results suggested that a
decrease in bladder tight junction protein expression level may
have been a potential cause of bladder epithelial barrier
impairment and the occurrence of OAB-like symptoms in the HSD
group. The TRPV4 channel senses chemical stimuli in the bladder and
the increased expression of TRPV4 has been previously reported to
induce sensitization of bladder afferent nerves and the onset of
the voiding reflex. TRPV4 has been reported to directly modulate
the contractility of the detrusor, which was associated with the
development of OAB (26,44). TRPV4 is also associated with
urothelial barrier function and a previous study has demonstrated
that the integrity of the bladder epithelium was disrupted in
TRPV4-/- mice (26). It
could be suggested that increased TRPV4 expression levels due to
the in vivo model of HSD that may have potentially
contributed to a positive feedback regulation of epithelial barrier
damage in the present study. In summary, the present study
demonstrated that an 8 week HSD in vivo could lead to
upregulation of markers of bladder barrier damage and OAB-like
symptoms.
Previous studies have suggested that inflammatory
responses induced by a HSD are associated with the activation of
oxidative stress and NLRP3 signaling markers. NF-κB signaling is
suggested to increase NLRP3 transcription, which together act
synergistically to induce a pro-inflammatory response (19,20).
In the present study, the activation of NLRP3 and NF-κB signal
pathway were obtained in an in vivo model of HSD-induced
bladder dysfunction. Bladder C fibers refer to a specific type of
nerve fibers, which play an important role in controlling the
process of urination, helping the brain perceive the status of the
bladder and regulate the timing of urination. In addition, NLRP3
activation has been reported to increase C-fiber populations in the
bladder and lead to OAB-like symptoms in diabetic mice (45). It was also reported that NLRP3
activation impaired the integrity of the urothelium barrier, and
the down-regulation of tight junction protein expression levels was
observed in the overactive stage in NLRP3-/- diabetic
mice (46). A previous study
further showed that activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
inhibited the transcription of caveolins and was associated with
smooth muscle hypertrophy in the bladder, which interfered with
normal bladder contraction in humans and mice (47). To the best of our knowledge, the
present study was the first to report that OAB-like symptoms
induced by HSD were associated with alterations in the NLRP3 and
NF-κB signaling pathways, as well as inducing the loss of
urothelium tight junction proteins.
The present study had a number of limitations. The
results drawn from the expression levels of tight junction proteins
cannot be entirely conclusive in terms of altered bladder barrier
function, although the present data provided some representative
indication of function. Due to limitations in the experimental
conditions of the present study, functional experiments, such as
measurement of transepithelial resistance, could not be performed.
Additionally, the TRPV ion channel family has many members, such as
TRPV1, that are also expressed in the bladder epithelium and
muscularis propria (48). In the
present study, the effects of a HSD regime on alternate TRPV
receptors, other than TRPV4, was not observed. Therefore, the
specific mechanisms underlying HSD-induced bladder barrier damage
warrants further investigation. Based on the research presented in
the current study, an appropriate dietary salt intake for humans
could not be recommended, as this requires further clinical studies
to be performed in the future.
In conclusion, the present study showed that an 8
week HSD in mice could induce OAB-like symptoms, which potentially
may have been associated with disruption of the bladder epithelial
barrier integrity, as well as increased TRPV4 expression levels. It
was demonstrated that high-salt treatment in vitro increased
uroepithelial oxidative stress and activation of the NLRP3 and
NF-κB signaling pathways. Results from the present study
highlighted the importance of the structural integrity of the
bladder barrier on the development of OAB and these results could
potentially suggest new avenues of future treatment for patients
with OAB.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: This work was supported by funding from the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 82370782).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
JX and ZZho conceived, designed, interpreted the
data and confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. ZZhu, QS and
YZ acquired and analyzed the data. JX and ZZho drafted and wrote
the manuscript. PW reviewed and revised the data and the final
manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of
the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The animal study protocol of the present study was
approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Care Committee of
Southern Medical University (approval no. NFYY-2021-0572;
Guangzhou, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Abrams P, Chapple C, Khoury S, Roehrborn C
and de la Rosette J: International Scientific Committee. Evaluation
and treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in older men. J Urol.
181:1779–1787. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nambiar AK, Arlandis S, Bø K,
Cobussen-Boekhorst H, Costantini E, de Heide M, Farag F, Groen J,
Karavitakis M, Lapitan MC, et al: European association of urology
guidelines on the diagnosis and management of female non-neurogenic
lower urinary tract symptoms. part 1: diagnostics, overactive
bladder, stress urinary incontinence, and mixed urinary
incontinence. Eur Urol. 82:49–59. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D,
Rosier P, Ulmsten U, Van Kerrebroeck P, Victor A and Wein A:
Standardisation Sub-Committee of the International Continence
Society. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract
function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the
International Continence Society. Urology. 61:37–49.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Farag F, Sakalis VI, Arteaga SM, Sihra N,
Karavitakis M, Arlandis S, Bø K, Cobussen-Boekhorst H, Costantini
E, de Heide M, et al: What Are the short-term benefits and
potential harms of therapeutic modalities for the management of
overactive bladder syndrome in women? A review of evidence under
the auspices of the European Association of urology, female
non-neurogenic lower urinary tract symptoms guidelines Panel. Eur
Urol. 84:302–312. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chow PM, Liu SP, Chuang YC, Lee KS, Yoo
TK, Liao L, Wang JY, Liu M, Sumarsono B and Jong JJ: The prevalence
and risk factors of nocturia in China, South Korea, and Taiwan:
Results from a cross-sectional, population-based study. World J
Urol. 36:1853–1862. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jeong JB, Lee JH, Choo MS, Ahn DW, Kim SH,
Lee DS, Cho MC, Son H, Jeong H and Yoo S: Association between
life-style, metabolic syndrome and lower urinary tract symptoms and
its impact on quality of life in men ≥ 40 years. Sci Rep.
12(6859)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yamamoto S, Hotta Y, Maeda K, Kataoka T,
Maeda Y, Hamakawa T, Shibata Y, Sasaki S, Ugawa S, Yasui T and
Kimura K: High salt loading induces urinary storage dysfunction via
upregulation of epithelial sodium channel alpha in the bladder
epithelium in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Pharmacol Sci.
135:121–125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Iwamoto T, Torimoto K, Gotoh D, Onishi S,
Hori S, Morizawa Y, Nakai Y, Miyake M and Fujimoto K: Reduced salt
intake partially restores the circadian rhythm of bladder clock
genes in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Life Sci.
306(120842)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kawata R, Hotta Y, Maeda K, Kataoka T and
Kimura K: Effects of high salt intake on detrusor muscle
contraction in dahl salt-sensitive rats. Nutrients.
13(539)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Andersson KE: Storage and voiding
symptoms: Pathophysiologic aspects. Urology. 62 (5 Suppl 2):S3–S10.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Andersson KE: Bladder activation: Afferent
mechanisms. Urology. 59 (5 Suppl 1):S43–S50. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Birder LA: Urothelial signaling. Auton
Neurosci. 153:33–40. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen YH, Chen CJ, Wang SJ, Lin YN, Chen
WC, Tsai MY and Chen HY: Downregulation of tight junction protein
zonula occludens-2 and urothelium damage in a
cyclophosphamide-induced mouse model of cystitis. Taiwan J Obstet
Gyne. 57:399–406. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen YH, Chen WC, Liu PL and Chen HY:
Astragalus polysaccharides and astragaloside IV ameliorates
cyclophosphamide-induced mouse model of overactive bladder. Taiwan
J Obstet Gyne. 59:248–255. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Montalbetti N, Rued AC, Taiclet SN, Birder
LA, Kullmann FA and Carattino MD: Urothelial tight junction barrier
dysfunction sensitizes bladder afferents. eNeuro.
4(ENEURO.0381-16.2017)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fredriksson K, Kalimo H, Westergren I,
Kåhrström J and Johansson BB: Blood-brain barrier leakage and brain
edema in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Effect of
chronic sympathectomy and low protein/high salt diet. Acta
Neuropathol. 74:259–268. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hu L, Zhu S, Peng X, Li K, Peng W, Zhong
Y, Kang C, Cao X, Liu Z and Zhao B: High salt elicits brain
inflammation and cognitive dysfunction, accompanied by alternations
in the gut microbiota and decreased SCFA production. J Alzheimers
Dis. 77:629–640. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fu J and Wu H: Structural Mechanisms of
NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation. Annu Rev Immunol.
41:301–316. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2(17023)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pitzer A, Elijovich F, Laffer CL, Ertuglu
LA, Sahinoz M, Saleem M, Krishnan J, Dola T, Aden LA, Sheng Q, et
al: DC ENaC-Dependent Inflammasome Activation Contributes to
Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Circ Res. 131:328–344. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shen S, Duan J, Hu J, Qi Y, Kang L, Wang
K, Chen J, Wu X, Xu B and Gu R: Colchicine alleviates inflammation
and improves diastolic dysfunction in heart failure rats with
preserved ejection fraction. Eur J Pharmacol.
929(175126)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
de Oliveira MG, de Medeiros ML, Tavares
EBG, Mónica FZ and Antunes E: Methylglyoxal, a reactive glucose
metabolite, induces bladder overactivity in addition to
inflammation in mice. Front Physiol. 11(290)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hughes FM Jr, Allkanjari A, Odom MR, Jin H
and Purves JT: Diabetic bladder dysfunction progresses from an
overactive to an underactive phenotype in a type-1 diabetic mouse
model (Akita female mouse) and is dependent on NLRP3. Life Sci.
299(120528)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen J, Li Q, Hong Y, Zhou X, Yu C, Tian
X, Zhao J, Long C, Shen L, Wu S and Wei G: Inhibition of the NF-κB
signaling pathway alleviates pyroptosis in bladder epithelial cells
and neurogenic bladder fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci.
24(11160)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mohanty S, Kamolvit W, Hertting O and
Brauner A: Vitamin D strengthens the bladder epithelial barrier by
inducing tight junction proteins during E. coli urinary tract
infection. Cell Tissue Res. 380:669–673. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu Y, Qi J, Wu C and Rong W: Emerging
roles of the TRPV4 channel in bladder physiology and dysfunction. J
Physiol. 599:39–47. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Girard BM, Campbell SE, Perkins M, Hsiang
H, Tooke K, Drescher C, Hennig GW, Heppner TJ, Nelson MT and
Vizzard MA: TRPV4 blockade reduces voiding frequency, ATP release,
and pelvic sensitivity in mice with chronic urothelial
overexpression of NGF. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 317:F1695–F1706.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gohar EY, De Miguel C, Obi IE, Daugherty
EM, Hyndman KA, Becker BK, Jin C, Sedaka R, Johnston JG, Liu P, et
al: Acclimation to a high-salt diet is sex dependent. J Am Heart
Assoc. 11(e020450)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hu J, Luo H, Wang J, Tang W, Lu J, Wu S,
Xiong Z, Yang G, Chen Z, Lan T, et al: Enteric dysbiosis-linked gut
barrier disruption triggers early renal injury induced by chronic
high salt feeding in mice. Exp Mol Med. 49(e370)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dörr W: Cystometry in mice-influence of
bladder filling rate and circadian variations in bladder
compliance. J Urol. 148:183–187. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kamiyama Y, Muto S, Masuda H, Ide H,
Ishizuka N, Saito K and Horie S: Inhibitory effects of nicorandil,
a K ATP channel opener and a nitric oxide donor, on overactive
bladder in animal models. BJU Int. 101:360–365. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Karakus S, Anele UA, Silva FH, Musicki B
and Burnett AL: Urinary dysfunction in transgenic sickle cell mice:
Model of idiopathic overactive bladder syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 317:F540–F546. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Chen Y, Gu D, Zhang G, Chen J,
Zhao J and Wu P: Ketamine-induced bladder fibrosis involves
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition mediated by transforming
growth factor-β1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 313:F961–F972.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Wu Q, Wang J, Chen Y, Zhang G,
Chen J, Zhao J and Wu P: Ketamine analog methoxetamine induced
inflammation and dysfunction of bladder in rats. Int J Mol Sci.
18(117)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gray KJ, Engelmann UH, Johnson EH and
Fishman IJ: Evaluation of misoprostol cytoprotection of the bladder
with cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) therapy. J Urol. 136:497–500.
1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen H, Zhang L, Hill WG and Yu W:
Evaluating the voiding spot assay in mice: A simple method with
complex environmental interactions. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
313:F1274–F1280. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang C, Huang Y, Ouyang F, Su M, Li W,
Chen J, Xiao H, Zhou X and Liu B: Extracellular vesicles derived
from mesenchymal stem cells alleviate neuroinflammation and
mechanical allodynia in interstitial cystitis rats by inhibiting
NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Neuroinflammation.
19(80)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Obaidul Islam M, Bacchetti T, Berrougui H,
Abdelouahed Khalil and Ferretti G: Effect of glycated HDL on
oxidative stress and cholesterol homeostasis in a human bladder
cancer cell line, J82. Exp Mol Pathol. 126(104777)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhao X, Zeng H, Lei L, Tong X, Yang L,
Yang Y, Li S, Zhou Y, Luo L, Huang J, et al: Tight junctions and
their regulation by non-coding RNAs. Int J Biol Sci. 17:712–727.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Khandelwal P, Abraham SN and Apodaca G:
Cell biology and physiology of the uroepithelium. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 297:F1477–F1501. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Monastyrskaya K, Sánchez-Freire V, Hashemi
Gheinani A, Klumpp DJ, Babiychuk EB, Draeger A and Burkhard FC:
miR-199a-5p regulates urothelial permeability and may play a role
in bladder pain syndrome. Am J Pathol. 182:431–448. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Beča KIK, Girard BM, Heppner TJ, Hennig
GW, Herrera GM, Nelson MT and Vizzard MA: The Role of PIEZO1 in
urinary bladder function and dysfunction in a rodent model of
cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Front Pain Res (Lausanne).
2(748385)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Perkins ME and Vizzard MA: Transient
receptor potential vanilloid type 4 (TRPV4) in urinary bladder
structure and function. Curr Top Membr. 89:95–138. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hughes FM Jr, Hirshman NA, Inouye BM, Jin
H, Stanton EW, Yun CE, Davis LG, Routh JC and Purves JT: NLRP3
promotes diabetic bladder dysfunction and changes in
symptom-specific bladder innervation. Diabetes. 68:430–440.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Odom MR, Hughes FM Jr, Jin H and Purves
JT: Diabetes causes NLRP3-dependent barrier dysfunction in mice
with detrusor overactivity but not underactivity. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 323:F616–F632. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Thangavel C, Gomes CM, Zderic SA, Javed E,
Addya S, Singh J, Das S, Birbe R, Den RB, Rattan S, et al: NF-κB
and GATA-Binding factor 6 repress transcription of caveolins in
bladder smooth muscle hypertrophy. Am J Pathol. 189:847–867.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Birder LA, Wolf-Johnston AS, Sun Y and
Chai TC: Alteration in TRPV1 and Muscarinic (M3) receptor
expression and function in idiopathic overactive bladder urothelial
cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 207:123–129. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|