Introduction
Intracranial infection poses a significant risk
following craniotomy, representing one of the most severe
complications (1). External
trauma, neurosurgical operations, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage
and the presence of external devices constitute a number of
potential risk factors for bacterial infiltration into the CSF
(2). There is a growing reported
incidence of intracranial infections caused by Acinetobacter
baumannii, with its contribution to the overall incidence rate
of bacterial meningitis ranging from 3.6-11.2% (3). Overall, the mortality rate from
Acinetobacter baumannii infection worldwide ranges from 15.0
to 71.5% (4,5). Acinetobacter baumannii is a
non-fermenting gram-negative bacterium that is one of the most
important members of the Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus
aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas
aeruginosa and Enterobacter spp. group of
microorganisms. It is a well-known hospital pathogen that poses a
serious threat to public health, especially to patients in
intensive care units (6-9).
Due to multiple factors, such as the irrational use of antibiotics,
cross-infection among inpatients and the transmission of resistance
genetic elements, an increasing number of strains of
Acinetobacter baumannii have evolved into multidrug
resistant (MDR), extensive drug resistant (XDR) and even pan-drug
resistant strains (10), which
limits the clinical treatment options of antibiotics. At present,
carbapenems are frequently utilized for treating Acinetobacter
baumannii. However, there have been numerous reports of
carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) in
recent years (11,12). Given the high mortality and
resistance rates, prompt treatment of brain infections caused by
MDR/XDR Acinetobacter baumannii is imperative. The primary
therapeutic methods for such conditions include polymyxin B and
tigecycline (13-16).
According to the International Consensus Guidelines
for the Optimal Use of the Polymyxins, colistin methanesulfonate
(CMS) is the recommended choice for intraventricular or intrathecal
injection for treating brain infections caused by
MDR/XDR-Acinetobacter baumannii (Ab) (17). However, the acquisition of CMS was
challenging and relatively costly in second- and third-tier cities
in China a few years ago. Therefore, polymyxin B is commonly used
in clinical practice for intraventricular or intrathecal injection.
However, polymyxin B can cause neurotoxicity. Following the
intraventricular administration of polymyxin B, patients may
experience symptoms resembling meningitis, such as fever, headache,
stiff neck, elevated CSF cell count and protein content (18). The aforementioned symptoms resemble
those of intracranial infections, potentially impacting the
assessment of treatment efficacy. According to the latest
advancements for the treatment of intracranial infections,
tigecycline has emerged as the preferred choice for clinical
application (19-21).
Due to the limitations of the blood-brain barrier, coupled with the
increasing resistance of bacteria to antibiotics, the ability of
different antibiotics to enter the CSF also varies, which limits
the options for treating Acinetobacter infections in the
brain. Therefore, the sole administration of intravenous
antibiotics is not likely to be an efficacious approach for
treating brain infections. There have been studies reporting that
combining intravenous (ITV) injection with intracerebral (ITC)
injection can enhance the concentration of the drug in the CSF
(13,14). Tigecycline demonstrates potent
antibacterial activity against both gram-negative and gram-positive
bacteria, which is consistent with the synergistic effects of a
number of antimicrobial drugs. However, ITV tigecycline is not
recommended for the treatment of intracranial infections due to its
limited ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (22,23).
In previous years, studies have been performed assessing the use of
tigecycline intraventricular injection for the treatment of
intracranial infections (19-21).
However, they are mostly individual case analyses. Therefore, to
validate the efficacy of this treatment and bolster the evidence
base, a retrospective analysis of the impact of ITV antibiotics
alone compared with combined ITV and ITC tigecycline injection in
15 patients with MDR/XDR-Ab intracranial infections following
neurosurgery was conducted. To the best of the authors' knowledge,
the present study represents the largest cohort investigation to
date regarding the efficacy of ITV and ITC administration of
tigecycline for treating MDR/XDR-Ab intracranial infections in
patients who underwent neurosurgery.
Patients and methods
Screening of patients
The present study was a retrospective cohort
analysis conducted at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong
First Medical University (Taian, China) spanning from January 2014
to December 2023. Consecutive adult patients (aged >18 years)
with a diagnosis of intracranial infection due to MDR/XDR-Ab after
a neurosurgery were recruited without any prior screening of the
participants. The exclusion criteria were as follows: i)
Polymicrobial results from CSF culture; ii) infections not caused
by MDR/XDR-Ab; iii) no complications occurring after neurosurgery;
or iv) there was intracranial colonization due to MDR/XDR-Ab. The
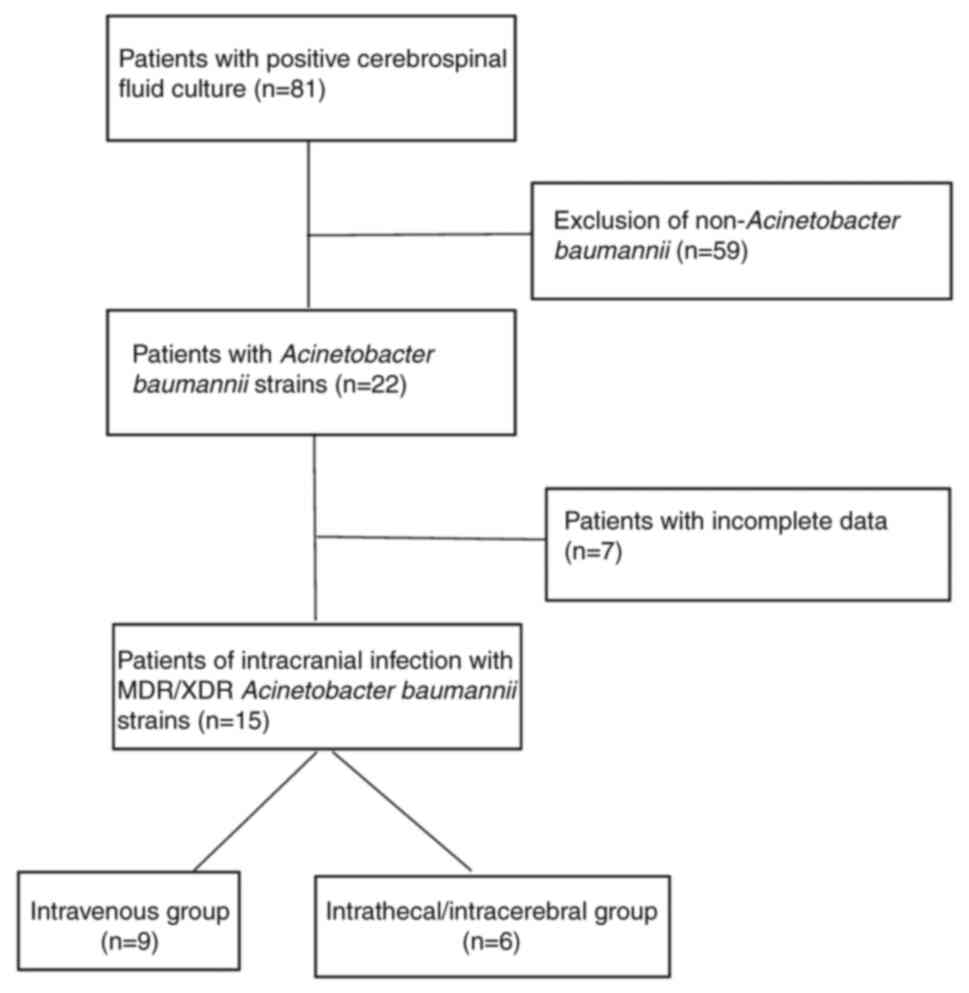
patient selection process is outlined in Fig. 1. The present study was approved
(approval no. 2023-H-007; Taian, China) by the Ethics Committee of
the Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University
and all patients or their families signed the informed consent.
Patient samples for which CSF cultures were positive
for multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (MDR-AB)
were collected after a neurosurgery at the Second Affiliated
Hospital of Shandong First Medical University (Taian, China) from
2014 to 2023. Simple cases of MDR-AB infection after neurosurgery
were rare. There were only 15 cases consistent with MDR-AB
infection after cranial surgery with complete data, of whom 9
received only ITV treatment as the ‘ITV’ group, whilst the
remaining 6 received ITV treatment combined with ITC treatment, who
were designated into the ‘ITV + ITC’ group.
The criteria for diagnosing MDR/XDR-Ab intracranial
infections following neurosurgical procedures are outlined as
follows (13,14): i) CSF culture is positive, with MDR
defined as resistance to at least three antibiotics whereas XDR was
defined as resistance to all but one or two antibiotics (15); ii) a minimum of two symptoms (a
fever >38˚C, headache, signs of meningitis or indications
related to cranial nerves) must be observed, with no alternative
explanation; and iii) CSF glucose level <2.4 mmol/l, CSF
nucleated cells >8x106/l or protein level in the CSF
>0.6 g/l. A positive CSF culture is classified as colonization
or contamination if the patient exhibits no clinical symptoms and
the levels of glucose, nucleated cells and protein in the CSF are
found to be within normal ranges (14).
Treatment protocol
In the ITV + ITC group, patients received
tigecycline (Nanjing Haichen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) through ITV
injection and ITC injection. The ITV dose was 100 mg every 12 h and
5 mg of tigecycline was administered through a lumbar puncture or
CSF drainage catheter twice daily. After ITC injection of
tigecycline, the CSF drainage tube was temporarily closed for 4 h.
Patients in the ITV group exclusively received antibiotic therapy
through the ITV route without ITC injection (24,25).
Collection of epidemiological
characteristics
The data from cases meeting the present study
criteria were collected from computer and electronic medical
records (Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical
University, Taian, China). Epidemiological features encompassing
age, sex, underlying diseases, co-morbidities, surgical procedures,
co-infections, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores and temperature were
recorded. The GCS was introduced in 1974 by Teasdale and Jennet to
evaluate consciousness levels and brain activity in patients
undergoing neurosurgery. This scale consists of the following three
primary components: i) Eye opening; ii) verbal response; and iii)
motor skills. Each component receives a score based on the
patient's reactions, culminating in a total score that can reach up
to 15 points (26,27).
Antimicrobial susceptibility
tests
The results of the antimicrobial susceptibility
tests for the isolated Acinetobacter baumannii and the
initial empiric antimicrobial therapy were recorded. The Second
Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University adopts the
BD Phoenix™ 100 bacterial identification drug sensitivity analyzer
(BD Biosciences). According to the microbroth dilution method
recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute in
2019(28), the minimum inhibitory
concentration (MIC) of Acinetobacter baumannii was
determined against nine antibacterial drugs. According to the
multiple dilution method, a series of antimicrobial solutions with
decreasing concentration gradient was obtained in each row of the
96-well plate. A volume of 100 µl/well bacterial suspension with
5x105 colony-forming unit (CFU)/ml prepared in
cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth (CaMHB; BD Biosciences) was
inoculated in 96-well plates. In addition, a positive control (only
bacterial liquid) and a negative control (only CaMHB) were added.
After the sample was added, the plate was incubated at 37˚C for
16-20 h. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of
antibiotic giving complete inhibition of visible growth. The MIC of
amikacin, tigecycline, carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem),
cephalosporins (cefazolin, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, cefepime), and
polymyxin B were measured.
Biochemical indicators and
microbiological clearance rate
The effectiveness of the treatment was evaluated
based on the aforementioned clinical and microbiological
parameters. Clinical efficiency was defined as either the
resolution or improvement of symptoms. The microbiological efficacy
was characterized by the eradication or clearance of
Acinetobacter baumannii in CSF samples following treatment,
which was confirmed by three consecutive CSF cultures (24). The overall effectiveness of the
treatment was determined by integrating clinical efficacy,
microbiological clearance rates and biochemical indicators
[polymorph nuclear neutrophils (PMNs), chlorine, glucose, and
protein levels] present in the CSF.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS
17.0 (SPSS, Inc.) software system. Categorical data are presented
as [n, (%)] and compared between the two groups utilizing the
Mann-Whitney U test. Continuous data were analyzed for differences
between groups using Student's t-test. A two-tailed P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Demographic characteristics of study
participants
In 81 cases of positive CSF culture, 22 patients
were found to be infected with Acinetobacter baumannii
(n=22; 27.16%). After excluding cases with incomplete data, a total
of 15 neurosurgical postoperative MDR/XDR-Ab intracranial infection
cases were ultimately incorporated into the present study. There
were 9 cases in the ITV group and 6 cases in the ITV + ITC group.
The baseline characteristics of patients in the two groups,
revealing no significant differences in sex, age, primary disease,
surgeries underwent, GCS scores or fever, are presented in Table I.
 | Table IBaseline characteristics of patients
enrolled in the study. |
Table I
Baseline characteristics of patients
enrolled in the study.
|
Characteristics | ITV group
(n=9) | ITV + ITC group
(n=6) | P-value |
|---|
| Sex (male), n
(%) | 8 (88.89%) | 5 (83.33%) | 0.864 |
| Age (years) | 50.22±14.31 | 44.33±11.02 | 0.4106 |
| Primary disease, n
(%) | | | 0.529 |
|
Cerebral
hemorrhage | 3 (33.33%) | 3 (50.00%) | |
|
Craniocerebral
trauma | 5 (55.56%) | 3 (50.00%) | |
|
Benign
intracranial tumor | 1 (11.11%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Comorbidities, n
(%) | | | 0.456 |
|
Diabetes | 2 (22.22%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
|
Hypertensive
disease | 2 (22.22%) | 1 (16.67%) | |
| Surgeries, n
(%) | | | 0.851 |
|
Craniotomy
evacuation of hematoma and decompressive craniectomy | 4 (44.44%) | 3 (50.00%) | |
|
Intracranial
tumor resection | 1 (11.11%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
|
Craniotomy
aneurysm clipping | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (16.67%) | |
|
Drainage of
intracranial hematoma | 2 (22.22%) | 2 (33.33%) | |
|
Ventricle
peritoneal shunt | 1 (11.11%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
|
Lumbar
cistern drainage | 9 (100.00%) | 5 (83.33%) | |
|
Ommaya
reservoir | 1 (11.11%) | 1 (16.67%) | |
| Coinfection, n
(%) | | | |
|
Lung | 5 (55.56%) | 3 (50.00%) | 0.864 |
| GCS score | 6.86±3.39 | 7.20±3.11 | 0.862 |
| Fever (˚C) | 38.30±0.88 | 38.82±0.49 | 0.217 |
Susceptibility testing and
antimicrobial therapies
A comprehensive overview of the antibiotic
resistance profiles observed in the 15 patients is presented in
Table II. Among the antibiotics
assessed, MDR/XDR-Ab exhibited complete resistance to carbapenems
and cephalosporins (with a resistance rate of 100%), whilst
demonstrating resistance rates of 0.00 and 6.67% to polymyxins and
tigecycline, respectively. The antibiotic resistance detection
results exhibited no statistically significant differences between
the two groups.
 | Table IISusceptibility testing results for
isolated Acinetobacter baumannii. |
Table II
Susceptibility testing results for
isolated Acinetobacter baumannii.
| Antibiotics | MIC breakpoint
(mg/l) | Total (n=15) | ITV group
(n=9) | ITV + ITC group
(n=6) | P-value |
|---|
| Antibiotic
resistance, n (%) | | | | | 0.888 |
| Amikacin | R≥32 | 13 (86.6%) | 7 (77.78%) | 6 (100%) | |
| Tigecycline | R≥8 | 1 (6.67%) | 1 (11.11%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Carbapenems | | | | | |
|
Imipenem | R≥8 | 15 (100%) | 9 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
|
Meropenem | R≥8 | 15 (100%) | 9 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
| Cephalosporins | | | | | |
|
Cefazolin | R≥16 | 15 (100%) | 9 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
|
Ceftazidime | R≥16 | 15 (100%) | 9 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
|
Cefotaxime | R≥32 | 15 (100%) | 9 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
|
Cefepime | R≥16 | 15 (100%) | 9 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
| Polymyxin B | R≤0.5 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
In Table III, it
was revealed that the most frequently utilized antibiotic
combination in the ITV group was tigecycline + meropenem (33.33%).
By contrast, in the ITV + ITC group, the most commonly used
combination was tigecycline + cefoperazone-sulbactam (50.00%).
There was no statistically significant difference in the empirical
antimicrobial therapy applied between the two groups (Table III).
 | Table IIIInitially applied empirical
antimicrobial therapies. |
Table III
Initially applied empirical
antimicrobial therapies.
| Antibiotics, n
(%) | ITV group
(n=9) | ITV + ITC group
(n=6) | P-value |
|---|
| Tigecycline +
cefperazone-sulbactam | 1 (11.11%) | 3 (50.00%) | 0.113 |
| Tigecycline +
meropenem | 3 (33.33%) | 1 (16.67%) | |
| Tigecycline +
cefperazone-sulbactam + meropenem | 1 (11.11%) | 2 (33.33%) | |
| Meropenem +
cefperazone-sulbactam | 2 (22.22%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Ceftriaxone +
cefperazone-sulbactam | 1 (11.11%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Meropenem +
vancomycin | 1 (11.11%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
Microbiological clearance, biochemical
indicators in CSF, white blood cell (WBC) and body temperature
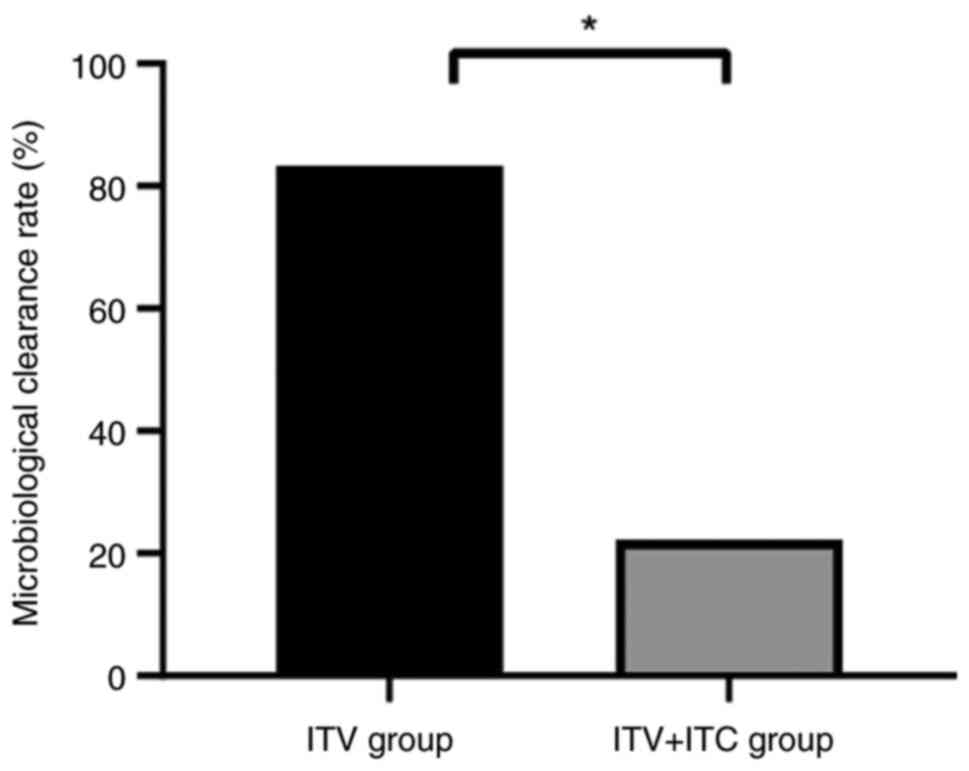
As demonstrated in Fig.
2, the ITV + ITC group demonstrated a significantly higher
microbiological clearance rate (5/6; 83.33%) compared with that in
the ITV group (2/9; 22.22%).
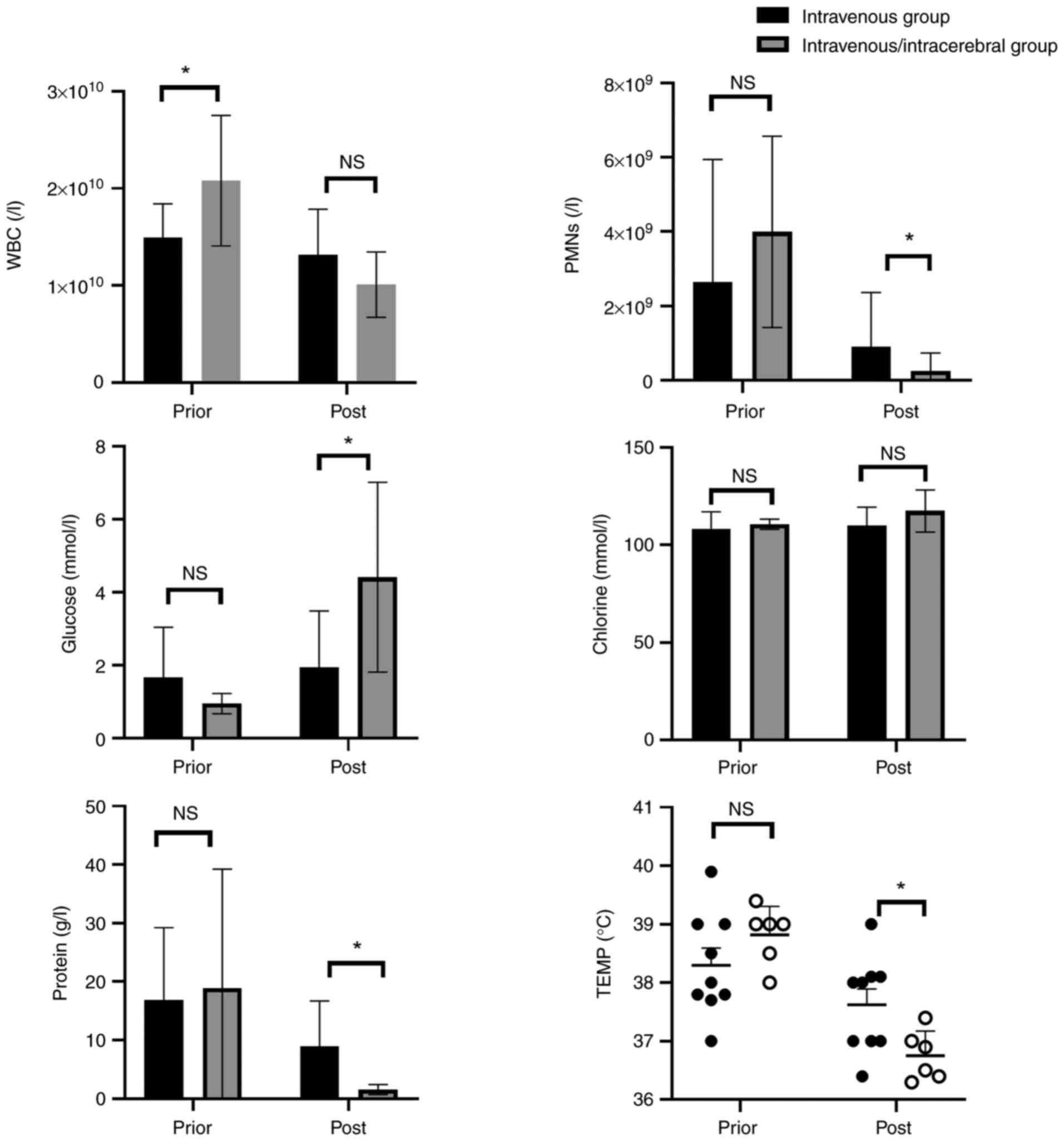
Prior to treatment, the WBC count was markedly
elevated in the ITV + ITC group compared with that in the ITV
group. Nevertheless, no significant differences were observed in
the PMNs, chlorine, glucose, protein levels in CSF or body
temperature between the two groups (Fig. 3).
After treatment, the ITV + ITC group exhibited a
significantly lower body temperature compared with that in the ITV
group (37.62±0.81˚C vs. 36.75±0.42˚C), a significantly reduced
number of PMNs in the CSF (1,268.8±1,538.3 vs.
79.8±135.6x106/l), a significantly superior recovery of
the glucose levels in the CSF (1.943±1.543 mmol/l vs. 4.413±2.60
mmol/l) and significantly reduced levels of total protein in the
CSF (7.76±8.54 g/l vs. 1.545±0.854 g/l). However, no statistically
significant differences were observed in WBC level or in the
chlorine level in the CSF between the two groups.
Discussion
Acinetobacter baumannii is a significant
pathogen that can cause serious hospital-acquired infections and is
considered to be one of the most perilous gram-negative bacteria
species (29,30). Acinetobacter baumannii is
capable of causing healthcare-associated infections, including
ventilator-associated pneumonia, sepsis, urinary tract infections,
meningitis and surgical site infections (29,30),
which may result in elevated mortality rates among affected
patients. The risk factors associated with these infections can
encompass mechanical ventilation, the administration of
broad-spectrum antibiotics, ICU length of stay and coma (31). According to statistics, ~1 million
individuals worldwide contract infections caused by
Acinetobacter baumannii each year, with 50% of such cases
attributed to MDR (32). The
mortality rate for ICU-acquired Acinetobacter baumannii
infections ranges from 45 to 60%, but can even reach 84.3% in the
case of XDR strains (33,34). According to the World Health
Organization's list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria released in
2017, CRAB were identified as the bacteria posing the greatest
threat to human health and being most in need of related antibiotic
development (35). In addition,
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important pathogen that can
cause central nervous system (CNS) infections, resulting in a
mortality rate ranging from 15 to 71% for Acinetobacter
meningitis (36). The occurrence
of CNS infections caused by MDR Acinetobacter baumannii
presents a significant challenge to neurosurgical patients.
Acinetobacter baumannii is a Gram-negative
opportunistic pathogen that has emerged as one of the most alarming
hospital-acquired infection pathogens over the last decade
(29,37). The majority of strains also
demonstrate MDR, where the majority of the globally prevalent major
clades are only susceptible to polymyxin and tigecycline (38,39).
Tigecycline and polymyxins are typically reserved as the last
resort options for treating infections caused by
carbapenem-resistant bacteria (38,39).
Furthermore, polymyxins are difficult to purchase and are typically
too expensive for certain patients. For these reasons, tigecycline
is often preferred as a treatment option for CNS infections.
Tigecycline belongs to a relatively novel category
of antibiotics known as ‘glycylcyclines’ (40), which demonstrate efficacy against
strains resistant to Acinetobacter baumannii (41). Pallotto et al (42) previously found difficulty in
delivering tigecycline into the CSF of a patient with a
ventriculoperitoneal shunt infection, where the concentration of
tigecycline in the CSF was found to be ~7.9% that found in the
serum. Despite the reported observations in which in vitro
sensitivity tests have indicated that tigecycline is effective
against CNS infections, the expected therapeutic outcomes in actual
clinical practice have remained elusive likely for this reason.
Previously, in a study by Abdallah et al (25), the addition of IVT tigecycline
successfully eradicated the MDR Acinetobacter baumannii from
the CSF, where the signs of infection disappeared. Additionally,
direct intrathecal/IVT injection of tigecycline could enhance its
concentration within the CNS. In addition, Long et al
(43) reported that 8 patients
with MDR Acinetobacter baumannii meningitis/ventriculitis
who were treated with ITC and/or ITV tigecycline demonstrated
favorable clinical efficacy without any associated complications.
Although numerous studies have reported that intracranial injection
of tigecycline significantly improved symptoms of meningitis caused
by MDR/XDR-Ab (18,25,43),
these studies are mostly case reports, where no statistical
analysis was conducted between the groups of ITV and ITC injection
of tigecycline. In the present study, medical records were
collected, which were classified, grouped and statistically
compared. Specifically, the intracranial injection group and the
non-intracranial injection group were compared, which confirmed
that the combination of ITV and intrathecal/intracranial injection
of tigecycline is superior to conventional ITV antibiotic therapy
for treating cerebral infections caused by MDR/XDR-Ab.
It must be noted that the intracranial
administration of tigecycline is still considered to be an
off-label method, where there is currently no universally accepted
standard for its dosage and frequency of administration (18). Due to the limited availability of
large-scale studies, there may be inherent biases in assessing its
efficacy and safety. In the present study, the intracranial dose of
tigecycline used was 5 mg twice daily. Compared with the ITV group,
the ITV + ITC group exhibited a significant improvement in the
clinical efficacy, where no adverse reactions were observed. The
results were consistent with recommended dose from Huang et
al (18).
The present study has several limitations. It is not
a formal treatment trial, but rather a retrospective analysis of
previous treatment regimens for MDR/XDR-Ab-induced intracranial
infections. There was a lack of pharmacokinetic data analysis and a
lack of monitoring of tigecycline concentration in the blood and
CSF. The optimal intrathecal dose of tigecycline still requires
verification and discussion in more trials. Additional multicenter
randomized controlled trials are required to confirm the efficacy
and safety of this strategy. In the future, data will be shared
with other medical institutions to jointly study the treatment of
intracranial MDR-AB infection. Nevertheless, the present results
suggest that ITC and ITV administration of tigecycline is superior
to ITV administration alone for the treatment of intracranial
infections caused by MDR/XDR-Ab. In addition, to the best of the
authors' knowledge, the present study is the largest cohort study
to date on the efficacy of ITV and ITC administration of
tigecycline for the treatment of MDR/XDR-Ab intracranial infections
in patients who underwent neurosurgery.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
RA, XT and XM designed the study. LG, GG and YL
collected the data. XM and TZ analyzed and interpreted the patient
general data. RA, XT and XM performed statistical analyses, wrote
the manuscript and reviewed the literature. All authors read and
approved the final version of the manuscript. XT and RA confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved (approval no.
2023-H-007; Taian, China) by the Ethics Committee of the Second
Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University and all
patients or their families signed the informed consent.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Fang C, Zhu T, Zhang P, Xia L and Sun C:
Risk factors of neurosurgical site infection after craniotomy: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Infect Control.
45:e123–e134. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Korinek AM, Baugnon T, Golmard JL, van
Effenterre R, Coriat P and Puybasset L: Risk factors for adult
nosocomial meningitis after craniotomy: Role of antibiotic
prophylaxis. Neurosurgery. 62 (Suppl 2):S532–S539. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Karaiskos I, Galani L, Baziaka F and
Giamarellou H: Intraventricular and intrathecal colistin as the
last therapeutic resort for the treatment of multidrug-resistant
and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
ventriculitis and meningitis: A literature review. Int J Antimicrob
Agents. 41:499–508. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huttova M, Freybergh PF, Rudinsky B,
Sramka M, Kisac P, Bauer F and Ondrusova A: Postsurgical meningitis
caused by Acinetobacter baumannii associated with high mortality.
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 28 (Suppl 2):S15–S16. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Metan G, Alp E, Aygen B and Sumerkan B:
Acinetobacter baumannii meningitis in post-neurosurgical patients:
Clinical outcome and impact of carbapenem resistance. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 60:197–199. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ranjbar R and Alam M: Antimicrobial
Resistance Collaborators (2022). Global burden of bacterial
antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Evid Based
Nurs: Jul 27, 2023 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
7
|
Ayoub Moubareck C and Hammoudi Halat D:
Insights into Acinetobacter baumannii: A review of microbiological,
virulence, and resistance traits in a threatening nosocomial
pathogen. Antibiotics (Basel). 9(119)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ibrahim S, Al-Saryi N, Al-Kadmy IMS and
Aziz SN: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii as an emerging
concern in hospitals. Mol Biol Rep. 48:6987–6998. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tokur ME, Korkmaz P, Alkan S, Yıldız E,
Arık Ö, Renders DP and Balcı C: Mortality predictors on the day of
healthcare-associated Acinetobacter baumanni bacteremia in
intensive care unit. J Infect Dev Ctries. 16:1473–1481.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ibrahim ME: Prevalence of Acinetobacter
baumannii in Saudi Arabia: Risk factors, antimicrobial resistance
patterns and mechanisms of carbapenem resistance. Ann Clin
Microbiol Antimicrob. 18(1)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhu Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Tao Y, Shao X, Li
Y and Li W: Insight into carbapenem resistance and virulence of
Acinetobacter baumannii from a children's medical centre in eastern
China. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 21(47)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mohajeri P, Sharbati S, Farahani A and
Rezaei Z: Evaluate the frequency distribution of nonadhesive
virulence factors in carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter
baumannii isolated from clinical samples in Kermanshah. J Nat Sci
Biol Med. 7:58–61. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nau R, Seele J, Djukic M and Eiffert H:
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antibiotics in central
nervous system infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 31:57–68.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nau R, Sörgel F and Eiffert H: Penetration
of drugs through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid/blood-brain barrier
for treatment of central nervous system infections. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 23:858–883. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
De Bonis P, Lofrese G, Scoppettuolo G,
Spanu T, Cultrera R, Labonia M, Cavallo MA, Mangiola A, Anile C and
Pompucci A: Intraventricular versus intravenous colistin for the
treatment of extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
meningitis. Eur J Neurol. 23:68–75. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mohajeri P, Farahani A, Feizabadi MM and
Norozi B: Clonal evolution multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter
baumannii by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Indian J Med
Microbiol. 33:87–91. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tsuji BT, Pogue JM, Zavascki AP, Paul M,
Daikos GL, Forrest A, Giacobbe DR, Viscoli C, Giamarellou H,
Karaiskos I, et al: International Consensus Guidelines for the
Optimal Use of the Polymyxins: Endorsed by the American College of
Clinical Pharmacy (ACCP), European Society of Clinical Microbiology
and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), Infectious Diseases Society of
America (IDSA), International Society for Anti-infective
Pharmacology (ISAP), Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), and
Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP). Pharmacotherapy.
39:10–39. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang Q, Zhang X, Jia A, Huang Q, Jiang Y
and Xie L: The pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics and neurotoxicity
of tigecycline intraventricular injection for the treatment of
extensively drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii intracranial
infection. Infect Drug Resist. 15:4809–4817. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fang YQ, Zhan RC, Jia W, Zhang BQ and Wang
JJ: A case report of intraventricular tigecycline therapy for
intracranial infection with extremely drug resistant Acinetobacter
baumannii. Medicine (Baltimore). 96(e7703)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li LM, Zheng WJ and Shi SW: Spinal
arachnoiditis followed by intrathecal tigecycline therapy for
central nervous system infection by extremely drug-resistant
Acinetobacter baumannii. J Int Med Res.
48(300060520920405)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Deng ZW, Wang J, Qiu CF, Yang Y, Shi ZH
and Zhou JL: A case report of intraventricular and intrathecal
tigecycline infusions for an extensively drug-resistant
intracranial Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Medicine
(Baltimore). 98(e15139)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rodvold KA, Gotfried MH, Cwik M,
Korth-Bradley JM, Dukart G and Ellis-Grosse EJ: Serum, tissue and
body fluid concentrations of tigecycline after a single 100 mg
dose. J Antimicrob Chemother. 58:1221–1229. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ray L, Levasseur K, Nicolau DP and Scheetz
MH: Cerebral spinal fluid penetration of tigecycline in a patient
with Acinetobacter baumannii cerebritis. Ann Pharmacother.
44:582–586. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pan S, Huang X, Wang Y, Li L, Zhao C, Yao
Z, Cui W and Zhang G: Efficacy of intravenous plus
intrathecal/intracerebral ventricle injection of polymyxin B for
post-neurosurgical intracranial infections due to MDR/XDR
Acinectobacter baumannii: A retrospective cohort study. Antimicrob
Resist Infect Control. 7(8)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Abdallah M, Alsaleh H, Baradwan A,
Alfawares R, Alobaid A, Rasheed A and Soliman I: Intraventricular
tigecycline as a last resort therapy in a patient with
difficult-to-treat healthcare-associated acinetobacter baumannii
ventriculitis: A case report. SN Compr Clin Med. 2:1683–1687.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Teasdale G, Maas A, Lecky F, Manley G,
Stocchetti N and Murray G: The Glasgow Coma Scale at 40 years:
Standing the test of time. Lancet Neurol. 13:844–854.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Capuano B and Cone DC: An Analysis of the
Distribution of Glasgow Coma Scale Scores across Pan-Asian Trauma
Outcomes Study (PATOS) Regions. Prehosp Disaster Med: Feb 14, 2022
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
28
|
Institute CALS. Performance standards for
antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Clin Microbiol Newsletter.
23:M100–M111. 2019.
|
|
29
|
Peleg AY, Seifert H and Paterson DL:
Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 21:538–582. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fishbain J and Peleg AY: Treatment of
Acinetobacter infections. Clin Infect Dis. 51:79–84.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ma MY, Xu J, Yu N and Huang GM: Analysis
of drug resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii and its related
factors in ICU. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 25:686–689.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Spellberg B and Rex JH: The value of
single-pathogen antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
12(963)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Inchai J, Pothirat C, Bumroongkit C,
Limsukon A, Khositsakulchai W and Liwsrisakun C: Prognostic factors
associated with mortality of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
ventilator-associated pneumonia. J Intensive Care.
3(9)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Uwingabiye J, Frikh M, Lemnouer A,
Bssaibis F, Belefquih B, Maleb A, Dahraoui S, Belyamani L, Bait A,
Haimeur C, et al: Acinetobacter infections prevalence and frequency
of the antibiotics resistance: Comparative study of intensive care
units versus other hospital units. Pan Afr Med J.
23(191)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Willyard C: The drug-resistant bacteria
that pose the greatest health threats. Nature.
543(15)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kim BN, Peleg AY, Lodise TP, Lipman J, Li
J, Nation R and Paterson DL: Management of meningitis due to
antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter species. Lancet Infect Dis.
9:245–255. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gordon NC and Wareham DW:
Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms of
virulence and resistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 35:219–226.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Vila J and Pachón J: Acinetobacter
baumannii resistant to everything: what should we do? Clin
Microbiol Infect. 17:955–956. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Durante-Mangoni E and Zarrilli R: Global
spread of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Molecular
epidemiology and management of antimicrobial resistance. Future
Microbiol. 6:407–422. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pankey GA: Tigecycline. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 56:470–480. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Karageorgopoulos DE and Falagas ME:
Current control and treatment of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter
baumannii infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 8:751–762. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pallotto C, Fiorio M, D'Avolio A, Sgrelli
A, Baldelli F, Di Perri G and De Socio GV: Cerebrospinal fluid
penetration of tigecycline. Scand J Infect Dis. 46:69–72.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Long W, Yuan J, Liu J, Liu J, Wu M, Chen
X, Peng G, Wu C, Zhang C, Wang X, et al: Multidrug resistant brain
abscess due to acinetobacter baumannii ventriculitis cleared by
intraventricular and intravenous tigecycline therapy: A case report
and review of literature. Front Neurol. 9(518)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|