Introduction
Notch is a signaling pathway which regulates
cell-to-cell signal transduction. Notch was thus named as its
inactivation caused notches in the wing blade of Drosophila
melanogaster (1,2). In mammals, the canonical Notch
signaling is mainly composed of five Notch ligands [Jagged1 and 2,
and Delta-like (DLL)1, 3 and 4] and four Notch receptors (Notch1-4)
(3,4). Notch signaling is initiated when
Notch ligands bind with the receptors, then the Notch intracellular
domain (NICD) is cleaved and released, followed by translocation
from the cellular membrane to the nucleus (5). In the nucleus, the NICD binds with
the transcriptional regulator of the CSL family to regulate
downstream targets (6). The CSL
family includes C promoter binding factor-1 (CBF-1) in mammals,
also known as recombination signal-binding protein for
immunoglobulin Jκ region (RBP-Jκ) in mice, Suppressor of Hairless
[Su(H)] in Drosophila and longevity assurance gene 1 (Lag1)
in Caenorhabditis (7).
Notch signaling is important for cell fate, proliferation,
apoptosis and cell migration (8–12).
Recent research has demonstrated that Notch signaling also plays an
important role in skeletal remodeling (13–15).
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are members of
the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily, and more than
20 BMP members have been identified (16,17). Mammalian BMP receptors include
seven type I receptors, which are activin-like kinase (ALK)1-7 and
five type II receptors, which include ActRIIA, ActRIIB, BMPRII,
TβRII, and AMHRII. BMP signaling is activated when BMPs bind with
type II receptors, and then type I receptor is rescuited and
phosphorylated, which activates the receptor Smad (R-Smad) protein.
In the cytoplasm, R-Smad binds to co-Smad (Smad4) and translocates
into the nucleus to regulate the expression of target genes
(18–20). BMPs have a broad spectrum of
biological functions, such as the regulation of cell proliferation
and differentiation during development (21–23). In addition, some BMPs have been
used in bone tissue engineering for various bone-associated
diseases (24–26). Yet, the mechanism underlying these
processes remains unclear. A thorough analysis of the osteogenic
activity of 14 human BMPs has been made and found that BMP9 is the
most efficient BMP in inducing the osteogenic differentiation of
MSCs both in vitro and in vivo (27–29). BMP9, also called growth
differentiation factor-2 (GDF-2), was discovered and isolated from
a liver cDNA library of embryonic mice. Its precursor protein
shares 50–55% amino acid sequence identity with BMP2, 4, 5, 6 and
7. The homology of BMP9 between the human and the mouse is ~80%
(30–33).
As mentioned above, Notch and BMP signaling have a
similar mode of function, and are both involved in regulating cell
fate and proliferation during development. Recently, research has
confirmed that Notch signaling interacts with the TGF-β pathway to
regulate cell growth and myogenic differentiation (34–38). Yet, it remains unclear whether
Notch crosstalks with BMP9 in bone formation.
In the present study, we investigated the possible
role of Notch signaling in BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation
in MSCs. Our results showed that the Notch pathway significantly
promoted BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation and proliferation
of MSCs, which may be mediated by the upregulation of ALK2
Materials and methods
Cell culture
C3H10T1/2 and C2C12 cells were purchased from the
American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) and
cultured in complete Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM)
(HyClone, Logan, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum
(FBS) (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA), 100 U/ml of penicillin and
100 μg/ml of streptomycin. Cells were incubated at 37°C in
5% CO2. Mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) were isolated
from post coitus day 12.5 mice (5 female and 5 male mice, purchased
from Beijing Institute of Chinese Medicine), as described
previously (39).
Reagents and antibodies
p-Smad1/5/8 (cat. no. 9516) was purchased from Cell
Signaling Technology, Inc. (Danvers, MA, USA) and Smad1/5/8 (cat.
no. sc-6031-R) was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.
(Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
(GAPDH; cat. no. TA-08) and β-actin (cat. no. TA-09) were purchased
from Zhongshan Golden Bridge Biotechnology (Beijing, China).
γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St.
Louis, MO, USA), dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and stored
at −80°C. The recombinant adenoviruses including Ad-BMP9, Ad-DLL1,
Ad-dnNotch1, Ad-dnALK1, Ad-dnALK2, Ad-GFP and Ad-RFP were kindly
provided by Dr Tong-Chuan He (University of Chicago Medical Center,
Chicago, IL, USA).
RNA extraction, reverse transcription
(RT), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and quantitative PCR
(qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from the cells with TRIzol
reagents (Takara, Otsu, Japan), and was reverse transcribed to cDNA
using the Takara PrimeScript RT reagent kit. Semi-quantitative
RT-PCR was performed as described previously (40,41). The cDNA products were further
diluted 5- to 10-fold and used in the successive experiments. A
touchdown cycling program was used as follows: 94°C for 5 min, 94°C
for 30 sec, 68°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 12 cycles with a decrease
in 1°C/cycle; then, 94°C for 30 sec, 55°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for
30 sec for 18–27 cycles depending on the abundance of the target
genes. The PCR products were resolved on 2% agarose gels. All
samples were normalized with the expression level of mouse
GAPDH.
qPCR analysis was performed using a SYBR Premix Ex
Taq kit (Takara). The cycling program consisted of 94°C for 2 min
and 30 cycles at 92°C for 20 sec, 57°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 20
sec, followed by a plate read at 78°C for each cycle. All samples
were evaluated in triplicate and normalized to GAPDH. The primer
pairs of target genes are presented in Table I.
 | Table IPrimer sequences. |
Table I
Primer sequences.
| Gene | Forward primer
(5′→3′) | Reverse primer
(5′→3′)′ |
|---|
| DLL1 |
CCGGCTGAAGCTACAGAAAC |
AGCCCCAATGATGCTAACAG |
| dnNotch1 |
GCAGAACAACAAGGAGGAGACT |
GAGGTCCTTAGCTTCCTTGCTAC |
| Hey1 |
GGCCTGCTTGGCTTTTCT |
CCAAGTGCAGGCAAGGTC |
| Runx2 |
GGTGAAACTCTTGCCTCGTC |
AGTCCCAACTTCCTGTGCT |
| Col1a1 |
CGGCTCCTGCTCCTCTTA |
TTCATTGCATTGCACGTCAT |
| OCN |
TCTGACAAAGCCTTCATGTCC |
AAATAGTGATACCGTAGATGC |
| OPN |
ACACTTTCACTCCAATCGTCC |
TGCCCTTTCCGTTGTTGTCC |
| Id1 |
ACGACATGAACGGCTGCT |
CAGCTGCAGGTCCCTGAT |
| Id2 |
CAGCATCCCCCAGAACAA |
TCTGGTGATGCAGGCTGA |
| Id3 |
CTACGAGGCGGTGTGCTG |
GCGCGAGTAGCAGTGGTT |
| ALK1 |
ACCTGGGACTGGCTGTGA |
GCAGTCTGTGCGGATGTG |
| ALK2 |
GTGGCTCCGGTCTTCCTT |
AGCGACATTTTCGCCTTG |
| GAPDH |
GGCTGCCCAGAACATCAT |
ATGATGTTCTGGGCAGCC |
Preparation of conditioned medium
BMP9-conditioned medium (BMP9-CM) was prepared as
described previously (42).
Briefly, subconfluent HCT116 cells (in a 75 cm2 flask)
were infected with an optimal titer of Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP control.
At 4 h after treatment, the medium was replaced with serum-free
DMEM. The conditioned medium was collected at 48 h after infection
and used as soon as possible.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) assays
ALP activity was analyzed by a modified Great EscAPe
SEAP chemiluminescence kit (Takara). Each assay condition was
performed in triplicate, and the results were repeated in three
independent experiments. ALP activity was normalized by the total
cellular protein concentrations among the samples.
Matrix mineralization assay (Alizarin Red
S staining)
Cultured cells were seeded in 24-well cell culture
plates and infected with Ad-DLL1 followed by treatment with
BMP9-CM, ascorbic acid (50 mg/ml) and β-glycerophosphate (10 mM).
On day 11, the mineralized matrix nodules were stained for calcium
precipitation by means of Alizarin Red S staining, as described
previously (41). Briefly, the
cells were fixed with 0.05% (v/v) glutaraldehyde at room
temperature for 10 min. After being washed with double-distilled
water, the fixed cells were incubated with 0.4% Alizarin Red S
(Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 min, followed by extensive washing with
double-distilled water. The staining of calcium mineral deposits
was recorded under a microscope.
Western blot analysis
The cells were seeded in 75-cm2 cell
culture dishes and subjected to the indicated treatments. At the
indicated time-points, the cells were harvested and washed with
cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and extracted in protein
buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1% P40, and 1 mM EDTA) in
the presence of protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Proteins were
fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Following electrophoretic separation,
the proteins were transferred onto a PVDF membrane. The membrane
was blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 2 h at 37°C and
probed with the primary antibody (diluted 1:1,000) overnight at
4°C, then washed three times with Tris-buffered saline contained
0.1% Tween-20 (TBST). The membrane was then incubated with
horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit (cat. no.
ZB-2301) or goat anti-mouse (cat. no. ZB-2305) secondary antibodies
(diluted 1:5,000; Zhongshan Golden Bridge Biotechnology). Finally,
the membrane was exposed with ECL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.,
Rockford, IL, USA).
Transfection and luciferase reporter
assay
The cells were transfected with 2 μg per
flask of BMP R-Smad-binding element luciferase reporter
(p12xSBE-Luc) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen Corp., Carlsbad,
CA, USA). At 24 h after transfection, the cells were replated in
24-well plates and treated with BMP9-CM and/or Ad-DLL1,
Ad-dnNotch1, DAPT. At 36 h after treatment, the cells were lysed
and harvested for luciferase assays using the Luciferase Assay kit
(Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA). Each assay condition was
performed in triplicate. The results were repeated in at least
three independent experiments. Luciferase activity was normalized
with the total cellular protein concentrations among the
samples.
Stem cell implantation and ectopic
ossification
MEFs were co-infected with Ad-BMP9 and/or Ad-DLL1,
Ad-dnNotch1 for 24 h, and harvested for subcutaneous injection
(5×106 cells per injection) into the flanks of athymic
nude (nu/nu) mice (4- to 6-week-old male Sprague-Dawley). At 4
week(s) after treatment, the animals were euthanized, and the bony
masses were collected for micro-CT imaging and histologic
evaluation. All animal experiments were approved by the Ethics
Committee of Chongqing Medical University.
Micro-CT imaging analysis, hematoxylin
and eosin (H&E) and Masson's trichrome staining
Animals were euthanized at 4 week(s) and bony masses
were imaged using high-performance micro-CT imager component of a
GE Triumph (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA) trimodality
preclinical imaging system. All image data analysis was performed
using Amira 5.3 (Visage Imaging, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Retrieved tissues were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered
formalin overnight and processed for paraffin embedding. Serial
sections of the embedded tissues were stained with H&E and
Masson's trichrome staining as previously described (43).
Flow cytometric (FCM) assay
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates and harvested
after a 72-h treatment, washed with PBS three times and fixed with
75% iced-ethanol at 4°C. The fixed cells were washed with PBS and
stained with propidium iodide-containing RNase followed by
fluorescence-activated cell sorting for cell cycle analysis.
Statistical analysis
Data are reported as the means ± SD. Statistical
analysis was conducted using SPSS software version 14 (SPSS, Inc.,
Chicago, IL, USA). P<0.05 was considered as statistically
significant.
Results
Effects of Notch signaling on
BMP9-induced early osteogenic differentiation in MSCs
We sought to explore whether or not Notch signaling
has any effect on a BMP9-induced early osteogenic marker. We first
adopted DAPT, an inhibitor of the γ-secretase complex, to inhibit
the Notch activity of MSCs. We also confirmed that Ad-DLL1
upregulated the level of DLL1 in MEFs, and the dominant-negative
mutant of Notch1 (dnNotch1) which contains extracellular and
transmembrane domains but lacks cytoplasmic domains was highly
expressed in the Ad-dnNotch1-infected cells (data not shown). We
used Ad-dnNotch1 and Ad-DLL1 to downregulate and upregulate Notch
signaling, respectively (data not shown). Moreover, by using ALP
staining and activity assay, we found that BMP9-induced ALP
activity was significantly inhibited by DAPT and Ad-dnNotch1 in a
concentration-dependent manner (Fig.
1A, B and D). Conversely, Ad-DLL1 enhanced BMP9-induced ALP
activity (Fig. 1C). These data
suggested that Notch signaling enhances the BMP9-induced early
osteogenic differentiation of MSCs.
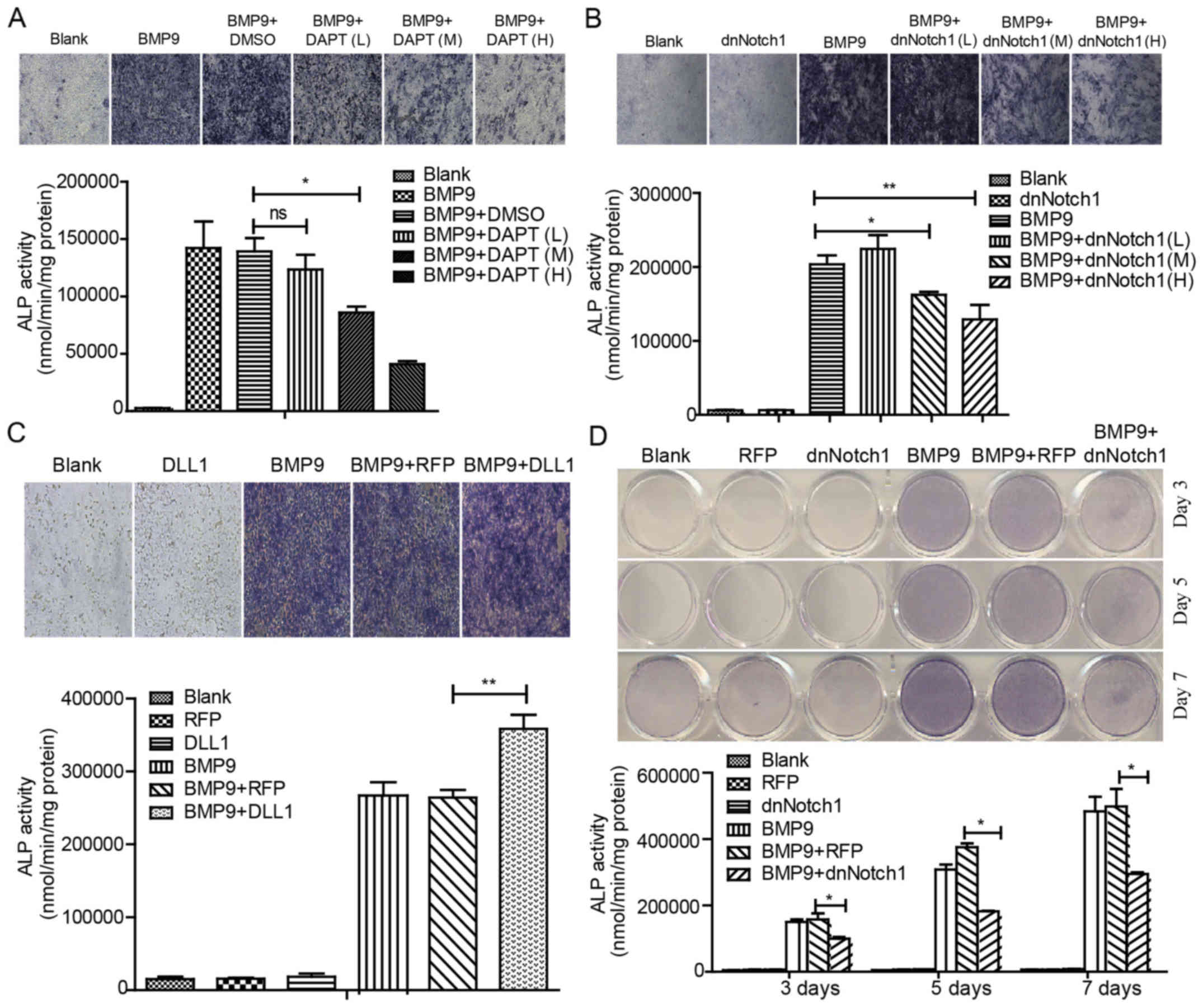 | Figure 1Notch signaling enhances BMP9-induced
early osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. (A) MEFs were treated
with Ad-BMP9 in the presence of various concentrations of DAPT (L=5
μM, M=10 μM and H=15 μM), and the BMP9-induced
ALP activity was assessed by quantitative assay and staining assay
at 7 day(s) post-treatment. (B) MEFs were infected with various
titers of Ad-dnNotch1, followed by treatment with BMP9-CM, ALP
activity was measured by quantitative assay and staining assay at 5
day(s) post-treatment. (C) MEFs were exposed to Ad-RFP or Ad-DLL1
in the presence of BMP9-CM, and the BMP9-induced ALP activity was
assessed by quantitative assay and staining assay at 7 day(s)
post-treatment. (D) MEFs were treated with BMP9-CM and/or
Ad-dnNotch1, and the ALP activity was measured by quantitative
assay and staining assay at 3, 5, 7 day(s) post-treatment.
Magnification, ×100. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. ns, no
statistical significance; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; MEFs,
mouse embryo fibroblasts; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; dnNotch1,
dominant-negative mutant of Notch1; BMP9-CM, BMP9-conditioned
media; DLL, Delta-like. |
Effects of Notch signaling on
BMP9-induced late osteogenic differentiation in MSCs
Although ALP is a well-established early osteogenic
marker, it may not be an accurate predictor of the late stage of
osteogenic differentiation and bone formation (41). Thus, we aimed to determine whether
Notch signaling has an effect on the expression of BMP9-induced
late osteogenic markers, such as osteopontin (OPN) and osteocalcin
(OCN). By RT-PCR or Alizarin Red S staining, we found that the
combination of Ad-BMP9 and DAPT treatment significantly decreased
the expression of OCN in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 2A); The expression of OCN and OPN
decreased when treated with Ad-dnNotch1 (Fig. 2B). Conversely, Ad-DLL1 treatment
was found to enhance the matrix mineralization induced by BMP9
(Fig. 2C). These data suggested
that Notch signaling facilitates BMP9-induced late osteogenic
differentiation in MSCs.
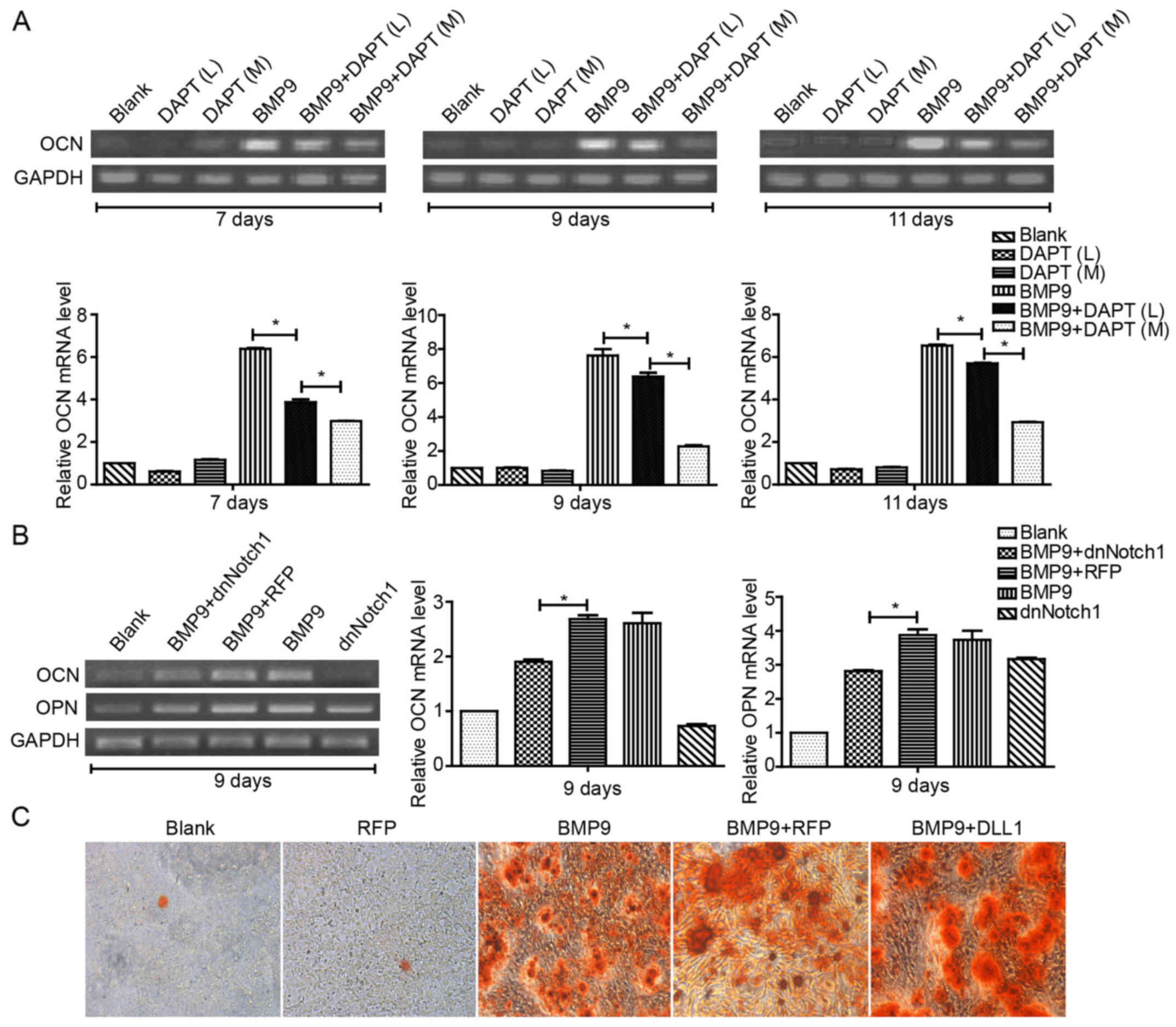 | Figure 2Notch signaling increases
BMP9-induced late osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. (A) C2C12
cells were treated with different concentrations of DAPT (M=10
μM, and H=15 μM, respectively) in the presence of
BMP9-CM, and the gene expression of OCN was determined by
semi-quantitative RT-PCR at 7, 9 and 11 day(s) post-treatment and
quantification by densitometry. (B) MEFs were exposed to
Ad-dnNotch1 in the presence of BMP9-CM, and the gene expression
levels of OPN and OCN were determined by semi-quantitative RT-PCR
at 9 day(s) post-treatment and quantification by densitometry. (C)
MEFs were infected with Ad-DLL1 in the presence of BMP9-CM, and
matrix mineralization was assessed at 11 day(s) post-treatment by
Alizarin Red S staining assay. Magnification, ×100.
*P<0.05. BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; BMP9-CM,
BMP9-conditioned media; OCN, osteocalcin; MEFs, mouse embryo
fibroblasts; dnNotch1, dominant-negative mutant of Notch1; OPN,
osteopontin; DLL, Delta-like. |
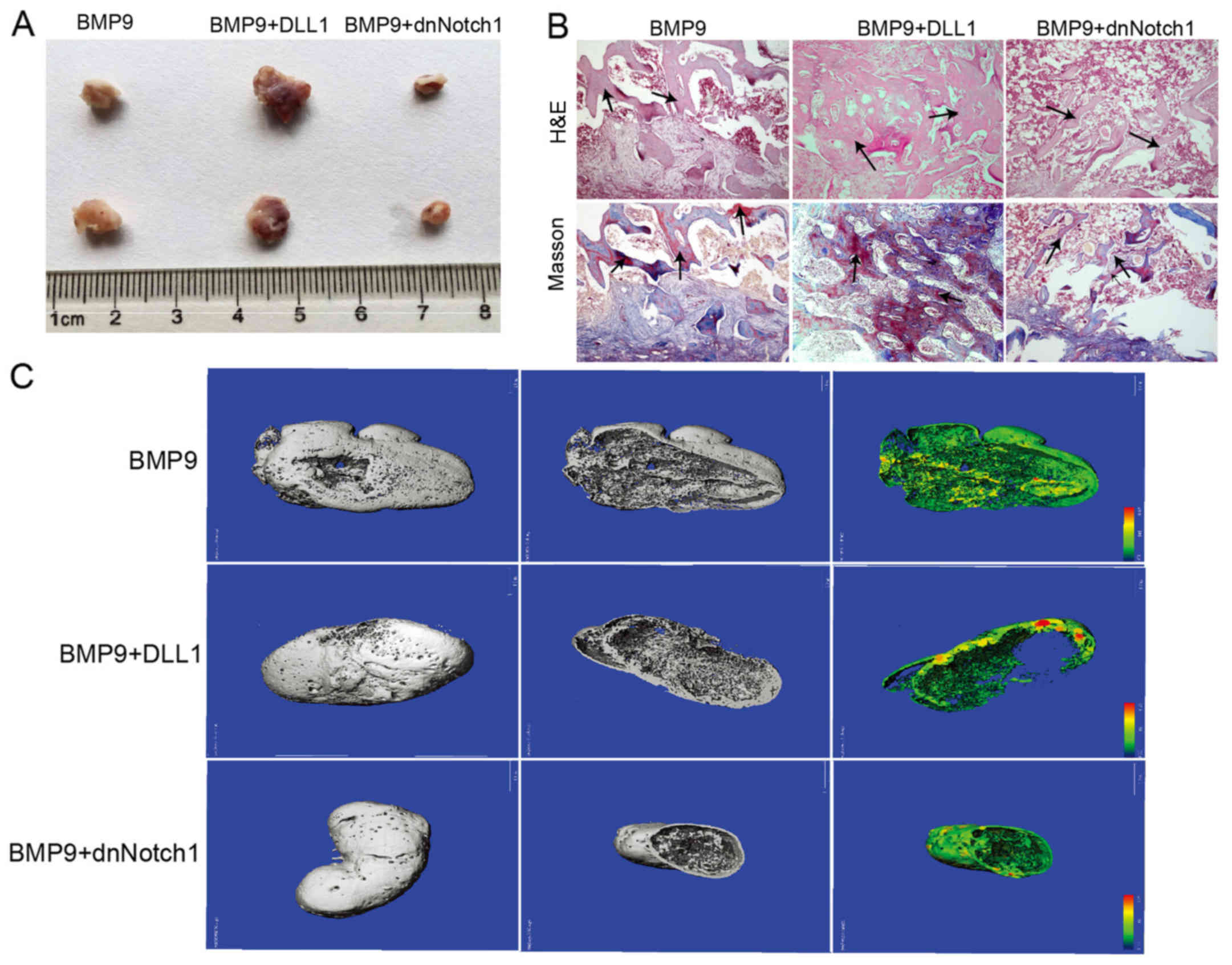
Effects of Notch signaling on
BMP9-induced ectopic ossification
Our in vitro data revealed that Notch
signaling plays an important role in BMP9-induced osteogenic
differentiation of MSCs. Thus, we determined the effect of Notch on
BMP9-induced ectopic bone formation. The infected MEFs were
collected and injected subcutaneously into athymic nude mice. After
4 week(s), the animals were sacrificed and the bony masses were
retrieved (Fig. 3A). The overall
sizes of bony masses from the Ad-BMP9 combined with Ad-DLL1 group
were apparently larger than that from the Ad-BMP9 group, and the
bony masses from the group treated with Ad-BMP9 and Ad-dnNotch1
were significantly smaller than that of the Ad-BMP9 group.
Histologic analysis indicated that, compared with the Ad-BMP9
group, the trabecular bone and osteoid matrix area was obviously
increased in the group of Ad-BMP9 combined with Ad-DLL1, and was
significantly decreased in the Ad-BMP9 combined with Ad-dnNotch1
group (Fig. 3B). Micro-CT
scanning analysis showed the same results (Fig. 3C). These data demonstrated that
Notch signaling enhances BMP9-induced ectopic bone formation.
Effects of Notch signaling on
BMP9-induced activation of BMP/Smad signaling
We then explored the possible mechanism behind the
effect of Notch signaling on the BMP9-induced osteogenic
differentiation of MSCs. BMP/Smad signaling is the classical
pathway for BMP9 to induced osteogenic differentiation in MSCs.
Thus, we aimed to ascertain whether or not Notch regulates this
signaling. In the presence of BMP9-CM, we treated the cells for 36
h with DAPT, Ad-dnNotch1 or Ad-DLL1, respectively. Western blot
analysis showed that DAPT had no obvious effects on total protein
level of Smad1/5/8, but decreased the phosphorylation level of
Smad1/5/8 in the C2C12 cells (Fig.
4A). Similar results were found in MEFs treated with Ad-BMP9
and Ad-dnNotch1 (Fig. 4A).
Conversely, Ad-DLL1 was found to enhance the phosphorylation level
of Smad1/5/8 induced by BMP9 in the C3H10T1/2 and C2C12 cells and
MEFs (Fig. 4B). Using the BMP
responsive Smad1/5/8 reporter, p12xSBE-luc, we found that Ad-DLL1
promoted BMP9-induced reporter activities prominently in the
C3H10T1/2 and C2C12 cells and MEFs, and Ad-dnNotch1 impaired the
BMP9-induced reporter act ivities (Fig. 4C). Collectively, these results
suggested that Notch signaling can enhance the BMP/Smad signaling
transduction induced by BMP9 in MSCs.
Effects of Notch signaling on
BMP9-induced expression of essential osteogenic factors in
MSCs
It has been demonstrated in our previous study that
runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), inhibitor of
differentiation (Id)1, 2 and 3 are targets of BMP9, and are
critical to BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation in MSCs
(40). Type I collagen (Colla1)
is the special collagen secreted by osteoblast cells. With RT-PCR
analysis, we found that the expression of Runx2 and Colla1 induced
by BMP9 was decreased by DAPT in a concentration-dependent manner
in C2C12 cells, and similar results were found in MEFs when treated
with Ad-dnNotch1 combined with BMP9-CM. Yet, the BMP9-induced
expression levels of Runx2 and Col1a1 were increased when treated
with Ad-DLL1 combined with BMP9-CM (Fig. 5A). We also found that the
expression levels of Id1, Id2 and Id3 were decreased by DAPT in the
presence of BMP9, but only Id1 was decreased by Ad-dnNotch1
combined with BMP9-CM treatment in MEFs (Fig. 5B). These results indicated that
Notch signaling was able to regulate BMP9-induced essential
osteogenic factors, but there may be some differences between
different ligands/receptors.
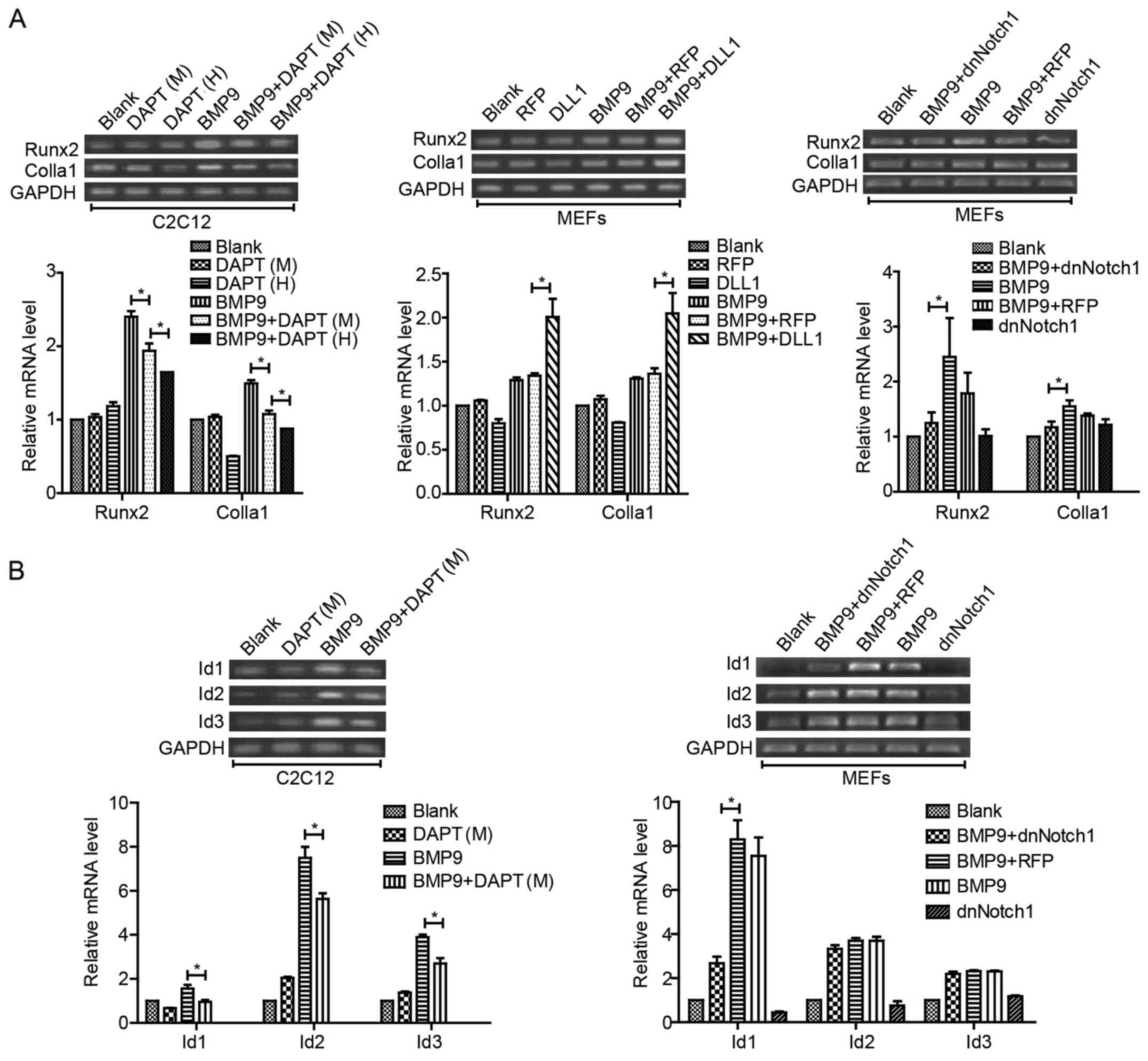 | Figure 5Notch signaling increases the
expression of essential osteogenic factors induced by BMP9 in MSCs.
(A) MEFs and C2C12 cells were treated with Ad-dnNotch1 or Ad-DLL1
or different concentrations of DAPT (M=10 μM, and H=15
μM, respectively) in the presence of BMP9-CM. The gene
expression of Runx2 and Colla1 was detected by semi-quantitative
RT-PCR at indicated time-points and quantification by densitometry.
(B) MEFs and C2C12 cells were treated with DAPT (M=10 μM) or
Ad-dnNotch1 in the presence of BMP9-CM, and the gene expression
levels of Id, Id2, Id3 were detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR at
24 h post-treatment and quantification by densitometry.
*P<0.05. BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; MEFs, mouse
embryo fibroblasts; dnNotch1, dominant-negative mutant of Notch1;
DLL, Delta-like; BMP9-CM, BMP9-conditioned media; Runx2,
runt-related transcription factor 2; Colla1, type I collagen; Id,
inhibitor of differentiation. |
Effects of Notch signaling on the
expression of ALK2 induced by BMP9
ALK1 and ALK2 are functional receptors essential for
BMP9 osteogenic activity (42).
BMP9 can increase the expression of ALK1 and ALK2 in MSCs, which is
likely to be a novel clue to demonstrate the molecular mechanism
underlying BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs.
Therefore, we aimed to ascertain whether or not Notch can affect
ALK1 and ALK2. With qPCR, we found that it was ALK2 but not ALK1
that was significantly downregulated by Ad-dnNotch1 combined with
BMP9-CM in MEFs (Fig. 6A).
Ad-DLL1 promoted the gene expression of ALK2 induced by BMP9 in
MEFs, but had no apparent effect on ALK1 gene expression (Fig. 6A). In order to ascertain whether
Notch signaling augments BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation by
increasing the gene expression of ALK2, we treated cells with
Ad-dnALK1 and Ad-dnALK2, respectively, in the presence of BMP9-CM.
We noted that BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation was markedly
impaired by Ad-dnALK1 and Ad-dnALK2, and Ad-DLL1 rescued the
inhibitory effect of dnALK2, but had no significant effect on
dnALK1 (Fig. 6B and C). These
results suggested that DLL1/Notch signaling may regulate
BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs by partly
increasing BMP9-dependent upregulation of ALK2.
 | Figure 6Notch signaling promotes BMP9-induced
ALK2 gene expression, and the inhibitory effect of dnALK2 on
BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation is rescued by
overexpression of DLL1. (A) MEFs were treated with Ad-DLL1 or
Ad-dnNotch1 in the presence of BMP9-CM, and the gene expression of
ALK1 and ALK2 was detected by qPCR at 3 day(s) post-treatment. (B)
C3H10T1/2 cells, C2C12 cells and MEFs were infected with Ad-DLL1
and/or Ad-dnALK1, Ad-dnALK2, or Ad-RFP for 24 h, and were
stimulated with BMP9-CM. ALP activity was assessed by staining
assay at 5 day(s) post-treatment. (C) Matrix mineralization was
assessed at 9 day(s) post-treatment by Alizarin Red S staining
assay. Magnification, ×100. *P<0.05. BMP, bone
morphogenetic protein; ALK, activin-like kinase; DLL, Delta-like;
MEFs, mouse embryo fibroblasts; dnNotch1, dominant-negative mutant
of Notch1; BMP9-CM, BMP9-conditioned media; ALP, alkaline
phosphatase. |
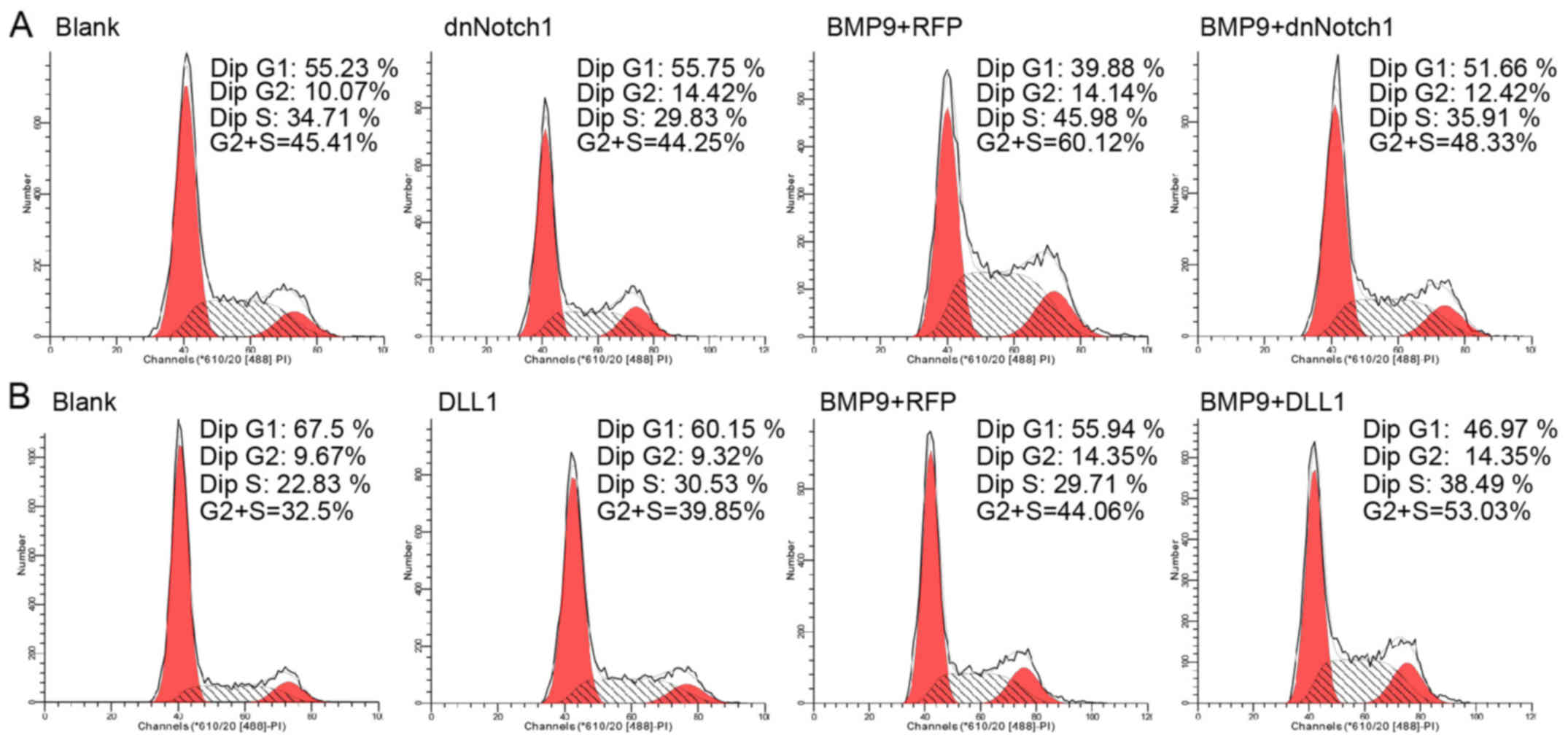
Effect of Notch signaling on the
proliferation of MSCs during BMP9-induced osteogenic
differentiation
Notch signaling is involved in regulating the
balance between cell differentiation and stem cell proliferation
during the development of numerous tissues. Notch signaling may
affect BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation by regulating the
proliferation of MEFs. Using FCM analysis, we found that following
treatment withAd-DLL1 combined with BMP9-CM the percentage of MEFs
in the S phase was increased compared to the percentage of cells
treated with Ad-RFP combined with BMP9-CM. In addition, the
percentage of cells in the G0/G1 phase decreased significantly. We
also noted that Ad-dnNotch1 decreased the S phase cell percentage
induced by BMP9-CM, but apparently increased the cell percentage in
G0/G1 (Fig. 7A and B). Based on
these data, Notch may promote the proliferation of MSCs in the
presence of BMP9-CM.
Discussion
In the present study, we investigated the effect of
Notch signaling on BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation in MSCs,
and the possible mechanism underlying this process. Our findings
suggested that Notch signaling can enhance the activity of BMP9 to
induce osteogenic differentiation in MSCs, and this effect may be
partly mediated by upregulation of ALK2.
BMP9, also called GDF-2, is one of the least studied
BMPs (44). Numerous studies have
indicated that BMP9 has pivotal biological functions in the areas
of liver fibrosis, iron metabolism, cartilage formation and
angiopoiesis, and recent studies have shown that BMP9 is the
strongest inducer of osteogenic differentiation, which has been
regarded as a potential factor in tissue engineering (45). The studies concerning BMP9-induced
osteogenesis mechanism are conducive to its application in
bone-related diseases. Previous research has indicated that
fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) inhibits BMP9-induced osteogenic
differentiation by blocking BMP9-induced Smad signaling and
subsequently reducing Smad-dependent upregulation of ALK1 and ALK2
in MSCs (41). Canonical
Wnt/β-catenin signaling acts synergistically on BMP9-induced
osteogenic differentiation (46).
p38 and ERK1/2 MAKPs exert opposing effects on BMP9-induced
osteogenic differentiation (43).
Cox2 is critical for BMP9 to induce osteogenic differentiation in
MSCs (39). Hedgehog signaling is
involved and plays a regulatory role in the osteogenic
differentiation of MSCs induced by BMP9 (40). Yet, little is known concerning the
effect of Notch signaling on BMP9-induced osteogenic
differentiation. Although the importance of Notch on bone
remodeling has been found, its role in bone formation remains
uncertain. Some studies have determined that Notch signaling can
crosstalk with BMP2 to regulate osteogenesis and skeletal
remodeling (47–49). However, the effects of Notch
signaling on BMP-induced osteogenesis are incompatible.
Delta1/Jagged1-activated Notch1 enhances BMP2-induced
differentiation in MC3T3-E1 and C2C12 cells (49). Similarly, Notch signaling promotes
osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of vascular SMCs by
directly activating Msx2 gene transcription via RBP-Jκ (50). Other groups have indicated the
opposite results that disruption of Notch signaling in the limb
skeletogenic mesenchyme markedly increased trabecular bone mass in
adolescent mice (51). In any
case, Notch signaling plays critical roles in BMP2-regulated
osteogenesis and skeletal remodeling. These different results may
be associated with the differentiation of cell lines and the
methods used to upregulate or downregulate the pathway. On the
other hand, these reports also suggest that there may be complex
crosstalk between Notch and BMP signaling.
Our mechanistic studies demonstrated that Notch may
enhance the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs by augmenting the
activity of BMP9/Smad signaling. The activation of BMP/Smad
signaling is initialized from the binding of BMPs and their
receptors (BMPRs). Thus, we aimed to clarify whether BMP9/Smad
signal transduction strengthened by Notch is derived from BMPRs. We
treated MSCs with Ad-DLL1, Ad-dnNotch and DAPT, respectively. We
found that the expression of ALK2 (a type of type I BMP receptor)
was markedly increased after upregulation of Notch and decreased
when Notch was downregulated. But other BMPRs had no changes. When
treated with Ad-dnALK2, BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of
MSCs was obviously suppressed, but this inhibition was rescued by
the presence of Ad-DLL1. These results showed that the effect of
Notch on the activation of the BMP9/Smad signaling may be mediated
by upregulation of ALK2 in MSCs.
ALK2, also known as activin A receptor type 1
(ACVR1, is a type I receptor which contributes to osteogenic
differentiation induced by BMP2, BMP6, BMP7 and BMP9 (17,52). It has been reported that ALK1 and
ALK2 are essential for BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation and
ALK2 is required for chondrogenesis during development (42,53,54). Gain-of-function mutation of ALK2
gene is involved in the pathogenesis of fibrodysplasia ossificans
progressiva (FOP), which is characterized by progressive
heterotopic endochon-dral ossification in muscles and other
non-skeletal tissues (55). Thus,
ALK2 plays a key role in osteogenic differentiation. Previous
studies have revealed that BMP9 upregulates ALK2 expression in MSCs
through BMP/Smad signaling (42).
Yet, the mechanisms regulating ALK2 expression are still poorly
understood. Our data suggested that the expression of ALK2 may be
regulated by BMP9 and Notch, but the mechanisms need to be further
studied.
It is generally believed that during the process of
cell differentiation, cell proliferation is inhibited to some
extent. We investigated the proliferation of MSCs during
osteoblastogenesis induced by BMP9. Our FCM data revealed that
Notch enhanced the proliferation of MSCs by decreasing the
percentage of cells in the G0/G1 phase, and increasing the
percentage of cells in the S phase
In conclusion, we demonstrated that Notch signaling
can potentiate the BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs.
In regards to the mechanism, we found that this effect may be
mediated by upregulation of the expression of ALK2 to enhance the
activation the BMP/Smad signaling induced by BMP9.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Tong-Chuan He (University of Chicago
Medical Center) for providing the recombinant adenoviruses. This
study was supported in part by research grants from the Chongqing
Natural Science Foundation (CSTC2012jjA10004 and KJ130305).
References
|
1
|
Hansson EM, Lendahl U and Chapman G: Notch
signaling in development and disease. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:320–328. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zanotti S and Canalis E: Notch and the
skeleton. Mol Cell Biol. 30:886–896. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Campbell DP, Chrysostomou E and
Doetzlhofer A: Canonical Notch signaling plays an instructive role
in auditory supporting cell development. Sci Rep. 6:194842016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Colombo M, Galletti S, Garavelli S,
Platonova N, Paoli A, Basile A, Taiana E, Neri A and Chiaramonte R:
Notch signaling deregulation in multiple myeloma: A rational
molecular target. Oncotarget. 6:26826–26840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xiao Z, Zhang J, Peng X, Dong Y, Jia L, Li
H and Du J: The Notch γ-secretase inhibitor ameliorates kidney
fibrosis via inhibition of TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway
activation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 55:65–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K and
Fortini ME: Notch signaling. Science. 268:225–232. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ehebauer M, Hayward P and Arias AM: Notch,
a universal arbiter of cell fate decisions. Science. 314:1414–1415.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bi P and Kuang S: Notch signaling as a
novel regulator of metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 26:248–255.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Colombo M, Thümmler K, Mirandola L,
Garavelli S, Todoerti K, Apicella L, Lazzari E, Lancellotti M,
Platonova N, Akbar M, et al: Notch signaling drives multiple
myeloma induced osteoclastogenesis. Oncotarget. 5:10393–10406.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kushwah R, Guezguez B, Lee JB, Hopkins CI
and Bhatia M: Pleiotropic roles of Notch signaling in normal,
malignant, and developmental hematopoiesis in the human. EMBO Rep.
15:1128–1138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wahi K, Bochter MS and Cole SE: The many
roles of Notch signaling during vertebrate somitogenesis. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 49:68–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tao J, Chen S, Yang T, Dawson B, Munivez
E, Bertin T and Lee B: Osteosclerosis owing to Notch gain of
function is solely Rbpj-dependent. J Bone Miner Res. 25:2175–2183.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong Y, Jesse AM, Kohn A, Gunnell LM,
Honjo T, Zuscik MJ, O'Keefe RJ and Hilton MJ: RBPjkappa-dependent
Notch signaling regulates mesenchymal progenitor cell proliferation
and differentiation during skeletal development. Development.
137:1461–1471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong Y, Long T, Wang C, Mirando AJ, Chen
J, O'Keefe RJ and Hilton MJ: NOTCH-mediated maintenance and
expansion of human bone marrow stromal/stem cells: A technology
designed for orthopedic regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Transl
Med. 3:1456–1466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sánchez-Duffhues G, Hiepen C, Knaus P and
Ten Dijke P: Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in bone
homeostasis. Bone. 80:43–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katagiri T and Watabe T: Bone
morphogenetic proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 8:82016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Miyazono K, Maeda S and Imamura T: BMP
receptor signaling: Transcriptional targets, regulation of signals,
and signaling cross-talk. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:251–263.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brazil DP, Church RH, Surae S, Godson C
and Martin F: BMP signalling: Agony and antagony in the family.
Trends Cell Biol. 25:249–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sieber C, Kopf J, Hiepen C and Knaus P:
Recent advances in BMP receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 20:343–355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic proteins:
Multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes Dev.
10:1580–1594. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen G, Deng C and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J
Biol Sci. 8:272–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Peng Y, Kang Q, Cheng H, Li X, Sun MH,
Jiang W, Luu HH, Park JY, Haydon RC and He TC: Transcriptional
characterization of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)-mediated
osteogenic signaling. J Cell Biochem. 90:1149–1165. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmidt-Bleek K, Willie BM, Schwabe P,
Seemann P and Duda GN: BMPs in bone regeneration: Less is more
effective, a paradigm-shift. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
27:141–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Beederman M, Lamplot JD, Nan G, Wang J,
Liu X, Yin L, Li R, Shui W, Zhang H, Kim SH, et al: BMP signaling
in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and bone formation. J
Biomed Sci Eng. 6:32–52. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poon B, Kha T, Tran S and Dass CR: Bone
morphogenetic protein-2 and bone therapy: Successes and pitfalls. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 68:139–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang Q, Sun MH, Cheng H, Peng Y, Montag
AG, Deyrup AT, Jiang W, Luu HH, Luo J, Szatkowski JP, et al:
Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity
of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery.
Gene Ther. 11:1312–1320. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, Manning D, Luo J,
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Montag AG, Haydon RC and He TC: Distinct roles
of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 25:665–677. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng H, Jiang W, Phillips FM, Haydon RC,
Peng Y, Zhou L, Luu HH, An N, Breyer B, Vanichakarn P, et al:
Osteogenic activity of the fourteen types of human bone
morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). J Bone Joint Surg Am.
85-A:1544–1552. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bi J and Ge S: Potential roles of BMP9 in
liver fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 15:20656–20667. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mi LZ, Brown CT, Gao Y, Tian Y, Le VQ,
Walz T and Springer TA: Structure of bone morphogenetic protein 9
procomplex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:3710–3715. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu N, Jiang D, Huang E, Liu X, Li R, Liang
X, Kim SH, Chen X, Gao JL, Zhang H, et al: BMP9-regulated
angiogenic signaling plays an important role in the osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Sci.
126:532–541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Song JJ, Celeste AJ, Kong FM, Jirtle RL,
Rosen V and Thies RS: Bone morphogenetic protein-9 binds to liver
cells and stimulates proliferation. Endocrinology. 136:4293–4297.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dahlqvist C, Blokzijl A, Chapman G, Falk
A, Dannaeus K, Ibâñez CF and Lendahl U: Functional Notch signaling
is required for BMP4-induced inhibition of myogenic
differentiation. Development. 130:6089–6099. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Viale-Bouroncle S, Gosau M and Morsczeck
C: NOTCH1 signaling regulates the BMP2/DLX-3 directed osteogenic
differentiation of dental follicle cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:500–504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shin M, Nagai H and Sheng G: Notch
mediates Wnt and BMP signals in the early separation of smooth
muscle progenitors and blood/endothelial common progenitors.
Development. 136:595–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guo X and Wang XF: Signaling cross-talk
between TGF-β/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 19:71–88. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sartori R, Gregorevic P and Sandri M:
TGFbeta and BMP signaling in skeletal muscle: Potential
significance for muscle-related disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
25:464–471. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang JH, Liu YZ, Yin LJ, Chen L, Huang J,
Liu Y, Zhang RX, Zhou LY, Yang QJ, Luo JY, et al: BMP9 and COX-2
form an important regulatory loop in BMP9-induced osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 57:311–321. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Dong Q, Wang Y, Feng Q, Zhou P, Ou
X, Meng Q, He T and Luo J: Hedgehog signaling is involved in the
BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Int J Mol Med. 35:1641–1650. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Song T, Wang W, Xu J, Zhao D, Dong Q, Li
L, Yang X, Duan X, Liang Y, Xiao Y, et al: Fibroblast growth factor
2 inhibits bone morphogenetic protein 9-induced osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by repressing Smads
signaling and subsequently reducing Smads dependent up-regulation
of ALK1 and ALK2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:1639–1646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Luo J, Tang M, Huang J, He BC, Gao JL,
Chen L, Zuo GW, Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, et al: TGFbeta/BMP type I
receptors ALK1 and ALK2 are essential for BMP9-induced osteogenic
signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem. 285:29588–29598.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao Y, Song T, Wang W, Wang J, He J, Wu
N, Tang M, He B and Luo J: P38 and ERK1/2 MAPKs act in opposition
to regulate BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal
progenitor cells. PLoS One. 7:e433832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang J, Weng Y, Liu X, Wang J, Zhang W,
Kim SH, Zhang H, Li R, Kong Y, Chen X, et al: Endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) stress inducible factor cysteine-rich with EGF-like domains 2
(Creld2) is an important mediator of BMP9-regulated osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 8:e730862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luther G, Wagner ER, Zhu G, Kang Q, Luo Q,
Lamplot J, Bi Y, Luo X, Luo J, Teven C, et al: BMP-9 induced
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: Molecular
mechanism and therapeutic potential. Curr Gene Ther. 11:229–240.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang H, Wang J, Deng F, Huang E, Yan Z,
Wang Z, Deng Y, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Ye J, et al: Canonical Wnt
signaling acts synergistically on BMP9-induced osteo/odontoblastic
differentiation of stem cells of dental apical papilla (SCAPs).
Biomaterials. 39:145–154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shimizu T, Tanaka T, Iso T, Matsui H,
Ooyama Y, Kawai-Kowase K, Arai M and Kurabayashi M: Notch signaling
pathway enhances bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) responsiveness
of Msx2 gene to induce osteogenic differentiation and
mineralization of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem.
286:19138–19148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
de Jong DS, Steegenga WT, Hendriks JM, van
Zoelen EJ, Olijve W and Dechering KJ: Regulation of Notch signaling
genes during BMP2-induced differentiation of osteoblast precursor
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 320:100–107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nobta M, Tsukazaki T, Shibata Y, Xin C,
Moriishi T, Sakano S, Shindo H and Yamaguchi A: Critical regulation
of bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblastic differentiation
by Delta1/Jagged1-activated Notch1 signaling. J Biol Chem.
280:15842–15848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shimizu T, Tanaka T, Iso T, Doi H, Sato H,
Kawai-Kowase K, Arai M and Kurabayashi M: Notch signaling induces
osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of vascular smooth
muscle cells: Role of Msx2 gene induction via Notch-RBP-Jk
signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1104–1111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hilton MJ, Tu X, Wu X, Bai S, Zhao H,
Kobayashi T, Kronenberg HM, Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP, Kopan R, et al:
Notch signaling maintains bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors by
suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat Med. 14:306–314. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y and Morikawa M: Bone
morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem.
147:35–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Culbert AL, Chakkalakal SA, Theosmy EG,
Brennan TA, Kaplan FS and Shore EM: Alk2 regulates early
chondrogenic fate in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
heterotopic endo-chondral ossification. Stem Cells. 32:1289–1300.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang D, Schwarz EM, Rosier RN, Zuscik MJ,
Puzas JE and O'Keefe RJ: ALK2 functions as a BMP type I receptor
and induces Indian hedgehog in chondrocytes during skeletal
development. J Bone Miner Res. 18:1593–1604. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Katagiri T: A door opens for
fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Trends Biochem Sci.
41:119–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|