1. Introduction
The immune system is comprised of white blood cells
(monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, eosinophils,
basophils and lymphocytes) and special immune molecules (cytokines,
antibodies, complement proteins and signaling pathways) that have
evolved to resist infections (1).
The immune system is classified into two broad categories: The
innate and adaptive immune system, which collaborate to protect the
body against foreign invaders and aid in the maintenance of the
normal homeostasis of the body. Innate immunity is a non-specific
immune system which provides immediate initial defense against
infections (2), while adaptive
immunity is a specific immune system which develops more slowly and
provides specific and effective defense against invading pathogens
(3). Several intrinsic and extrinsic
agents can affect the functioning of the immune system, rendering
it either immunostimulatory or immunosuppressive (3). Immunomodulation is the alteration of
the responsiveness of the body's immune system caused by a chemical
substance that can suppress or activate its function in the fight
against diseases (4). A
malfunctioning or imbalanced immune system can result in the
development of a variety of chronic diseases, such as cancer,
autoimmune disorders, allergies, viral infections, inflammatory
bowel diseases and numerous others (5). Immunomodulators are bioactive agents
that can regulate immunological events, such as stimulating
phagocytes, natural killer cell, and activating T- and B-cells
(6). The organic entity of natural
or artificial sources with the characteristics of inhibiting,
stimulating or modulating the constituents of either non-specific
or specific immunity are also referred to as immune modulators or
biological response modifiers. Generally, in medical practice,
these sources are grouped as immunosuppressant, immunostimulant and
immunoadjuvant (7,8). Advancements in immunological research
indicate that the suppression of the immune system due to stressful
environmental conditions can result in the development of a variety
of diseases (9). Therefore, it is
evident that immunomodulators can serve as alternative therapies
for the management of various diseases, such as activating immune
responsiveness impairment by HIV (10,11) or
suppressing it during transplantation (12). Additionally, the application of these
modulators in cancer treatment is crucial due to their central role
in supporting immune responses (13). As biological response modifiers,
immunomodulatory agents inhibit tumor cells directly or by
enhancing host defense mechanism such as induction of apoptosis
against the tumor (14). The
immunological effects of immunomodulators can be evaluated by their
specified actions on immune cells, effector mechanisms, inhibition
of nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production,
the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, signaling pathways in
macrophage cells and phagocytosis activity (15).
Cortex moutan, the root bark of Paeonia
suffruticosa has been extensively utilized as a traditional
Chinese medicine for the prevention and control of several diseases
for years with a good safety and efficacy profile (16). Paeonol is a pharmacologically
effective phenolic constituent isolated from Cortex Moutan. Paeonol
has been reported to possess extensive therapeutic effects on the
innate and adaptive immune system in several human diseases
(17-21)
and cancers (22-24),
which are associated with inhibition of immune signaling pathways
(25-27),
NO (21) and ROS production
(28), inflammatory cytokines
(29,30), immune cells (20,31),
phagocytes (17,32) and the induction of apoptosis
(14,25,33).
Paeonol has been applied together with other drugs to effectively
protect against oropharyngeal candidiasis (34), hepatotoxicity (35) and cardiotoxicity (36), indicating that paeonol can
potentially act as an alternative or complementary medicine to
offset deficiencies and unresolved safety of current drugs for
treatment of diseases. In the light of the therapeutic prospects
and pharmacological activities of paeonol, the present review
provides an overview of the underlying mechanisms of paeonol in
immunomodulation and chemoprevention.
2. Literature search methods
To assess the existing studies on the
immunomodulatory and chemotherapeutic potentials of paeonol for a
wide range of human diseases, the Pubmed, Medline, Google Scholar
and Web of Science, SciFinder and Science Direct databases were
used to search for literature published from 2013 up to 2024.
Paeonol and immunomodulation or cancer were the key words used for
the search. All relevant full-text research articles with
titles/abstract were incorporated without language restrictions.
Citations from selected publications were tracked and potential
papers added.
3. Botanical characteristics of Paeonia
suffruticosa
Peonies mainly thrive well in northwest Africa,
temperate Eurasia and western North America. Nevertheless, wild
peony is endemic to China, where it was initially domesticated
(37). It is a perennial shrub with
brown-gray stems and grows to a height of 1.5 m. It has long oval
leaflets, solitary, single or double flowers with an asymmetrical
apex. The bark of the root is yellow to brown with lignified fleshy
center and a completely developed root system (38-40).
It has a tube-shaped bark, with breaks along the entire length. The
bark is slightly curly inward, 3-8 cm long, 0.5-1.2 cm in diameter
and 0.1-0.4 cm thick. The external surface of the bark is
reddish-brown or grayish-brown. The cork drop is pink with
projecting pore spaces, light brown or grayish-yellow inner surface
with a fine longitudinal texture and sparkling crystals (16).
4. Paeonol: The principal active ingredient
of Paeonia suffruticosa
Cortex moutan has several bioactive constituents,
such as gallic acid derivatives, flavonoids, triterpenes,
monoterpene glycosides, and in particular, phenolic compounds. The
principal active elements of Cortex moutan comprise, paeoniflorin,
gallic acid, 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-gallic acid-β-D-glucose and
the phenolic compound paeonol (16).
The active ingredients have been reported to be extracted using
methods, such as organic solvent extraction, ultrasonic assisted
extraction, steam distillation, and CO2 supercritical
fluid extraction (41-43).
5. Immunomodulatory effects of paeonol
In vitro and in vivo immunosuppressive effects of
paeonol. Diverse in vitro and in vivo research
exploiting paeonol has indicated its potential immunosuppressive
activities. Paeonol administration was previously shown to inhibit
inflammation by downregulating lipase, amylase, IL-1β and IL-6.
Moreover, the drug decreased ROS, restored mitochondrial membrane
potential and suppressed M1 macrophage polarization through the
NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) pathway in bone marrow-derived
macrophages (21). In another study,
paeonol improves fluconazole or amphotericin B application during
the treatment of EC109 cells and in a mouse model of oropharyngeal
candidiasis by suppressing HIF-1α, IL-17A and IL-23 expression at
the mRNA and protein level (34). A
previous study also demonstrates that out of seven components of
Cortex moutan Radicis studied in the treatment of
antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice and RAW 264.7 cells, paeonol
attenuated NO production and IL-6 expression, decreased the level
of TNF-α in a concentration-dependent manner, as well as the mRNA
levels of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α (30). Also, COX-2 and NF-κB levels decreased
as confirmed by western blot analysis; however, at the
concentration of 25 µM, the p-p38 MAPK level was upregulated and
was downregulated at 50 µM. Furthermore, compared with the control
group, the TNF-α and IL-4 levels were decreased (30). As previously reported, Miao et
al (32) indicated that paeonol
improved the phagocytic capacity of macrophages by restricting
high-mobility group box 1 to the nucleus. Additionally, it promoted
the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase to stimulate the
development of pseudopod in enhancing phagocytosis (32). Paeonol has been documented to
suppress the miR-155/JAK1-STAT1 pathway to inhibit
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and IFN-γ-induced macrophage M1
polarization via the downregulation of F4/80 and CD86, IL-6 and
TNF-α in mice and RAW264.7 cells (44). A previous study demonstrated that the
oral administration of paeonol suppressed the development of
1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene-induced AD-like lesions in BALB/c mice
by downregulating the lesion severity, epidermal thickness and
infiltration of mast cells (31).
Moreover, this led to decreased levels of immunoglobulin E and
IL-4, histamine, IL-13, IL-31 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin,
together with the modulation of the T-helper (Th1/Th2) ratio.
Paeonol regulated the (Th) cell subset (Th1/Th2) ratio by
downregulating immunoglobulin E, IL-4, histamine, IL-13, IL-31 and
thymic stromal lymphopoietin levels. Furthermore, its application
attenuated phosphorylated (p)-p38 and p-ERK. In addition, the
production of TNF-α and histamine was decreased, and p38/ERK/MAPK
signaling inhibited in P815 cells. The aforementioned demonstrates
that the drug act on cluster of differentiation 4+ T-and mast cells
to inhibit allergic inflammatory conditions (31). In another report, paeonol suppressed
NF-κB, IL-6 and TNF-α through denosine 5'-monophosphate-activated
protein kinase (AMPK) and the glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3)
pathway to prevent inflammation (29). Liu et al (45) investigated the effects of paeonol on
THP-1 cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
The authors concluded that the drug upregulated miR-223 in THP-1
extracted exosomes and in HUVECs following the intake of exosomes,
but reduced STAT3 and p-STAT3 expression in HUVECs. In addition,
IL-1β, IL-6, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 levels were downregulated in HUVECs,
and THP-1 cell adhesion to HUVECs was attenuated to reduce the
inflammatory response (45). Another
study demonstrated that paeonol, at various concentrations, exerted
anti-inflammatory effects against IL-1β-induced inflammation by
suppressing NO and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production (46). Additionally, that study revealed that
inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), COX-2, MMP-1, MMP-3 and
MMP-13 overexpression were reversed together with inhibition of
NF-κB, PI3K and AKT activated signals (46). In a study investigating the effects
of paeonol in a mouse model of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like
skin lesions and murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells
stimulated by R848, it was demonstrated that the drug inhibited
IL-23 and downregulated dendritic cells expressing MHCII, CD80 and
CD86 in vitro (17). This
indicated that paeonol suppressed the maturation and activation of
dendritic cells by downregulating MyD88 and Toll-like receptor
(TLR)8 proteins (17). Another study
demonstrated that paeonol, in a dose-dependent manner, attenuated
LPS-stimulated inflammation to protect kidney injury (18). That study employed ELISA, western
blot analysis and immunohistochemistry to determine the expression
of inflammatory cytokines, TLR4-NF-κB pathway, and phospho-NF-κB
p65, respectively. The results revealed that paeonol repressed
pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulated anti-inflammatory
cytokines. Furthermore, the p-IκBα and p-IKKβ, NF-κB p65, and NF-κB
p65 DNA-binding activities were inhibited. In addition, it
suppressed the TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway (18). Paeonol has been demonstrated to
suppress the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway to reduce hepatotoxicity
(35). As previously demonstrated,
pre-treatment of BV-2 cells and mice with paeonol revealed its
ability to regulate p-AMPK-α and GSK 3α/β to suppress the
expression of NO, iNOS, COX-2 and ROS induced by LPS/INF-γ.
Furthermore, the drug suppressed STAT3 and p38 pathways (47). In another study, the administration
of paeonol suppressed IL-8 via its antioxidant activity to inhibit
MAPKs/NF-κB signaling to alleviate inflammation induced by chronic
cigarette smoke (26). Chen et
al (48) reported that paeonol,
in a concentration-dependent manner, downregulated the release of
TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and increased IL-10 in LPS-induced RAW 264.7
via the deactivation of IκBα, ERK1/2, JNK and p38 MAPK. The in
vitro and in vivo mechanisms of action of paeonol
reported above are presented in Table
I.
 | Table IIn vitro and in vivo
immunosuppressive effects of paeonol. |
Table I
In vitro and in vivo
immunosuppressive effects of paeonol.
| Authors, year of
publication | Study type | Mechanism of
action | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Yuan et al,
2022 | In vivo and
in vitro | Downregulation of
IL-1β, IL-6 and ROS, and the suppression of M1 macrophage
polarization and NLRP3 inflammasome | (21) |
| Pan et al,
2022 | In vivo and
in vitro | Suppresses the
HIF-1α, IL-17A and IL-23 protein level | (34) |
| Kang et al,
2022 | In vivo and
in vitro | Downregulates NO,
COX-2 and IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-4 and NF-κB and MAPK | (30) |
| Miao et al,
2020 | In vivo and
in vitro | Restricts HMGB1 to
the nucleus and promotes focal adhesion kinase; stimulates the
development of pseudopods to upregulate phagocytosis | (32) |
| Sun et al,
2020 | In vivo and
in vitro | Suppresses
miR-155/JAK1-STAT1 and downregulates F4/80 and CD86, IL-6 and
TNF-α | (44) |
| Meng et al,
2019 | In vivo and
in vitro | Regulates the
Th1/Th2 ratio by downregulating IgE, IL-4, histamine, IL-13, IL-31,
TNF-α and p38/ERK/MAPK | (31) |
| Liu et al,
2018 | In vivo and
in vitro | Suppresses NF-κB,
IL-6 and TNF-α through the adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated
protein kinase (AMPK) and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3)
pathways | (29) |
| Liu et al,
2018 | In vivo and
in vitro | Upregulates
miR-223, but reduces STAT3, p-STAT3, IL-1β, IL-6, ICAM-1, VCAM-1
expression | (45) |
| Lou et al,
2017 | In vivo and
in vitro | Downregulates NO,
INOS, COX-2, MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, and inhibits NF-κB, PI3K and
AKT | (46) |
| Meng et al,
2017 | In vivo and
in vitro | Inhibits IL-23 and
downregulates dendritic cells expressing MHCII, CD80 and CD86 | (17) |
| Fan et al,
2016 | In vivo and
in vitro | Represses
pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulates anti-inflammatory
cytokines; inhibits IκBα and IKKβ, NF-κB p65, and restricts NF-κB
p65 DNA-binding activity as well as TLR4-NF-κB | (18) |
| Wu et al,
2016 | In vivo and
in vitro | Suppresses the
PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway. | (35) |
| Lin et al,
2015 | In vivo and
in vitro | Regulates AMPK-α
and GSK 3α/β to suppress NO, iNOS, COX-2, ROS and STAT3 as well as
p38 pathways | (47) |
| Liu et al,
2014 | In vivo and
in vitro | Inhibits
MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways. | (26) |
| Chen et al,
2014 | In vivo and
in vitro | Downregulates
TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, upregulates IL-10 via the deactivation of IκBα,
ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK | (48) |
In summary, a critical analysis of both in
vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory mechanisms
demonstrated that paeonol suppresses the discharge of
pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and IL-8,
while upregulating the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10, in the
treatment of several inflammation in various models. However, the
specific genomic and proteomic changes induced by paeonol remain
underexplored. Additionally, paeonol regulates the function of
macrophages in promoting tissue repair by modulating polarization
to an M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype while inhibiting M1. It
promotes the maturation and activation of dendritic cells to
initiate T-cell adaptive immunity. The drug mitigates allergy by
decreasing immunoglobulin E, histamine, hence can be used to manage
conditions such as asthma, atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis.
Moreover, paeonol protects against kidney injury and hepatotoxicity
by inhibiting oxidative stress, NF-κB and MAPK pathways, and
decreases the generation of ROS. Furthermore, it modulates the
NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, AMPK and MAPK pathways to exert multiple level
immunosuppressive effects to attenuate inflammation extensively. In
addition, it exerts synergistic effects when combined with
conventional antifungal agents or anti-inflammatory drugs.
In vitro immunosuppressive effects of
paeonol
Recently, studies have demonstrated that paeonol
promotes M2 macrophage polarization by suppressing M1 polarization
(49,50) through the inhibition of the NF-κB and
MAPK pathways (49). Miao et
al (51) demonstrated that the
promotion of nuclear p53 by paeonol served as a transcript and
increased triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 to
activate macrophage lipid metabolic capacity and phagocytic
function. In another study, paeonol downregulated IL-1β and
caspase-1 level, attenuated the monosodium urate (MSU)-induced
interaction of pro-caspase-1 and apoptosis-associated speck-like
protein containing caspase recruitment domain (ASC) in J774A.1
cells induced by LPS plus MSU (52).
The drug decreased IL-1β, NLRP3, p-IKK, p-IκBα, and p-p65 in
J774A.1 cells induced by LPS alone but did not affect the ASC
level. Moreover, the IκBα content was stimulated and a greater
amount of cytoplasmic p65 retained. Furthermore, paeonol decreased
p65 DNA-binding action and curtailed p-JNK, p-ERK and p-p38 level.
The study concluded that the inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome,
NF-κB and MAPK pathway activation by paeonol occurred through the
suppression of IL-1β (52). Another
study assessed the paeonol-mediated suppression of LPS-activated
inflammation through the TLR4 signaling pathway in N9 microglia
cells (53). That study evaluated
NO, IL-1β and PGE2 using ELISA. Additionally, COX-2, iNOS, TLR4,
MyD88, IRAK4, TNFR-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), p-IkB-α, and NF-kB
p65, as well as p-P38, p-JNK and p-ERK were examined using western
blot analysis. The results revealed that paeonol significantly
repressed the production of pro-inflammatory products, including
NO, IL-1β, and PGE2 as well as the expression of iNOS and COX-2. In
addition, the TLR4, MyD88, IRAK4, TRAF6, p-IkB-α and NF-κB p65, as
well as p-p38, p-JNK and p-ERK expression levels were significantly
reduced (53). In another study,
paeonol upregulated NO, iNOS and downregulated ROS (28). Moreover, the drug attenuated TNF-α,
IL-1β, IL-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) with a
significant decrease in RAGE and CD36, and an increase in SR-A and
SR-B1 levels. The authors of that study reported that the
anti-inflammatory response was likely mediated via the RAGE, CD36,
SR-A and SR-B1-pathways with NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation
(28). The aforementioned in
vitro studies have revealed that paeonol decreases IL-1β to
repress several inflammatory mediators, such as NO, iNOS, COX2 and
PEG2 in the inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and also inhibits
the NF-κB, MAPK and TLR4 pathways to provide a broad-spectrum
effect on immune-related diseases, to function as an
anti-inflammatory agent.
In vivo immunosuppressive effects of
paeonol
In a previous study, the administration of paeonol
downregulated M1 polarization markers (IL1β, iNOS, CD32 and IL6),
and upregulated the M2 polarization markers (IL10, CD206 and ARG-1)
by decreasing iNOS, IL1β, RhoA and Rock1 in LPS-stimulated
microglia (54). Additionally,
during thermal hyperalgesia, the drug downregulated IL1β and IL8
and upregulated IL4 and TGF-β levels in the serum. It was revealed
that in the spinal dorsal horn the drug downregulated IBA-1, IL1β,
RhoA, RhoA-GTP, COX2, Rock1, and p-p38MAPK levels to reduce
neuropathic pain (54). It has also
been demonstrated that paeonol acts via the dectin-1/NF-κB pathway
together with TLR2 and TLR4 to relieve fungal dysbiosis-associated
ulcerative colitis (27). Recently,
paeonol has been reported to significantly suppress NF-κB and MCP-1
in vivo (55). In another
study, paeonol was shown to inhibit the inflammatory response by
suppressing the mycobiota-mediated dectin-1/IL-1β signaling pathway
(56). Paeonol administration has
also been shown to attenuate liver injury and fibrosis. In a
previous study, paeonol downregulated ALT and AST levels, and
inhibited the TGF-b/Smad3 pathway by suppressing the activation of
hepatic stellate cells to downregulate IL-6 and TNF-α, and reduced
oxidative stress (57). Another
study indicated that paeonol modulated nuclear factor E2-related
factor 2 (Nrf2)/NF-κB/NFATc1 signaling in the inhibition of
osteoclastogenesis to protect against periodontitis (58). It has been well-documented that
paeonol improves the asthmatic condition by downregulating IFN-γ
and upregulating IL-4 via the suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB and
MAPK pathway (59). In another
study, in LPS/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure, paeonol
at 100 mg/kg markedly suppressed the iNOS, NO, COX-2 and PGE2
levels (60). The phosphorylation
levels of IκB kinase (IKK), IκB and NF-κB (p65), which constitute
the NF-κB pathway and MAPK signaling pathway molecules, including
ERK, JNK and p38 were significantly inhibited. Moreover, the
decreased expression of caspase-3, -8 and -9, and Bax, with the
upregulated expression of Bcl-2 observed following paeonol
treatment was attributed to the inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis
(60). Another study reported that
paeonol at 200 and 400 mg/kg significantly decreased IL-17 and
IL-6, and upregulated TGF-β1 expression in rats with
2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis
(61). In their study, Ding et
al (62) investigated the
anti-oxidative stress activity of paeonol against acetaminophen
(APAP)-induced hepatotoxicity and indicated that it suppressed JNK
phosphorylated protein. Moreover, the drug exerted a significant
suppressive effect of H2O2 or APAP-induced
ROS production. Furthermore, the levels of TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-1β and
IL-6 were decreased in a concentration-dependent manner, while
IKKα/β, IκBα and p65 phosphorylation were significantly inhibited
(62). Paeonol has been documented
to exert neuroprotective effects by repressing TLR-2 and TLR-4,
Iba1, NF-κB (p50) and IL-1β, as well as by suppressing apoptosis in
a Sprague-Dawley rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
(63). Lee et al (64) evaluated the renal toxic effects of
paeonol and reported that it downregulated TNF-α, IL-1β and NO, as
well as decreased blood urea nitrogen and serum creatine levels
(64). Key signaling pathways and
mediators downregulated by paeonol in vitro or in
vivo are presented in Fig. 1.
The in vitro or in vivo mechanisms mentioned above
are presented in Table II. In
summary, paeonol has the capacity to be employed for the treatment
of hepatotoxicity, acute liver diseases, liver failure,
gastrointestinal disorders, ulcerative colitis, renal disorders and
neurological conditions. However, further transcriptomics studies
are required to elucidate its molecular mechanisms and maximize its
therapeutic application in medical settings.
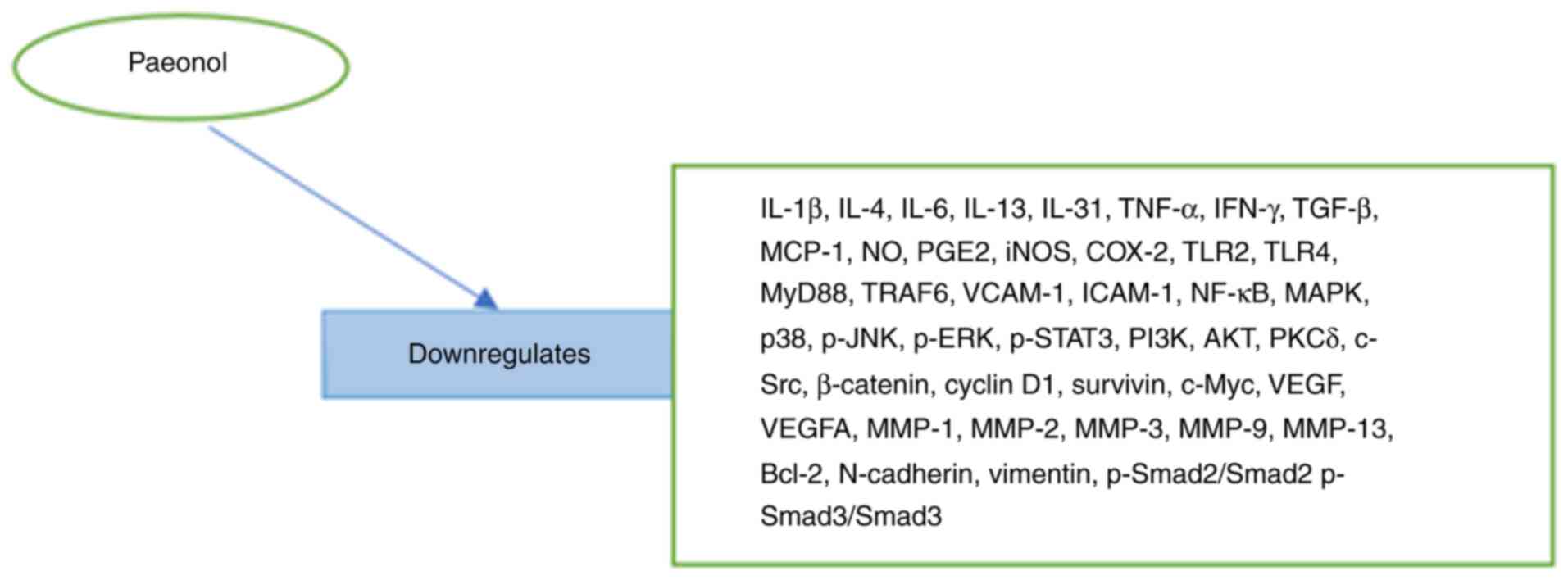 | Figure 1Key signaling pathways and mediators
downregulated by paeonol described above. IL, interleukin; TNF-α
tumor necrosis α; IFN-γ, interferon γ; TGF-β tumor growth factor β;
MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein; NO, nitric oxide; PGE2,
prostaglandin E2; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2,
cyclooxygenase 2; TLR, Toll-like receptor; MyD88, myeloid
differentiation primary response 88; IRAK4, interleukin 1 receptor
associated kinase 4; TRAF6, TNF receptor associated factor 6;
VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; ICAM-1, intercellular
adhesion molecule 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; MAPK,
mitogen-activated protein kinase; p38, 38-kDa mitogen-activated
protein kinase; p- JNK, phosphorylated Jun N-terminal kinase;
p-ERK, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase; STAT3,
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; P13K,
phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, serine/threonine kinase; PKCδ,
protein kinase Cδ; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MMP,
matrix metalloproteinase; Bcl-2, B cell lymphoma 2. |
 | Table IIIn vitro or in vivo
immunosuppressive effects of paeonol. |
Table II
In vitro or in vivo
immunosuppressive effects of paeonol.
| Authors, year of
publication | Study type | Mechanism of
action | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Niu et al,
2024 | In
vitro | Regulates M1/M2
polarization of macrophages | (49) |
| Chen et al,
2022 | In
vitro | Suppresses IL-1β
and inhibits NLRP3, NF-κB, and MAPK activated pathways | (52) |
| He et al,
2016 | In
vitro | Represses NO, IL-1β
and PGE2, as well as the expression of iNOS and COX-2; reduces
TLR4, MyD88, IRAK4, TNFR-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), p-IkB-α, and
NF-κB p65, as well as p-p38, p-JNK, and p-ERK | (53) |
| Ping et al,
2014 | In
vitro | Upregulates NO,
iNOS, downregulates ROS, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and MCP-1 through the
RAGE-, CD36-, SR-A- and SR-B1-mediated pathway | (28) |
| Li et al,
2023 | In vivo | Modulating
microglial M1 and M2 polarization via the RhoA/p38MAPK pathway | (54) |
| Ge et al,
2021 | In vivo | Decreases the
dectin-1/NF-κB pathway together with TLR2 and TLR4 | (27) |
| Adki et al,
2021 | In vivo | Suppresses NF-κB
and MCP-1 | (55) |
| Wu et al,
2020 | In vivo | Suppresses the
dectin-1/IL-1β signaling pathway | (56) |
| Wu et al,
2019 | In vivo | Inhibits
TGF-β/Smad3 and downregulates IL-6 and TNF-α | (57) |
| Li et al,
2019 | In vivo | Upregulates Nrf2 to
downregulate NF-κB/NFATc1 | (58) |
| Tang et al,
2018 | In vivo | Downregulates IFN-γ
and upregulates IL-4, suppresses TLR4/NF-κB and MAPK pathway | (59) |
| Gong et al,
2017 | In vivo | Suppresses iNOS,
nitric oxide, COX-2, prostaglandin E2 and inhibitsNF-κB, and MAPK
pathways as well as decreased hepatocyte apoptosis | (60) |
| Zong et al,
2017 | In vivo | Decreases IL-17 and
IL-6 and upregulates TGF-β1 | (61) |
| Ding et al,
2016 | In vivo | Suppresses c-Jun
N-terminal kinase and decreases TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-1β, IL-6 and
inhibits IKKα/β, IκBα and p65 phosphorylation | (62) |
| Liao et al,
2016 | In vivo | Represses TLR2,
TLR4, Iba1-, NF-κB- (P50-), and IL-1β and inhibits apoptosis | (63) |
| Lee et al,
2013 | In vivo | Downregulates
TNF-α, IL-1β and nitric oxide | (64) |
6. Clinical trials
A recent phase 2a randomized, placebo-controlled
trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination
of apocynin (AP) and paeonol (PA) (APPA) in patients with
symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) (65). The study enrolled 152 participants
with Kellgren-Lawrence grade 2-3 knee OA and moderate to severe
pain (WOMAC pain ≥40/100). Over a period of 28 days, APPA at 800 mg
twice daily demonstrated no statistically significant improvement
in primary (WOMAC pain) or secondary outcomes (WOMAC function and
total score) compared to the placebo. However, predefined subgroup
analyses revealed a significant benefit of APPA in participants
with nociplastic or neuropathic pain features. The treatment was
well-tolerated with mild to moderate adverse events, primarily
gastrointestinal. These findings highlight the safety profile of
APPA and suggest its potential efficacy in specific OA subgroups,
warranting further targeted research (65).
7. Chemopreventive potential of paeonol
The antitumor effects of paeonol on breast (14,24,36,66,67),
bladder (68), colorectal (23,69),
colon (70), gastric (22,71,72),
lung (73-75),
osteosarcoma (76), ovarian
(77-81),
prostate (82), chondrosarcoma
(83), pancreatic (84), cervical (33,85),
melanoma (25), renal (86), hepatocellular (87-89)
and oral (90) cancers have been
documented.
In a previous study, paeonol induced the apoptosis
of breast cancer by regulating CXCL4/CXCR3-B signaling to
downregulate heme oxygenase and Nrf2 to upregulate BACH1(14). In another study, paeonol and
epirubicin synergistically inhibited tumor growth and promoted
apoptosis via the activation of PARP, Bax and caspase-3 by
suppressing p38/JNK/ERK MAPKs compared to epirubicin alone
(36). Additionally, paeonol
inhibited the NF-κB pathway to alleviate epirubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity (36). Zhang et
al (66) demonstrated that
paeonol downregulated SET, protein phosphatase 2A and the PI3K/Akt
pathway to prevent paclitaxel resistance in MCF-7/PTX cells. In a
similar study, paeonol decreased P-glycoprotein, multidrug
resistance associated protein 1, and breast cancer resistance
protein to suppress transgelin 2-mediated paclitaxel resistance
(67). In another study, the
significant decrease in tumor weight observed by morphological
analysis using hematoxylin and eosin staining, as well as TUNEL
staining indicated that paeonol induced the apoptosis of tumor
cells (24). Moreover,
immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis demonstrated that
the downregulation of Bcl-2 led to the upregulation of Bax,
caspase-8 and caspase-3 to confirm the induction of apoptosis as
the mechanism of inhibition employed by paeonol (24). In a recent study, the administration
of paeonol exerted an inhibitory effect on cell proliferation and
induced both in vitro and in vivo apoptosis by
decreasing the Bcl-2/Bax ratio with the upregulation of
caspase-3(68). The drug also
suppressed the PI3K/AKT pathway in the inhibition of bladder cancer
cell growth (68). In colorectal
cancer (CRC), paeonol administration has been shown to induce
apoptosis and arrest the cell cycle at the G0/G1-phase (69). Additionally, the drug downregulated
β-catenin, cyclin D1, survivin and c-Myc in a
concentration-dependent manner to suppress the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway (69). Li et
al (23) investigated the
effects of paeonol on CRC cells and revealed that paeonol
suppressed cell proliferation by reducing COX-2 and PGE2
expression, and induced mitochondrial pathway apoptosis in a
time-dependent manner. The apoptotic mechanism was associated with
the upregulation of Bax and decreased Bcl-2 expression.
Furthermore, the drug activated caspase-3 and caspase-9 and induced
the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (23). Flow cytometry analysis performed by
Li et al (70) demonstrated
that paeonol induced apoptosis and arrested the cell cycle at the
G1 to S transition phase. Moreover, the treatment led to an
upregulated intracellular calcium concentration and RUNX3
expression suggesting its antitumor mechanism (70). The administration of paeonol
suppressed apatinib-resistant gastric cancer cell malignancy by
downregulating LINC00665 and MAPK1, while upregulating
miR-665(71). Paeonol has been shown
to inhibit the NF-κB pathway by decreasing ERBB2 expression to
suppress the proliferation of gastric cancer and induce apoptosis
(72). The anticancer mechanism of
paeonol has been shown to be associated with the downregulation of
MMP-2 and-9 in a concentration-dependent manner to prevent invasion
and migration (22). The anticancer
effects of paeonol on lung cancer have been reported to be
associated with the upregulation of miR-126-5p and the
downregulation of zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 to suppress
cell viability and metastasis (73).
In another study, paeonol repressed TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and TGF-β in
the inhibition of non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation,
invasion and migration by suppressing the STAT3/NF-κB pathway
(74). Lei et al (75) reported that paeonol improved
radiation-induced apoptosis via the suppression of the PI3K/AKT
pathway to decrease downstream COX-2 and survivin. Recently, Zhou
et al (76) investigated the
effects of paeonol on osteosarcoma. They reported that the
antitumor mechanisms were associated with the suppression of the
invasion and migration potential, as well as the suppression of
TLR4 to inhibit the activation of the MAPK/NF-κB downstream
signaling pathway (76). In ovarian
cancer, paeonol has been shown to suppress Akt/mTOR signaling by
upregulating autophagy (77). Han
et al (78) demonstrated that
paeonol activated PTEN to suppress P-glycoprotein, multidrug
resistant mutation 1 and metadherin to overturn resistant ovarian
cancer. In another study, paeonol induced apoptosis via the
upregulation of caspase-3 and caspase-9, and decreased p-Akt and
p-GSK-3β signaling to inhibit ovarian cell proliferation (79). Zhou et al (80) demonstrated that paeonol increased the
responsiveness of ovarian cancer cells to radiotherapy-induced
apoptosis by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/phosphatase, VEGF and HIF-1α
pathways. In another study, cell viability, apoptosis, caspase-3
and survivin levels were evaluated by MTT assay, flow cytometry and
Hoechst staining, and western blot analysis, respectively (81). The results revealed that cell
viability was decreased, and apoptosis induced. Additionally,
caspase-3 expression was upregulated and survivin protein
expression was downregulated (81).
In another study, paeonol administered in vivo and in
vitro to human prostate cancer decreased tumor cell
proliferation and suppressed tumor growth (82). In the process, the drug induced
apoptosis which resulted in the upregulation of caspase-3,
caspase-8, and caspase-9 levels and the downregulation of Bcl-2
with an enhanced Bax expression. Moreover, the activated PI3K/Akt
pathway was inhibited. These findings suggest that the drug induces
apoptosis by activating both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways,
and via the suppression PI3K/Akt pathway to inhibit tumor cell
growth (82). Another study
demonstrated that paeonol administration increased miR-141 by
downregulating the protein kinase Cδ and c-Src pathway in the
suppression of metastatic chondrosarcoma (83). Paeonol has been reported to possess
anti-metastatic properties in pancreatic cancer. Researchers
employed cell scratch-wound healing assay and Boyden chamber
invasion assay to evaluate the migration and invasion abilities
(84). In addition, the RNA and
protein levels of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, vimentin and TGF-β1/Smad
pathway were determined using RT-qPCR and western blot analysis.
The findings revealed that paeonol suppressed
epithelial-mesenchymal-transition by enhancing E-cadherin and
reducing N-cadherin and vimentin. The expression levels of TGF-β1,
p-Smad2/Smad2 and p-Smad3/Smad3 were also decreased to suppress the
TGF-β1/Smad pathway (84). Paeonol
induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway and inhibits the
PI3K/Akt pathway in the suppression of cervical cancer (85). It has been demonstrated that paeonol
decreases 5-lipoxygenase to promote apoptosis in the inhibition of
cervical cancer migration and invasion (33). It has been documented that paeonol
suppresses cell proliferation, induces apoptosis and inhibits
pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated NF-κB and STAT3 signaling in the
inhibition of melanoma metastasis (25). A previous study on renal cell
carcinoma revealed that paeonol reduced the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in the
induction of apoptosis and downregulated VEGFA to inhibit cell
proliferation, invasion and metastasis (86). In another in vitro and in
vivo study, paeonol downregulated miR-21-5p to upregulate KLF6
to promote apoptosis and inhibit the proliferation, migration and
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells (87). Li et al (88) evaluated the apoptotic activity of
paeonol in hepatocellular carcinoma and reported that the drug
decreased NF-κB p65/50 and protein apoptosis inhibitor-5 in the
promotion of apoptosis and suppressed NF-κB signaling pathway. Fan
et al (89) demonstrated the
ability of paeonol to overturn endoplasmic reticulum
stress-promoted resistance to doxorubicin by downregulating COX-2
to inactivate the PI3K/AKT/CHOP pathway. Paeonol has been reported
to suppress tumor growth and promotes apoptosis by inhibiting
mutant p53 and COX-2 and upregulating caspase-9 in
7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced oral carcinogenesis
(90). The mechanism of paeonol in
tumor immunity revealed that the drug downregulates PD1 via
upregulating miR-139-5p to suppress melanoma growth (91). Research on aminothiazole-paeonol
derivatives has shown that these compounds exhibit higher potency
against AGS (gastric) and HT-29 (colorectal) human cancer cell
lines compared to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a commonly used
chemotherapeutic agent. Additionally, these derivatives
demonstrated lower cytotoxicity towards normal cells, suggesting a
potentially improved therapeutic index (92). Key signaling pathways and mediators
downregulated by paeonol are illustrated in Fig. 1. The chemopreventive mechanisms
mentioned above are presented in Table
III.
 | Table IIIIn vitro and in vivo
chemopreventive effects of paeonol. |
Table III
In vitro and in vivo
chemopreventive effects of paeonol.
| Authors, year of
publication | Study type | Mechanism of
action | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Saahene et
al, 2018 | In
vitro | Regulates
CXCL4/CXCR3-B signal to downregulate heme oxygenase (HO-1) and
nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) to upregulate BACH1 to
induce apoptosis in breast cancer | (14) |
| Wu et al,
2016 | In vivo and
in vitro | Induces apoptosis
via activation of PARP, Bax, caspase 3 and suppresses MAPKs/NF-κB
pathways in breast cancer | (35) |
| Zhang et al,
2015 | In
vitro | Decreases SET,
protein phosphatase 2A and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt
pathway in breast cancer | (66) |
| Cai et al,
2014 | In
vitro | Decreases
P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance associated protein 1, and
breast cancer resistance protein to suppress transgelin 2
resistance | (67) |
| Qu et al,
2014 | In
vitro | Downregulates
Bcl-2, upregulates Bax, caspase-8 and caspase-3 to induce breast
cancer apoptosis | (24) |
| Zhang et al,
2021 | In vivo and
in vitro | Decreases Bcl-2/Bax
ratio upregulates caspase 3 and suppresses PI3K/AKT pathway in
bladder cancer | (68) |
| Liu et al,
2020 | In
vitro | Induces apoptosis,
arrest the cell cycle at G0/G1-phase, downregulates β-catenin,
cyclin D1, survivin and c-Myc to suppress Wnt/β-catenin pathway in
colorectal cancer | (69) |
| Li et al,
2014 | In vivo and
in vitro | Decreases
cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 and decreased Bcl-2 and
upregulates Bax, caspase 3 and caspase 9 in colorectal cancer | (23) |
| Li et al,
2013 | In
vitro | Induces apoptosis,
arrests the cell cycle at the G1 to S transition phase;
upregulation of intracellular calcium concentration and RUNX3 in
colon cancer | (70) |
| Li et al,
2022 | In
vitro | Downregulation of
LINC00665 and MAPK1, upregulating miR-665 in gastric cancer | (71) |
| Fu et al,
2018 | In
vitro | Inhibits NF-κB by
decreasing ERBB2 and induces apoptosis gastric cancer | (72) |
| Lyu et al,
2017 | In
vitro | Downregulation of
MMP-2 and MMP-9 in gastric cancer | (22) |
| Lv et al,
2022 | In
vitro | Upregulates
miR-126-5p and downregulates ZEB2 to suppress cell viability and
metastasis in lung cancer | (73) |
| Zhang et al,
2020 | In vivo and
in vitro | Inhibits TNF-α,
IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β and suppressed STAT3/NF-κB pathways in lung
cancer | (74) |
| Lei et al,
2013 | In
vitro | Enhances apoptosis,
suppression of PI3K/AKT pathway and decreased cyclooxygenase-2 and
survivin in lung cancer | (75) |
| Zhou et al,
2020 | In vivo and
in vitro | Suppresses TLR4 to
inhibit MAPK/NF-κB to prevent invasion and migration and induces
apoptosis in osteosarcoma | (76) |
| Gao et al,
2019 | In vivo and
in vitro | Suppresses Akt/mTOR
signal by upregulating autophagy in ovarian cancer | (77) |
| Han et al,
2018 | In
vitro | Upregulation of
PTEN suppresses P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistant mutation 1 and
metadherin in ovarian cancer | (78) |
| Li et al,
2017 | In
vitro | Upregulates
caspase-3 and caspase-9 to induces apoptosis and decreased
phosphorylated-Akt and phosphorylated-GSK-3β in ovarian cancer | (79) |
| Zhou et al,
2017 | In
vitro | Inhibits P13K/Akt,
VEGF and HIF-1α pathways via radiation induced apoptosis in ovarian
cancer | (80) |
| Yin et al,
2013 | In
vitro | Upregulates
caspase-3 and downregulate of survivin to induce apoptosis in
ovarian cancer | (81) |
| Xu et al,
2017 | In vivo and
in vitro | Upregulates
caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 events and downregulated Bcl-2
with an enhanced Bax; inhibits P13K/Akt pathway in prostate
cancer | (82) |
| Horng et al,
2014 | In
vitro | Increases miR-141
and downregulated protein kinase C (PKC) δ and c-Src pathways in
chondrosarcoma | (83) |
| Cheng et al,
2020 | In
vitro | Increases
E-cadherin and reduced N-cadherin and vimentin; decreased TGF-β1,
p-Smad2/Smad2 and p-Smad3/Smad3 in pancreatic cancer | (84) |
| Du et al,
2021 | In
vitro | Downregulates
Bcl-2/Bax proportion, upregulated caspase-3 by inhibiting P13K/Akt
pathway in cervical cancer | (85) |
| Sheng et al,
2021 | In
vitro | Downregulates
5-lipoxygenase to promote apoptosis to prevent invasion and
migration in cervical cancer. | (33) |
| Zhang et al,
2015 | In vivo and
in vitro | Induces apoptosis
and inhibits proinflammatory cytokines mediated NF-κB and STAT3
signaling to prevent melanoma metastasis | (25) |
| Chen et al,
2022 | In
vitro | Increases Bax
decreased Bcl-2 and downregulated VEGFA to prevent invasion and
metastasis in renal cell carcinoma | (86) |
| Cai et al,
2020 | In vivo and
in vitro | Downregulates
miR-21-5p to upregulate KLF6 in the promotion of apoptosis and
inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma. | (87) |
| Li et al,
2019 | In
vitro | Decreases NF-κB
p65/50 and protein apoptosis inhibitor-5 in the induction of
apoptosis and suppressed NF-κB pathway in HCC | (88) |
| Fan et al,
2013 | In
vitro | Downregulates COX-2
to inactivate the PI3K/AKT/CHOP pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. | (89) |
| Ramachandhiran
et al, 2018 | In vivo | Promotes apoptosis
by inhibiting mutant p53 and COX-2 and upregulating caspase-9 in
oral carcinogenesis | (90) |
The chemopreventive capacity of paeonol relies on
its multifaceted anticancer mechanisms by directly inhibiting cell
growth and proliferation, inducing apoptosis, suppressing invasion
and metastasis (MMP-2 and-9, VEGF and HIF-1α), and inhibiting the
TLR4/NF-κB/STAT3/MAPK/PI3K/AKT/CHOP pathways to inhibit cancer
development and progression. Moreover, the drug has demonstrated
potential for combination therapy and synergy with natural
compounds, by improving their potency while potentially reducing
their harmful effects. Additionally, paeonol reduces drug
resistance in breast cancer and ovarian cancer, by decreasing drug
efflux transporters and overturning resistance-associated signaling
pathways.
Whilst there are data demonstrating the anticancer
potential of paeonol, a search through published literature
revealed limited in vitro and in vivo information
regarding the toxicity of the compound on normal cells and organs.
On the contrary, there is a huge volume of data on its ability to
protect against chemical induced toxicity (26,35,62).
Subchronic toxicity studies in male and female laboratory rats
showed no major safety concerns (64,93).
This attests to the potential of paeonol as a safe alternative
agent for immunomodulation.
8. Clinical relevance and therapeutic
effects on the NF-κB, MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways
The NF-κB signaling pathway is crucial in regulating
immune responses and inflammation. Paeonol has been shown to
inhibit this pathway, thereby reducing the expression of
pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting apoptosis in cancer cells.
For instance, studies have demonstrated that paeonol can
effectively decrease NF-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells, leading to enhanced apoptosis and reduced cell proliferation
(88,94). The inhibition of NF-κB in preclinical
models by paeonol has been associated with decreased tumor growth
and improved outcomes in inflammatory conditions such as ulcerative
colitis (94,95).
The MAPK pathway is essential in cellular response
to stress and growth. The regulation of MAPK by paeonol has been
demonstrated to be linked to suppressed cell migration and invasion
in lung cancer models, indicating its significant anti-metastatic
potential (74,94). The dysregulation of the MAPK cascade
by paeonol, not only inhibits cancer growth, but also alleviates
inflammation in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases or
cancer (74,96).
The PI3K/AKT pathway modulates cell survival,
proliferation and metabolism, and its hyperactivation is commonly
associated with cancer progression and resistance to apoptosis.
Paeonol has demonstrated the ability to inhibit PI3K/AKT signaling
to induce apoptosis and suppress tumor growth (68,75,82,94,97). The
PI3K/AKT signaling modulation by paeonol has been linked to an
improved sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents and diminished
adverse effects from treatment, suggesting its potential as an
adjunct therapy in distinct populations (66,94,97).
9. Conclusion and future perspectives
Paeonol, a bioactive component of Cortex moutan has
shown promise as a naturally occurring pharmacological agent for
suppressing immunological events in a variety of human diseases.
The mechanism is attributed to its multifactorial activities,
including immunomodulatory effects, anti-inflammatory effects and
antioxidant properties. Overall, paeonol decreases IL-1β expression
to repress several inflammatory mediators, such as NO, iNOS, COX2,
PEG2 in the inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB, MAPK and
TLR4 pathways to provide multiple levels immunosuppressive effects
of immune-related diseases. Current research demonstrates the
anti-inflammatory properties of paeonol through the suppression of
cytokines and the modulation of immune pathways. However, further
investigations are required to focus on RNA-seq analyses to
identify global gene expression changes in response to paeonol.
Moreover, integrating multi-omics approaches (e.g.,
transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics) to build a
systems-level understanding of the actions of paeonol could
ultimately lead to the development of improved therapeutic
strategies for conditions characterized by inflammation. The
present review suggests that paeonol may serve as an alternative
immunomodulator to conventional therapeutic agents; however, its
probable negative effects in clinical applications need to be
assessed. The repression of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways may not
only reduce pro-inflammatory determinants, but may also attenuate
the induction of certain key factors in the immune response. Thus,
the effects of paeonol on different cytokines, inflammatory
mediators and immune responses signaling pathways need to be
explored. There are limited reports available of its application in
relation to the cells of the immune system, effector mechanisms and
phagocytosis, and thus, further studies are warranted.
As regards cancers, it has been reported that
paeonol directly suppresses the proliferation and growth of several
cancer cells, arrests the cancer cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and
prevents invasion and metastasis. Furthermore, the drug inhibits
cancer cell growth and proliferation through the suppression of the
VEGF, HIF-1α, TLR4/ NF-κB/STAT3/MAPK/PI3K/AKT/CHOP pathways.
Despite promising preclinical findings, there is a notable lack of
clinical trial studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of
paeonol treatment for human diseases. This underscores the need to
conduct large-scale, multicenter clinical trials to validate
preclinical findings in conditions such as asthma, atopic
dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis, kidney injury and
hepatotoxicity, breast cancer, gastric cancer and ovarian cancer to
assess the therapeutic efficacy and safety of this drug in diverse
patient populations. Moreover, exploring the synergistic effects of
paeonol in combination with paclitaxel, epirubicin, doxorubicin,
and apatinib in cancer treatment is warranted.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
PB and ROS were involved in the conceptualization
and design of the review, as well as in the drafting and writing of
the manuscript. EA, FHL, KD, SVN, DOY and ESY were involved in the
literature review, and in the drafting of the manuscript. All
authors have read, edited and approved the final manuscript. Data
authentication is not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Use of artificial intelligence tools
During the preparation of this work, AI tools were
used to improve the readability and language of the manuscript and
subsequently, the authors revised and edited the content produced
by the AI tools as necessary, taking full responsibility for the
ultimate content of the present manuscript.
References
|
1
|
Jantan I, Haque MA, Ilangkovan M and
Arshad L: An insight into the modulatory effects and mechanisms of
action of Phyllanthus species and their bioactive metabolites on
the immune system. Front Pharmacol. 10(878)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Greenberg S and Grinstein S: Phagocytosis
and innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 14:136–145. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Janeway C, Travers P, Walport M and
Shlomchik M: Immunobiology. In: TheImmune System in Health and
Disease. Vol 2: Garland Science, New York, 2001.
|
|
4
|
Siracusano A, Riganò R, Ortona E, Profumo
E, Margutti P, Buttari B, Delunardo F and Teggi A: Immunomodulatory
mechanisms during Echinococcus granulosus infection. Exp Parasitol.
119:483–489. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
M. D. Bagatini, ‘Immune System and Chronic
Diseases 2018.’.
|
|
6
|
Wolska K, Górska A, Antosik K and Ługowska
K: Immunomodulatory effects of propolis and its components on basic
immune cell functions. Indian J Pharm Sci. 81:575–588. 2019.
|
|
7
|
Ilangkovan M, Jantan I, Mesaik MA and
Bukhari SNA: Immunosuppressive effects of the standardized extract
of Phyllanthus amarus on cellular immune responses in Wistar-Kyoto
rats. Drug Des Devel Ther. 26:4917–4930. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khandelwal V, Bhati A and Anjana G:
Immunomodulatory activity of hot aqueous extract of Anthocephalus
cadamba leaves in albino rats. Adv Bioresearch. 7:203–206.
2016.
|
|
9
|
Stromberg SP and Carlson JM: The
suppression of immune system disorders by passive attrition. PLoS
One. 5(e9648)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Okoye AA and Picker LJ: CD 4+ T-cell
depletion in HIV infection: Mechanisms of immunological failure.
Immunol Rev. 254:54–64. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wherry EJ and Kurachi M: Molecular and
cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol.
15:486–499. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Alpdogan O and van den Brink MR: Immune
tolerance and transplantation. Semin Oncol. 39:629–642.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Redman JM, Gibney GT and Atkins MB:
Advances in immunotherapy for melanoma. BMC Med. 14:1–11.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Saahene RO, Wang J, Wang ML, Agbo E and
Pang D: The antitumor mechanism of paeonol on CXCL4/CXCR3-B signals
in breast cancer through induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 33:233–240. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pang KL, Vijayaraghavan K, Al Sayed B and
Seyed MA: Betulinic acid-induced expression of nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide phosphate-diaphorase in the immune organs of mice: A
possible role of nitric oxide in immunomodulation. Mol Med Rep.
17:3035–3041. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu M, Yu Z, Li X, Zhang X, Wang S, Yang S,
Hu L and Liu L: Paeonol for the treatment of atherosclerotic
cardiovascular disease: A pharmacological and mechanistic overview.
Front Cardiovasc Med. 8(690116)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Meng Y, Wang M, Xie X, Di T, Zhao J, Lin
Y, Xu X, Li N, Zhai Y, Wang Y and Li P: Paeonol ameliorates
imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice by
inhibiting the maturation and activation of dendritic cells. Int J
Mol Med. 39:1101–1110. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fan HY, Qi D, Yu C, Zhao F, Liu T, Zhang
ZK, Yang MY, Zhang LM, Chen DQ and Du Y: Paeonol protects
endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury: Potential mechanism of
inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway. Oncotarget. 7:39497–39510.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Du Q, Feng GZ, Shen L, Cui J and Cai JK:
Paeonol attenuates airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a
murine model of ovalbumin-induced asthma. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
88:1010–1016. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim SH, Kim SA, Park MK, Kim SH, Park YD,
Na HJ, Kim HM, Shin MK and Ahn KS: Paeonol inhibits anaphylactic
reaction by regulating histamine and TNF-α. Int Immunopharmacol.
4:279–287. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yuan C, Xu X, Wang N, Zhu Q, Zhang J, Gong
W, Ding Y, Xiao W, Chen W, Lu G, et al: Paeonol protects against
acute pancreatitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization via the
NLRP3 inflammasomes pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 600:35–43.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lyu ZK, Li CL, Jin Y, Liu YZ, Zhang X,
Zhang F, Ning LN, Liang ES, Ma M, Gao W, et al: Paeonol exerts
potential activities to inhibit the growth, migration and invasion
of human gastric cancer BGC823 cells via downregulating MMP-2 and
MMP-9. Mol Med Rep. 16:7513–7519. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li M, Tan SY and Wang XF: Paeonol exerts
an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through
inhibition of PGE2 synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncol Rep.
32:2845–2853. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ou Y, Li Q, Wang J, Li K and Zhou S:
Antitumor and apoptosis induction effects of paeonol on mice
bearing EMT6 breast carcinoma. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 22:341–346.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Tao L, Shi T, Zhang F, Sheng X,
Cao Y, Zheng S, Wang A, Qian W, Jiang L and Lu Y: Paeonol inhibits
B 16 F 10 melanoma metastasis in vitro and in vivo via disrupting
proinflammatory cytokines-mediated NF-κB and STAT 3 pathways. IUBMB
life. 67:778–788. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu MH, Lin AH, Lee HF, Ko HK, Lee TS and
Kou YR: Paeonol attenuates cigarette smoke-induced lung
inflammation by inhibiting ROS-sensitive inflammatory signaling.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014(651890)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ge Y, Pan M, Zhang C, Wang C, Ma K, Yan G,
Wang T, Wu D and Shao J: Paeonol alleviates dextran sodium sulfate
induced colitis involving Candida albicans-associated dysbiosis.
Med Mycol. 59:335–344. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ping M, Xiao W, Mo L, Xiao X, Song S, Tang
W and Yang X: Paeonol attenuates advanced oxidation protein
product-induced oxidative stress injury in THP-1 macrophages.
Pharmacology. 93:286–295. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu CM, Yang HX, Ma JQ, Yang W, Feng ZJ,
Sun JM, Cheng C, Li J and Jiang H: Role of AMPK pathway in
lead-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in kidney and in
paeonol-induced protection in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 122:87–94.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kang B, Park DH, Lee MJ, Jeon CY, Kang KS
and Choi YK: Beneficial effect of paeonol on antibiotic-associated
inflammatory response in mice with diarrhea. Biomolecules.
12(1634)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Meng Y, Liu Z, Zhai C, Di T, Zhang L,
Zhang L, Zhang L, Xie X, Lin Y, Wang N, et al: Paeonol inhibits the
development of 1-chloro-2, 4-dinitrobenzene-induced atopic
dermatitis via mast and T cells in BALB/c mice. Mol Med Rep.
19:3217–3229. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Miao J, Ye P, Lan J, Ye S, Zhong J,
Gresham A, Li S, You A, Chen X, Liu X and Li H: Paeonol promotes
the phagocytic ability of macrophages through confining HMGB1 to
the nucleus. Int Immunopharmacol. 89(107068)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sheng SQ, Yu LY, Zhou XW, Pan HY, Hu FY
and Liu JL: Paeonol prevents migration and invasion, and promotes
apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase.
Mol Med Rep. 23:1–8. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Pan M, Wang Q, Liu Y, Xiao N, Niu X, Wu D,
Wang T, Yan G and Shao J: Paeonol enhances treatment of fluconazole
and amphotericin B against oropharyngeal candidiasis through HIF-1α
related IL-17 signaling. Med Mycol. 60(myac011)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wu J, Xue X, Zhang B, Jiang W, Cao H, Wang
R, Sun D and Guo R: The protective effects of paeonol against
epirubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in 4T1-tumor bearing mice via
inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway. Chem Biol Interact.
244:1–8. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu J, Xue X, Zhang B, Cao H, Kong F, Jiang
W, Li J, Sun D and Guo R: Enhanced antitumor activity and
attenuated cardiotoxicity of Epirubicin combined with Paeonol
against breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 37:12301–12313. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhou ZQ: Taxonomy, geographic distribution
and ecological habitats of tree peonies. Genetic Resources and Crop
Evolution. 53:11–22. 2006.
|
|
38
|
Zhao M and Wu S: A review of the
ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology of tree peony (Sect.
Moutan). South African J Botany. 124:556–563. 2019.
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Fan H, Li Y, Sun X, Sun X, Wang W
and Zheng C: Analysis of genetic relationships in tree peony of
different colors using conserved DNA-derived polymorphism markers.
Scientia Horticulturae. 175:68–73. 2014.
|
|
40
|
He L, Suo Z, Zhang C, Jin X, Zhao D, Zhao
X, Hou B and Deng C: Classification of Chinese medicinal tree peony
cultivars based on chloroplast DNA sequences. Aasri Procedia.
1:344–352. 2012.
|
|
41
|
Feng Y, Yin L, Liu Y, Cao L, Zheng N, Li M
and Zhan S: Quantitative determination and optimun extraction
technique of nine compounds of Paeoniae Radix Alba. Zhejiang Da Xue
Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 49:356–363. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
42
|
Sun M, Huang L, Zhu J, Bu W, Sun J and
Fang Z: Screening nephroprotective compounds from cortex Moutan by
mesangial cell extraction and UPLC. Arch Pharm Res. 38:1044–1053.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jiao MJ, Deng Z, Zhang J, Wang SH, Cui WJ,
Zhang GY and Liu A: Preparation and quality standard of standard
decoction of Chinese herbal medicine containing volatile
components-case study of Moutan Cortex. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
43:891–896. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
44
|
Sun Y, Liu L, Shi XY, He H, Huang HW and
Dai M: Paeonol inhibits macrophage M1 polarization by
down-regulating miR-155/JAK1-STAT1 pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za
Zhi. 45:2158–2164. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
45
|
Liu Y, Li C, Wu H, Xie X, Sun Y and Dai M:
Paeonol attenuated inflammatory response of endothelial cells via
stimulating monocytes-derived exosomal MicroRNA-223. Front
Pharmacol. 9(1105)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lou Y, Wang C, Tang Q, Zheng W, Feng Z, Yu
X, Guo X and Wang J: Paeonol inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation
via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathways: In vivo and vitro studies.
Inflammation. 40:1698–1706. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lin C, Lin HY, Chen JH, Tseng WP, Ko PY,
Liu YS, Yeh WL and Lu DY: Effects of paeonol on
anti-neuroinflammatory responses in microglial cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:8844–8860. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen N, Liu D, Soromou LW, Sun J, Zhong W,
Guo W, Huo M, Li H, Guan S, Chen Z and Feng H: Paeonol suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokines in macrophage
cells and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 28:268–276. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Niu Y, Jin Y, Hao Y, Liang W, Tang F, Qin
Z, Liang T and Shi L: Paeonol interferes with lupus nephritis by
regulating M1/M2 polarization of macrophages. Mol Immunol.
169:66–77. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang Z, Chen T, Liu W, Xiong J, Jiang L
and Liu M: Paeonol accelerates skin wound healing by regulating
macrophage polarization and inflammation in diabetic rats. Korean J
Physiol Pharmacol. 27:437–448. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Miao J, Liu X, Liao Y, Li Y, Kuang Y,
Zheng J, Li Z and Lan J: Paeonol enhances macrophage phagocytic
function by modulating lipid metabolism through the P53-TREM2 axis.
Front Pharmacol. 14(1214756)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chen G, Guo T and Yang L: Paeonol reduces
IL-β production by inhibiting the activation of nucleotide
oligomerization domain-like receptor protein-3 inflammasome and
nuclear factor-κB in macrophages. Biochem Cell Biol. 100:28–36.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
He LX, Tong X, Zeng J, Tu Y, Wu S, Li M,
Deng H, Zhu M, Li X, Nie H, et al: Paeonol suppresses
neuroinflammatory responses in LPS-activated microglia cells.
Inflammation. 39:1904–1917. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li X, Shi H, Zhang D, Jing B, Chen Z,
Zheng Y, Chang S, Gao L and Zhao G: Paeonol alleviates neuropathic
pain by modulating microglial M1 and M2 polarization via the
RhoA/p38MAPK signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 29:2666–2679.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Adki KM and Kulkarni YA: Neuroprotective
effect of paeonol in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Life
Sci. 271(119202)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wu J, Wu D, Ma K, Wang T, Shi G, Shao J,
Wang C and Yan G: Paeonol ameliorates murine alcohol liver disease
via mycobiota-mediated Dectin-1/IL-1β signaling pathway. J Leucoc
Biol. 108:199–214. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wu S, Liu L, Yang S, Kuang G, Yin X, Wang
Y, Xu F, Xiong L, Zhang M, Wan J and Gong X: Paeonol alleviates
CCl4-induced liver fibrosis through suppression of hepatic stellate
cells activation via inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad3 signaling.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 41:438–445. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Li J, Li Y, Pan S, Zhang L, He L and Niu
Y: Paeonol attenuates ligation-induced periodontitis in rats by
inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via regulating Nrf2/NF-κB/NFATc1
signaling pathway. Biochimie. 156:129–137. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Tang Y, Huang W, Song Q, Zheng X, He R and
Liu J: Paeonol ameliorates ovalbumin-induced asthma through the
inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2018(3063145)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gong X, Yang Y, Huang L, Zhang Q, Wan RZ,
Zhang P, Wan RZ, Zhang P and Zhang B: Antioxidation,
anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis by paeonol in
LPS/d-GalN-induced acute liver failure in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 46:124–132. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zong SY, Pu YQ, Xu BL, Zhang T and Wang B:
Study on the physicochemical properties and anti-inflammatory
effects of paeonol in rats with TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis.
Int Immunopharmacol. 42:32–38. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ding Y, Li Q, Xu Y, Chen Y, Deng Y, Zhi F
and Qian K: Attenuating oxidative stress by paeonol protected
against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. PLoS One.
11(e0154375)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Liao WY, Tsai TH, Ho TY, Lin YW, Cheng CY
and Hsieh CL: Neuroprotective effect of paeonol mediates
anti-inflammation via suppressing toll-like receptor 2 and
toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathways in cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2016(3704647)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lee H, Lee G, Kim H and Bae H: Paeonol, a
major compound of moutan cortex, attenuates Cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity in mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013(310989)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Bihlet AR, Byrjalsen I, Andersen JR,
Reynolds A, Larkins N, Alexandersen P, Rovsing H, Moots R and
Conaghan PG: The efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of
apocynin and paeonol, APPA, in symptomatic knee OA: A double-blind,
randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 32:952–962. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhang W, Cai J, Chen S, Zheng X, Hu S,
Dong W, Lu J, Xing J and Dong Y: Paclitaxel resistance in MCF-7/PTX
cells is reversed by paeonol through suppression of the
SET/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep.
12:1506–1514. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Cai J, Chen S, Zhang W, Hu S, Lu J, Xing J
and Dong Y: Paeonol reverses paclitaxel resistance in human breast
cancer cells by regulating the expression of transgelin 2.
Phytomedicine. 21:984–991. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhang J, Cai L, Pang K, Dong Y, Zhang Z,
Li B, Li R and Han CH: Paeonol inhibits proliferation and induces
cell apoptosis of human T24 and 5637 bladder cancer cells in vitro
and in vivo. Clin Transl Oncol. 23:601–611. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Liu LH, Shi RJ and Chen ZC: Paeonol exerts
anti-tumor activity against colorectal cancer cells by inducing
G0/G1 phase arrest and cell apoptosis via inhibiting the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 46:675–684.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Li M, Tan SY, Zhang J and You HX: Effects
of paeonol on intracellular calcium concentration and expression of
RUNX3 in LoVo human colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:1425–1430.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Li M, Cai O, Yu Y and Tan S: Paeonol
inhibits the malignancy of Apatinib-resistant gastric cancer cells
via LINC00665/miR-665/MAPK1 axis. Phytomedicine.
96(153903)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Fu J, Yu L, Luo J, Huo R and Zhu B:
Paeonol induces the apoptosis of the SGC-7901 gastric cancer cell
line by downregulating ERBB2 and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 42:1473–1483. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Lv J, Zhu S, Chen H, Xu Y, Su Q, Yu G and
Ma W: Paeonol inhibits human lung cancer cell viability and
metastasis in vitro via miR-126-5p/ZEB2 axis. Drug Dev Res.
83:432–446. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhang L, Chen WX, Li LL, Cao YZ, Geng YD,
Feng XJ, Wang AY, Chen ZL, Lu Y and Shen AZ: Paeonol suppresses
proliferation and motility of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by
disrupting STAT3/NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol.
11(572616)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lei Y, Li HX, Jin WS, Peng WR, Zhang CJ,
Bu LJ, Du YY, Ma T and Sun GP: The radiosensitizing effect of
Paeonol on lung adenocarcinoma by augmentation of radiation-induced
apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Radiat
Biol. 89:1079–1086. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Zhou J, Liu Q, Qian R, Liu S, Hu W and Liu
Z: Paeonol antagonizes oncogenesis of osteosarcoma by inhibiting
the function of TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Acta Histochem.
122(151455)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Gao L, Wang Z, Lu D, Huang J, Liu J and
Hong L: Paeonol induces cytoprotective autophagy via blocking the
Akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
10(609)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Han L, Guo XJ, Chen Z, Bian H, Zhang CY,
Zang WH, Wang Q and Hu JL: The mechanisms of paeonol reversing
multidrug resistance in ovarian cancer SKOV3/DDP cells. Acta Pharm
Sin. 53:1511–1517. 2018.
|
|
79
|
Li B, Yang J, Hong L, Tang J, Li Q and Fu
Q: Paeonol induces apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through the
AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 10:10170–10178.
2017.
|
|
80
|
Zhou HM, Sun QX and Cheng Y: Paeonol
enhances the sensitivity of human ovarian cancer cells to
radiotherapy-induced apoptosis due to downregulation of the
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/phosphatase and tensin homolog
pathway and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp
Ther Med. 14:3213–3220. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Yin J, Wu N, Zeng F, Cheng C, Kang K and
Yang H: Paeonol induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells.
Acta Histochem. 115:835–839. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Xu Y, Zhu JY, Lei ZM, Wan LJ, Zhu ZW, Ye F
and Tong YY: Anti-proliferative effects of paeonol on human
prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC-3. J Physiol Biochem.
73:157–165. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Horng CT, Shieh PC, Tan TW, Yang WH and
Tang CH: Paeonol suppresses chondrosarcoma metastasis through
up-regulation of miR-141 by modulating PKCδ and c-Src signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 15:11760–11772. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Cheng CS, Chen JX, Tang J, Geng YW, Zheng
L, Lv LL, Chen LY and Chen Z: Paeonol inhibits pancreatic cancer
cell migration and invasion through the inhibition of TGF-β1/smad
signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal-transition. Cancer Manag Res.
29:641–651. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Du J, Song D, Li J, Li Y, Li B and Li L:
Paeonol triggers apoptosis in HeLa cervical cancer cells: The role
of mitochondria-related caspase pathway. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
239:1–10. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Chen Y, Jia Y, Li Y, Zheng Y, Chen G and
Shi Y: Investigation on the antitumor effects of paeonol against
renal cell carcinoma based on network pharmacology and experimental
validation. J Ethnopharmacol. 285(114857)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Cai M, Shao W, Yu H, Hong Y and Shi L:
Paeonol inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion and
induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
miR-21-5p/KLF6 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 17:5931–5943.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Li Q, Zhang Y, Sun J and Bo Q:
Paeonol-mediated apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
NF-κB pathway. Oncol Lett. 17:1761–1767. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Fan L, Song B, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F and
Wei W: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced resistance to
doxorubicin is reversed by paeonol treatment in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 8(e62627)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ramachandhiran D, Vinothkumar V and
Babukumar S: Paeonol exhibits anti-tumor effects by apoptotic and
anti-inflammatory activities in 7,12-dimethylbenz (a) anthracene
induced oral carcinogenesis. Biotech Histochem. 94:10–25.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Chen X, Xu Z, Lu M, Ding W, Zhong J, Deng
S, Li S, Miao J, Liu X, Wen Q, et al: Paeonol inhibits melanoma
growth by targeting PD1 through upregulation of miR-139-5p. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 656:86–96. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Tsai CY, Kapoor M, Huang YP, Lin HH, Liang
YC, Lin YL, Huang SC, Liao WN, Chen JK, Huang JS and Hsu MH:
Synthesis and evaluation of aminothiazole-paeonol derivatives as
potential anticancer agents. Molecules. 21(145)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Adki KM, Murugesan S and Kulkarni YA: In
silico and in vivo toxicological evaluation of paeonol. Chem
Biodivers. 17(e2000422)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Chang X, Feng X, Du M, Li S, Wang J, Wang
Y and Liu P: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of paeonol on
antitumor and prevention of side effects of cancer therapy. Front
Pharmacol. 14(1194861)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Cheng S, Chen W, Guo Z, Ding C, Zuo R,
Liao Q and Liu G: Paeonol alleviates ulcerative colitis by
modulating PPAR-γ and nuclear factor-κB activation. Sci Rep.
14(18390)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Himaya S, Ryu B, Qian ZJ and Kim SK:
Paeonol from Hippocampus kuda Bleeler suppressed the
neuro-inflammatory responses in vitro via NF-κB and MAPK signaling
pathways. Toxicology In Vitro. 26:878–887. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Morsy MA, Ibrahim YF, Hafez SMN, Zenhom
NM, Nair AB, Venugopala KN, Shinu P and Abdel-Gaber SA: Paeonol
attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating the
Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB signaling pathways. Antioxidants
(Basel). 11(1687)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|















