Introduction
A somatic point mutation in the JAK2 gene,
1849G>T, which changes amino acid residue 617 of the kinase from
valine to phenylalanine (termed JAK2 V617F), has been identified by
various studies in a substantial number of Philadelphia
chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasm (Ph-MPN) patients
(1). This mutation has also been
identified in a small number of other myeloid malignancies
(2,3), however, rarely presents in lymphoid
malignancies (4,5). Following a search of the English
language literature between 2006 and January 2013 using the search
terms ‘B-cell lymphocytic leukemia’ (B-CLL) and ‘JAK2’, 28 JAK2
V617F-positive B-CLL patients were identified (6–15). All
of these patients exhibited a Ph-MPN concomitantly. The coexistence
of two chronic myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms in a patient raises
the possibility that the neoplasms are derived from the same
pluripotent stem cell, however, they may be purely coincidental.
This led to the retrospective analysis of the JAK2 V617F mutation
in 63 B-CLL patients that were diagnosed at the Department of
Hematology (Shanghai First People’s Hospital, Shanghai, China)
between January 2008 and December 2012. Two B-CLL patients were
identified to carry the JAK2 V617F allele. Notably, these two
patients did not have a history of Ph-MPN, which is not consistent
with the previously reported cases. Patients provided written
informed consent.
Case reports
Case 1
A 57-year-old male patient was admitted to the
Department of Hematology (Shanghai First People’s Hospital,
Shanghai, China) with leukocytosis in September 2006. The patient’s
whole blood count (WBC) was elevated (14.5×109/l;
reference range, 3.97–9.15×109/l), while the hemoglobin
(Hb) and platelet (PLT) counts were within the reference ranges
[14.7 g/dl (reference range, 13.1–17.2 g/dl) and
231×109/l (reference range, 85–303×109/l),
respectively]. The circulating lymphocyte percentage was 49%. In
the bone marrow (BM), the cellularity and lymphocyte compartment
size were increased. Clinical examination revealed an enlarged
spleen and flow cytometric analysis of the patient’s peripheral
blood (PB) exhibited the B-CLL phenotype. The total lymphocyte
count was 7.1×109/l and gated CD45+ cells
showed positivity for cluster of differentiation (CD)19 (88.4%),
CD20 (39%), CD5 (65.9%), CD41 (16.9%) and HLA-DR (93.2%). The
patient was negative for CD38 (5.1%) and ZAP70 (2.6%). The
diagnosis of stage II B-CLL was determined according to the Rai
classification (16). The patient
was followed up for four years with fludarabine (50
mg/m2 on days one to five) treatment. Blood examination
showed that the WBC was between 6.3 and 40×109/l, the
lymphocyte percentage was between 45 and 79%, the Hb level was
between 139 and 149 g/l and the PLT count was between 161 and
231×109/l. In October 2010, cytogenetic analysis
revealed a normal karyotype and the JAK2 V617F mutation was
detected by allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR;
Fig. 1) (1). The patient did not exhibit any
identifiable signs, symptoms or laboratory findings for Ph-MPN. In
April 2011, the patient was diagnosed with advanced carcinoma of
the gallbladder during the course of B-CLL and succumbed to the
disease in December 2012.
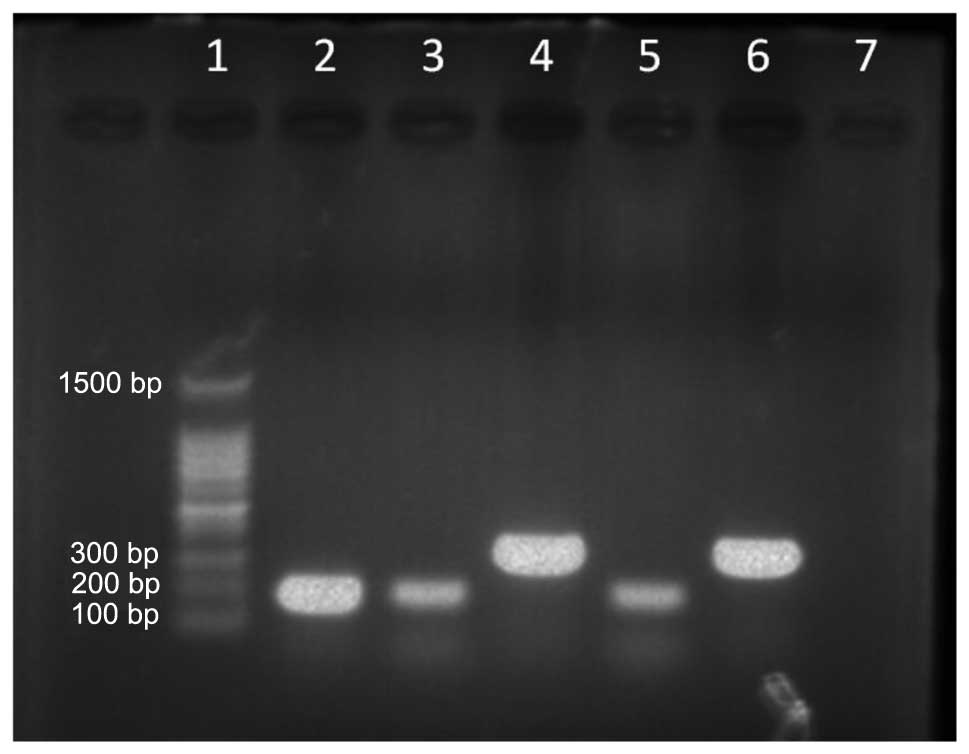 | Figure 1JAK2 V617F mutation detected by
allele-specific polymerase chain reaction. Lanes; 1, molecular
weight marker (100–1,500 bp); 2, JAK2 V617F-positive control (203
bp); 3, JAK2 V617F mutation allele (case 1); 4, wild-type allele
for JAK2 (364 bp, case 1); 5, JAK2 V617F mutation allele (case 2);
6, wild-type allele for JAK2 (364 bp, case 2); and 7, negative
control. |
Case 2
A 63-year-old female patient was admitted to the
Department of Hematology (Shanghai First People’s Hospital) with
leukocytosis in November 2010. The patient’s WBC was elevated
(98.6×109/l; reference range,
3.69–9.16×109/l), whilst the Hb and PLT counts were
within the reference ranges [11.5 g/dl (reference range, 11.3–15.1
g/dl) and 101×109/l (reference range,
85–303×109/l), respectively]. The circulating lymphocyte
percentage was 91%. The PB smear demonstrated an absolute
lymphocytosis of predominantly small, mature lymphocytes. The BM
showed an increased number of lymphocyte compartments and
splenomegaly was present on the abdominal ultrasound. Flow
cytometric analysis of the patient’s PB exhibited the B-CLL
phenotype. The total lymphocyte count was 89.7×109/l and
the gated CD45+ cells showed positivity for CD19
(77.1%), CD20 (77.7%), CD13 (11.7%), CD5 (7.4%), CD2 (8.8%), CD4
(7.6%), CD10 (7.6%), CD22 (1.4%), CD14 (1.6%), CD15 (6.4%), CD33
(2.5%), CD38 (3.6%), CD41 (6.07%) and CD7 (7.7%). Cytogenetic
analysis of the BM revealed a normal karyotype and the JAK2 V617F
mutation was detected by AS-PCR (Fig.
1). The typical characteristics of B-CLL, such as trisomy 12
and the deletion of 11q22.3, 13q14 and 17p13, were not detectable
by fluorescent in situ hybridization. The diagnosis of stage
II B-CLL according to the Rai classification was determined. The
patient was treated with rituximab (500 mg/m2 on day
one) plus fludarabine (35 mg/m2 on days two and three).
Owing to the complete remission status over the following 1.5
years, the patient returned to the Xinyang Sixth People’s Hospital
(Henan, China) in March 2012.
Discussion
Of the 28 cases of JAK2 V617F-positive B-CLL
patients reported in the literature (Table 1) (6–15), the
male and female ratio was 1.6:1 (17 males vs. 11 females), the
median age of the males was 69 years (range, 55–94 years) and was
74 years (range, 58–82 years) for the females. In total, 27
patients exhibited coexistent Ph-MPN (essential thrombocythemia,
n=16; polycythemia vera, n=10; and idiopathic myelofibrosis, n=1).
The remaining B-CLL patient reported by Musolino et al
(13) was without detailed clinical
data. The current study presents two younger JAK2 V617F-positive
B-CLL patients without any history of Ph-MPN; the JAK2 V617F allele
was detected in one patient after the fourth year of follow-up and
the other was a newly diagnosed B-CLL patient.
 | Table ICases of JAK2 V617F reported in B-cell
CLL patients. |
Table I
Cases of JAK2 V617F reported in B-cell
CLL patients.
| Year | First author
(ref.) | Age,
years/Gender | Initial
diagnosis | Clinical disease
process |
|---|
| 2006 | Hussein et al
(15) | 79/M | PV | PV to CLL |
| 2007 | Henry et al
(14) | 58/F | ET | ET to CLL |
| 2009 | Tabaczewski et
al (9) | 72/M | CLL and ET | CLL and ET |
| | 82/M | CLL and ET | CLL and ET |
| 2009 | Kodali et al
(8) | 80/M | CLL and ET | CLL and ET |
| 2009 | Musolino et al
(13) | 72/F | ET | ET to CLL |
| | 57/M | CLL | NA |
| | 68/F | CLL and ET | CLL and ET |
| | 78/F | ET | ET to CLL |
| | 74/F | CLL | CLL to ET |
| | 67/M | ET | ET to CLL |
| | 74/M | CLL | CLL to ET |
| | 69/M | PV | PV to CLL |
| 2011 | Laurenti et al
(10) | 73/F | CLL and PV | CLL and PV |
| | 82/F | ET | ET to CLL |
| | 76/M | PV | PV to CLL |
| | 80/F | ET | ET to CLL |
| | 55/M | CLL | CLL to ET |
| | 79/M | CLL | CLL to ET |
| | 77/M | CLL | CLL to PV |
| | 69/M | PMF | PMF to CLL |
| 2012 | Stijnis et al
(6) | 60/M | PV | PV to CLL |
| | 60/M | PV | PV to CLL |
| 2012 | Wei et al
(11) | 94/M | CLL | CLL to ET |
| 2012 | Eskazan et al
(7) | 56/M | CLL and ET | CLL and ET |
| 2013 | Swierczek et
al (12) | 79/F | PV | PV to CLL |
| | 67/F | PV | PV to CLL |
| | 78/F | CLL and PV | CLL and PV |
| 2013 | Current report | 57/M | CLL | CLL |
| | 63/F | CLL | CLL |
In order to understand why the JAK2 V617F mutation
existed in B-CLL patients it is necessary to determine whether the
JAK2 V617F mutation exists in lymphocytes. The JAK2 V617F mutation
in Ph-MPN patients was hypothesized to be present in stem, myeloid
and erythroid cells rather than in lymphocytes (17). Previous studies (18–21)
identified the JAK2 V617F mutation in B and T lymphocytes, as well
as in natural killer cells in Ph-MPN patients. However, this
remains controversial in JAK2 V617F-positive CLL patients. This
mutation has been identified in B or T cells by various studies
(6–8), while other studies have drawn
contrasting conclusions (11–15).
As the DNA samples used in the current patients had been stored,
identification of the JAK2 V617F mutation in the lymphoid
compartment using cell sorting was not possible. However, it was
agreed that JAK2 V617F may exist in the lymphoid and myeloid cells,
which are involved in the progress of B-CLL.
The role of JAK2 V617F in the pathogenic mechanism
of B-CLL requires investigation. The V617F substitution induces a
conformational shift that alleviates repressive interactions
between its JH1 and JH2 domains, resulting in the constitutive
activation of JAK2 (22,23), which enhances downstream signaling
pathways, such as Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducers and
activators of transcription (STAT) and leads to the proliferation
of cells in Ph-MPN (24).
Furthermore, the activation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway has
been documented in lymphoid malignancies (25–28).
Thus, it is reasonable to propose that JAK2 V617F mutations lead to
the constitutive activation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in
lymphocytes, subsequently resulting in cellular proliferation in
the absence of normal cytokine stimulation. This may lead to
increased cell numbers and indicate a novel mechanism that results
in B-CLL.
Notably, the two JAK2 V617F-positive B-CLL patients
described in the current study were without a Ph-MPN. One
explanation for this is that the JAK2 V617F mutation alone is not
sufficient to induce a Ph-MPN, as it may occasionally be found in
hematologically normal individuals. Sidon et al (29), reported that the JAK2 V617F mutation
is detectable at low levels in ~10% of the PB of healthy donors. A
larger study of 3,700 individuals in Chinese hospitals revealed the
presence of JAK2 V617F in 1% of the normal population (30). An additional explanation is that the
JAK2 V617F mutation only represents an early molecular event, which
precedes clinical and hematologic abnormalities. Certain patients
may never reach the full-scale MPN phenotype prior to succumbing to
other diseases. Due to mortality and loss to follow-up in the
patients included in the current study, it was impossible to
determine whether the patients later developed Ph-MPNs.
In conclusion, the current study presents two B-CLL
patients with the JAK2 V617F mutation. Compared with patients in
previous reports (6–15), the present patients did not exhibit
the Ph-MPN phenotype. Although JAK2 V617F existence in B-CLL is
rare, clinicians must be aware that it is a possibility. By
comparing the previous and current cases, the existence of JAK2
V617F in lymphocytes was reviewed and a novel mechanism that
results in B-CLL was proposed. In order to support these views,
further larger studies regarding JAK2 V617F-positive B-CLL are
required.
References
|
1
|
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al;
Cancer Genome Project. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase
JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 365:1054–1061.
2005.
|
|
2
|
Jelinek J, Oki Y, Gharibyan V, et al: JAK2
mutation 1849G>T is rare in acute leukemias but can be found in
CMML, Philadelphia chromosome-negative CML, and megakaryocytic
leukemia. Blood. 106:3370–3373. 2005.
|
|
3
|
Levine RL, Loriaux M, Huntly BJ, et al:
The JAK2V617F activating mutation occurs in chronic myelomonocytic
leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia, but not in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 106:3377–3379.
2005.
|
|
4
|
Wang YL, Lee JW, Kui JS, et al: Evaluation
of JAK2 in B and T cell neoplasms: identification of JAK2(V617F)
mutation of undetermined significance (JMUS) in the bone marrow of
three individuals. Acta Haematol. 118:209–214. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Zhao W, Gao R, Lee J, Xing S, et al:
Relevance of JAK2V617F positivity to hematological diseases -
survey of samples from a clinical genetics laboratory. J Hematol
Oncol. 4:42011.
|
|
6
|
Stijnis C, Kroes WG, Balkassmi S, et al:
No evidence for JAK2(V617F) mutation in monoclonal B cells in 2
patients with polycythaemia vera and concurrent monoclonal B cell
disorder. Acta Haematol. 128:183–186. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Eskazan AE, Salihoglu A, Diz-Kucukkaya R,
et al: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia developing in a patient with
Janus kinase 2 V617F mutation positive myeloproliferative neoplasm.
Ann Hematol. 91:305–306. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Kodali S, Chen C, Rathnasabapathy C and
Wang JC: JAK2 mutation in a patient with CLL with coexistent
myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). Leuk Res. 33:e236–e239.
2009.
|
|
9
|
Tabaczewski P, Nadesan S and Lim SH:
Zap-70 positive chronic lymphocytic leukemia co-existing with Jak 2
V671F positive essential thrombocythemia: a common defective stem
cell? Leuk Res. 33:854–855. 2009.
|
|
10
|
Laurenti L, Tarnani M, Nichele I, et al:
The coexistence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and
myeloproliferative neoplasms: a retrospective multicentric GIMEMA
experience. Am J Hematol. 86:1007–1012. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Wei J, Wang C, Qin YW, et al: JAK2 V617F
positive essential thrombocythemia developing in a patient with
CD5− chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chin Med J (Engl).
125:2076–2079. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Swierczek S, Nausova J, Jelinek J, et al:
Concomitant JAK2 V617F-positive polycythemia vera and B-cell
chronic lymphocytic leukemia in three patients originating from two
separate hematopoietic stem cells. Am J Hematol. 88:157–158.
2013.
|
|
13
|
Musolino C, Allegra A, Penna G, et al:
Absence of the V617F JAK2 mutation in the lymphoid compartment in a
patient with essential thrombocythemia and B-chronic lymphocytic
leukemia and in two relatives with lymphoproliferative disorders.
Acta Haematol. 122:46–49. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Henry L, Carillo S, Jourdan E, et al:
Association of essential thrombocythemia and chronic lymphocytic
leukemia: absence of the V617F JAK2 mutation in the lymphoid
compartment. Am J Hematol. 82:500–501. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Hussein K, Brakensiek K, Ballmaier M, et
al: B-CLL developing in a patient with PV is not affected by V617F
mutation of the Janus kinase 2. Eur J Haematol. 77:539–541.
2006.
|
|
16
|
Hallek M: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia:
2013 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am J
Hematol. 88:803–816. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Zehentner BK, Loken MR and Wells DA:
JAK2V617F mutation can occur exclusively in the erythroid lineage
and be absent in granulocytes and progenitor cells in classic
myeloproliferative disorders. Am J Hematol. 81:806–807. 2006.
|
|
18
|
Ishii T, Bruno E, Hoffman R and Xu M:
Involvement of various hematopoietic-cell lineages by the JAK2V617F
mutation in polycythemia vera. Blood. 108:3128–3134. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Larsen TS, Christensen JH, Hasselbalch HC
and Pallisgaard N: The JAK2 V617F mutation involves B- and
T-lymphocyte lineages in a subgroup of patients with
Philadelphia-chromosome negative chronic myeloproliferative
disorders. Br J Haematol. 136:745–751. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Tonetti C, et al:
Evidence that the JAK2 G1849T (V617F) mutation occurs in a
lymphomyeloid progenitor in polycythemia vera and idiopathic
myelofibrosis. Blood. 109:71–77. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Bogani C, Guglielmelli P, Antonioli E, et
al: B-, T-, and NK-cell lineage involvement in JAK2V617F-positive
patients with idiopathic myelofibrosis. Haematologica. 92:258–259.
2007.
|
|
22
|
Khwaja A: The role of Janus kinases in
haemopoiesis and haematological malignancy. Br J Haematol.
134:366–384. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Kaushansky K: On the molecular origins of
the chronic myeloproliferative disorders: it all makes sense.
Blood. 105:4187–4190. 2005.
|
|
24
|
James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, et al: A
unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signaling
causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 434:1144–1148. 2005.
|
|
25
|
dos Santos NR and Ghysdael J: A transgenic
mouse model for TEL-JAK2-induced B-cell lymphoma/leukemia.
Leukemia. 20:182–185. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Adélaïde J, Pérot C, Gelsi-Boyer V, et al:
A t(8;9) translocation with PCM1-JAK2 fusion in a patient with
T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 20:536–537. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Zhang Q, Raghunath PN, Xue L, et al:
Multilevel dysregulation of STAT3 activation in anaplastic lymphoma
kinase-positive T/null-cell lymphoma. J Immunol. 168:466–474.
2002.
|
|
28
|
Melzner I, Bucur AJ, Brüderlein S, et al:
Biallelic mutation of SOCS-1 impairs JAK2 degradation and sustains
phospho-JAK2 action in the MedB-1 mediastinal lymphoma line. Blood.
105:2535–2542. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Sidon P, El Housni H, Dessars B and
Heimann P: The JAK2V617F mutation is detectable at very low level
in peripheral blood of healthy donors. Leukemia. 20:16222006.
|
|
30
|
Xu X, Zhang Q, Luo J, et al: JAK2(V617F):
Prevalence in a large Chinese hospital population. Blood.
109:339–342. 2007.
|















