Introduction
Chemotherapy is widely used for the treatment of
cancer; however, acquired drug resistance is considered to be a
substantial obstacle for effective chemotherapy (1). Drug resistance is a phenomenon that
occurs due to a combination of factors and may involve individual
differences in patients as well as genetic and epigenetic
variations in tumors (2,3). Numerous previous studies have
demonstrated that non-mutational microRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene
expression has a crucial role in acquired drug resistance (4–6).
The classic antimetabolite, 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is
widely used in colon cancer therapy and results in cytotoxic
effects that induce cell death through affecting nucleoside
metabolism (7). However, acquired
5-FU resistance is a severe hindrance for the clinical treatment of
cancer (7,8). Although several studies have attempted
to elucidate the molecular events that result in 5-FU resistance,
limited evidence has been provided for the role of epigenetic
modification (9–11). Therefore, it is important to reveal
the distinct mechanisms involved in 5-FU resistance.
The multidrug-resistant phenotype observed in
adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells was found to be
accompanied by epigenetic modification and overexpression of DNA
methyltransferase (DNMT) genes (12).
This therefore implicated the involvement of DNMTs in DNA
hypermethylation, which has been reported to be involved in the
onset of anticancer drug resistance in cancer patients. However,
DNA demethylases as well as ten-eleven translocation enzymes
(TETs), TET1, TET2 and TET3, are able to reverse this methylation
process through the conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) to
5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) and
5-carboxylcytosine, eventually resulting in the production of
cytosine (13,14). These modified bases act as
intermediates for the DNA demethylation process as well as enhance
the epigenetic variation of genomic DNA.
Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)
is a transcription factor that has been suggested to be associated
with cancer development and progression, including in lung
(15), breast (16) and colorectal cancer (17). Nrf2 enables the adaptation of normal
cells to oxidants and electrophiles that are generated by harmful
exogenous agents, in order to reactive oxygen species and their
secondary metabolites (18). Keap1 is
a negative regulator of Nrf2 and its main function is to serve as
an adaptor for cullin3/ring box1 (Cul3/Rbx1) E3 ubiquitin ligase
complex (19,20) Under physiological conditions, Nrf2 is
principally repressed by Keap1, which functions as an intracellular
redox sensor, targeting Nrf2 for proteasomal degradation (21). Once a cell is exposed to oxidative
stress, Keap1 releases Nrf2, which translocates to the nucleus and
activates antioxidant response elements and xenobiotics element
genes (including NQO1). This results in the protein
expression of growth factors and receptors, drug efflux pumps,
drug-metabolizing enzymes, heat shock proteins and various
transcription factors (22,23).
Two previous studies have investigated Keap1/Nrf2 in
colorectal cancer (CRC) cells (24,25).
Activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway mediates protective
responses to mitigate nitric oxide (NO)-induced damage and may
contribute to the resistance of CRC cells to NO-induced
cytotoxicity (23). Arlt et al
reported that Nrf2 activity was elevated in colon cancer, resulting
in overexpression of the proteasome subunit proteins and thus
increased proteasome activity (25).
The present study aimed to explore the mechanisms
underlying anticancer drug resistance in CRC cells through
investigating epigenetic modification in the promoter DNA of the
nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) gene.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
The human SNU-C5 CRC cell line and the
5-FU-resistant SNU-C5R cell line were purchased from the cell bank
of the Chinese Academy of Science (Shanghai, China). Cells were
cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Grand
Island, NY, USA) containing 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum
(Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 37°C in a 5% CO2
incubator. A total of 1×104 SNU-C5R cells/well were then
subcultured at 37°C in 140 mM 5-FU twice per week for >6 months
in order to establish stable drug-resistant cell lines (26).
Cell proliferation assay
Cell viability was assessed using a colorimetric
assay with the tetrazolium salt, MTT. Transfection with short
interference (si)RNA was performed using the JetSI Transfection
Reagent for siRNA (Polyplus-Transfection, Illkirch, France) at 50
nM, according to the manufacturer's instructions. After 24 h of
transfection with siRNA, the cells were exposed to different
concentrations of 5-FU (0, 10 or 100 µM; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis,
MO, USA) for 72 h at room temperature. MTT (0.5 mg/ml;
Sigma-Aldrich) was then added to each well and incubated for 3 h at
room temperature. Plates were centrifuged at 4,500 × g for 5 min at
room temperature, the medium was then removed and 100 µl acidic
isopropanol (40 mM) was added to solubilize the crystals. The
absorbance was measured at 570 mm using a microplate reader (Victor
3; Perkin Elmer, Turku, Finland).
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
detection
Cells (3×105/well) were seeded onto
six-well plates and administered 25 mM dichlorodihydrofluorescein
diacetate (DCF-DA; 30 µl). Next, 2,7-dichlorofluorescein (DCF)
fluorescence levels were then detected using a flow cytometer (BD
FACSCanto™; BD Bioscience, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). CellQuest
software (version 6.0; BD Biosciences) was used to analyze the flow
cytometry results. In order to evaluate the production of
intracellular ROS, image analysis was performed through seeding
cells (2×105/well) onto a coverslip-loaded six-well
plate. Cells were then stained with 1 µM H2-DCFH-DA
(Invitrogen Life Technologies) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
for 30 min at room temperature. Cells were then washed twice with
PBS and visualized using an Eclipse TE2000-U fluorescent microscope
(Nikon Corp., Tokyo, Japan) using a green filter (450–490 nm).
Protein blot analysis
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (Cell
Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA) was used to lyse
cells. A total of 10–20 µg/µl soluble proteins were separated using
12% SDS-PAGE and then blotted onto polyvinylidene fluoride
membranes. Membranes were then blocked using 5% non-fat dry milk
for 1 h at room temperature prior to incubation overnight at 4°C
with the following primary antibodies for: Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1;
cat. no. sc-10789), Nrf2 (cat. no. sc-722;), TET1 (cat. no.
HPA019032), TET2 (cat. no. sc-136926), TET3 (cat. no. sc-139186),
DNMT3B (cat. no. sc-130740) and β-actin (cat. no. sc-130657), which
were all rabbit polyclonal IgG antibodies, used at a dilution of
1:200 and purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas,
TX, USA), with the exception of TET1 that was obtained from
Sigma-Aldrich. In addition, DNMT1 (cat. no. ab19905; rabbit
polyclonal IgG), phospho-Nrf2 (cat. no. ab76026; rabbit monoclonal
IgG), TATA box binding protein (TBP; cat. no. ab52701; mouse
polyclonal IgG) and DNMT3A (cat. no. ab23565; mouse polyclonal IgG)
were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA) and used at a
dilution of 1:200. Membranes were washed with PBS and then
incubated with secondary antibodies (goat anti-rabbit polyclonal
IgG; cat. no. SAB3700843; dilution, 1:500; Sigma-Aldrich) for 1 h
at room temperature. Membranes were incubated with luminol reagent
(Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Rockford, IL, USA) and the bands
were visualized using a Bio-Rad XRS system (Bio-Rad Laboratories,
Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
Reverse transcription quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis
Total RNA was isolated from SNU-C5 and SNU-C5R cells
using Quick-RNA™MicroPrep solution (Zymo Research Corp., Irvine,
CA, USA). iScript™ Reverse Transcription Supermix for real-time PCR
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) was used to reverse transcribe column
purified total RNA, which was analyzed using a MiniOpticon™
Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) using
SsoFast™ EvaGreen® Supermix (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) as
previously described (27).
ProbeFinder software (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) was used to design
the primers, which were then commercially synthesized by Shanghai
Generay Biotech Co. (Shanghai, China; http://www.generay.com.cn/). The primers used were as
follows: Nrf2 forward, 5′-GAGAGCCCAGTCTTCATTGC-3′, and reverse,
5′-TTGGCTTCTGGACTTGGAAC-3′; GAPDH forward,
5′-AACGTGTCAGTGGTGGACCTG-3′, and reverse,
5′-AGTGGGTGTCGCTGTTGAAGT-3′. The PCR conditions were as follows:
denaturation program (95°C for 10 min), followed by an
amplification and quantification program repeated 40 times (95°C
for 15 sec, 60°C for 10 sec, 72°C for 60 sec). Agarose gel
electrophoresis (2%; Sigma-Aldrich) was then used to visualize the
PCR products of the primers, which were verified by DNA sequencing
that was performed by Shanghai Generay Biotech Co. All reactions
were performed in triplicate and three independent experiments were
run. Serial dilutions of a reference sample were used to construct
standard curves for determining the individual PCR amplification
efficiencies; this was included in each quantitative run in order
to correct for variations in product amplification. Standard curves
were used to obtain relative copy numbers, which were normalized to
the values obtained for Gapdh, the internal control. CFX manager
3.1 software (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) was employed for data
acquisition, analysis and determining PCR efficiencies.
Bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing
The genomic DNA of SNU-C5 and SNU-C5R cells was
subjected to bisulfite conversion using an EZ DNA
Methylation-Direct™ kit (Zymo Research Corp.). Amplification of the
bisulfite-modified DNA was then performed through bisulfite
sequencing PCR (Bio-Rad T100; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) using
Platinum® PCR SuperMix High Fidelity (Invitrogen Life Technologies)
with human Nrf2 promoter-specific primers: Nrf2 forward,
5′-TGAGATATTTTGCACATCCGATA-3′ and reverse,
5′-ACTCTCAGGGTTCCTTTACACG-3′. Subsequently, the PCR amplification
products were purified through gel extraction with Zymoclean™ Gel
DNA recovery kit (Zymo Research Corp.). A TOPO TA Cloning® kit
(Invitrogen Life Technologies) was then used to clone the purified
products into pCR®4-TOPO vectors. The recombinant plasmids were
transformed into One Shot® TOP10 chemically competent E.
coli (Invitrogen Life Technologies) using the calcium chloride
transformation method (28). The
plasmid DNA of ~10 independent clones of each amplicon was isolated
using a PureLink™Quick PlasmidMiniprep kit (Invitrogen Life
Technologies) and then sequenced in order to determine the
cytosine-phosphate-guanine methylation status. Clones with an
insert with N 99.5% bisulfite conversion, i.e. non-methylated
cytosine residues to thymine, were included in the present study
and the remaining were excluded. Bisulfite Sequencing DNA
Methylation Analysis software (http://biochem.jacobs-university.de/BDPC/BISMA/) was
then used to analyze the sequenced data of each clone for DNA
methylation in the Nrf2 promoter, using default filtering threshold
settings.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with the
SPSS 20.0 software (IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA). Quantitative data
are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. The statistically
significant differences between patient and control groups were
tested using t-test and ANOVA test. P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
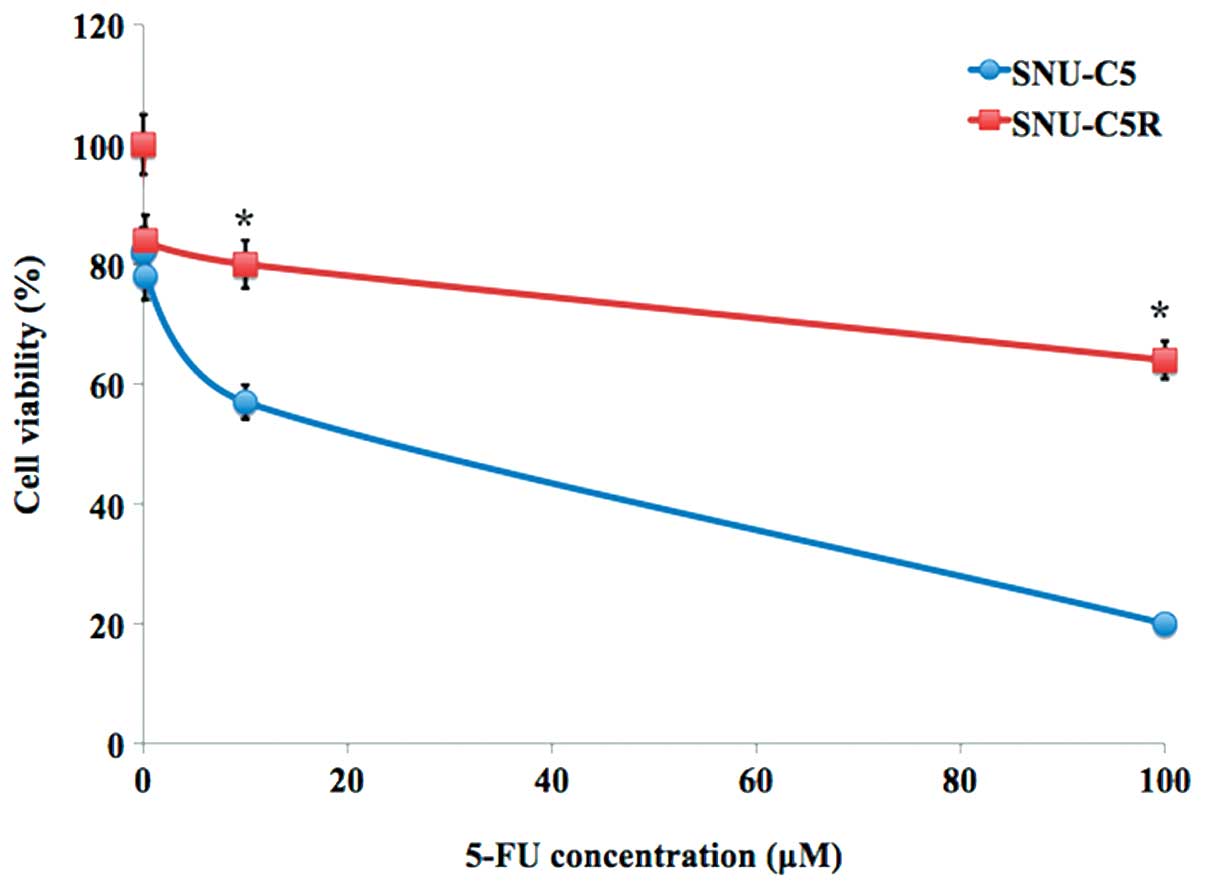
Chemosensitivity of SNU-C5R cells to
5-FU
The relative chemosensitivity of the SNU-C5R
5-FU-resistant cell line was confirmed using an MTT cell viability
assay. As shown in Fig. 1, 5-FU
treatment for 72 h resulted in a dose-dependent suppression of cell
growth in SNU-C5 cells, which was significantly decreased compared
with that of the SNI-C5R cells (Fig.
1). The 5-FU concentrations causing a 50% growth inhibition as
compared with control cells (IC50) were calculated by a
modified Kärbers method (29). The
IC50 value for 5-FU in SNU-C5R cells was 118.7±4.9 µM,
whereas the corresponding value for their parental SNU-C5 cells was
23.2±3.4 µM (P<0.05).
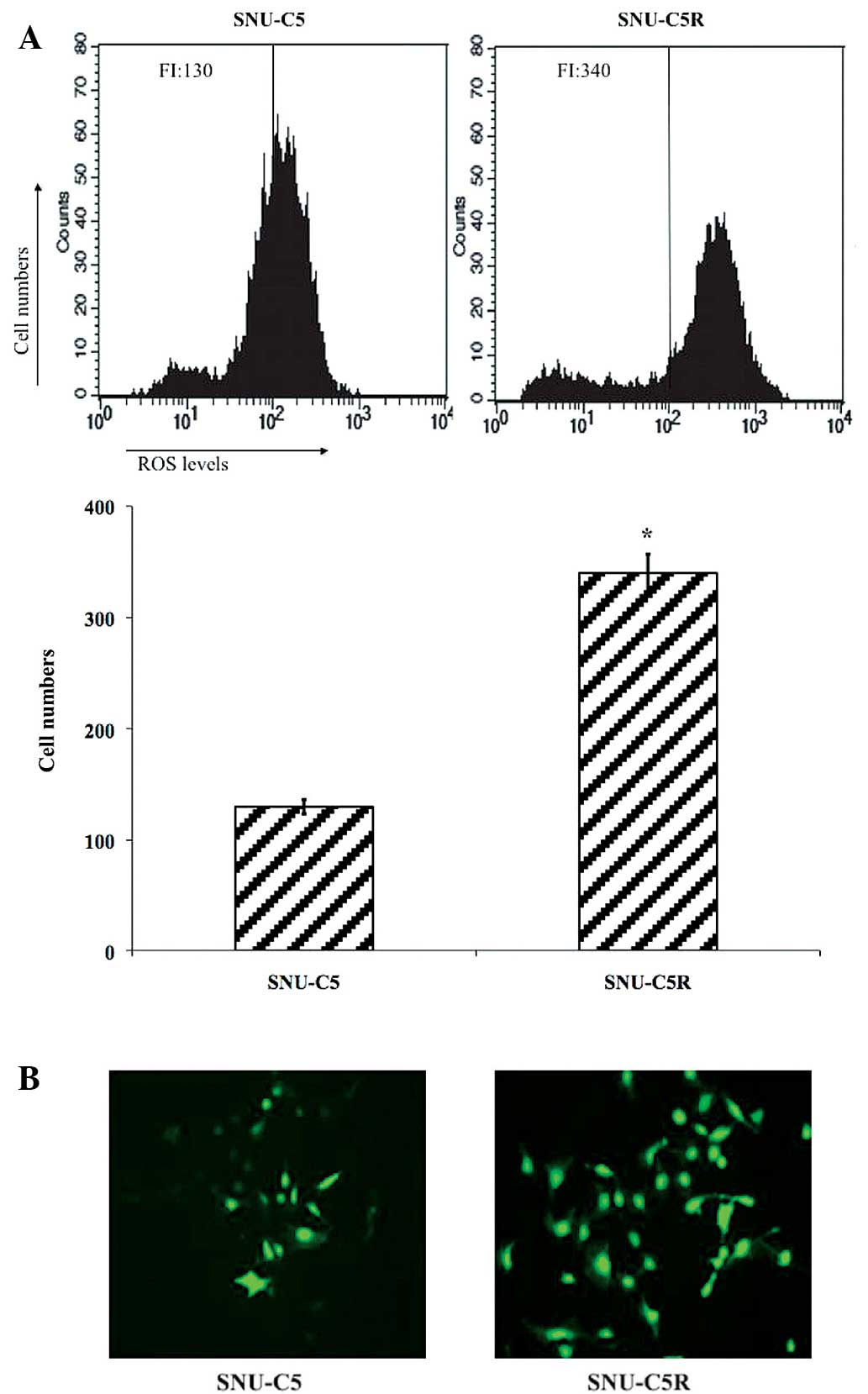
Intracellular ROS levels in SNU-C5 and
SNU-C5R cells
Flow cytometric analysis data revealed that ROS
levels were significantly elevated in SNU-C5R cells [fluorescence
intensity (FI), 340] compared with SNU-C5 cells (FI, 130;
P<0.05) (Fig. 2A). Fluorescent
microscopic imaging confirmed these results, as it demonstrated
that the ROS green FI was markedly enhanced in SNU-C5R cells
compared with SNU-C5 cells (Fig. 2B).
This therefore suggested that SNU-C5R cells were exposed to an
increased level of oxidative stress conditions compared with SNU-C5
cells.
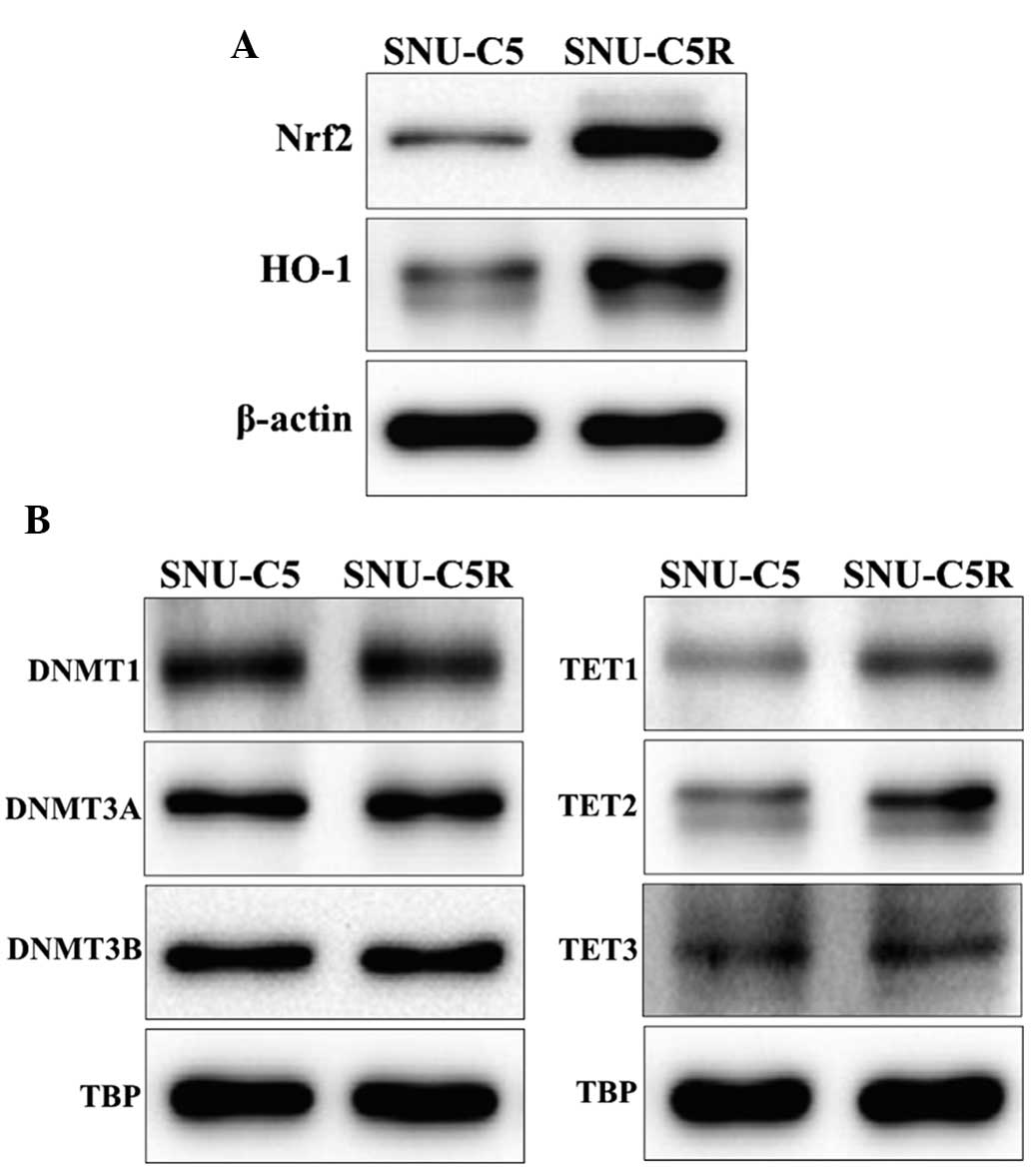
Antioxidant and DNA
methylation-associated protein expression in SNU-C5 and SNU-C5R
cells
HO-1 and Nrf2 protein levels were observed to be
increased in SNU-C5R cells compared with SNU-C5 cells (Fig. 3A). In addition, the expression levels
of the epigenetic modification-associated proteins, in terms of
those for DNA methylation, was investigated by assessing the
protein levels of DNMTs DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B as well as the DNA
demethylases, including TET1, TET2 and TET3. The results revealed
that DNMT expression was not significantly different between SNU-C5
and SNU-C5R cells, whereas TET expression was elevated in SNU-CR
cells compared with SNU-C5 cells (Fig.
3B).
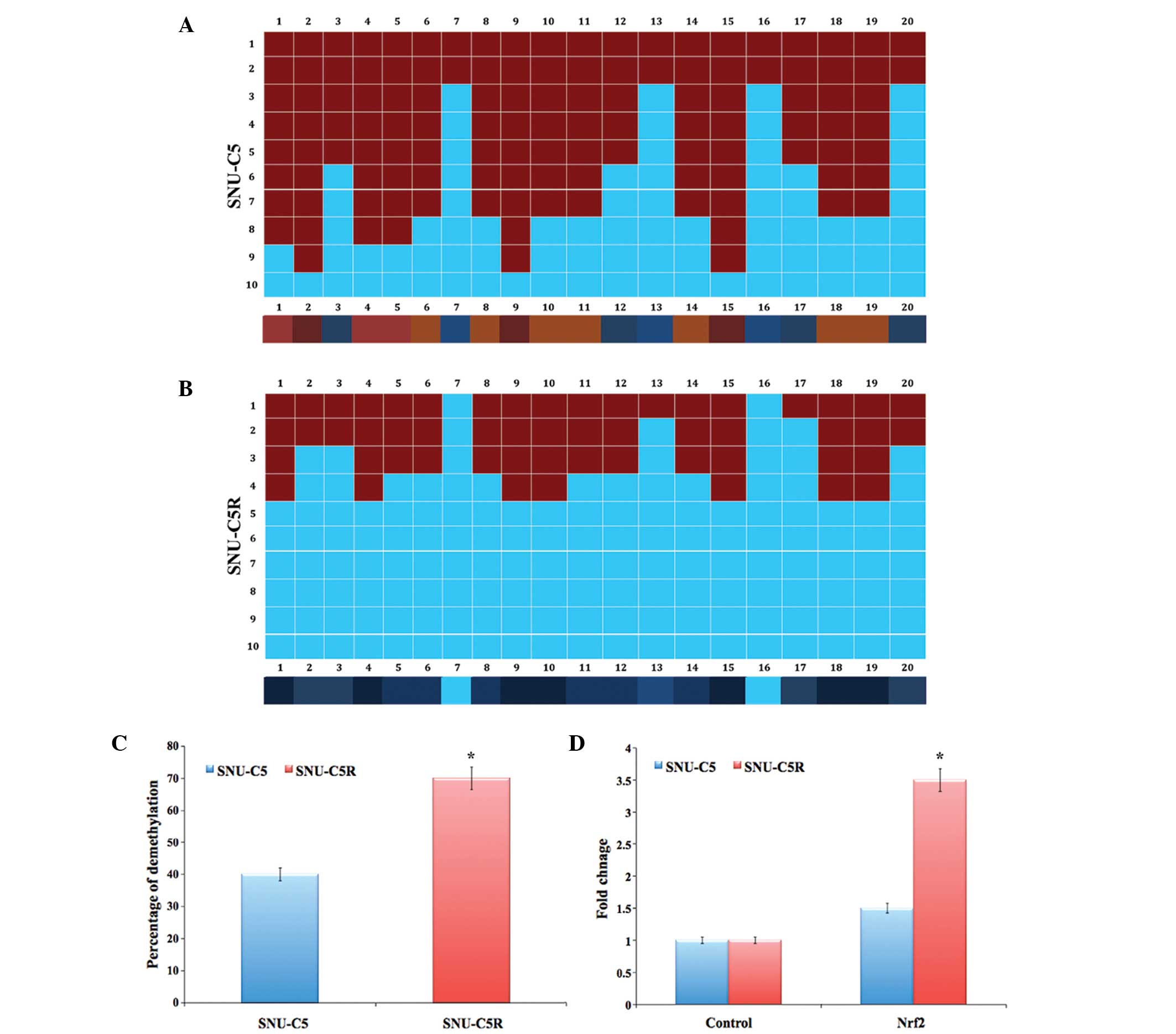
Epigenetic analysis and gene
expression of Nrf2 in SNU-C5 and SNU-C5R cells
The bisulphate DNA sequencing of the Nrf2 promoter
region revealed significant demethylation in SNU-C5R cells compared
with that of SNU-C5 cells (P<0.05) (Fig. 4A and B). The overall percentage of
Nrf2 promoter demethylation was ~40% in SNU-C5 cells and ~70% in
SNU-C5R cells (P<0.05) (Fig. 4C).
In addition, messenger (m)RNA levels of Nrf2 in SNU-C5R cells
exhibited a 3.5-fold increase, which was significantly increased
compared with the 1.5-fold increase observed in SNU-C5 cells
(P<0.05); increases were compared to that of the control house
keeping gene (Fig. 4D).
Discussion
Despite the occurrence of drug resistance, 5-FU was
used as the standard treatment for CRC patients for several years
(30,31). Novel therapeutic strategies for CRC
are required; thus, elucidating the underlying mechanisms of 5-FU
resistance is essential for the generation of novel molecular
targeted therapies for overcoming drug resistance (7,11,31). There has been increasing evidence to
suggest the role of epigenetic alterations in drug resistance in
numerous types of cancer, such as CRC (32–35); this
therefore indicates that epigenetic modification may occur
following the administration of 5-FU. In the present study, the
epigenetic status of Nrf2, a master transcription factor for major
protective genes, was compared between the normal CRC SNU-C5 cell
line and the 5-FU-resistant SNU-C5R cell line. Nrf2 is involved in
the regulation of numerous genes, such as HO-1, which has a role in
protecting cells against the chemical and oxidative stresses that
are activated in CRC cells (25). In
addition, 5-FU induces the activation of Nrf2, the mechanism of
which was reported to occur via enhanced ROS production following
drug treatment in the human HT-29 colon cancer cells (36). The results of the present study were
consistent with these previous studies, as significant increases
were observed in ROS production as well as Nrf2 and HO-1 expression
in SNU-C5R cells compared with SNU-C5 cells. The upregulated
expression and activity of HO-1 and Nrf2 in SNU-C5R cells indicated
that Nrf2 protein translocation from the cytosol to the nucleus was
enhanced and that Nrf2 interacted with the AU-rich element sequence
in the HO-1 promoter region, therefore inducing cellular
protection.
Previous studies have demonstrated that ROS promote
epigenetic modifications, which therefore alter the genome and have
a crucial role in carcinogenesis (37). In particular, ROS production was
reported to be associated with the modification of DNA methylation
patterns (38). In the present study,
increased ROS production was observed in SNU-C5R cells compared
with the SNU-C5 cells. Subsequently, the expression levels of DNA
methylation-associated proteins, including DNMT1, DNMT3A and
DNMT3B, as well as DNA demethylases, including TET1, TET2 and TET3,
were investigated. The results clearly demonstrated that there was
no change in the levels of DNMTs, whereas TET protein levels were
markedly increased in SNU-C5R cells compared with SNU-C5 cells.
TET1 is the main enzyme that catalyzes 5-mC oxidation to 5-fC; the
remaining TET proteins, TET2 and TET3, were reported to compensate
for reduced levels of TET1 (39,40). In
the present study, bisulphate DNA sequence analysis revealed a high
level of demethylation in the 5-FU-resistant cells, SNU-C5R. In
concurrence with these results, Nrf2 mRNA levels were found to have
increased ~3.5-fold in the drug-resistant cells.
In conclusion, the results of the present study
suggested that 5-FU was responsible for inducing excess ROS
production, resulting in epigenetic alterations. Increased levels
of TET proteins further confirmed the epigenetic alterations;
however, no difference was observed in DNMT protein levels, which
suggested that they were not involved in the methylation process.
Therefore, demethylation was confirmed. Furthermore, promoter DNA
demethylation of the Nrf2 gene was confirmed by elevated levels of
Nrf2 mRNA in drug-resistant SNU-C5R cells. Therefore, epigenetic
modification in Nrf2 may provide a potential novel therapeutic
target for counteracting the resistance of CRC cells against 5-FU
treatment.
References
|
1
|
Kang H, Kim C, Lee H, Kim W and Lee EK:
Post-transcriptional controls by ribonucleoprotein complexes in the
acquisition of drug resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 14:17204–17220.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raguz S and Yagüe E: Resistance to
chemotherapy: New treatments and novel insights into an old
problem. Br J Cancer. 99:387–391. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan DS, Gerlinger M, Teh BT and Swanton C:
Anti-cancer drug resistance: Understanding the mechanisms through
the use of integrative genomics and functional RNA interference.
Eur J Cancer. 46:2166–2177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mishra PJ: The miRNA-drug resistance
connection: A new era of personalized medicine using noncoding RNA
begins. Pharmacogenomics. 13:1321–1324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mishra PJ and Bertino JR: MicroRNA
polymorphisms: The future of pharmacogenomics, molecular
epidemiology and individualized medicine. Pharmacogenomics.
10:399–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu X, Chen H, Lin Y, Hu Z, Mao Y, Wu J, Xu
X, Zhu Y, Li S, Zheng X and Xie L: MicroRNA-409-3p inhibits
migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via targeting c-Met.
Mol Cells. 36:62–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang N, Yin Y, Xu SJ and Chen WS:
5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of resistance and reversal strategies.
Molecules. 13:1551–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peters GJ, Backus HH, Freemantle S, van
Triest B, Codacci-Pisanelli G, et al: Induction of thymidylate
synthase as a 5-fluorouracil resistance mechanism. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1587:194–205. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boyer J, Allen WL, McLean EG, Wilson PM,
McCulla A, Moore S, Longley DB, Caldas C and Johnston PG:
Pharmacogenomic identification of novel determinants of response to
chemotherapy in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 66:2765–2777. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karasawa H, Miura K, Fujibuchi W, Ishida
K, Kaneko N, et al: Down-regulation of cIAP2 enhances 5-FU
sensitivity through the apoptotic pathway in human colon cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 100:903–913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kurokawa K, Tanahashi T, Iima T, Yamamoto
Y, Akaike Y, Nishida K, Masuda K, Kuwano Y, Murakami Y, Fukushima M
and Rokutan K: Role of miR-19b and its target mRNAs in
5-fluorouracil resistance in colon cancer cells. J Gastroenterol.
47:883–895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Segura-Pacheco B, Perez-Cardenas E,
Taja-Chayeb L, Chavez-Blanco A, Revilla-Vazquez A,
Benitez-Bribiesca L and Duenas-González A: Global DNA
hypermethylation-associated cancer chemotherapy resistance and its
reversion with the demethylating agent hydralazine. J Transl Med.
4:322006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB,
Swenberg JA, He C and Zhang Y: Tet proteins can convert
5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine.
Science. 333:1300–1303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ito S, D'Alessio AC, Taranova OV, Hong K,
Sowers LC and Zhang Y: Role of Tet proteins in 5mc to 5hmc
conversion, ES-cell self-renewal and inner cell mass specification.
Nature. 466:1129–1133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh A, Misra V, Thimmulappa RK, et al:
Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer.
PloS Med. 3:e4202006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nioi P and Nguyen T: A mutation of Keap1
found in breast cancer impairs its ability to repress Nrf2
activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 362:816–821. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hanada N, Takahata T, Zhou Q, et al:
Methylation of the KEAP1 gene promoter region in human colorectal
cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hayes JD and McMahon M: NRF2 and KEAP1
mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer.
Trends Biochem Sci. 34:176–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang DD, Lo SC, Cross JV, Templeton DJ
and Hannink M: Keap1 is a redox regulated substrate adaptor protein
for a Cul3-dependent ubiquitin ligase complex. Mol Cell Biol.
24:10941–10953. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cullinan SB, Gordan JD, Jin J, Harper JW
and Diehl JA: The Keap1-BTB protein is an adaptor that bridges Nrf2
to a Cul3-based E3 ligase: oxidative stress sensing by a Cul3-Keap1
ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 24:8477–8486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN,
et al: Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the
sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect
against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:11908–11913. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wakabayashi N, Dinkova-Kostova AT,
Holtzclaw WD, et al: Protection against electrophile and oxidant
stress by induction of the phase 2 response: fate of cysteines of
the Keap1 sensor modified by inducers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2040–2045. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thimmulappa RK, Mai KH, Srisuma S, Kensler
TW, Yamamoto M and Biswal S: Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes
induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by
oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res. 62:5196–5203.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li CQ, Kim MY, Godoy LC, Thiantanawat A,
Trudel LJ and Wogan GN: Nitric oxide activation of Keap1/Nrf2
signaling in human colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:14547–14551. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arlt A, Bauer I, Schafmayer C, et al:
Increased proteasome subunit protein expression and proteasome
activity in colon cancer relate to an enhanced activation of
nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Oncogene. 28:3983–3996.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jung GR, Kim KJ, Choi CH, Lee TB, Han SI,
Han HK and Lim SC: Effect of betulinic acid on anticancer
drug-resistant colon cancer cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
101:277–285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bourhy P, Bremont S, Zinini F, Giry C and
Picardeau M: Comparison of real-time PCR assays for detection of
pathogenic Leptospira spp. in blood and identification of
variations in target sequences. J Clin Microbiol. 49:2154–2160.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dagert M and Ehrlich SD: Prolonged
incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of
Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 6:23–28. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu GF: Median effective dose. Medical
Statistics. Jiang ZJ: 1st. People's Medical Publishing House;
Beijing: pp. 136–153. 1997
|
|
30
|
Was H, Dulak J and Jozkowicz A: Heme
oxygenase-1 in tumor biology and therapy. Curr Drug Targets.
11:1551–1570. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Becker JC, Fukui H, Imai Y, Sekikawa A,
Kimura T, Yamagishi H, Yoshitake N, Pohle T, Domschke W and
Fujimori T: Colonic expression of heme oxygenase-1 is associated
with a better long-term survival in patients with colorectal
cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol. 42:852–858. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Arnold CN, Goel A and Boland CR: Role of
hMLH1 promoter hypermethylation in drug resistance to
5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer.
106:66–73. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feinberg AP, Ohlsson R and Henikoff S: The
epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer. Nat Rev Genet.
7:21–33. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dworkin AM, Huang TH and Toland AE:
Epigenetic alterations in the breast: Implications for breast
cancer detection, prognosis and treatment. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:165–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Balch C, Huang TH, Brown R and Nephew KP:
The epigenetics of ovarian cancer drug resistance and
resensitization. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 191:1552–1572. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Akhdar H, Loyer P, Rauch C, Corlu A,
Guillouzo A and Morel F: Involvement of Nrf2 activation in
resistance to 5-fluorouracil in human colon cancer HT-29 cells. Eur
J Cancer. 45:2219–2227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ziech D, Franco R, Pappa A and
Panayiotidis MI: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) - induced genetic
and epigenetic alterations in human carcinogenesis. Mutat Res.
711:167–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Donkena KV, Young CY and Tindall DJ:
Oxidative stress and DNA methylation in prostate cancer. Obstet
Gynecol Int. 2010:3020512010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dawlaty MM, Ganz K, Powell BE, Hu YC,
Markoulaki S, et al: Tet1 is dispensable for maintaining
pluripotency and its loss is compatible with embryonic and
postnatal development. Cell Stem Cell. 9:166–175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rudenko A, Dawlaty MM, Seo J, Cheng AW, et
al: Tet1 is critical for neuronal activity-regulated gene
expression and memory extinction. Neuron. 79:1109–1122. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|