Introduction
Sarcomas are a rare and heterogeneous group of
malignant tumors of mesenchymal origin, which account for <1% of
all adult cancers and ~21% of all pediatric cancers worldwide
(1). There are >100 histological
subtypes of sarcoma, most of which can occur at any age and are not
limited to any specific part of the body. Soft tissue sarcomas
often form in the muscles, nerves, fat, deep skin tissues and blood
vessels (1), and the most common
metastatic site is the lungs via the vasculature (1). The most common subtypes are
liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, osteosarcoma,
pleomorphic and synovial sarcoma (2).
Similar to most other types of cancer, surgery is
the primary treatment for patients with sarcoma (3). In metastatic disease, long-term
disease-free survival and cure can be achieved by performing
metastasectomy in selected patient groups, particularly those who
have isolated lung metastasis (2).
However, for most patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcoma, the
goal of systemic therapy is to reduce the tumor burden, relieve
symptoms, improve the quality of life and prolong survival
(4). Targeted therapies have become
increasingly important in recent years due to the limited response
obtained with classical cytotoxic agents. Tyrosine kinase
inhibitors, such as pazopanib and regorafenib, trabectidin and anti
PDL-1 agents have been used to treat soft tissue sarcoma (4).
Pazopanib was the first tyrosine kinase inhibitor
used to treat metastatic soft tissue sarcoma (5). It is generally preferred as salvage
therapy for patients who progress after standard cytotoxic therapy
(4). Considering that most patients
eventually succumb to the disease, the main purpose of pazopanib
treatment is to prolong their life expectancy (6). Therefore, progression-free survival
and clinical response were considered to be the most important
criteria of treatment success in the present study. The parameters
predicted to affect these data were histological subtype, number of
metastatic sites, line of pazopanib therapy and tumor grade. The
aim of the present study was to evaluate the progression-free
survival time and clinical response of patients with metastatic
soft tissue sarcoma receiving pazopanib therapy, and to determine
factors that may affect these data, such as histological subtype,
number of metastatic sites, line of drug used, age, sex and
tolerance to treatment side effects.
Materials and methods
Study design
The present study was a retrospective, single-center
study conducted at Ege University (Bornova, Turkey). A total of 81
patients diagnosed with metastatic soft tissue sarcoma who received
pazopanib therapy were evaluated between January 2012 and October
2020. All of the patients were followed up at Ege University.
Notably, there were no exclusion criteria, patients who had
metastatic disease and received pazopanib therapy were
included.
Progression-free survival was defined as the time
between the start of therapy and the date of progression or death,
and overall survival was defined as the time between the date of
diagnosis of metastatic disease and the date of death.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as the median and
range, and categorical variables are presented as number and
percentage. Survival data were evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier
method and were compared between groups using the log-rank test.
The Stata program (version 14.2; Stata Corp LP) was used for all
statistical analysis. The χ2 test and Fisher's exact
test were used to compare categorical variables. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Demographic data
Of the 81 patients included in the present study, 30
were male and 51 were female. The patients were diagnosed between
2012 and 2020. General patient characteristics are shown in
Table I.
 | Table I.Demographic characteristics and
histological subtypes. |
Table I.
Demographic characteristics and
histological subtypes.
| Characteristic | Patients |
|---|
| Total cohort, n
(%) | 81 (100) |
| Mean age, years
(±SD) | 44.75 (±14.9) |
| Sex, n (%) |
|
|
Female | 51 (63) |
| Male | 30 (37) |
| Histological
subtypes, n (%) |
|
| Synovial
sarcoma | 12 (14.8) |
|
Plemorphic sarcoma | 13 (16) |
|
Leiomyosarcoma | 26 (32.1) |
| Alveolar
soft part sarcoma | 4 (4.9) |
| Malignant
peripheral nerve sheath tumor | 4 (4.9) |
|
Fibrosarcoma | 6 (7.4) |
|
Angiosarcoma | 5 (6.2) |
|
Chondrosarcoma | 4 (4.9) |
| Ewing
sarcoma | 3 (3.7) |
|
Epitheloid sarcoma | 2 (2.5) |
|
Hemangioendhotelioma | 2 (2.5) |
Progression-free and overall survival
data
A total of 81 patients were included in the study,
and 18 of them were reported to be alive at the time of writing.
The median overall survival time of the entire study cohort was 46
months (95% CI, 36.7–55.25).
Clinical progression had not yet developed in 3
patients whose follow-up continues. These patients were diagnosed
with alveolar soft part sarcoma, pleomorphic sarcoma and
hemangioendothelioma. In 1 patient diagnosed with synovial sarcoma,
treatment was stopped due to the development of severe intolerance
shortly after starting treatment, and progression-free survival
could not be evaluated. The median progression-free survival time
in the entire study cohort was 5 months (95% CI, 3.98–6.01;
Table II).
 | Table II.Progression-free survival according to
histological subtypes. |
Table II.
Progression-free survival according to
histological subtypes.
| Histological
subtype | Patients, n (%) | Median
progression-free survival, months | P-value |
|---|
| Synovial sarcoma | 11 (13.75) | 5 (2.9–7.1) |
|
| Pleomorphic
sarcoma | 13 (16.25) | 4 (2.5–5.4) |
|
| Leiomyosarcoma | 26 (32.5) | 4 (2.3–5.6) |
|
| Alveolar soft part
sarcoma | 4 (5) | 15 (6–23.9) |
|
| Malignant peripheral
nerve sheath tumor | 4 (5) | 1.5 (0–3.5) |
|
| Fibrosarcoma | 6 (7.5) | 2 (0.4–3.6) |
|
| Angiosarcoma | 5 (6.25) | 5 (0.7–9.3) |
|
| Chondrosarcoma | 4 (5) | 8 (3.1–12.9) |
|
| Ewing sarcoma | 3 (3.75) | 7.5 (0–17.9) |
|
| Epitheloid
sarcoma | 2 (2.5) | 5 (4.7–5.7) |
|
|
Hemangioendhotelioma | 2 (2.5) | 23 (18.1–52.8) |
|
| Total | 80 (100) | 5 (3.98–6.01) | 0.09 |
Response to pazopanib therapy
In terms of the clinical response, the disease
status at the first control imaging after starting pazopanib
treatment was compared with that before treatment. Responses were
grouped as complete response, partial response, stable disease and
progressive disease.
Of the 81 patients included in the study, 80 were
evaluated for clinical response. None of the patients showed a
complete response. A total of 15 (18.75%) patients had a partial
response, 22 (27.5%) patients had stable disease and 43 (53.75%)
patients exhibited progressive disease.
The detection of a partial response or stable
disease on initial follow-up imaging under pazopanib therapy was
considered clinically significant, and both conditions were
considered as a clinical response. The clinical response rate
(partial response + stable disease) was 46.3% during the study
period (Table III).
 | Table III.Clinical response rates according to
histological subtypes. |
Table III.
Clinical response rates according to
histological subtypes.
| Histological
subtype | Patients, n (%) | Partial response, n
(%) | Stable disease, n
(%) | Progressive disease,
n (%) | P-value |
|---|
| Synovial sarcoma | 11 (13.75) | 2 (2.5) | 3 (3.7) | 6 (7.5) |
|
| Pleomorphic
sarcoma | 13 (16.25) | 2 (2.5) | 3 (3.7) | 8 (10.0) |
|
| Leiomyosarcoma | 26 (32.5) | 5 (6.25) | 6 (7.5) | 15 (18.7) |
|
| Alveolar soft part
sarcoma | 4 (5) | 2 (2.5) | 2 (2.5) | 0 (0) |
|
| Malign peripheral
nerve sheath tumor | 4 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (5.0) |
|
| Fibrosarcoma | 6 (7.5) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.2) | 5 (6.25) |
|
| Angiosarcoma | 5 (6.25) | 0 (0) | 3 (3.7) | 2 (2.5) |
|
| Chondrosarcoma | 4 (5) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.5) | 2 (2.5) |
|
| Ewing sarcoma | 3 (3.75) | 1 (1.2) | 1 (1.2) | 1 (1.2) |
|
| Epitheloid
sarcoma | 2 (2.5) | 1 (1.2) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0) |
|
|
Hemangioendhotelioma | 2 (2.5) | 2 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
|
| Total | 80 (100) | 15 (18.8) | 22 (27.5) | 43 (53.7) | 0.093 |
Factors affecting the response to
pazopanib therapy
Histological subtypes
The present study included 12 patients with synovial
sarcoma, 13 patients with pleomorphic sarcoma, 26 patients with
leiomyosarcoma, 4 patients with alveolar soft part sarcoma, 4
patients with malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors, 6 patients
with fibrosarcoma, 5 patients with angiosarcoma, 4 patients with
chondrosarcoma, 3 patients with Ewing sarcoma, 2 patients with
epithelioid sarcoma and 2 patients with hemangioendothelioma
(Table I).
The median progression-free survival time was 5
months (95% CI, 2.9–7.1) in patients with synovial sarcoma, 4
months (95% CI, 2.5–5.4) in patients with pleomorphic sarcoma, 4
months (95% CI, 2.3–5.6) in patients with leiomyosarcoma, 15 months
(95% CI, 6.0–23.9) in patients with alveolar soft part sarcoma, 1.5
months (95% CI, 0–3.5) in patients with malignant peripheral nerve
sheath tumors, 2 months (95% CI, 0.4–3.6) in patients with
fibrosarcoma, 5 months (95% CI, 0.7–9.3) in patients with
angiosarcoma, 8 months (95% CI, 3.1–12.9) in patients with
chondrosarcoma, 7.5 months (95% CI, 0–17.9) in patients with Ewing
sarcoma, 5 months (95% CI, 4.7–5.7) in patients with epithelioid
sarcoma and 23 months (95% CI, 18.1–52.8) in patients with
hemangioendothelioma (Table II).
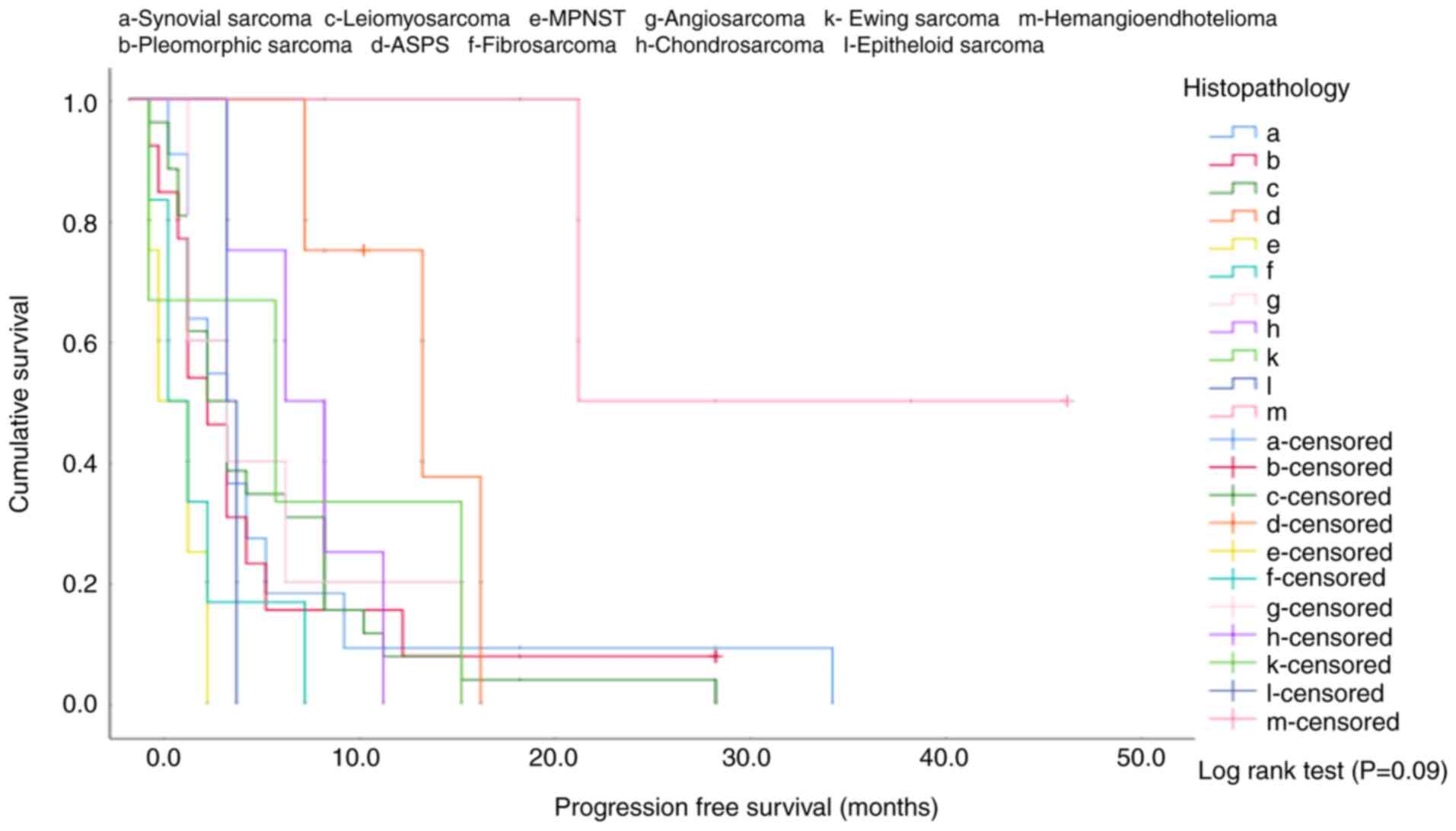
It was determined that different histological subtypes had no
effect on the median progression-free survival (log-rank test,
P=0.09; Table II; Fig. 1).
In the χ2 analysis performed to compare
groups of patients based on histological subtypes, the
hemangioendothelioma group had a significantly longer median
progression-free survival time compared with the leiomyosarcoma
(P=0.02), malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (P=0.049),
fibrosarcoma (P=0.032), angiosarcoma (P=0.037) and chondrosarcoma
(P=0.049) groups. In addition, the alveolar soft part sarcoma group
had a significantly longer median progression-free survival time
compared with the malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
(P=0.007), fibrosarcoma (P=0.008) and epithelioid sarcoma (P=0.018)
groups. When comparing all subtypes between each other, no effect
of the histological subtype on the clinical response was detected
in the analysis (Pearson's χ2 test, P=0.093; Table III).
Tumor grade
The tumor grade was evaluated in 33 patients. Among
them, 1 patient had a grade 1–2 tumor, 4 patients had grade 2
tumors, 3 patients had grade 2–3 tumors and 25 patients had grade 3
tumors (Table SI).
The progression-free survival time was 10 months in
the 1 patient with tumor grade 1–2, the median progression-free
survival time was 21 months (min-max, 5–36 months) in the 4
patients with tumor grade 2, 3 months (min-max, 3–10 months) in the
3 patients with tumor grade 2–3 and 5 months (min-max, 1–17 months)
in the 25 patients with tumor grade 3 (Table SI).
Due to the small number of patients, when the 8
patients with a tumor grade <3 were evaluated as a single group,
the median progression-free survival time was calculated as 10
months (min-max, 3–36 months). No statistically significant
difference was found in the comparison of these patients with the
remaining 25 patients with grade 3 tumors (log-rank test, P=0.103;
Table SI).
A clinical response was obtained in 1 patient with
tumor grade 1–2 (100%) and in 4 patients with tumor grade 2 (100%).
A clinical response was obtained in 1 of 3 patients with tumor
grade 2–3 (33.3%) and 9 of 25 patients with tumor grade 3 (36%). No
statistically significant association was found between tumor grade
and clinical response (Pearson's χ2 test, P=0.069;
Table SII).
Line of pazopanib treatment
A total of 3 patients received pazopanib as
first-line treatment, 26 patients received pazopanib as second-line
treatment, 35 patients received pazopanib as third-line treatment,
13 patients received pazopanib as fourth-line treatment and 3
patients received pazopanib as fifth-line treatment.
A total of 40 of the 81 patients received
ifosfamide-adriamycin as first-line treatment. The most commonly
prescribed second-line treatment regimens were
gemcitabine-docetaxel and pazopanib.
A total of 2 of the 3 patients who were treated with
pazopanib as first-line treatment did not develop clinical
progression until follow-up, and the progression-free survival time
was 23 months in a single patient that developed progression. The
median progression-free survival time was 5 months (95% CI,
3.8–6.1) in patients who received pazopanib as second-line
treatment, 5 months (95% CI, 3.4–6.6) in patients who received
pazopanib as third-line treatment, 3 months (95% CI, 1.2–4.76) in
patients who received pazopanib as fourth-line treatment and 7.5
months (95% CI, 0–16.3) in patients who received pazopanib as
fifth-line treatment (Table SIII).
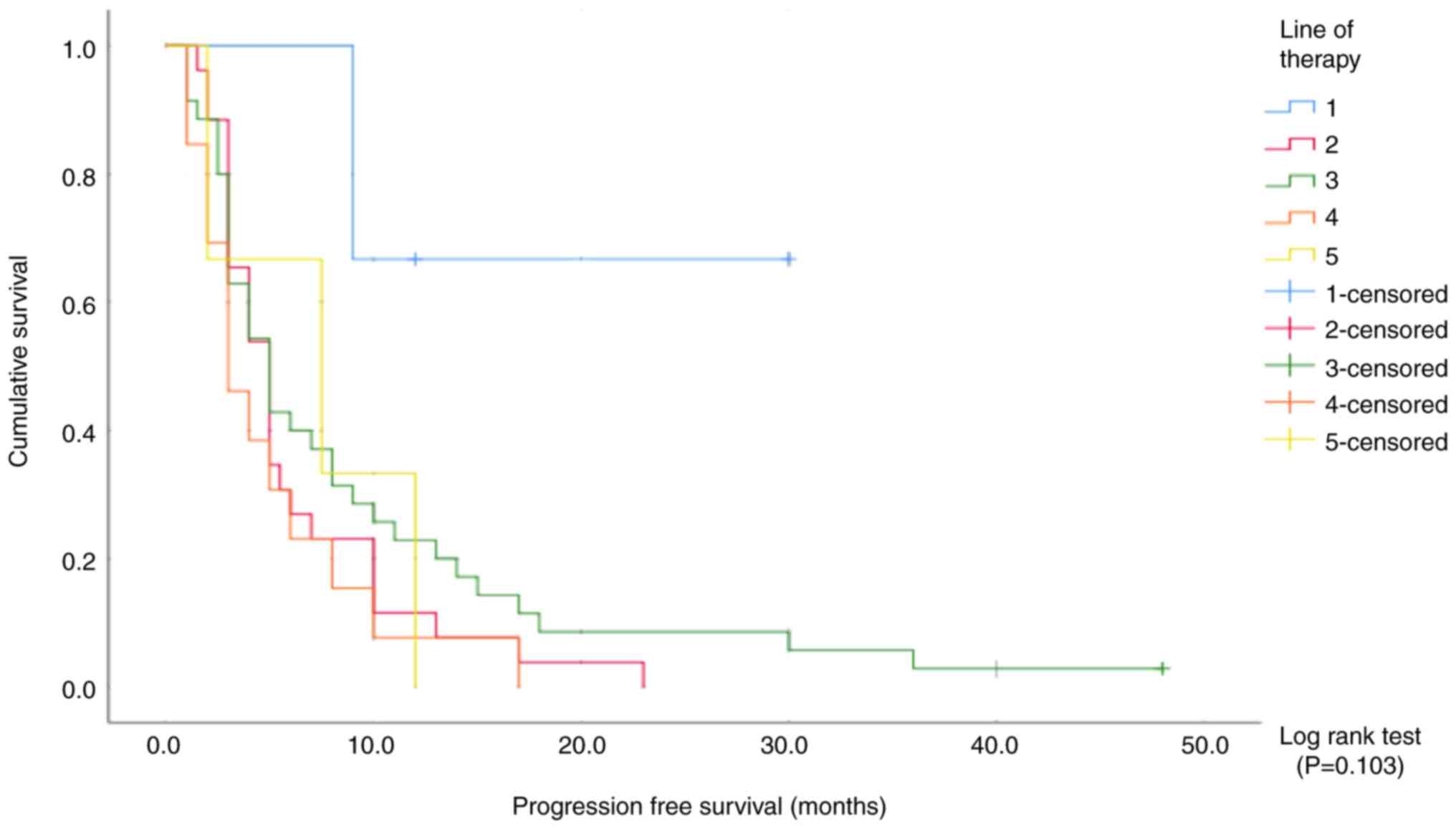
No significant association between progression-free survival and
the line of pazopanib therapy was observed (log-rank P=0.103;
Fig. 2).
The clinical response rate was 100% in patients who
received pazopanib therapy as first-line treatment, 46.2% in those
who received pazopanib therapy as second-line treatment, 48.6% in
those who received pazopanib therapy as third-line treatment, 15.4%
in those who received pazopanib therapy as fourth-line treatment
and 66.7% in those who received pazopanib therapy as fifth-line
treatment.
The patients were first evaluated separately and
then divided into three groups: i) First- and second-line therapy;
ii) third-line therapy; and iii) fourth- and fifth-line therapy. In
both evaluations of the groups, no effect of the line of therapy on
the clinical response was observed (Pearson's χ2 test,
P=0.053; Table SIV).
Number of metastatic sites
Overall, 64 patients had lung metastases (80%); 12
of them had only lung metastases (15%) and 52 of them had lung and
other metastases. Only 1 patient who received pazopanib did not
have a metastatic disease. Of the remaining 80 patients, 14 had 1
metastatic site, 34 had 2 metastatic sites, 22 had 3 metastatic
sites, 9 had 4 metastatic sites and 1 had 5 metastatic sites.
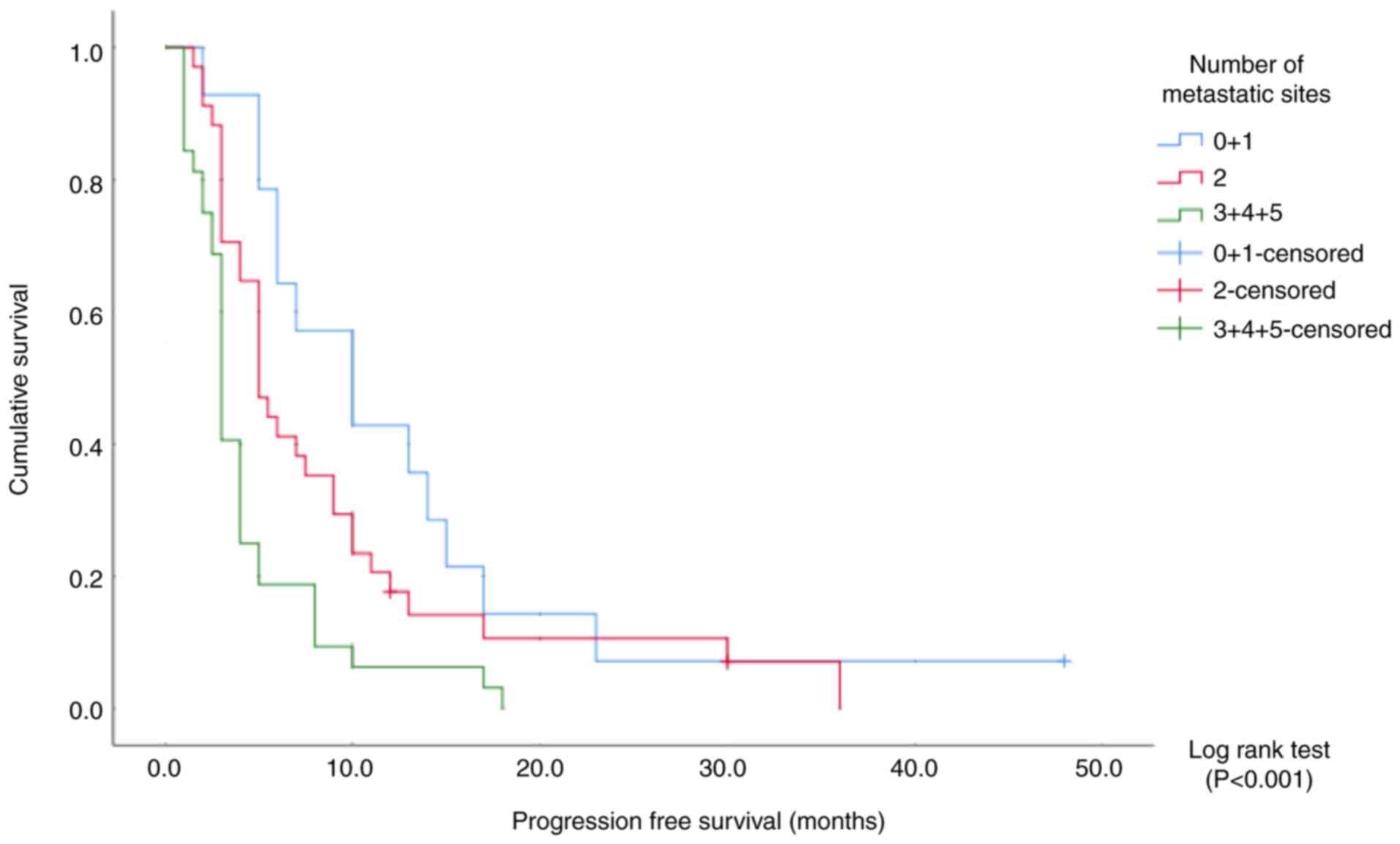
The median progression-free survival time was 10
months (95% CI, 4.5–15.4) in patients with ≤1 metastatic site, 5
months (95% CI, 3.8–6.2) in those with 2 metastatic sites, and 3
months (95% CI, 2.6–3.3) in those with ≥3 metastatic sites
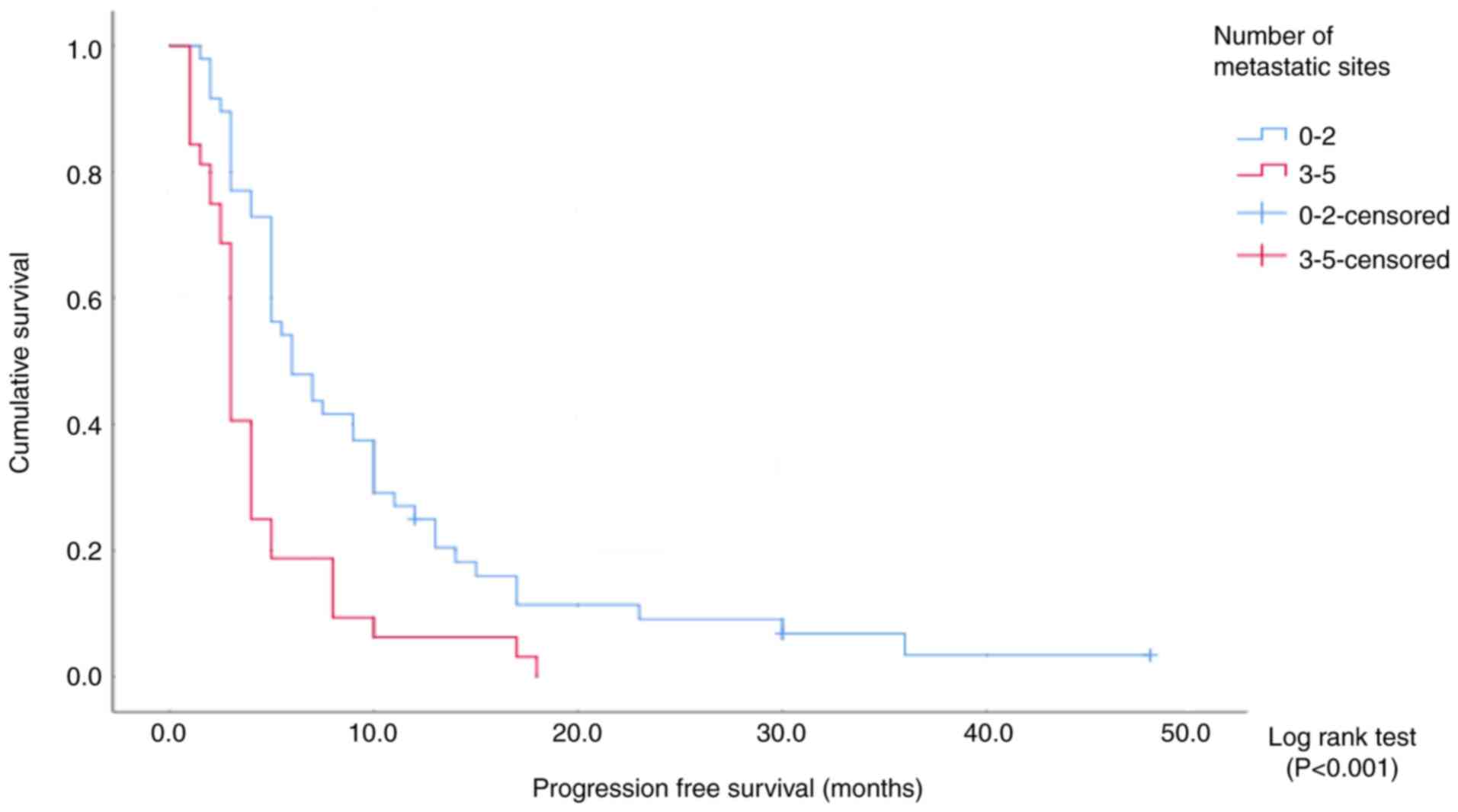
(Fig. 3 and Table IV). Patients were also divided into
groups of patients with 0–2 and ≥3 sites. The median
progression-free survival time was 6 months (95% CI, 3.7–8.2) in
the first group and 3 months (95% CI, 2.6–3.3) in the second group
(Fig. 4 and Table V). In both cases, the number of
metastatic sites had an effect on the progression-free survival
(log-rank P<0.001; Tables IV
and V). By contrast, there was no
significant difference in progression-free survival between
patients with 0–1 sites and those with 2 sites (Pearson
χ2 analysis, P=0.150).
 | Table IV.Progression-free survival according
to the number of metastatic sites (analysis 1). |
Table IV.
Progression-free survival according
to the number of metastatic sites (analysis 1).
| No. of metastatic
sites | Patients, n
(%) | Median
progression-free survival, months (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|
| 0-1 | 14 (17.5) | 10 (4.5–15.4) |
|
| 2 | 34 (42.5) | 5 (3.8–6.2) |
|
| ≥3 | 32 (40) | 3 (2.6–3.3) |
|
| Overall | 80 (100) |
| <0.001 |
 | Table V.Progression-free survival according
to the number of metastatic sites (analysis 2). |
Table V.
Progression-free survival according
to the number of metastatic sites (analysis 2).
| No. of metastatic
sites | Patients, n
(%) | Median
progression-free survival, months (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|
| 0-2 | 48 (60) | 6 (3.7–8.2) |
|
| ≥3 | 32 (40) | 3 (2.6–3.3) |
|
| Overall | 80 (100) |
| <0.001 |
The clinical response rate was 78% in patients with
0 or 1 metastatic sites, 55% in those with 2 sites, 27% in those
with 3 sites, and 10% in those with 4 or 5 sites. The patients were
first divided into three groups: i) 0 or 1 sites; ii) 2 sites; and
iii) ≥3 sites. In the analysis, the number of metastatic sites was
significantly associated with clinical response (Pearson's
χ2 test, P=0.001; Table
VI). When the patients were divided into two groups: i) 0, 1 or
2 sites; and ii) ≥3 sites), the number of metastatic sites was also
significantly associated with the clinical response (Fisher's exact
test two-sided test, P=0.001; Tables
VI and VII).
 | Table VI.Clinical response rates according to
the number of metastatic sites (analysis 1). |
Table VI.
Clinical response rates according to
the number of metastatic sites (analysis 1).
| No. of metastatic
sites | Patients, n
(%) | Partial response, n
(%) | Stable disease, n
(%) | Progressive
disease, n (%) | P-value |
|---|
| 0-1 | 14 (17.5) | 5 (6.3) | 6 (7.5) | 3 (3.7) |
|
| 2 | 34 (42.5) | 7 (8.8) | 12 (15.0) | 15 (18.7) |
|
| ≥3 | 32 (40.0) | 3 (3.7) | 4 (5.0) | 25 (31.3) |
|
| Overall | 80 (100) | 15 (18.8) | 22 (27.5) | 43 (53.7) | <0.001 |
 | Table VII.Clinical response rates according to
the number of metastatic sites (analysis 2). |
Table VII.
Clinical response rates according to
the number of metastatic sites (analysis 2).
| No. of metastatic
sites | Patients, n
(%) | Partial response, n
(%) | Stable disease, n
(%) | Progressive
disease, n (%) | P-value |
|---|
| 0-2 | 48 (60.0) | 12 (15.0) | 18 (22.5) | 18 (22.5) |
|
| ≥3 | 32 (40.0) | 3 (3.7) | 4 (5.0) | 25 (31.3) |
|
| Overall | 80 (100) | 15 (18.8) | 22 (27.5) | 43 (53.7) | <0.001 |
Safety
A total of 65 patients were evaluated for tolerance
to treatment (data not shown). In 4 patients, the treatment was
continued with dose reduction. Pazopanib treatment could not be
continued as planned in 1 patient because of grade 4 fatigue and
was stopped before the first cycle was completed.
The adverse effects were evaluated in 65 patients.
No side effects were observed in 29 patients. A total of 16
patients had grade 1–2 side effects, 19 patients had grade 3–4 side
effects and 2 patients had both grade 1–2 and grade 3–4 side
effects.
The most common side effects were hypothyroidism
(29.7%), elevated liver enzymes (18.9%), hypertension (16.2%),
fatigue (16.2%), emesis (10.8%), graying of hair (10.8%), diarrhea
(10.8%), pneumothorax (8.1%), cardiac side effects (8.1%),
hand-foot syndrome (5.4%) and neutropenia (5.4%). The side effects
that led to treatment discontinuation or interruption were fatigue,
arrhythmia, pnomotorax, hand-foot syndrome and dyspnea.
Discussion
In the present study, the median overall survival
time was 46 months. The overall survival time was the time from
detection of metastasis to death. A previous prospective study had
a period of 24 months for overall survival in 212 patients
diagnosed with soft tissue sarcoma at the University of Mannheim
(Germany) (7). The overall survival
time may have been markedly longer in the present study compared
with this previous study because most patients that received
pazopanib therapy were in the later stages of disease; therefore,
patients who died in the earlier stages without receiving this
therapy were not included in the present study.
The median progression-free survival time in the
entire study cohort was 5 months, which is consistent with the
literature. In the sub-analysis of two clinical studies organized
by the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer
(EORCT), median progression-free survival time was found to be 4.4
months in the patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcoma that
received pazopanib therapy (8).
No statistical significance was found in the
analysis based on histological subtypes for progression-free
survival. This is considered to be due to the large differences in
the number of patients between the groups. The synovial sarcoma,
leiomyosarcoma and pleomorphic sarcoma groups included a total of
51 patients, the median progression-free survival times were found
to be 5, 4 and 4 months, respectively, and the clinical response
rates were close to each other. The histological subtype did not
affect the success of treatment in these three groups, in which
pazopanib treatment was administered most frequently.
The median progression-free survival time was 1.5
months in patients with malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
and 2 months in patients with fibrosarcoma. Notably, only 1 of the
10 patients achieved a clinical response in these groups. The
median progression-free survival time of the placebo group was
calculated as 1.5 months in the PALETTE study organized by the
EORCT, which led to United States Food and Drug Administration
approval of pazopanib (4).
In the χ2 analysis performed to compare
groups of patients with different histological subtypes, a notably
longer progression-free survival was observed in patients with
hemangioendothelioma (23 months) and alveolar soft part sarcoma (15
months) compared with that of patients with other subtypes; There
were 2 patients in the hemangioendothelioma group and 1 patient did
not progress during the 48-month follow-up period. Pazopanib
therapy appears to be an ideal option for hemangioendothelioma. In
addition, pazopanib therapy has been used as a first-line treatment
for alveolar soft part sarcoma (9).
The data from the present study therefore supports administering
pazopanib as a first-line treatment in metastatic alveolar soft
part sarcoma.
It has been demonstrated that low and moderate grade
tumors have longer progression free and overall survival under
pazopanib therapy (8). However, in
the present study, no statistically significant effect of tumor
grade on progression-free survival and clinical response was
observed. This may have been due to the small number of patients
that were evaluated.
Pazopanib is generally not recommended for
first-line use in the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas. In the
present study, only 3 patients received pazopanib as the first-line
treatment. Among them, 2 had alveolar soft part sarcoma and 1 had
low-grade leiomyosarcoma. In the analysis, the line of treatment
had no effect on progression-free survival or clinical response
rates. The fact that these parameters were lower in patients given
pazopanib as fourth- or fifth-line treatment was considered to be
due to increase in the tumor burden as a result of the increase in
the number of failed lines and the worsening of the performance
status of the patients. In subtypes in which pazopanib was most
often used, such as synovial sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, pleomorphic
sarcoma and angiosarcoma, it still seems to be the most appropriate
option after regimens containing anthracyclines and ifosfamide.
Furthermore, 3 patients with Ewing sarcoma in the study received
this treatment as fourth- or later-line treatment, and 2 had a
clinical response (both had isolated lung metastases). There were
four different metastatic sites in 1 patient who showed disease
progression. It was suggested that pazopanib could also be
considered as an option for later-line treatment for patients with
Ewing sarcoma whose disease is still under control.
It was predicted that increased tumor burden may
adversely affect treatment success, because it is considered that
it may be harder to maintain disease control (8). The present analyses demonstrated that
the number of metastatic sites affected both progression-free
survival and clinical response rates. It was not possible to
clearly differentiate between patients with oligometastatic and
multimetastatic disease. In the present study, no significant
difference was found in the progression-free survival of patients
with 0–1 sites and 2 sites. This suggested that patients with ≤2
different metastatic sites could be considered as to have
oligometastatic disease.
An advantage of pazopanib over conventional
cytotoxic therapies is its tolerance; this is especially true for
elderly patients (8). In the
present study, treatment tolerance was generally good. The most
common adverse effects were hypothyroidism, elevated liver enzyme
levels, hypertension, fatigue, diarrhea, hair graying and emesis.
This is similar to the side effects reported in another study
(10). None of the patients
developed grade 3–4 anemia or neutropenia. In 3 patients,
pneumothorax and cardiac side effects (arrhythmia and heart
failure) developed, and the clinical recommendation was close
follow-up of these patients.
In summary, the success of pazopanib therapy and the
factors affecting its success have been discussed. Pazopanib
therapy was the most successful in patients with alveolar soft part
sarcoma and hemangioendothelioma, whereas it was less successful in
patients with malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors and
fibrosarcoma.
It was concluded that regardless of the subtype, the
response rates of patients with a small number of metastatic sites
were improved compared with those of higher number of metastatic
sites. In addition, administering the treatment as a second- or
third-line treatment appeared to be more successful than
administering it as a later-line therapy. Therefore, pazopanib
should be evaluated as an option for a selected group of patients
in whom the aforementioned factors present together.
Studies to predict the success of pazopanib therapy
for soft tissue sarcomas are ongoing. Although there is currently
no definitive biomarker to identify patients with soft tissue
sarcoma that may benefit from pazopanib therapy, the TP53 mutation
status stands out in this regard. A retrospective analysis of 19
patients with advanced soft tissue sarcoma who received pazopanib
therapy at the Ohio State James Comprehensive Cancer Center
(Columbus, OH, USA) demonstrated a markedly longer median
progression-free survival time in the group with TP53 mutations
(6). In another retrospective study
involving 67 patients at Yonsei Cancer Center (Seoul, South Korea)
between 2013 and 2019, biopsy samples were re-examined for
programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, and an inverse
association was found between PD-L1 expression and the success of
pazopanib treatment (11). As a
result, a clinical study assessing the use of pazopanib in
combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors has been initiated
and early results are promising (12); the progression-free suvival was 7.7
months and it was found to be longer compared with that obtained in
the EORCT trial and the present study, which were 4.4 and 5 months
rescpectively (8,12). As studies on these issues become
more comprehensive, clearer data will emerge. Notably, the use of
next-generation sequencing technology has become increasingly
widespread to provide additional genetic information in cancer
treatment (13). In a previous
report in which a patient achieved a complete response under
pazopanib therapy, several somatic mutations and chromosome
amplifications were identified by NGS. For example, somatic
mutations, including platelet-derived growth factor receptor α
p.T83S and platelet-derived growth factor receptor β exon 13
skipping were found. These findings are consistent with the
mechanism of action of pazopanib. Pazopanib is a multiple kinase
inhibitor that limits tumor growth by targeting angiogenesis via
inhibition of enzymes including vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor, platelet-derived growth factor receptor and c-KIT.
Patients with these genetic alterations may be better responders to
pazopanib therapy (13).
A major limitation of the present study was that it
was a single-center, retrospective study. As the study covers
patients over a long period, certain patient data could not be
accessed, and factors such as tumor grade and treatment tolerance
could not be fully evaluated. However, considering how rare
sarcomas are and that pazopanib treatment is given only in
metastatic disease and generally in later-line therapy, the number
of patients increased the reliability and generalizability of the
present study. In conclusion, the progression-free survival and
response rates of patients with a small number of metastatic sites
were better regardless of subtype.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
CMS collected all the data, performed the
statistical analysis and wrote the manuscript. PG contributed to
analyzing the data, writing and drafting the manuscript, and
organizing the tables and figures. UAS treated the patients, helped
in collecting the data and designing the study. All authors have
read and approved the final version of the manuscript. CMS and UAS
confirm the authenticity of all the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ege University
Ethics committee (approval no. 21-6-1T/83; Bornova, Turkey). The
patients provided written informed consent for their participation
in the study.
Patient consent for publication
The patients provided written informed consent for
the publication of any data and images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Burningham Z, Hashibe M, Spector L and
Schiffman JD: The epidemiology of sarcoma. Clin Sarcoma Res.
2:142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ramu EM, Houdek MT, Isaac CE, Dickie CI,
Ferguson PC and Wunder JS: Management of softtissue sarcomas;
treatment strategies, staging, and outcomes. SICOT J.
3:20170102017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gebhardt MC: Surgical resection of primary
soft tissue sarcoma of the extremities. UpToDate:. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/surgical-resection-of-primary-soft-tissue-sarcoma-of-the-extremities?csi=713bac06-a2a1-474f-85e3-00037d327ff8&source=contentShareJuly
29–2021
|
|
4
|
George S and Razak ARA: Overview of the
initial treatment of metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. UpToDate:.
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-the-initial-treatment-of-metastatic-soft-tissue-sarcoma?csi=fac78e3c-5a2f-44ae-a398-db74f544d104&source=contentShareAugust
12–2023
|
|
5
|
Nguyen DT and Shayahi S: Pazopanib:
Approval for soft-tissue sarcoma. J Adv Pract Oncol. 4:53–57.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koehler K, Liebner D and Chen JL: TP53
mutational status is predictive of pazopanib response in advanced
sarcomas. Ann Oncol. 27:539–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lochner J, Menge F, Vassos N, Hohenberger
P and Kasper B: Prognosis of patients with metastatic soft tissue
sarcoma: Advances in recent years. Oncol Res Treat. 43:613–619.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kasper B, Sleijfer S, Litière S, Marreaud
S, Verweij J, Hodge RA, Bauer S, Kerst JM and van der Graaf WTA:
Long-term responders and survivors on pazopanib for advanced soft
tissue sarcomas: Subanalysis of two European organisation for
research and treatment of cancer (EORTC) clinical trials 62043 and
62072. Ann Oncol. 25:719–724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stacchiotti S, Mir O, Cesne AL, Vincenzi
B, Fedenko A, Maki RG, Somaiah N, Patel S, Brahmi M, Blay JY, et
al: Activity of pazopanib and trabectedin in advanced alveolar soft
part sarcoma. Oncologist. 23:62–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Le Cesne A, Bauer S, Demetri GD, Han G,
Dezzani L, Ahmad Q, Blay JY, Judson I, Schöffski P, Aglietta M, et
al: Safety and efficacy of Pazopanib in advanced soft tissue
sarcoma: PALETTE (EORTC 62072) subgroup analyses. BMC Cancer.
19:7942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim SK, Kim JH, Kim SH, Lee YH, Han JW,
Baek W, Woo HY, Jeon MK and Kim HS: PD-L1 tumour expression is
predictive of pazopanib response in soft tissue sarcoma. BMC
Cancer. 21:3362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho HJ, Yun KH, Shin SJ, Lee YH, Kim SH,
Baek W, Han YD, Kim SK, Ryu HJ, Lee J, et al: Durvalumab plus
pazopanib combination in patients with advanced soft tissue
sarcomas: A phase II trial. Nat Commun. 15:6852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suehara Y, Kohsaka S, Yamaguchi S, Hayashi
T, Kurihara T, Sano K, Sasa K, Akaike K, Ueno T, Kojima S, et al:
Assessment of predictive biomarkers of the response to pazopanib
based on an integrative analysis of high-grade soft-tissue
sarcomas: Analysis of a tumor sample from a responder and patients
with other soft-tissue sarcomas. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
478:2461–2476. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|