Introduction
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of
cancer-related death globally and remains the most common
malignancy among women worldwide (1,2).
Breast cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease. Previous studies
have shown that early diagnosis and timely treatment can
significantly improve the prognosis and increase the survival time
of patients with breast cancer (3,4). At
present, mammography and ultrasound imaging are widely used for
early breast cancer screening (5,6), and
new bioinformatics indicators, such as tumor-associated
macrophages, microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) and long noncoding RNAs, may
hold promise in further optimizing individualized treatment
approaches for breast cancer.
miRNAs are a class of non-coding RNAs that are 19–24
nucleotides in length. They function as epigenetic regulators by
modulating post-transcriptional gene expression (7,8). The
dysregulated expression of miRNAs can have significant effects on
various aspects of cancer progression, including metastasis, cell
proliferation and chemotherapy resistance. Aberrant expression of
specific miRNAs has been associated with the development and
recurrence of several types of cancer, including breast, prostate,
lung and colon cancer (9). Tumor
cells exhibit distinctive miRNA expression profiles, which can lead
to a downregulation in the expression levels of numerous tumor
suppressor genes or oncogenes during the process of cancer
transformation (9,10). Recently, miRNAs have emerged as
stable biomarkers in various biological samples, such as tissues,
blood, saliva and urine, offering a promising non-invasive approach
for diagnostic and prognostic purposes (11,12).
Previous studies have shown that miR-96 is significantly
upregulated in various types of tumors, including prostate cancer,
hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer, colorectal cancer,
endometrial cancer and breast cancer (13–15).
miR-96 exhibits diverse target genes in different types of cancer.
For example, in esophageal cancer, one of its target genes is RECK,
whereas in hepatocellular carcinoma, it targets EphrinA5 (16). miR-96-5p has been implicated in
promoting tumor progression by negatively regulating the tumor
suppressor gene FOXO3, which ultimately leads to enhanced cell
proliferation (17). However, to
date, the biological function of miR-96 in breast cancer is still
largely unknown. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to
evaluate the association between miR-96 and breast cancer, and to
explore the potential target genes of miR-96.
TGFβ is a crucial regulator in various biological
processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis
and immune responses. Proper regulation of TGFβ signaling is
essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis and preventing
tumorigenesis (18). The TGF-β
signaling pathway plays a significant role in promoting the
proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells, as well as
aiding in immune evasion by cancer cells (19). Within this pathway, there are
inhibitory Smad proteins, namely Smad6 and Smad7, which negatively
regulate the activity of the TGF-β signaling pathway (20–22).
Smad7, which is one of the key inhibitors of TGF-β signal
transduction, negatively regulates the whole pathway through a
variety of mechanisms (23,24). miR-96-5p, by targeting Smad7, can
exacerbate PPAR-γ/C/EBPα signaling-induced adipogenic
differentiation of orbital fibroblasts (25). Another study reported that miR-96
can promote collagen deposition in keloids by targeting Smad7
(26,27).
miR-96, as an oncogene, may be an important
regulator of breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and
invasion. The present study focused on miR-96 expression in tissue
specimens from patients with breast cancer and breast cancer cell
lines.
Materials and methods
Human specimens
Breast cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues (~2
cm from tumor tissue) were collected from patients with breast
cancer (n=5). The patients were aged between 26 and 43 years (mean
± SD age, 31.12±2.27 years). The numbers of patients with stage I,
II and III breast cancer were 2, 2 and 1, respectively, according
to the Union for International Cancer Control TNM classification
and stage (28). Frozen samples (at
−80°C) were obtained from patients with breast cancer who had
undergone tumorectomy or mastectomy after fine needle biopsy
diagnosis of breast cancer. Tissues were fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature and were prepared
into 6-µm sections. The thickness was assessed by a professional
pathologist. The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee
of The People's Hospital of Xinghua City (approval no.
JSXHRYLL-YJ-202026; Xinghua, China) and was performed in compliance
with The Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was
obtained from all participants before surgery.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
(RT-q) PCR
A total of five samples of breast cancer tissues and
paracancerous tissues were collected. Total RNA was extracted from
the tissues using TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a
PrimeScript RT Kit (Takara Bio, Inc.) according to the
manufacturer's instructions. PCR amplification was performed using
the following reaction mixture: 10 µl SYBR Green Mix (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.), 0.4 µl forward primers, 0.4 µl reverse primers,
7.2 µl ddH2O and 2 µl cDNA template, resulting in a
total volume of 20 µl. The amplification conditions were as
follows: 94°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles at 94°C for 20 sec,
55°C for 20 sec and 72°C for 20 sec. The relative expression levels
of target genes were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCq method
(29). GAPDH was used as the
internal control for mRNA detection and U6 was used as the internal
control for miRNA detection. The primer sequences are listed in
Table I.
 | Table I.Primer sequences. |
Table I.
Primer sequences.
| Name | Primer sequence,
5′-3′ |
|---|
| miR-96-5p
(human)-F |
ACACTCCAGCTGGGTTTGGCACTAGCACATT |
| URP |
TGGTGTCGTGGAGTCG |
| Smad7
(human)-F |
CAACCGCAGCAGTTACCC |
| Smad7
(human)-R |
CGAAAGCCTTGATGGAGA |
| hsa-mir-96-5p
mature sequence |
TTTGGCACTAGCACATTTTTGCT |
| RT reverse
primers |
CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGAGCAAAAA |
| U6 (human)-F |
CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6 (human)-R |
AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| GAPDH
(human)-F |
AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG |
| GAPDH
(human)-R |
AGGGGCCATCCACAGTCTTC |
Western blot analysis
Total protein was extracted from tissues and cells
using RIPA cleavage fluid (cat. no. P0013B; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology), and its concentration was determined using the BCA
protein assay kit (QPBCA; MilliporeSigma). The proteins (35 µg)
were separated by SDS-PAGE on 8% gels and subsequently transferred
to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. After blocking with 5% BSA
(cat. no. BS114; Biosharp Life Sciences) at room temperature for 1
h, the membranes were incubated with specific primary antibodies at
4°C overnight and then washed three times with PBS-0.1% Tween. The
primary antibodies used were Smad7 (cat. no. ab216428; Abcam), AKT
(cat. no. ab89402; Abcam), TGF-β (cat. no. ab215715; Abcam), PI3K
(cat. no. 20584-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.), BAX (cat. no.
ab182733; Abcam), BCL2 (cat. no. ab182858; Abcam), caspase 3 (cat.
no. ab13585; Abcam), caspase 9 (cat. no. ab202068; Abcam) and GAPDH
(cat. no. 60004-1-Ig; Proteintech Group, Inc.). The primary
antibodies were used at a dilution of 1:1,000. The membranes were
subsequently incubated with the corresponding horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (HRP-labeled sheep
anti-mouse secondary antibody, cat. no. ZB2305; HRP-labeled sheep
anti-rabbit secondary antibody, cat. no. ZB2301; both from OriGene
Technologies, Inc.; 1;5,000 dilution) at room temperature for 1 h.
The gray values were analyzed by ImageJ 2X software (National
Institutes of Health) and the relative expression levels of
proteins in each group were calculated.
Cell culture
Breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231,
MDA-MB-436 MDA-MB-468 and ZR-75-1) were purchased from Nanjing
KeyGen Biotech Co., Ltd. and were cultured in DMEM supplemented
with 10% fetal bovine serum (Procell Life Science & Technology
Co., Ltd.), 1% L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 mg/ml
streptomycin. The cell lines were authenticated using the short
tandem repeat method. The cells were incubated at 37°C in a
humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. The cells were
negative for mycoplasma. On reaching 80–90% confluence, the cells
were transferred to the appropriate plates for subsequent
analyses.
Immunohistochemistry
A total of five samples of breast cancer tissues and
paracancerous tissues were collected fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde
at room temperature for 30 min, dehydrated in a graded ethanol
series and then prepared as paraffin-embedded sections (5 µm).
Histological slices were blocked with 10% normal goat serum
(Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) at room temperature for 1 h.
Subsequently, the sections were incubated overnight at 4°C with
primary antibodies against Smad7 (cat. no. ab216428; Abcam; 1:100),
Ki67 (cat. no. ab21700; Abcam), followed by a 1-h incubation at
37°C with a HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (ready to use; cat.
no. PV-9001; OriGene Technologies, Inc.). The nuclei were stained
with hematoxylin at room temperature for 5–8 min and the expression
levels of Smad7 in tissues were examined by light microscopy.
Dual luciferase assay for verifying
the interaction between miR-96 and Smad7
A dual luciferase kit (cat. no. E1910; Promega
Corp.) was used to determine the interrelationship between miR-96
and Smad7. The miR-96 binding site in the 3′-UTR of Smad7 was
identified using TargetScan version 7.2 (https://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/). Calculations
were made by comparing firefly luciferase activity to
Renilla luciferase activity. The wild-type (WT) Smad7
sequence containing miR-96 binding sites was found on NCBI
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/KT584248.1) and
was used to design a mutant (MUT) sequence (usually complementary
to the miR-96 binding site). The sequences were then sent to
General Biology (Anhui) Co., Ltd. for direct synthesis into pmirGLO
vectors [provided by General Biology (Anhui) Co., Ltd.].
Hsa-miR-96-5p mimics, pmirglo-Smad7 WT-3′ UTR and pmirglo-Smad7
MUT-3′ UTR were synthesized by Oligobio [provided by General
Biology (Anhui) Co., Ltd.] and were transfected into 293T cells
(60% confluence; Wuxi Puhe Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd.) using
Lipofectamine® 2000 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The
transfection efficiency was assessed by dual luciferase assay at 48
h post-transfection. The following sequences were used: miR-96-5p
mimic, 5′-UUUGGCACAGCACAUUUUUGCUCAAAAAUGUGCUAGUGCCAAAUU-3′; mimic
NC, 5′-AGAGGAAACGUGCUAGUGCCAGG-3′.
Knockdown of Smad7 target
sequence
For Smad7 knockdown, the
plvx-shRNA2-Zsgreen-T2A-puro vector [General Biology (Anhui) Co.,
Ltd.] was used. Using a second-generation lentiviral vector system,
293T cells were transfected with a combination of the plasmid
containing the target sequence, packaging plasmids (pGag/Pol,
pRev), envelope plasmid (pVSV-G) and Lipo8000™ transfection reagent
(cat. no. C0533; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology); the plasmid
ratio for the target gene plasmid, packaging plasmids and envelope
plasmid was 1:4:3, corresponding to 2.5, 10 and 7.5 µg,
respectively. Transfection was carried out at 37°C in a 5%
CO2 incubator for 6 h. After 6 h, the medium was
replaced with complete culture medium and the cells were cultured
for 72 h. Subsequently, the cell supernatant enriched with
lentiviral particles was collected by centrifugation at 3,000 × g
for 4 min at 4°C. The supernatant was filter through a 0.45-µm
filter, and the lentiviral particles were concentrated by
ultracentrifugation at 32,000 × g for 2 h at 4°C. The concentrated
viral suspension was then aliquoted into labeled tubes and stored
at −80°C. The day before infection, 4×103 MDA-MB-231
cells were seeded into each well of a 96-well plate. When the
MDA-MB-231 cell density reached 50%, the virus was directly added
to the complete culture medium at a multiplicity of infection of
100. The cells were incubated with the virus for 72 h at 37°C. To
create a stable cell line, transduced cells were selected using
puromycin solution (cat. no. BL528A; Biosharp) at a concentration
of 2.5 µg/ml. The sequences were as follows: shRNANC,
5′-GGTATAGCCAGCTAACTAGAA-3′; shRNA-Smad7-1,
5′-GCTTTCAGATTCCCAACTTCT-3′; shRNA-Smad7-2,
5′-GGTTTCTCCATCAAGGCTTTC-3′; shRNA-Smad7-3,
5′-GCTCCCATCCTGTGTGTTAAG-3′. The data were analyzed by ABI Prism
7500 SDS software (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). RT-qPCR assays were conducted to verify the expression
levels of target genes following transfection.
Functional analysis of miR-96-5p and
its interaction with Smad7
MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells
(1×105/well) were seeded into a 24-well plate and
incubated under standard conditions in complete medium. The
transfection reagents were prepared by mixing miR-96-5p negative
control (NC), miR-96-5p mimics + overexpression-negative control
(OE-NC; empty pcDNA3.1-EGFP plasmid), miR-96-5p NC +
overexpression-Smad7 (OE-Smad7) and miR-96-5p inhibitor [all
supplied by General Biology (Anhui) Co., Ltd.] with Lipo8000 to
form the transfection complex. In addition, cells that had already
been virally infected with shRNA-Smad7 were subsequently
transfected with the miR-96-5p inhibitor. This step was based on
the protocol for Lipo8000 transfection reagent, using 500 ng
plasmid/well in a 24-well plate, with an RNA concentration of 20
pmol. The transfection complex was added to the cells and incubated
under standard conditions for 4–6 h. Subsequently, the supernatant
was removed and the cells were incubated in complete medium for
another 48 h before being collected for further analysis. The
following sequences were used: miR-96-5p mimics,
5′-UUUGGCACAGCACAUUUUUGCUCAAAAAUGUGCUAGUGCCAAAUU-3′; miR-96-5p
inhibitor NC, 5′-CAGUACUUUUGUGUAGUACAA-3′; miR-96-5p mimic NC,
5′-AGAGGAAACGUGCUAGUGCCAGG-3′; miR-96-5p inhibitor,
5′-AGCAAAAAUGUGCUAGUGCCAAA-3′.
Transwell assays for cell invasion and
migration
First, 100 µl serum-free medium was added to the
upper chamber of a Transwell system (pore size, 8 µm; cat. no.
3422; Corning, Inc.), while 600 µl complete medium was added to the
lower chamber. Subsequently, transfected MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468
cells were added to the upper chamber at a density of
4×104/well and were cultured 24 h 37°C. Next, the cells
were fixed with pre-cooled 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature
for 30 min and stained with 0.5% crystal violet at room temperature
for 10 min. Finally, the polycarbonate film was obtained from the
upper chamber, sealed and observed under a light microscope. In
addition, the upper chamber of the Transwell system was coated with
Matrigel at 37°C for 30 min for the cell invasion assay, and the
rest of the steps were the same as those performed for the cell
migration assay.
Determination of cell adhesion
First, 100 µl coating solution in the Cell Adhesion
Assay Kit (cat. no. BB-48120; Bstbio) was added to a 96-well plate
at 2–8°C overnight. The coating fluid was removed and the culture
vessels were dried. The washing solution (PBS) was used to wash the
vessels 1–3 times. Transfected MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells were
digested with trypsin and collected, washed with PBS and then
suspended in the corresponding medium to prepare a cell suspension.
Cell suspensions containing 5×104 cells/well were
incubated in a 96-well plate with three multiple wells. To each
well of the 96-well plate 10 µl cell staining solution B was added
and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The OD450 nm values of
the sample wells were measured.
Nude mouse tumorigenicity model
Nude mice were obtained from Changzhou Cavens
Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. All experiments were approved by the
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Affiliated
Hospital of Yangzhou University (this hospital has a partnership
with Yangzhou University; approval no. JSXHRYLL-YJ-202026; Jiangsu,
China). All animal experiments were performed in compliance with
animal ethics (30) and EU
Directive 2010/63/EU (31). A total
of 9 specific pathogen-free-rated healthy male nude mice (age, 4–6
weeks; weighing, 20 g), housed at 40–60% humidity and ~25°C, under
a 12-h light/dark environment. The mice were maintained in a clean
environment, avoiding bright light and noise, and were given free
access to food and water. On an ultra-clean table, the skin at the
injection site of the nude mice was disinfected using 75% alcohol.
Subsequently, 100 µl 1X PBS containing 5×106 MDA-MB-231
cells was injected into the armpits of the nude mice according to
their respective groups. For cell inoculation, the needle was
inserted under the skin, about 1 cm deep, in order to minimize the
overflow of the cell suspension from the eye of the needle after
the injection. This was to prevent liquid leakage, sterilize the
skin and facilitate observation of tumor formation. Tumor size in
the nude mice was measured every 3 days. The longest and shortest
tumor diameters were measured using vernier calipers and the tumor
volume (V, in mm3) was calculated using the formula
V=(AB2)/2, where A and B represent the longest and
shortest tumor diameters, respectively. The tumor size of nude mice
was measured every 3 days and recorded. When tumor mass was ~100
mm3, each mouse was injected with 100 µl 20 nmol
miR-96-5p mimics NC, miR-96-5p mimics or miR-96-5p inhibitor for 3
consecutive days. The following sequences were used: miR-96-5p
mimic: 5′-UUUGGCACAGCACAUUUUUGCUCAAAAAUGUGCUAGUGCCAAAUU-3′,
miR-96-5p inhibitor: 5′-AGCAAAAAUGUGCUAGUGCCAAA-3′ and mimics NC:
5′-AGAGGAAACGUGCUAGUGCCAGG-3′. The mice in the control group were
intratumorally injected with normal saline. After 3 weeks of
treatment, the nude mice were sacrificed for tumor collection. The
method used was isoflurane inhalation at a concentration of 5%.
Cell cycle analysis
For cell cycle analysis, the transfected MDA-MB-231
and MDA-MB-468 cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of
1×106 cells per well. Then, the cells were harvested,
fixed with 80% ethanol at 4°C overnight, then treated with 50 µg/ml
PI and 100 µl RNase (100 µg/ml) for 30 min at room temperature in
the dark. The fixed/stained cells were analyzed using a FACSCalibur
flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and ModFit LT 5.0 (Verity Software
House).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted with GraphPad
Prism 5.0 software (Dotmatics). Data are presented as the mean ±
SD; in vitro experiments n=3, clinical experiments n=5. For
data that followed a normal distribution, Student's unpaired t-test
was used to compare the difference between two groups. For
multi-group comparisons of variables, one-way ANOVA was used with
the Tukey's post hoc test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Expression levels of miR-96 and Smad7
are significantly increased and decreased in breast cancer tissues,
respectively
The present study explored the differences in miR-96
and Smad7 expression levels between breast cancer tissues and
adjacent tissues, and verified the roles of miR-96-5p and Smad7 in
breast cancer. Breast cancer and adjacent non-tumor tissues were
collected from five patients with breast cancer, and the
differences in miR-96 and Smad7 expression levels between the
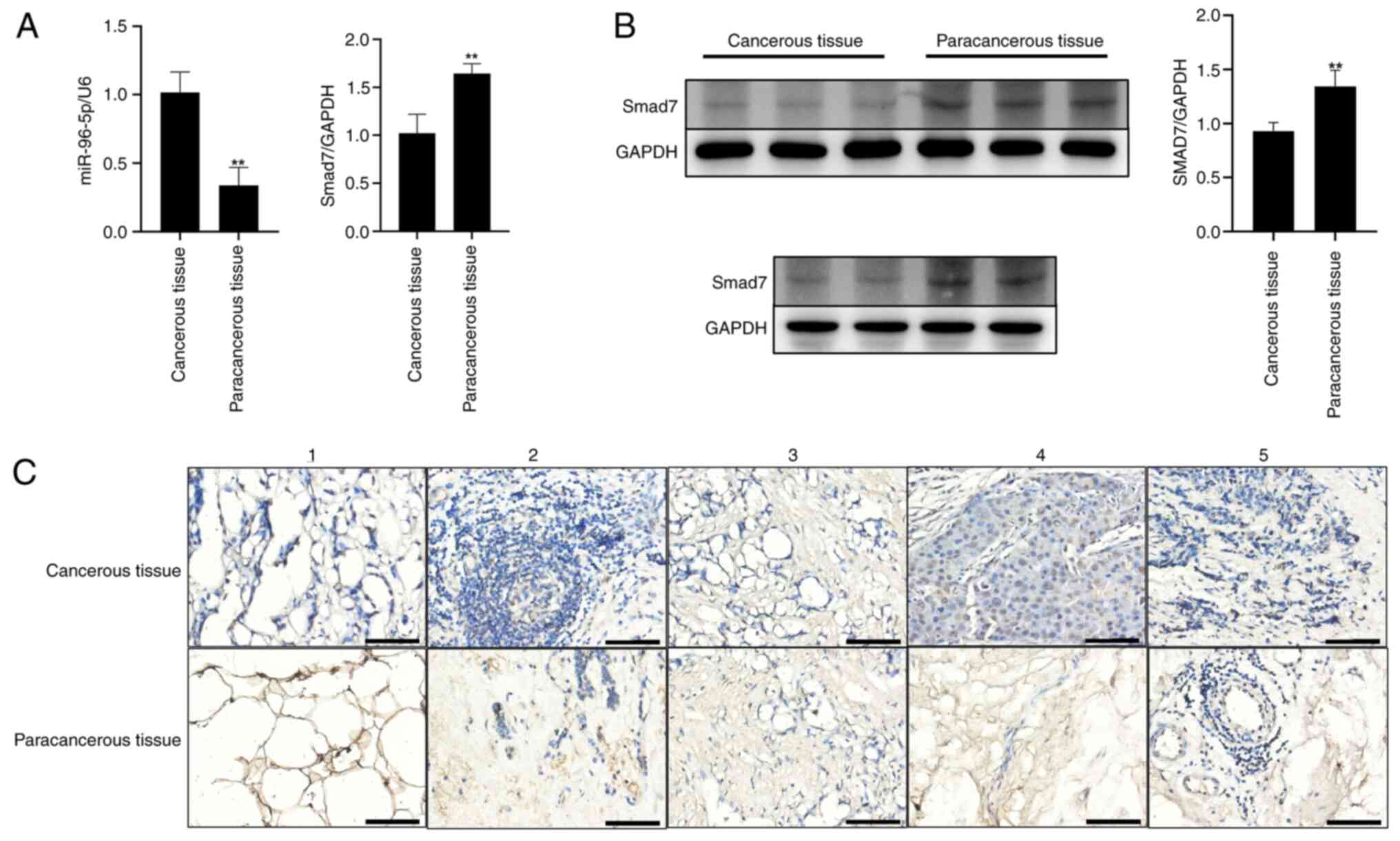
tissues were detected by RT-qPCR. As shown in Fig. 1A, the expression levels of miR-96-5p
were significantly higher in breast cancer tissues than in adjacent
tissues, while the expression levels of Smad7 were significantly
lower in breast cancer tissues than in adjacent tissues. Western
blot analysis and immunohistochemical staining revealed that the
expression levels of Smad7 were markedly reduced in breast cancer
tissues compared with those in adjacent tissues (Fig. 1B and C). Expression of the target
protein appears as brown staining.
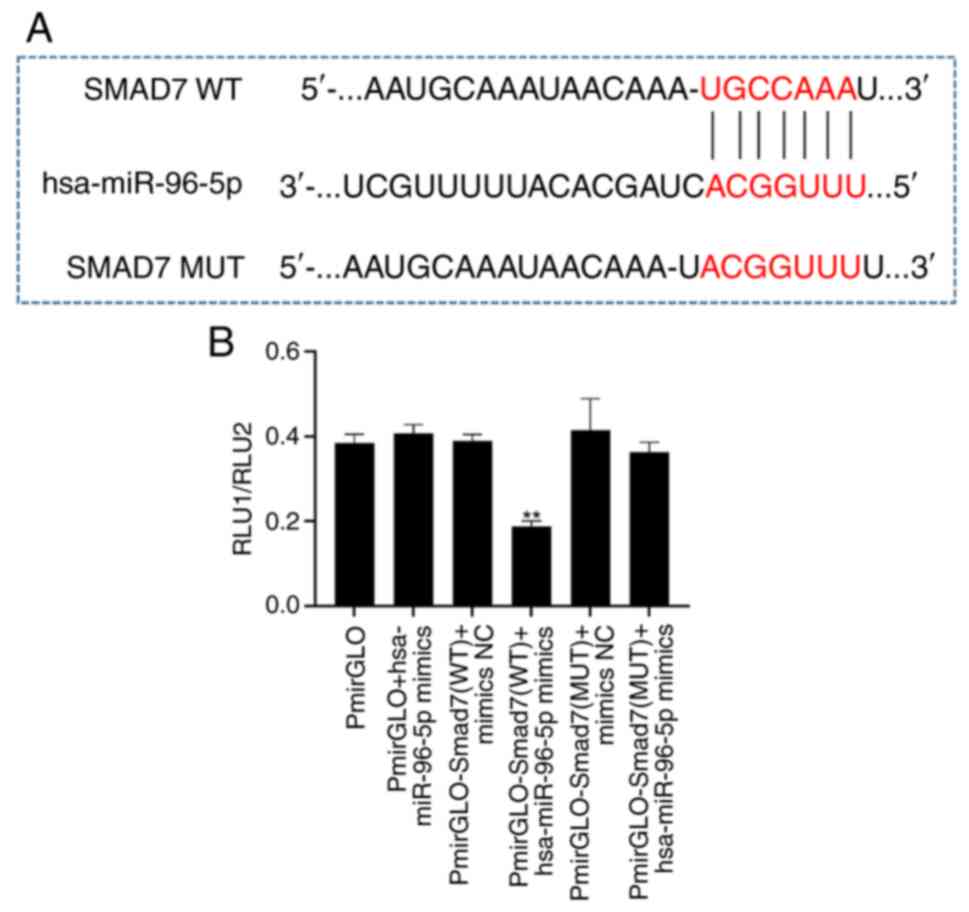
miR-96 can bind Smad7
To investigate the relationship between miR-96 and
Smad7, miR-96-5p mimics were first synthesized, and WT and MUT
plasmids for Smad7-3′UTR constructed. Subsequently, 293T cells were
transfected and changes in activity were measured using a dual
luciferase kit. The experimental results demonstrated that, in
comparison to the NC group, co-transfection of 293T cells with the
WT Smad7 vector and miR-96-5p mimics led to a significant reduction
in luciferase activity (Fig. 2).
However, when the predicted binding site (g.51537A>G) was
mutated, there was no significant difference in luciferase activity
compared with the NC group (Fig.
2). These findings indicated that miR-96-5p has the ability to
target and bind to Smad7.
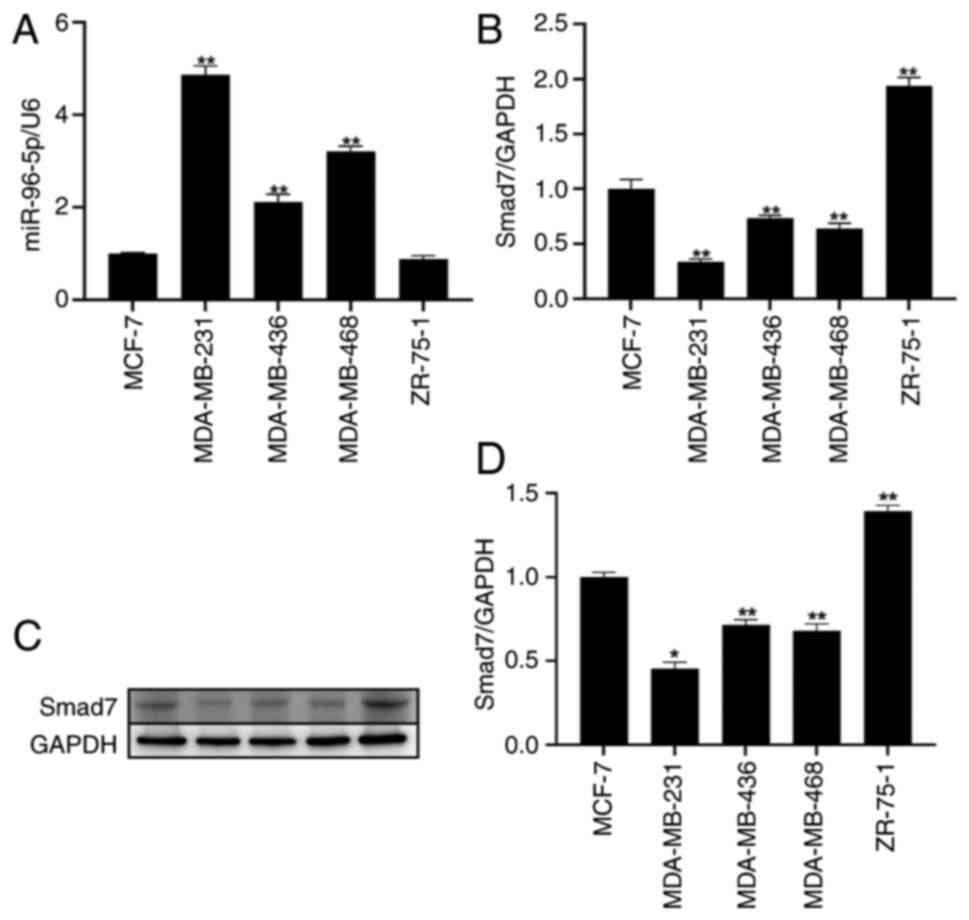
Among the five breast cancer cell
lines, miR-96 expression is highest and Smad7 expression is lowest
in MDA-MB-231 cells
To determine the expression levels of miR-96 and
Smad7 in breast cancer, RT-qPCR was conducted to detect their mRNA
expression levels in different breast cancer cell lines, including
MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-468 and ZR-75-1. The
experimental results showed that miR-96 exhibited the highest
expression in MDA-MB-231 cells. Conversely, the expression levels
of Smad7 were found to be the lowest in MDA-MB-231 cells (Fig. 3A and B). Subsequently, western
blotting was conducted to assess the expression levels of Smad7 in
different breast cancer cell lines. The findings demonstrated that
Smad7 expression was the lowest in MDA-MB-231 cells (Fig. 3C and D).
miR-96 reduces the expression of Smad7
in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells
The present study designed and synthesized three
shRNA-Smad7 plasmids. All of the plasmids were transfected into the
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. After transfection, RNA was
extracted from each group of cells and was reverse-transcribed into
cDNA for RT-qPCR analysis. The experimental results, as shown in
Fig. S1A, indicated that different
shRNAs had distinct knockdown effects on Smad7 mRNA expression
levels. Among them, shRNA-Smad7-2 exhibited the most marked
knockdown effect.
As shown in Fig.
S2, compared with in the mimics NC group, miR-96-5p expression
was increased after MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells were
transfected with miR-96-5p mimics. Compared with in the inhibitor
NC group, the expression levels of miR-96-5p were decreased
post-transfection with the miR-96-5p inhibitor. As shown in
Fig. S3, compared with in the OE
NC group, an increase in Smad7 expression was detected in
MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells transfected with OE Smad7, and
compared with in the shRNA NC group, a decrease in Smad7 expression
was detected after transfection with shRNA Smad7. These findings
indicated that transfection was successful. Since the expression
levels of miR-96-5p in the mimics NC and inhibitor NC groups were
consistent, both were subsequently represented by a mimics NC.
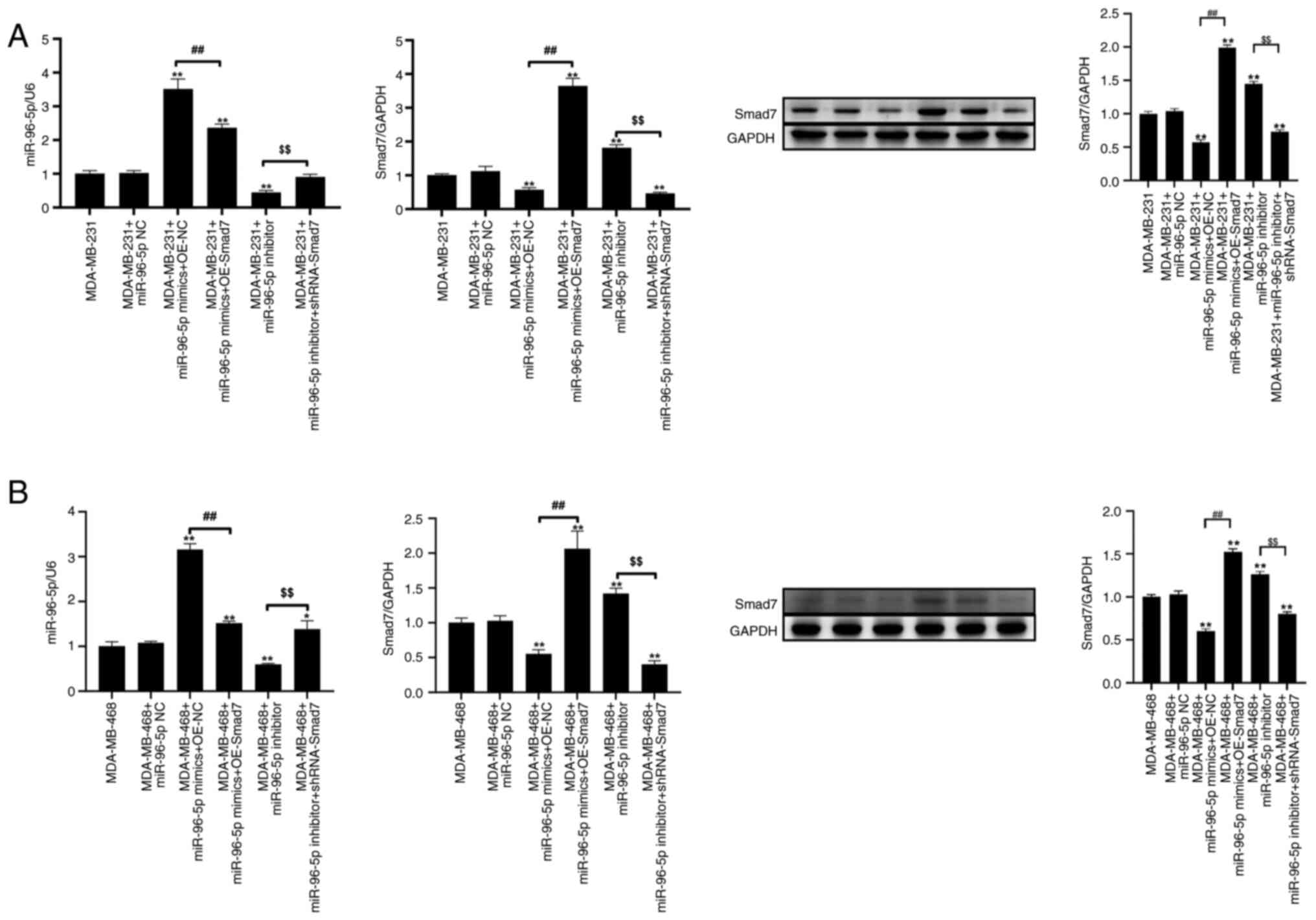
RT-qPCR was used to verify the expression levels of
target genes in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells following
transfection with miR-96-5p mimics and shRNA-Smad7 plasmids. Total
RNA was extracted and reverse-transcribed into cDNA. RT-qPCR and
western blotting results showed that, compared with miR-96-5p NC
group, the expression levels of miR-96-5p and Smad7 were
significantly increased and decreased post-transfection with
miR-96-5p mimics, respectively (Fig.
4A-D). Furthermore, compared with in cells transfected with
miR-96-5p mimics, the expression levels of miR-96-5p and Smad7 were
significantly decreased and increased, respectively, in response to
overexpression of Smad7. Compared with in the miR-96-5p NC group,
post-transfection with the miR-96-5p inhibitor, the expression
levels of miR-96-5p were significantly decreased, whereas those of
Smad7 were significantly increased. Furthermore, compared with in
cells transfected with miR-96-5p inhibitor, the expression levels
of miR-96-5p and Smad7 were significantly increased and decreased,
respectively, following transfection with shRNA-Smad7.
miR-96 promotes the migration and
invasion of breast cancer cells by inhibiting the expression of
Smad7
Following transfection with miR-96-5p mimics +
OE-Smad7, there was a reduction in the number of cells in the
G0/G1 phase compared with control group
(Fig. S1B). Compared with control
group, transfection with the miR-96-5p inhibitor resulted in an
increase in cells in the G0/G1 phase. In
addition, compared with in cells transfected with the miR-96-5p
inhibitor, miR-96-5p inhibitor + shRNA-Smad7 led to a decrease in
cells in the G0/G1 phase; this decrease was
significant in MDA-MB-468 cells. Compared with in the control
group, transfection with miR-96-5p mimics + OE Smad7 could increase
the number of cells in the G2/M phase. Transfection with
miR-96-5p inhibitor + shRNA-Smad7 significantly increased the
number of cells in the G2/M phase, compared with in the
miR-96-5p inhibitor group. Furthermore, compared with control
group, the number of cells in S phase decreased after transfection
with the miR-96-5p inhibitor.
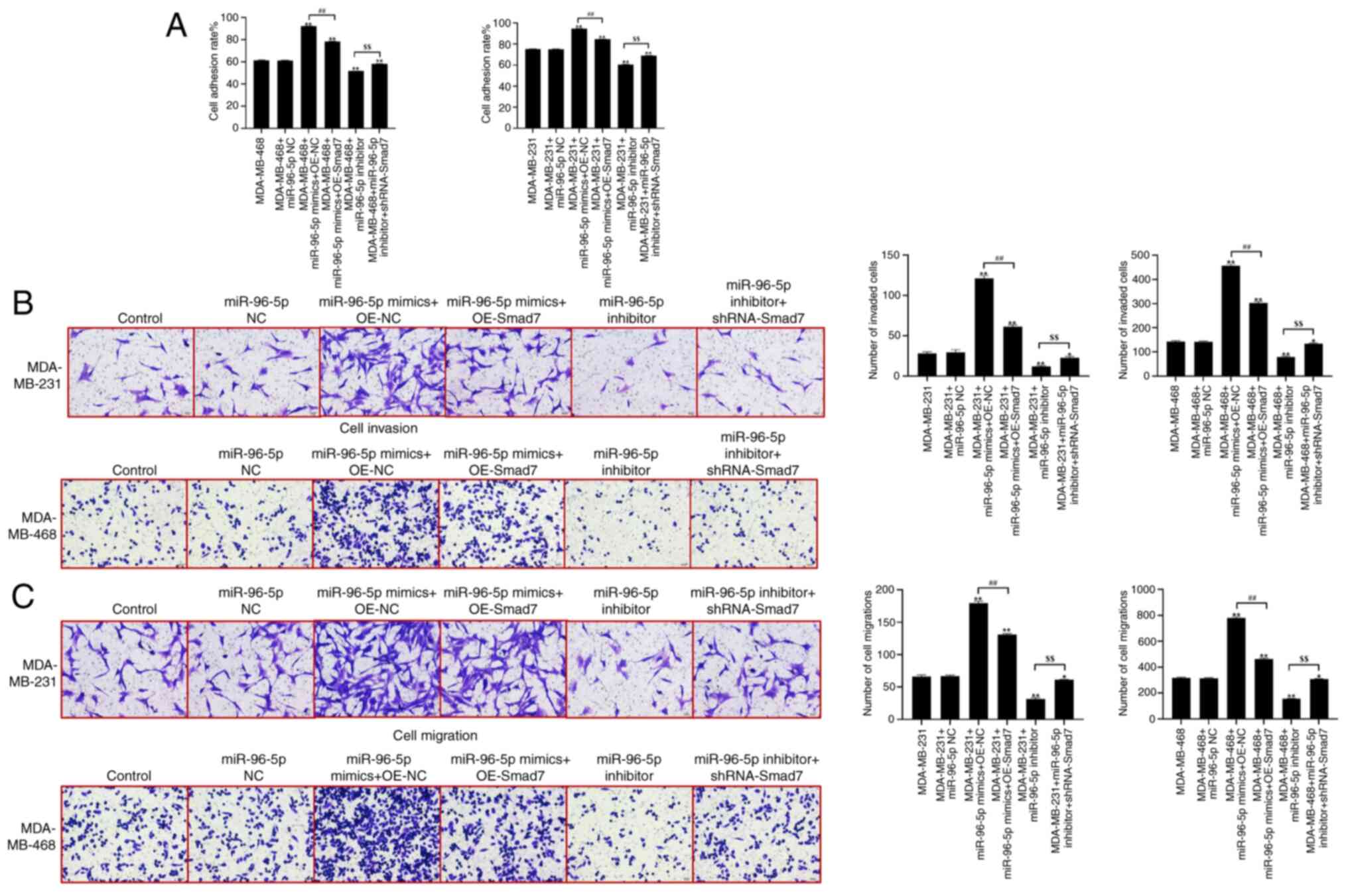
In comparison with the control group, there were no
significant differences in cell adhesion ability observed in the
miR-96-5p NC group (Fig. 5A).
However, compared with in the control group, cell adhesion ability
was significantly enhanced in the miR-96-5p mimics + OE-NC group.
Conversely, the cell adhesion ability was significantly decreased
in the miR-96-5p inhibitor group. When comparing the miR-96-5p
mimics + OE-NC group with the miR-96-5p mimics + OE-Smad7 group,
the cell adhesion ability was significantly reduced. Additionally,
the cell adhesion ability of the miR-96-5p inhibitor + shRNA-Smad7
group was significantly enhanced compared with the miR-96-5p
inhibitor group. Furthermore, a Transwell assay was performed to
assess the migration and invasion of cells, as shown in Fig. 5B and C. Compared with in the control
group, there were no significant differences in the migration and
invasion of cells observed in the miR-96-5p NC group. However,
compared with in the control group, the migration and invasion of
cells were significantly enhanced in the miR-96-5p mimics + OE-NC
group. Conversely, the invasion and migration of cells were
significantly reduced in the miR-96-5p inhibitor group. When
comparing the miR-96-5p mimics + OE-NC group with the miR-96-5p
mimics + OE-Smad7 group, the migration and invasion of cells were
significantly reduced. In addition, the migration and invasion of
the miR-96-5p inhibitor + shRNA-Smad7 group were significantly
enhanced compared with in the miR-96-5p inhibitor group.
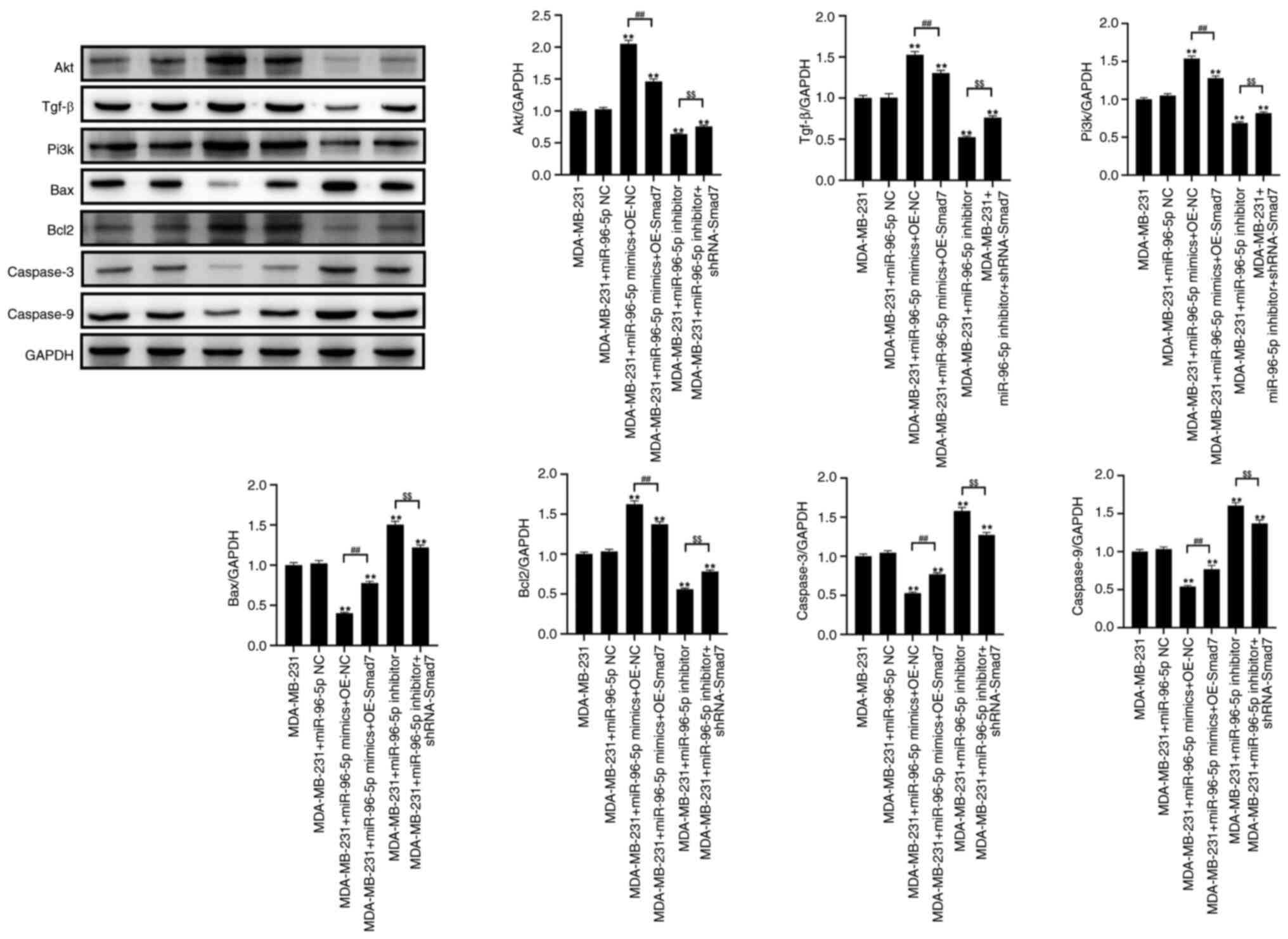
miR-96 can promote activation of the
TGF-β signaling pathway
As shown in Fig. 6,
the transfection of MDA-MB-231 cells with miR-96-5p mimics
significantly increased the expression levels of AKT, TGF-β, PI3K
and Bcl-2, while significantly decreasing the expression levels of
Bax, caspase 3 and caspase 9, compared with those in the control
group. Compared with in the miR-96-5p mimics + OE NC group,
transfection with miR-96-5p mimics + OE Smad7 led to a significant
decrease in the expression levels of TGF-β, PI3K and Bcl-2, and an
increase in the expression levels of Bax, caspase 3 and caspase 9.
Compared with in the control group, after transfection with the
miR-96-5p inhibitor, the expression levels of TGF-β, PI3K and Bcl-2
were significantly decreased, whereas those of Bax, caspase 3 and
caspase 9 were significantly increased. Furthermore, transfection
with miR-96-5p inhibitor + shRNA-Smad7 resulted in increased
expression levels of TGF-β, PI3K and Bcl-2, while the expression
levels of Bax, caspase 3 and caspase 9 were significantly decreased
compared with those in the miR-96-5p inhibitor group.
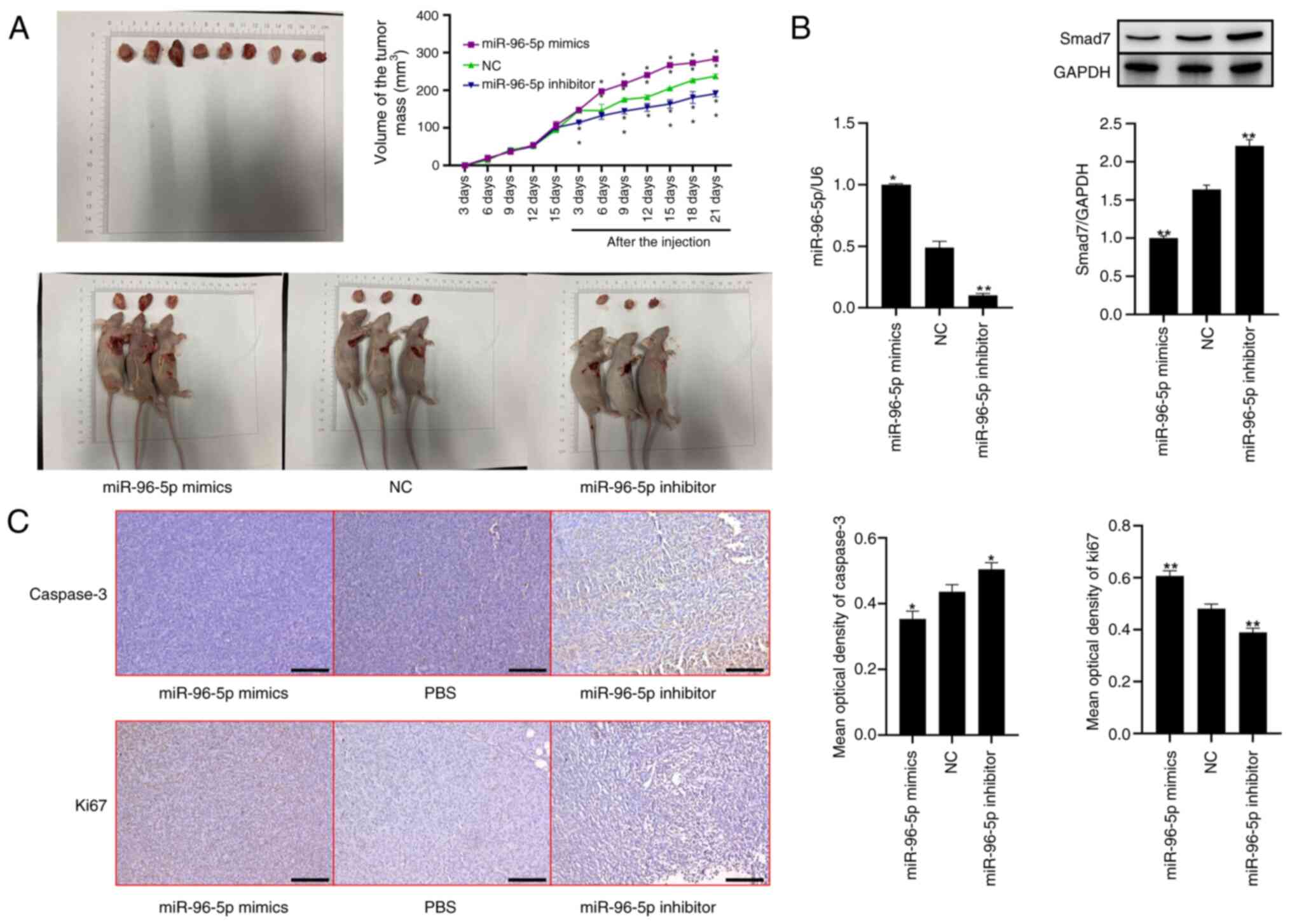
miR-96 can promote the proliferation
of breast cancer cells in a nude mouse tumorigenicity model
To explore the effects of miR-96 on the
proliferation of breast cancer in vivo, the present study
established a nude mouse tumorigenicity model. The results
demonstrated that, in comparison with the NC group, the tumor size
in mice treated with miR-96-5p mimics was significantly increased;
however, after treatment with the miR-96-5p inhibitor, the tumor
size decreased (Fig. 7A). The
RT-qPCR results indicated that the expression levels of miR-96-5p
in tumor tissues were significantly increased and reduced following
treatment with miR-96-5p mimics and the miR-96-5p inhibitor,
compared with NC group, respectively. Western blot analysis
revealed that the expression levels of Smad7 in tumor tissues were
significantly decreased and increased after treatment with
miR-96-5p mimics and the miR-96-5p inhibitor, respectively
(Fig. 7B). Next, the present study
investigated the expression of the tumor-related gene caspase 3.
The results of histological staining demonstrated that the
expression levels of caspase 3 were decreased and increased after
treatment with miR-96-5p mimics and the miR-96-5p inhibitor,
respectively. Compared with in the NC group, Ki67 expression was
increased in the miR-96-5p mimics group and decreased in the
miR-96-5p inhibitor group (Fig.
7C).
Discussion
Breast cancer accounts for ~15% of cancer-related
deaths in women worldwide. Although surgical treatment can
effectively remove malignant tumors, it can seriously damage the
physical and mental health of patients (32,33).
Based on molecular and histological evidence, breast cancers can be
divided into three categories: Breast cancers expressing hormone
receptors (estrogen receptor or progesterone receptor), breast
cancers expressing human epidermal receptor 2 and triple-negative
breast cancers (34).
Single-stranded miRNA molecules contain ~22 nucleotides and
function as a central dogma of molecular biology by inhibiting the
process of translation. It has been shown that any alteration in
miRNA sequences, especially single-nucleotide polymorphisms, can
lead to an increased risk of breast cancer (35).
miRNAs play important roles in several biological
functions, such as regulation of cell development, differentiation,
apoptosis and metastasis (36). In
the pathological state, miRNAs can function as both tumor
suppressors and tumor promoters, and they play a significant role
in the occurrence and development of tumors (37). It has also been reported that
miR-96-5p promotes the proliferation and migration of ovarian
cancer by inhibiting caveolin 1 (CAV1), which is a 21–24 kDa
protein that functions as the primary structural protein component
of caveolae. Through interactions with other protein and nonprotein
components, CAV1 aids in vesicular trafficking and signal
transduction (38). The present
study found that the expression levels of miR-96-5p in breast
cancer were significantly increased, suggesting that miR-96-5p
overexpression may lead to the development of breast cancer.
Polypeptides of the TGF-β family exert their
functions by interacting with two related, functionally distinct
transmembrane receptor kinases, first interacting with the type II
receptor (TβR II) and subsequently with the type I receptor (TβR
I). First, TβR II autophosphorylates its amino acid residue, and
then interacts with and activates TβR I. Next, the activated TβR I
phosphorylates the downstream signaling molecules, Smad2 and Smad3.
Then, Smad4 trimer complexes enter the nucleus. With the assistance
of DNA-binding cofactors, the trimer complexes bind to the
Smad-binding element region on DNA to induce transcription, and
ultimately regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and
apoptosis (39,40). Smad7 is a negative modulator of the
TGF-β signal transduction pathway (41). Smad7 forms a stable complex with TβR
I under ligand stimulation and inhibits the recruitment of R-Smads
(42). Upon activation, several E3
ubiquitin ligases, such as SmurF1/2 and NEDD4-2 and WWP1/Tiul1, can
be recruited, resulting in the polyubiquitination and degradation
of TβR I.
The present study revealed that the expression
levels of Smad7 were decreased in breast cancer tissues, and
RT-qPCR was used to verify the expression levels of target genes
following transfection with miR-96-5p mimics and shRNA-Smad7.
Following transfection of MDA-MB-231 cells with miR-96-5p mimics
and shRNA-Smad7, the expression levels of miR-96-5p were
significantly increased, whereas those of Smad7 were significantly
decreased. By contrast, the expression levels of miR-96-5p and
Smad7 were significantly decreased and increased, respectively,
following overexpression of Smad7. After transfection with the
miR-96-5p inhibitor, the expression levels of miR-96-5p were
significantly decreased, whereas those of Smad7 were significantly
increased. By contrast, the expression levels of miR-96-5p and
Smad7 were significantly increased and decreased, respectively,
following transfection with shRNA-Smad7. Altogether, the results
suggested that miR-96 is highly expressed in breast cancer tissues.
Notably, miR-96 can inhibit the expression of Smad7, which in turn
may activate TGF-β signaling pathway. According to the results of
previous studies, lncRNA-Smad has anti-apoptotic functions. In
response to TGF-β stimulation in the mouse breast cancer cell line
JygMC(A), lncRNA-Smad7 manifested a discernible anti-apoptotic
effect (43). Furthermore, the
transcription of the antisense strand upstream of the Smad7 gene
produces a lncRNA-Smad7, which interacts with the inhibitor of
TGF-β signaling, BMP2 (44,45), thereby selectively preventing
TGF-β-induced apoptosis in cancer cells (46).
Tumor invasion and migration are critical factors in
breast cancer progression. Growing evidence has suggested that
Smad7 can interfere with the carcinogenic effects of TGF-β and
other cancer-promoting pathways, thereby inhibiting tumor
progression (47,48). TGF-β signal transduction is involved
in the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation pathway, which can
promote tumor invasion and migration. The present study
demonstrated that the expression levels of miR-96 in breast cancer
tissues were significantly higher than those in adjacent tissues.
Overexpression of miR-96 could promote the migration of breast
cancer cells by downregulating Smad7 expression, which is
consistent with the findings of a previous study (49). However, miR-96 inhibition could
promote the expression of Smad7 and activate the TGF-β signaling
pathway, which is in agreement with previous findings (50). These data imply that miR-96 may
serve as a prognostic marker for breast cancer.
The present study aimed to examine how miR-96
affects the migration and proliferation of breast cancer cells.
Overexpression of miR-96 could promote the proliferation, migration
and invasion of breast cancer cells by inhibiting the expression of
Smad7; therefore, miR-96 may promote breast cancer via blocking
Smad7. In addition, the present study found that silencing Smad7 by
RNA interference was able to mimic the carcinogenic effect of
miR-96. However, further studies are needed to investigate the
relationship between genes and proteins associated with breast
cancer by combining more techniques, such as co-immunoprecipitation
and chromatin immunoprecipitation. In conclusion, the present study
may provide a basic experimental and theoretical basis for the
clinical diagnosis of breast cancer.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Science and Technology
Support Program Social Development (Instructive) Project of Taizhou
(grant no. 2020-30).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
XZ and YZ conceived and designed the study.
Experiments were performed by XZ, LC and XH. RY, QY and YZ analyzed
and interpretation of data. XZ and YZ wrote the manuscript. YZ and
XZ confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read
and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the ethics
committee of The People's Hospital of Xinghua City (Jiangsu, China;
approval number: JSXHRYLL-YJ-202026) and was performed in
compliance with The Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed
consent was obtained from all participants before surgery. Animal
experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use
Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University
(approval no. JSXHRYLL-YJ-202026; Jiangsu, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Aini S, Bolati S, Ding W, Liu S, Su P,
Aili S, Naman Y and Xuekelaiti K: LncRNA LncRNA SNHG10 suppresses
the development of doxorubicin resistance by downregulating
miR-302b in triple-negative breast cancer. Bioengineered.
13:11430–11439. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alves MT, da Conceição IMCA, de Oliveira
AN, Oliveira HHM, Soares CE, de Paula Sabino A, Silva LM, Simões R,
Luizon MR and Gomes KB: microRNA miR-133a as a biomarker for
Doxorubicin-Induced cardiotoxicity in women with breast cancer: A
signaling pathway investigation. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 22:655–662.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Azadeh M, Salehzadeh A, Ghaedi K and
Talesh Sasani S: NEAT1 can be a diagnostic biomarker in the breast
cancer and gastric cancer patients by targeting XIST, hsa-miR-612
and MTRNR2L8: Integrated RNA targetome interaction and experimental
expression analysis. Genes Environ. 44:162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cantini L, Bertoli G, Cava C, Dubois T,
Zinovyev A, Caselle M, Castiglioni I, Barillot E and Martignetti L:
Identification of microRNA clusters cooperatively acting on
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast
cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:2205–2215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen WH, Luo GF, Sohn YS, Nechushtai R and
Willner I: miRNA-specific unlocking of drug-loaded metal-organic
framework nanoparticles: Targeted cytotoxicity toward cancer cells.
Small. 15:e19009352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Cosimo S, Appierto V, Pizzamiglio S,
Tiberio P, Iorio MV, Hilbers F, de Azambuja E, de la Peña L,
Izquierdo M, Huober J, et al: Plasma miRNA levels for predicting
therapeutic response to neoadjuvant treatment in HER2-positive
breast cancer: Results from the NeoALTTO trial. Clin Cancer Res.
25:3887–3895. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hajivalili M, Baghaei K, Mosaffa N, Niknam
B and Amani D: Engineering tumor-derived small extra cellular
vesicles to encapsulate miR-34a, effectively inhibits 4T1 cell
proliferation, migration and gene expression. Med Oncol. 39:932022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He C, Wang M, Sun X, Zhu Y, Zhou X, Xiao
S, Zhang Q, Liu F, Yu Y, Liang H and Zou G: Integrating PDA
microtube waveguide system with heterogeneous CHA amplification
strategy towards superior sensitive detection of miRNA. Biosens
Bioelectron. 129:50–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang R, Yang Z, Liu Q, Liu B, Ding X and
Wang Z: CircRNA DDX21 acts as a prognostic factor and sponge of
miR-1264/QKI axis to weaken the progression of triple-negative
breast cancer. Clin Transl Med. 12:e7682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang W, Wu X, Xiang S, Qiao M, Cen X, Pan
X, Huang X and Zhao Z: Regulatory mechanism of miR-20a-5p
expression in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 8:2622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iranparast S, Tahmasebi-Birgani M,
Motamedfar A, Amari A and Ghafourian M: Altered expression levels
of MicroRNA-155 and SOCS-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
newly diagnosed breast cancer patients. Iran J Allergy Asthma
Immunol. 21:12–19. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jahangiri L and Ishola T: Dormancy in
breast cancer, the role of autophagy, lncRNAs, miRNAs and exosomes.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:52712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee JU, Kim WH, Lee HS, Park KH and Sim
SJ: Quantitative and specific detection of exosomal miRNAs for
accurate diagnosis of breast cancer using a Surface-Enhanced raman
scattering sensor based on Plasmonic Head-Flocked gold Nanopillars.
Small. 15:e18049682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Gao X, Zhang Z, Lai Y, Lin X, Lin B,
Ma M, Liang X, Li X, Lv W, et al: CircCD44 plays oncogenic roles in
triple-negative breast cancer by modulating the miR-502-5p/KRAS and
IGF2BP2/Myc axes. Mol Cancer. 20:1382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Z, Spoelstra NS, Sikora MJ, Sams SB,
Elias A, Richer JK, Lee AV and Oesterreich S: Mutual exclusivity of
ESR1 and TP53 mutations in endocrine resistant metastatic breast
cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 8:622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lukianova N, Zadvornyi T, Kashuba E,
Borikun T, Mushii О and Chekhun F: Expression of markers of bone
tissue remodeling in breast cancer and prostate cancer cells in
vitro. Exp Oncol. 44:39–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yin Z, Wang W, Qu G, Wang L, Wang X and
Pan Q: MiRNA-96-5p impacts the progression of breast cancer through
targeting FOXO3. Thorac Cancer. 11:956–963. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peng D, Fu M, Wang M, Wei Y and Wei X:
Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer
therapy. Mol Cancer. 21:1042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi X, Yang J, Deng S, Xu H, Wu D, Zeng Q,
Wang S, Hu T, Wu F and Zhou H: TGF-β signaling in the tumor
metabolic microenvironment and targeted therapies. J Hematol Oncol.
15:1352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Richard V, Davey MG, Annuk H, Miller N and
Kerin MJ: The double agents in liquid biopsy: Promoter and
informant biomarkers of early metastases in breast cancer. Mol
Cancer. 21:952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
San A, Palmieri D, Saxena A and Singh S:
In silico study predicts a key role of RNA-binding domains 3 and 4
in nucleolin-miRNA interactions. Proteins. 90:1837–1850. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sirkisoon SR, Wong GL, Aguayo NR, Doheny
DL, Zhu D, Regua AT, Arrigo A, Manore SG, Wagner C, Thomas A, et
al: Breast cancer extracellular vesicles-derived miR-1290 activates
astrocytes in the brain metastatic microenvironment via the
FOXA2→CNTF axis to promote progression of brain metastases. Cancer
Lett. 540:2157262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Søiland H, Janssen EAM, Helland T,
Eliassen FM, Hagland M, Nordgård O, Lunde S, Lende TH, Sagen JV,
Tjensvoll K, et al: Liquid biopsies and patient-reported outcome
measures for integrative monitoring of patients with early-stage
breast cancer: A study protocol for the longitudinal observational
prospective breast cancer biobanking (PBCB) study. BMJ OPen.
12:e0544042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Storci G, De Carolis S, Papi A, Bacalini
MG, Gensous N, Marasco E, Tesei A, Fabbri F, Arienti C, Zanoni M,
et al: Genomic stability, anti-inflammatory phenotype and
up-regulation of the RNAseH2 in cells from centenarians. Cell Death
Differ. 26:1845–1858. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang J..Li Y, Zou Y, Zhao Z, Jiao L and
Zhang H: miR-96-5p induces orbital fibroblasts differentiation by
targeting Smad7 and promotes the development of thyroid-associated
ophthalmopathy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. Feb 27;8550307.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chao L, Hua-Yu Z, Wen-Dong B, Mei S, Bin
X, Da-Hai H and Yi L: miR-96 promotes collagen deposition in
keloids by targeting Smad7. Exp Ther Med. 17:773–781.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi Y, Zhao Y, Shao N, Ye R, Lin Y, Zhang
N, Li W, Zhang Y and Wang S: Overexpression of microRNA-96-5p
inhibits autophagy and apoptosis and enhances the proliferation,
migration and invasiveness of human breast cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 13:4402–4412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Uehiro N, Horii R, Iwase T, Tanabe M,
Sakai T, Morizono H, Kimura K, Iijima K, Miyagi Y, Nishimura S, et
al: Validation study of the UICC TNM classification of malignant
tumors, seventh edition, in breast cancer. Breast Cancer.
21:748–753. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Farstad W: Ethics in animal breeding.
Reprod Domest Anim. 53 (Suppl 3):S4–S13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 18:e30004102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan L, Mai D, Zhang B, Jiang X, Zhang J,
Bai R, Ye Y, Li M, Pan L, Su J, et al: PIWI-interacting RNA-36712
restrains breast cancer progression and chemoresistance by
interaction with SEPW1 pseudogene SEPW1P RNA. Mol Cancer. 18:92019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang H, Huang X, Wang J, Yang L, Kong Y,
Gao G, Zhang L, Chen ZS and Xie X: circKIF4A acts as a prognostic
factor and mediator to regulate the progression of triple-negative
breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 18:232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Barzaman K, Karami J, Zarei Z,
Hosseinzadeh A, Kazemi MH, Moradi-Kalbolandi S, Safari E and
Farahmand L: Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments.
Int Immunopharmacol. 84:1065352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bahreini F, Rayzan E and Rezaei N:
microRNA-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms and breast cancer.
J Cell Physiol. 236:1593–1605. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y and Li C: lncRNA GHET1 promotes the
progression of Triple-Negative breast cancer via regulation of
miR-377-3p/GRSF1 signaling axis. Comput Math Methods Med.
2022:83665692022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weng YS, Tseng HY, Chen YA, Shen PC, Al
Haq AT, Chen LM, Tung YC and Hsu HL: MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R
signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2
macrophage polarization in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol
Cancer. 18:422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu B, Zhang J and Yang D: miR-96-5p
promotes the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells by
suppressing Caveolae1. J Ovarian Res. 12:572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou J, Sun X, Zhang X, Yang H, Jiang Z,
Luo Q, Liu Y and Wang G: miR-107 is involved in the regulation of
NEDD9-mediated invasion and metastasis in breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 22:5332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou Y, Cai W and Lu H: Overexpression of
microRNA-145 enhanced docetaxel sensitivity in breast cancer cells
via inactivation of protein kinase B gamma-mediated
phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B pathway. Bioengineered.
13:11310–11320. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yan W, Cao M, Ruan X, Jiang L, Lee S,
Lemanek A, Ghassemian M, Pizzo DP, Wan Y, Qiao Y, et al:
Cancer-cell-secreted miR-122 suppresses O-GlcNAcylation to promote
skeletal muscle proteolysis. Nat Cell Biol. 24:793–804. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang R, Xing L, Zheng X, Sun Y, Wang X and
Chen J: The circRNA circAGFG1 acts as a sponge of
miR-195-5p to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression
through regulating CCNE1 expression. Mol Cancer. 18:42019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arase M, Horiguchi K, Ehata S, Morikawa M,
Tsutsumi S, Aburatani H, Miyazono K and Koinuma D: Transforming
growth factor-β-induced lncRNA-Smad7 inhibits apoptosis of mouse
breast cancer JygMC(A) cells. Cancer Sci. 105:974–982. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kong X, Yan K, Deng P, Fu H, Sun H, Huang
W, Jiang S, Dai J, Zhang QC, Liu JG and Xi Q: LncRNA-Smad7 mediates
cross-talk between Nodal/TGF-β and BMP signaling to regulate cell
fate determination of pluripotent and multipotent cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 50:10526–10543. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gao X, Cao Y, Yang W, Duan C, Aronson JF,
Rastellini C, Chao C, Hellmich MR and Ko TC: BMP2 inhibits
TGF-β-induced pancreatic stellate cell activation and extracellular
matrix formation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
304:G804–G813. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tang PC, Zhang YY, Li JS, Chan MK, Chen J,
Tang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang D, Leung KT, To KF, et al: LncRNA-Dependent
mechanisms of transforming growth Factor-β: From tissue fibrosis to
cancer progression. Noncoding RNA. 8:362022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Luo L, Li N, Lv N and Huang D: SMAD7: A
timer of tumor progression targeting TGF-β signaling. Tumour Biol.
35:8379–8385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhong C, Xie Z, Shen J, Jia Y and Duan S:
LINC00665: An emerging biomarker for cancer diagnostics and
therapeutics. Cells. 11:15402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Qin WY, Feng SC, Sun YQ and Jiang GQ:
MiR-96-5p promotes breast cancer migration by activating MEK/ERK
signaling. J Gene Med. 22:e31882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luo X, Zhang D, Xie J, Su Q, He X, Bai R,
Gao G and Pan W: MicroRNA-96 promotes schistosomiasis hepatic
fibrosis in mice by suppressing smad7. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev.
11:73–82. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|