Introduction
Lung cancer is a common malignant tumor, with
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounting for 80–85% of lung
cancer cases. The morbidity and mortality rates associated with
lung cancer are significantly higher than those of other cancer
types worldwide. The latest statistics indicate that 609,820
individuals in the United States died from cancer in 2023, 127,070
of whom died from lung cancer (1,2).
The traditional treatments for NSCLC mainly include
chemotherapy, surgical resection and radiotherapy. However,
chemotherapy can provide only moderate benefits with limited
safety, and as such immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) that have
been introduced in recent years have become the primary treatment
method (3). In particular, ICIs
targeting programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) and programmed death
ligand-1 (PD-L1) enhance antitumor effects by restoring the
function of suppressed effector T cells and producing durable
responses in a number of patients with metastatic and advanced
NSCLC (4). To date, a total of 10
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors have been approved to treat NSCLC in China
and the United States. Among them, camrelizumab, sugemalimab and
sintilimab are listed only in China, whereas cemiplimab is listed
only in the United States. Nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab,
durvalumab, tislelizumab and toripalimab are all available in both
the United States and China. With the exception of durvalumab,
sugemalimab and atezolizumab, which are PD-L1 inhibitors, the
remaining seven are PD-1 inhibitors.
Although previous network meta-analyses (NMAs) have
examined the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the
treatment of advanced NSCLC, these studies typically included a
limited number of drugs, most of which were Food and Drug
Administration (FDA)-approved. By contrast, the present study aimed
to expand the scope by including a broader range of PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors that are approved for first-line treatment of advanced
NSCLC, providing a more comprehensive evaluation of available
therapies. Moreover, a broader range of outcome measures were
assessed in the present study, offering a more comprehensive
evaluation of both efficacy and safety. Thus, the present
meta-analysis provides a more complete and updated perspective,
which may offer valuable insights for selecting the most
appropriate PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor in the first-line treatment of
advanced NSCLC.
Materials and methods
The present NMA followed the Preferred Reporting
Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension
statement.
Search strategies
The PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), Cochrane Library
(https://www.cochranelibrary.com/) and
Embase (www.embase.com/) databases were searched
for all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the treatment of
NSCLC with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors from January 1, 2005 to May 31,
2023. The search consisted of three domains: Intervention
(PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors or individual drugs), patients with NSCLC
and RCTs (Table SI).
Selection criteria
RCTs were included if they met the following
criteria: i) Studies based on phase III RCTs; ii) patients with
NSCLC (stage III or IV) confirmed either histologically or
cytologically; iii) patients who received a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor
(sintilimab, tislelizumab, camrelizumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab,
atezolizumab, sugemalimab, durvalumab, cemiplimab or toripalimab);
iv) patients with long-term assessment data, including overall
survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), short-term
assessment data, including the objective response rate (ORR) and
the disease control rate (DCR), and safety outcomes based on the
incidence of grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) or
grade ≥3 immune-related adverse events (irAEs); v) RCTs with a
sample size in a single group (sum of all dose groups) >50; and
vi) the study had been published and was written in the English
language. Studies that did not meet these criteria and those that
shared the same dataset were excluded. In cases where more than two
articles were published for the same clinical trial, the most
recent data for each outcome were obtained from each article.
Literature screening and data
extraction
In total, two authors independently conducted the
literature screening and data extraction, with verification by the
third author. The extracted data included the basic characteristics
of the study, such as the first author and publication year, median
follow-up time, experiment type and stage, pathological type,
number of included cases, median age, sex, intervention measures,
smoking status, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance
status score, liver metastasis and brain metastasis. The extracted
clinical outcome data included the most recent OS and PFS rates,
95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the hazard ratios (HRs), ORRs,
DCRs and the incidences of ≥3 TRAEs and ≥3 irAEs.
Risk of bias and certainty of evidence
assessment
In total, two authors independently assessed the
risk of bias in eligible studies via the revised Cochrane
Collaboration Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2.0) tool for RCTs (5). Any discrepancies were resolved through
consensus with a third author. All endpoints from the five domains
were assessed, and the overall risk of bias was rated as ‘low
risk’, ‘some concerns’ or ‘high risk’. RoB 2.0 includes five
modules to assess the risk of bias in RCTs, each containing
multiple signal questions. The possible answers are ‘Yes (Y)’,
‘Probably Yes (PY)’, ‘Probably No (PN)’, ‘No (N)’ and ‘No
Information (NI)’. In some cases, ‘Not Applicable (NA)’ may also be
used. Each module is evaluated independently to determine the
overall risk of bias. If all five modules are rated as low risk,
the overall risk is considered low. If none of the modules are high
risk but some raise concerns, the overall risk is categorized as
‘some concerns’. If any module is assessed as high risk, or
multiple modules show potential risks with significant impact, the
overall risk is deemed high. This entire process is based on a
qualitative evaluation of the signal issues in each module, without
using quantitative ratings or thresholds to define ‘low risk’,
‘some concerns’ or ‘high risk’.
Statistical analysis
In the study, HRs with 95% CIs were used as the
effect sizes for OS and PFS rates, and ORs with 95% CIs were used
as the effect sizes for ORRs, DCRs, ≥3 TRAEs and ≥3 irAEs. Bayesian
network meta-analysis was conducted using a random effects model
via R software (version 4.2.2; http://www.R-project.org/) and the gemtc package
(version 1.0; cran.r-project.org/package=gemtc). The result was 4
chains with 100,000 iterations per chain and 10,000 burn-in
iterations (with an interval of 10). R software was also used to
identify the probability of each treatment being the optimal
ranking for the 10 endpoints, and the surface under the cumulative
ranking curve (SUCRA) was presented in the ranking graph. An
I2 test was employed to assess statistical
heterogeneity. An I2 value ≤50% indicated minimal
heterogeneity, whereas values >50% suggested significant
heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses were conducted to identify the
origins of heterogeneity and explore the factors associated with
clinical advantages.
Results
Study selection
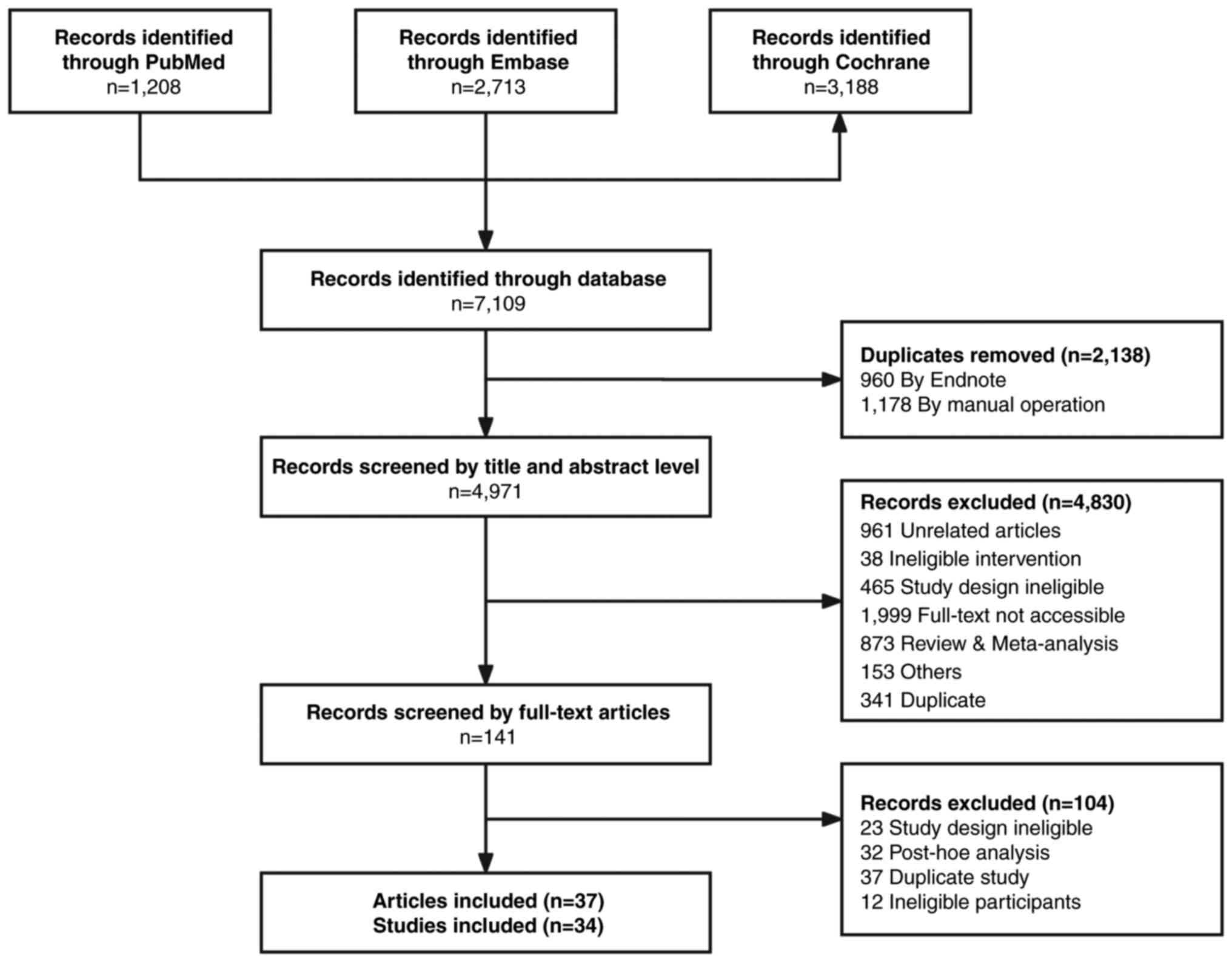
A total of 7,109 articles were identified through
the initial database search, with 1,208 from PubMed, 2,713 from
Embase and 3,188 from the Cochrane Library. After 2,138 duplicate
records were removed, 4,971 articles were screened. The initial
search results and selection process are detailed in Fig. 1. Ultimately, 37 RCTs (including
31,935 patients) were included in the systematic review, including
3 that reported extended follow-up (further publications of the
patient follow-up) (6–8).
Characteristics of the included
studies
Among the 37 RCTs analyzed, 13 (including 15,758
patients) included comparisons of an intervention group receiving
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor monotherapy and a control group receiving
chemotherapy (9–21). Additionally, 13 RCTs (including
8,668 patients) included comparisons of an intervention group
treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor monotherapy and a control group
administered a placebo (periodic combination chemotherapy)
(7,8,22–32).
Furthermore, 11 RCTs (including 7,509 patients) compared an
intervention group treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with
chemotherapy with a control group receiving chemotherapy only
(6,33–42).
The characteristics of the RCTs are listed in Table SII.
Assessment of the risk of bias
The risk of bias assessment results for OS, PFS,
ORR, DCR, grades ≥3 TRAEs and grades ≥3 irAEs are outlined in
Table SIII, with 23, 22, 15, 15,
24 and 13 studies rated as high risk for each indicator. These
high-risk studies were still included in the analyses to ensure a
comprehensive evaluation of the available evidence. This approach
was taken to avoid potential bias from selective exclusion and to
provide a balanced representation of the data.
Comparisons of OS, PFS, ORR and
DCR
The NMA included an intervention group treated with
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor monotherapy and a control group treated with
chemotherapy, an intervention group treated with PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors combined with chemotherapy and a control group treated
with chemotherapy only, and an intervention group treated with
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor monotherapy and a control group treated with
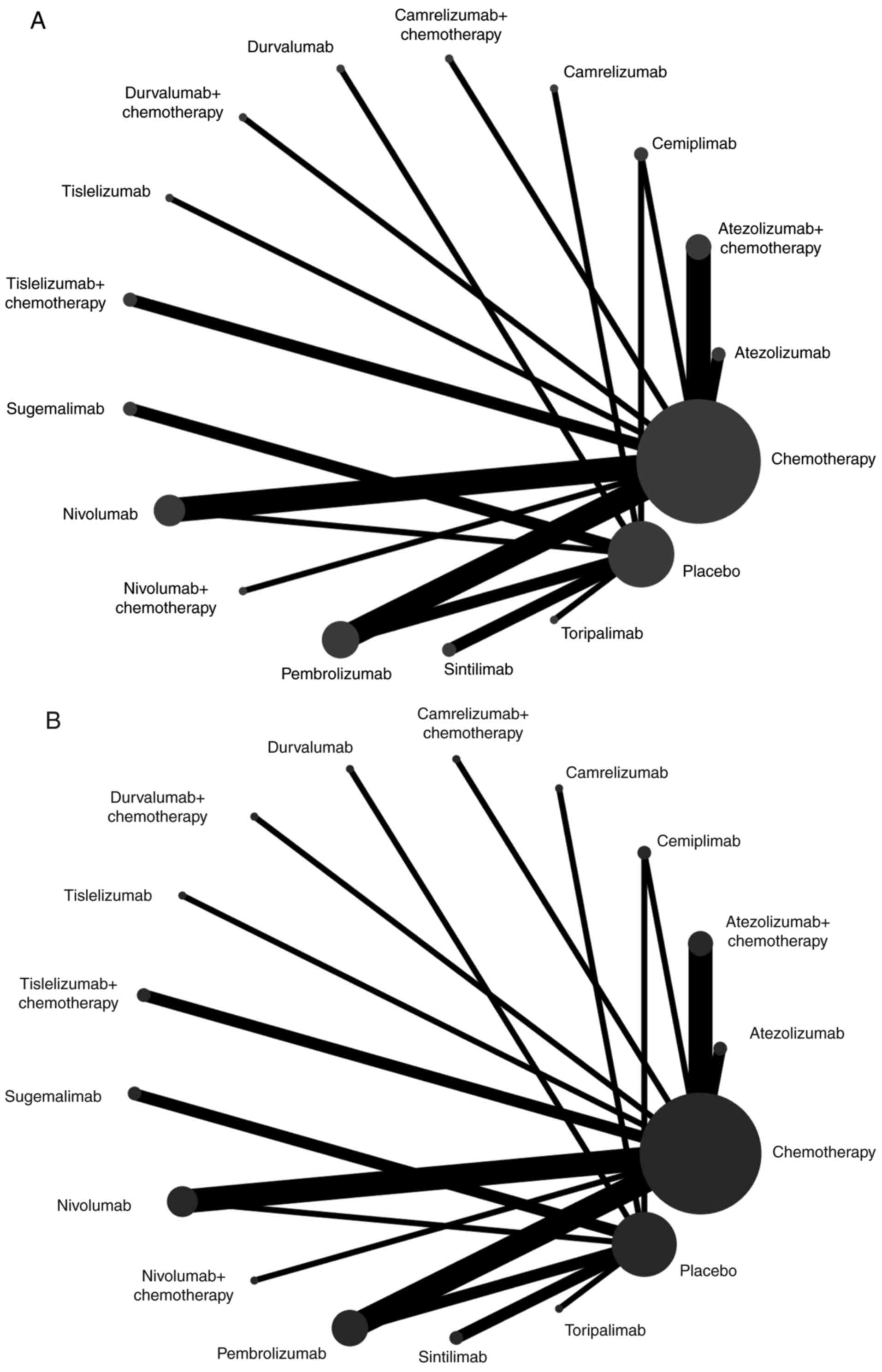
placebo. The OS and PFS network plots are depicted in Fig. 2A and B, respectively.
The NMA of the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors vs.
chemotherapy model included 13 RCTs (9–21)
(Figs. S1A, S2A, S3A,
S4A, S5A and S6A). In terms of OS, there were 4,674
patients in the intervention group receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor
monotherapy and 4,091 patients in the chemotherapy group.
Tislelizumab (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.44–0.98), pembrolizumab (HR,
0.72; 95% CI, 0.59–0.88) and nivolumab (HR, 0.76; 95% CI,
0.61–0.94) showed significant advantages over chemotherapy
(Fig. 3). Tislelizumab had the
highest probability (43%) of ranking as the best treatment (Table
SIV). Toripalimab and tislelizumab had the highest SUCRA values for
OS (0.93 and 0.78, respectively; Table SV). Patients receiving
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors did not demonstrate significantly greater
benefits in terms of PFS than patients receiving standard
chemotherapy (Fig. 3). Notably,
while no significant differences were observed, cemiplimab had the
highest probability (49%) of being ranked as the most effective
treatment (Table SIV). Both cemiplimab and tislelizumab were the
top contenders for improving PFS, with respective SUCRA values of
0.80 and 0.74 (Table SV). In terms of both the ORR and DCR,
tislelizumab had the highest probability of being ranked as the
best treatment, with probabilities of 61 and 75%, respectively
(Table SIV).
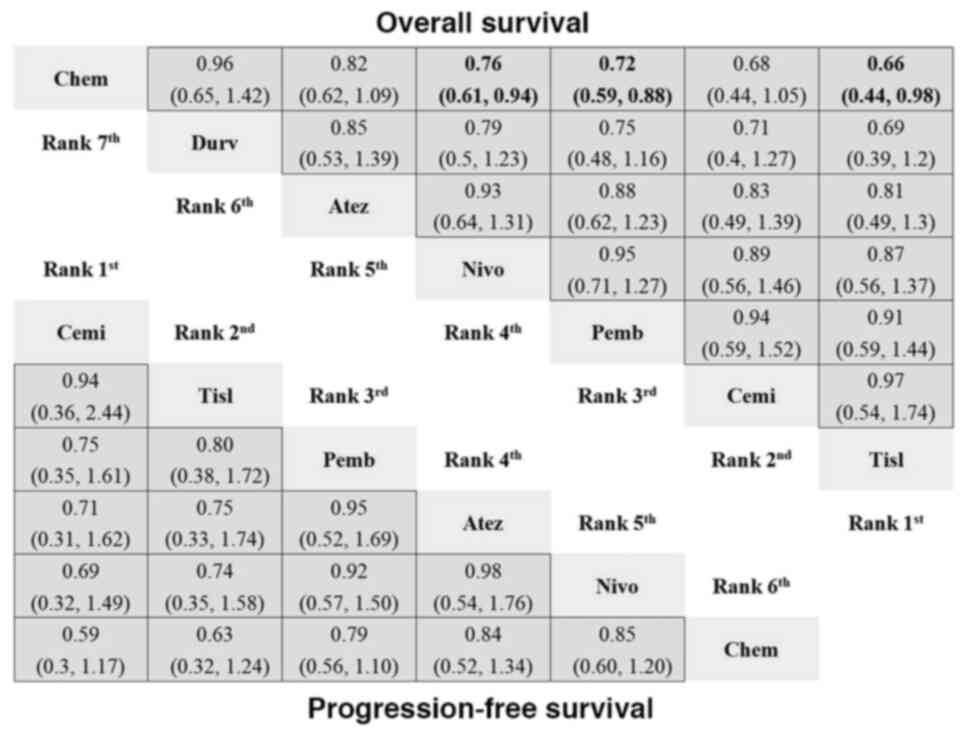 | Figure 3.Network meta-analysis for OS and PFS
of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors vs. chemotherapy. The analysis presents
the HR with 95% confidence interval for each treatment, showing the
ranking and relative efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors compared
with chemotherapy. For comparisons of the OS (right upper half) and
PFS (left lower half), a HR <1 favors the column defining
treatment. Significant differences are show in bold in the figure.
Chem, chemotherapy; Durv, durvalumab; Atez, atezolizumab; Nivo,
nivolumab; Pemb, pembrolizumab; Cemi, cemiplimab; Tisl,
tislelizumab; HR, hazard ratio; OS, overall survival; PFS,
progression-free survival; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1,
programmed death-ligand 1. |
The NMA of the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor vs. placebo
model included 13 RCTs (7,8,22–32)
(Figs. S1B, S2B, S3B,
S4B, S5B and S6B). In terms of OS, the intervention
group comprised 3,264 patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor
monotherapy or a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor in combination with
chemotherapy, whereas the control group included 1,999 patients
receiving a placebo (Table SIV). In terms of OS and PFS, both
sugemalimab and sintilimab significantly outperformed the placebo
(Fig. 4). Camrelizumab and
sugemalimab ranked the best for OS, with SUCRA values of 0.76 and
0.72, respectively (Table SV), whereas camrelizumab and sintilimab
ranked the best for PFS, with SUCRA values of 0.91 and 0.61,
respectively (Table SV). In terms of ORR, camrelizumab (vs.
placebo) still led, with a 30% probability of being the most
effective (Table SIV), whereas for DCR, sintilimab (vs. placebo)
maintained a 36% probability of ranking as the best treatment
(Table SV).
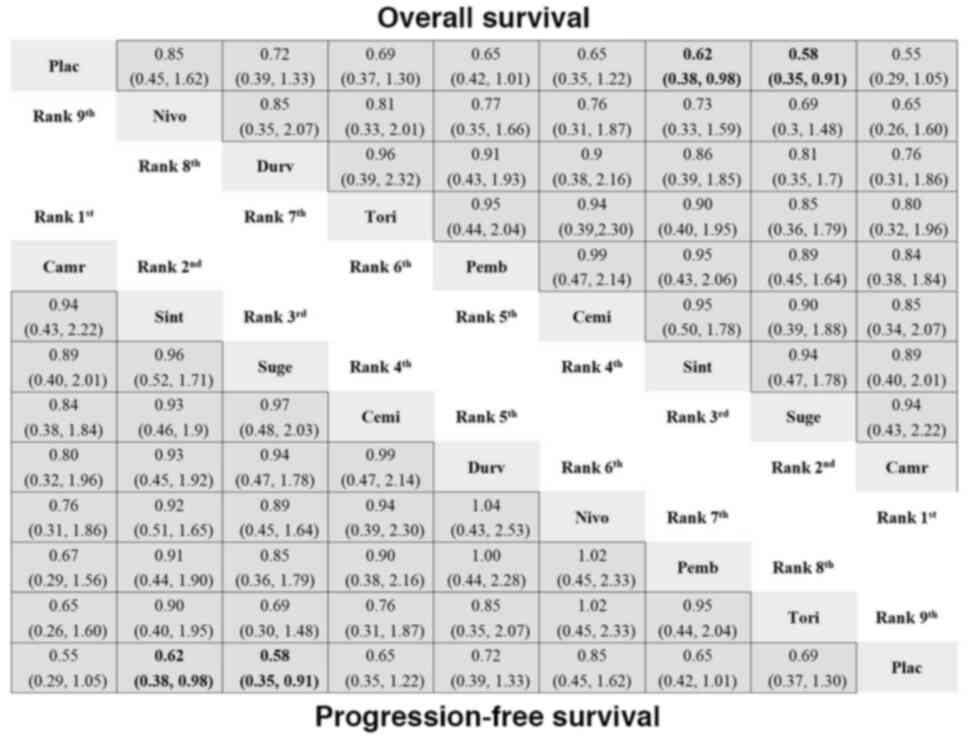 | Figure 4.Network meta-analysis for OS and PFS
of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors vs. placebo. The analysis presents HR with
95% confidence interval for each treatment, showing the ranking and
relative efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors compared with placebo.
For comparisons of the OS (right upper half) and PFS (left lower
half), a HR <1 favors the column defining treatment. Significant
differences are boldly shown in the figure. Plac, placebo; Durv,
durvalumab; Atez, atezolizumab; Nivo, nivolumab; Pemb,
pembrolizumab; Cemi, cemiplimab; Tisl, tislelizumab; Tori,
toripalimab; Sint, sintilimab; Suge, sugemalimab; Camr,
camrelizumab; HR, hazard ratio; OS, overall survival; PFS,
progression-free survival; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1,
programmed death-ligand 1. |
The NMA of the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with
chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy model included 11 RCTs (6,33–42)
(Figs. S1C, S2C, S3C,
S4C, S5C and S6C). The intervention group receiving
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy consisted of
2,728 patients, whereas the chemotherapy-only group comprised 2,372
patients. Nivolumab (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.35–0.93) or cemiplimab
(HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.71–0.98) in combination with chemotherapy
demonstrated a significant advantage over chemotherapy alone in
terms of the OS metric (Fig. 5).
Compared with chemotherapy, nivolumab + chemotherapy consistently
had a higher probability (77%) of being ranked as the best
treatment (Table SIV). Nivolumab + chemotherapy and camrelizumab +
chemotherapy ranked the best for OS, with SUCRA values of 0.91 and
0.70, respectively (Table SV). With respect to PFS, PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors + chemotherapy consistently resulted in an improved PFS
than standard chemotherapy monotherapy, with the only exception
being durvalumab + chemotherapy (Fig.
5). Camrelizumab + chemotherapy had the highest probability
(46%) of being ranked as the best treatment (Table SIV).
Camrelizumab + chemotherapy and tislelizumab + chemotherapy ranked
as the best treatments for PFS, with SUCRA values of 0.80 and 0.71,
respectively (Table SV). For the ORR and DCR, camrelizumab +
chemotherapy had the highest probability of being ranked as the
best treatment, with probabilities of 45 and 55%, respectively
(Table SIV).
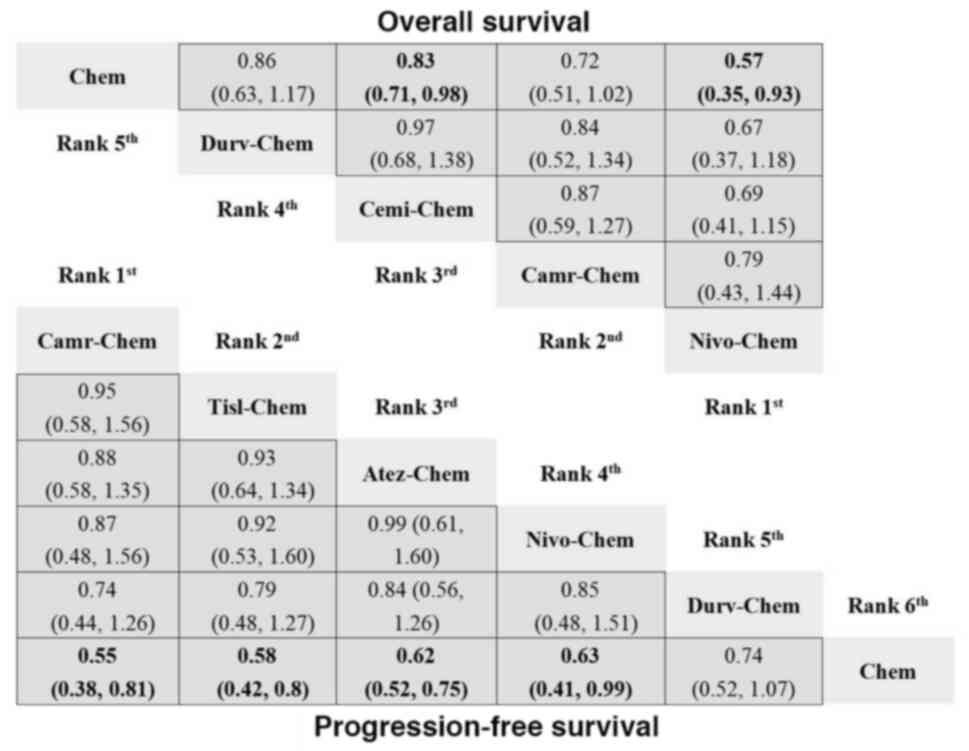 | Figure 5.Network meta-analysis for OS and PFS
of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors + chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy. The
analysis presents HR with 95% confidence interval for each
treatment, showing the ranking and relative efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors + chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy. For
comparisons of the OS (right upper half) and PFS (left lower half),
a HR <1 favors the column defining treatment. Significant
differences are boldly shown in the figure. Chem, chemotherapy;
Dur-Chem, durvalumab + chemotherapy; Cemi-Chem, cemiplimab +
chemotherapy; Cam-Chem, camrelizumab + chemotherapy; Niv-Chem,
nivolumab + chemotherapy; Tis-Chem, tislelizumab + chemotherapy;
Ate-Chem, atezolizumab + chemotherapy; HR, hazard ratio; OS,
overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PD-1, programmed
cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1. |
Safety
The NMA comparing PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with
chemotherapy revealed that cases of grade ≥3 TRAEs were identified
in 12 RCTs (9–18,20,21),
whereas instances of grade ≥3 irAEs were noted in 8 RCTs (9,10,12–15,20,21).
With respect to grade ≥3 TRAEs, all PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor groups,
except for durvalumab (OR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68–2.30), showed a
reduction in severe TRAEs (Fig.
S5A). Chemotherapy was associated with a greater incidence of
grade ≥3 TRAEs, with a SUCRA value of 0.94 (Table SV). In terms of
grade ≥3 irAEs, cemiplimab (OR, 19.00; 95% CI,
1.10–9.9×102) and pembrolizumab (OR,8.40; 95% CI,
2.80–41.00) were more susceptible to severe irAEs (Fig. S6A), ranking poorly with SUCRA
values of 0.79 and 0.62, respectively (Table SV).
Compared with placebo (22–24,27–32),
no significant differences were found for grade ≥3 TRAEs (Fig. S5B). However, sugemalimab (OR,
21.00; 95% CI, 2.60–6.80×102), nivolumab (OR, 10.00; 95%
CI, 1.40–72.00) and pembrolizumab (OR, 3.90; 95% CI, 1.00–16.00)
were more likely to result in severe irAEs (22–25,27–32)
(Fig. S6B), with sugemalimab
having the highest SUCRA value of 0.88 (Table SV).
When combination therapies (PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors +
chemotherapy) were compared with chemotherapy alone (6,33–42),
cemiplimab (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.30–2.00), camrelizumab (OR, 2.60;
95% CI, 1.50–4.30) and tislelizumab (OR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.20–2.90)
in combination with chemotherapy were associated with increased
grade ≥3 TRAEs (Fig. S5C).
Camrelizumab and tislelizumab combinations had high SUCRA values of
0.96 and 0.80 for severe TRAEs, respectively (Table SV). Both
combinations were also linked to higher incidences of grade ≥3
irAEs (36–41) (Fig.
S6C), with SUCRA values of 0.79 and 0.69, respectively (Table
SV).
Subgroup analysis according to the
tumor histology characteristics
The 32 RCTs included information on tumor histology
characteristics. Among them, 27 RCTs exclusively included patients
with non-squamous NSCLC, whereas 20 RCTs specifically focused on
patients with squamous NSCLC (Table
SII). In the analysis of direct comparisons of OS in patients
with non-squamous NSCLC, all experimental treatments demonstrated
superior outcomes compared with chemotherapy (Fig. 6). Toripalimab exhibited the most
significant improvement in OS (HR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.31–0.75). In the
indirect comparisons, toripalimab showed superior OS benefits over
atezolizumab (HR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.37–0.94) and nivolumab (HR, 0.57;
95% CI, 0.36–0.92), whereas sintilimab exhibited greater OS
benefits over nivolumab (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.56–0.98). In the
analysis of direct comparisons for PFS in patients with
non-squamous NSCLC, toripalimab, sintilimab, pembrolizumab,
cemiplimab, durvalumab and atezolizumab demonstrated a significant
advantage over chemotherapy (Fig.
6).
 | Figure 6.Network meta-analysis for OS and PFS
of patients with non-squamous NSCLC. HR with 95% confidence
interval are presented for various treatment regimens, including
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy. Both direct and indirect
comparison results for patients with non-squamous NSCLC are
illustrated, showing the comparative efficacy of each therapy in
extending OS and PFS. For comparisons of the OS (right upper half)
and PFS (left lower half), a HR <1 favors the column defining
treatment. Significant differences are boldly shown in the figure.
Chem, chemotherapy; Durv, durvalumab; Atez, atezolizumab; Nivo,
nivolumab; Pemb, pembrolizumab; Cemi, cemiplimab; Tisl,
tislelizumab; Tori, toripalimab; Sint, sintilimab; Suge,
sugemalimab; Camr, camrelizumab; HR, hazard ratio; OS, overall
survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PD-1, programmed cell
death-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; NSCLC, non-small cell
lung cancer. |
In the subgroup of patients with squamous NSCLC,
treatments were administered to 3,383 patients, whereas 2,693
patients were in the control arms (Table SII). In the analysis of direct
comparisons of OS in patients with squamous NSCLC, the cemiplimab,
camrelizumab, tislelizumab and nivolumab experimental treatments
were associated with a greater OS than chemotherapy (Fig. 7). According to the results of the
indirect comparison analysis, cemiplimab outperformed atezolizumab,
toripalimab and durvalumab. Camrelizumab was superior to
toripalimab and atezolizumab. In addition, both sintilimab and
pembrolizumab were superior to toripalimab (Fig. 7). For PFS in patients with squamous
NSCLC, toripalimab, sintilimab, pembrolizumab, cemiplimab,
durvalumab and atezolizumab all demonstrated superiority over
chemotherapy (Fig. 7).
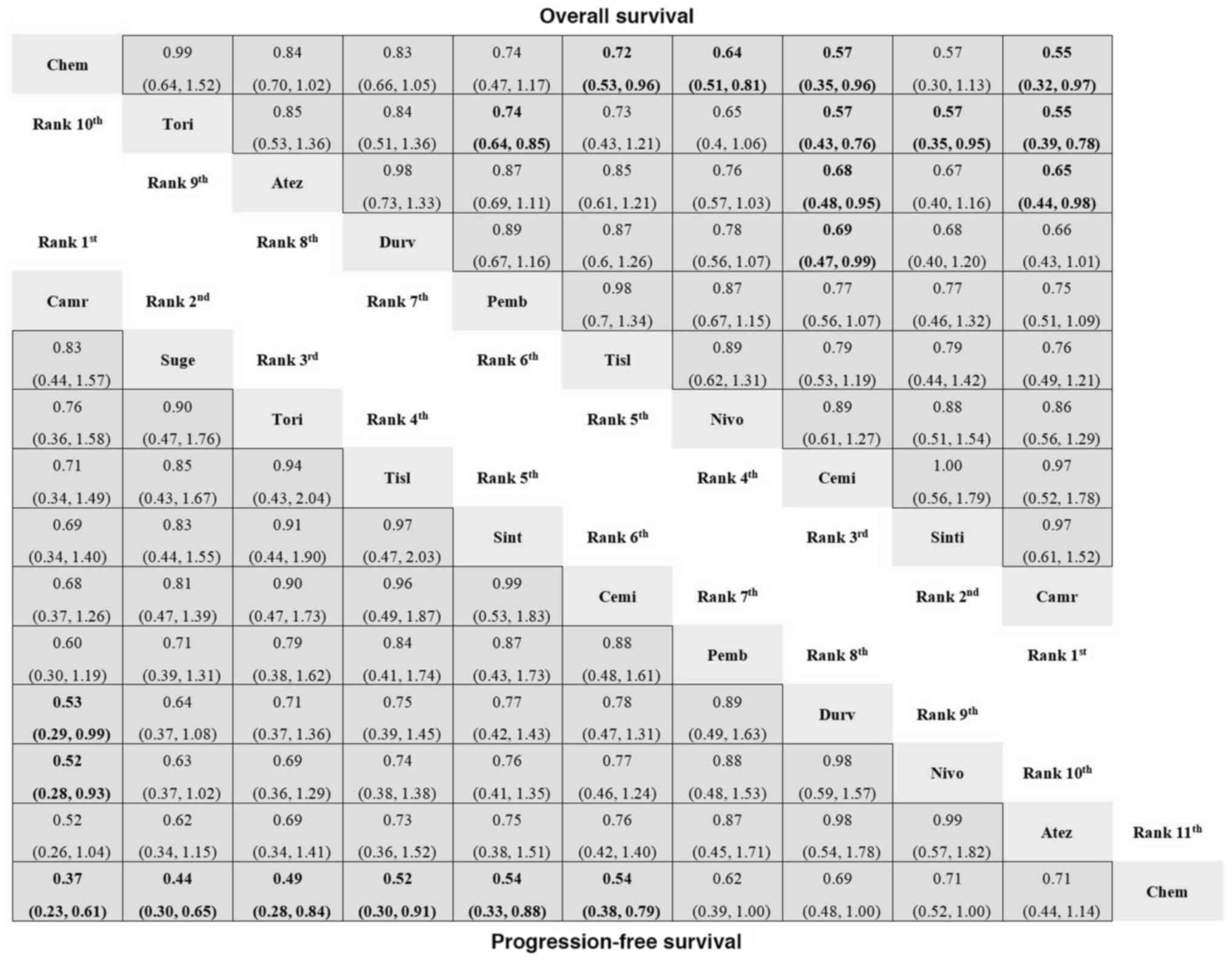 | Figure 7.Network meta-analysis for OS and PFS
of patients with squamous NSCLC. HR with 95% confidence interval
are presented for various treatment regimens, including PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors and chemotherapy. Both direct and indirect comparison
results for patients with squamous NSCLC are illustrated, showing
the comparative efficacy of each therapy in extending OS and PFS.
For comparisons of the OS (right upper half) and PFS (left lower
half), a HR <1 favors the column defining treatment. Significant
differences are boldly shown in the figure. Chem, chemotherapy;
Durv, durvalumab; Atez, atezolizumab; Nivo, nivolumab; Pemb,
pembrolizumab; Cemi, cemiplimab; Tisl, tislelizumab; Tori,
toripalimab; Sint, sintilimab; Suge, sugemalimab; Camr,
camrelizumab; HR, hazard ratio; OS, overall survival; PFS,
progression-free survival; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1,
programmed death-ligand 1; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer. |
Discussion
The landscape of cancer immunotherapy has
significantly evolved with the introduction of PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors, offering novel avenues for enhancing patient survival
and delaying disease progression. As each PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor has
distinct advantages, the present study aimed to evaluate the
efficacy and safety profiles of 10 PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors that have
been approved by the FDA and the National Medical Products
Administration for the treatment of NSCLC.
Several previous NMAs have evaluated first-line
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for NSCLC (43–45),
but the present study offers a more comprehensive and updated
synthesis. Unlike the study by Wang et al (43), which recommends therapies based on
PD-L1 status and only considered grade 3 or higher TRAEs for the
safety assessment, the present study evaluated both efficacy and
safety profiles. Additionally, the analysis by Wang et al
was limited to only four drugs and found pembrolizumab combined
with chemotherapy the most effective for the general cohort. The
results of the present study highlighted tislelizumab,
pembrolizumab and nivolumab as demonstrating significant advantages
over conventional chemotherapy in improving OS. Jiang et al
(44) assessed only five inhibitors
with a focus on OS and TRAEs, suggesting cemiplimab as having a
favorable risk-benefit profile but noting limitations due to short
follow-up data. By contrast, the present study provides a more
robust evaluation by incorporating longer follow-up data and
considering a broader range of outcomes, including OS, PFS, ORR,
DCR and both TRAEs and irAEs, for 10 approved PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors. In terms of efficacy, the present study also highlights
cemiplimab and tislelizumab for their notable benefits in PFS. Li
et al (45) focused
exclusively on combination therapies with chemotherapy for
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) and similarly
noted that treatment with serplulimab plus chemotherapy was the
superior modality. However, the present study focused on NSCLC and
went beyond combination therapies, encompassing monotherapies and
other combination options. The results of the present study
indicated that, when combined with chemotherapy, nivolumab and
cemiplimab achieved notable improvements in OS compared with
chemotherapy alone.
The findings from a study based on summarized
subgroup data and studies with similar, though not identical,
inclusion criteria suggested that ethnic differences did not
significantly affect response rates or survival outcomes in
patients with NSCLC receiving immunotherapy with nivolumab,
pembrolizumab, atezolizumab or durvalumab (46). Further analyses on ethnic
differences in treatment responses to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors,
including nivolumab, pembrolizumab and atezolizumab, in real-world
settings have shown variable outcomes across ethic groups.
Specifically, African-American patients with advanced NSCLC treated
with these agents experienced longer times to treatment
discontinuation and OS compared with White patients, suggesting
that a lower occurrence of hyperprogressive disease may contribute
to these favorable outcomes (47).
While efficacy differences in survival outcomes across ethnic
groups appear limited, previous research has indicated that the
characteristics of AEs in Asian cancer populations using PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors differed from those observed in Western patients. For
example, in Asian patients, camrelizumab has been linked to a high
rate of reactive capillary hemangiomas, a side effect that has not
been reported among Western patients (48). In addition, the results of the
present study further indicated that camrelizumab combined with
chemotherapy was more likely to result in severe TRAEs. Similarly,
a retrospective review of patients with stage IV solid tumors
treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors at MedStar Georgetown Cancer
Institute between 2013 and 2018 found a significantly higher
incidence of irAEs in Caucasian patients (60.4%) than in
African-American patients (30.8%) (49).
Tislelizumab, China's first independently developed
PD-1 inhibitor, was launched in December 2019 and received
approvals in Europe and the United States in 2023 and 2024,
respectively. Regulatory approval in China has facilitated its
widespread use in clinical practice. A study indicated that the
combination of tislelizumab with chemotherapy was not a
cost-effective first-line treatment option for ES-SCLC in either
China or the United States; however, the margin of
cost-effectiveness was narrow in China, while it was clearly not
cost-effective in the United States. This discrepancy may be
attributed to differences in healthcare systems, willingness-to-pay
thresholds and drug costs between the two countries (50). Tislelizumab is primarily used in
Chinese populations and has been included in the National Medical
Insurance Drug List in China. By contrast, as a newly launched drug
in other countries, its insurance coverage may not yet be
widespread, resulting in high prices that affect patient
accessibility. A study examining Black patients with metastatic
lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab found that the safety
profile and treatment response were similar to those of White
patients (51). Pembrolizumab was
launched earlier than tislelizumab, and research has shown that the
efficacy and safety of tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy are
similar to those of pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy
(52). In a real-world study, no
significant differences were found in the efficacy and safety of
domestically produced tislelizumab and camrelizumab compared with
imported pembrolizumab (53). In
the present study, nivolumab stood out when used in combination
with chemotherapy. This combination approach highlights the
potential of nivolumab in improving survival outcomes in patients
with advanced NSCLC. In the present study, as a monotherapy,
nivolumab also showed notable efficacy, offering flexibility in
treatment planning. The choice to use nivolumab, particularly in
combination therapy, should be guided by the goal of maximizing
survival benefits, especially in advanced disease stages. However,
in certain cases, such as patients with significant comorbidities
or a preference for maintaining quality of life, treatment
decisions may prioritize palliation or minimizing toxicities over
aggressive survival-focused strategies. A recent studies has shown
that the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab can serve as a
promising new first-line treatment option for patients with
advanced NSCLC, as it leads to significant improvements in OS while
maintaining a favorable risk-benefit profile (54).
The rapid advancement of domestic PD-1/PD-L1
antibody drugs has introduced new options for cancer immunotherapy
in China, increasing the treatment standards for patients across
the country. These drugs have not only demonstrated comparable
efficacy and safety as imported alternatives but also offer
economic advantages, thereby enabling more patients to access
effective treatment. A previous randomized clinical trial revealed
that patients with resectable stage IIIA or IIIB (T3N2) NSCLC
experienced a significant improvement in the pathological complete
response rate when treated with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy as
opposed to chemotherapy alone and demonstrated good tolerance to
adverse effects (55). Grade 3
adverse events that occurred at a rate of ≥1% included anemia,
hypernatremia and pulmonary infection (56). Sugemalimab ranked highly for both OS
and PFS in the present study. From the perspective of the Chinese
health care system, the use of sugemalimab in combination with
platinum-based chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for squamous
or non-squamous metastatic NSCLC may be more cost-effective than
the use of a placebo plus platinum-based chemotherapy (57). This makes sugemalimab a valuable
option for improving patient outcomes while also considering its
economic feasibility in clinical practice.
Whereas the general safety profile of PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors appeared favorable in terms of TRAEs, the results of the
present study highlighted a concerning aspect with respect to
irAEs. At present, the mechanisms underlying the occurrence of
irAEs have not been fully elucidated and different organs may have
distinct pathological drivers for them (58). As T cells are considered key to the
antitumor responses triggered by ICIs and are commonly found to
dominate immune cell infiltrates in tissue biopsies of irAEs across
various organ systems, a previous study investigated the connection
between T cells in irAEs and their corresponding tumors (59). In addition, certain irAEs are
associated with autoantibodies similar to those seen in classical
autoimmune diseases, and there is evidence regarding the
involvement of autoantibodies and B cell responses in both irAEs
and antitumor responses (60).
Although the reported incidence of severe irAEs has been low thus
far, an increase in clinically significant toxicities is
inevitable, especially with the increasing use of ICIs (61). The focus on safety can significantly
influence treatment choices for NSCLC, guiding clinicians to weigh
the benefits of PD-1/PD-L1 therapy against the risk of severe
toxicity, ultimately leading to more personalized and safer
treatment protocols. ICIs enhance antitumor effects by restoring
the function of suppressed effector T cells, making them prone to
induce checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis (CIP) during the treatment
of NSCLC (4). Given the risk of
irAEs, clinicians are advised to assess the immune status of the
patient and the history of autoimmune diseases carefully before
initiating ICI therapy. Monitoring for early symptoms of CIP is
crucial, as timely intervention can mitigate severe complications.
Specifically, in the present study, cemiplimab and pembrolizumab
demonstrated greater susceptibility to severe irAEs of grade ≥3
than chemotherapy, indicating a notably increased risk of these
events. By contrast, another study has shown that cemiplimab
exhibits balanced efficacy and safety in the treatment of advanced
NSCLC, which may be attributed to differences in the safety
evaluation criteria (62).
In the present study, in non-squamous NSCLC,
toripalimab exhibited the most significant benefit. Another NMA
recommended pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, tislelizumab plus
chemotherapy and sintilimab plus chemotherapy as effective
treatment options for patients with non-squamous NSCLC and PD-L1
expression ≥50% (63). It was
evident that PD-L1 expression was a crucial factor to consider when
selecting PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. In the present study, compared
with chemotherapy, cemiplimab, camrelizumab, tislelizumab and
nivolumab were associated with a longer OS time in patients with
squamous NSCLC. These histology-specific findings highlight the
importance of tailored treatment approaches on the basis of tumor
characteristics.
Despite the strengths of the NMA performed in the
present study, including its comprehensive nature and large sample
size, certain limitations must be acknowledged. Potential
heterogeneity across the included studies, variations in follow-up
periods and possible publication bias may have influenced the
interpretation of the results. Moreover, the lack of direct
head-to-head comparisons between all the inhibitors necessitated a
cautious interpretation of the indirect comparison results.
In conclusion, the choice of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor
should be tailored to individual patient needs, balancing efficacy
with safety profiles. Tislelizumab, pembrolizumab and nivolumab are
highly effective options for improving survival outcomes. By
contrast, camrelizumab and cemiplimab offer notable benefits in
terms of PFS but require careful management of side effects.
Long-term follow-up studies are needed to confirm the durability of
the observed survival benefits.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
ZZ and KY contributed to the conception and design
of the study. Data collection was performed by LL and YW,
statistical analysis was performed by LL and YY and interpretation
of the data was performed by LY and ZL. LL and YY drafted and
revised the manuscript. ZZ and KY confirm the authenticity of all
the raw data. All authors read and approved the final version of
the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sequist LV, Rolfe L and Allen AR:
Rociletinib in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J
Med. 373:578–579. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yin J, Wu Y, Yang X, Gan L and Xue J:
Checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis induced by anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy
in non-small-cell lung cancer: Occurrence and mechanism. Front
Immunol. 13:8306312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG,
Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng HY, Corbett MS, Eldridge
SM, et al: RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 366:l48982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Socinski MA, Nishio M, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo
F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodríguez-Abreu D,
Moro-Sibilot D, Thomas CA, et al: IMpower150 final overall survival
analyses for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in
first-line metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol.
16:1909–1924. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Sun J, Wang Z, Fang J, Yu Q, Han
B, Cang S, Chen G, Mei X, Yang Z, et al: Updated overall survival
data and predictive biomarkers of sintilimab plus pemetrexed and
platinum as first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic
nonsquamous NSCLC in the phase 3 ORIENT-11 study. J Thorac Oncol.
16:2109–2120. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Wang Z, Fang J, Yu Q, Han B, Cang
S, Chen G, Mei X, Yang Z, Stefaniak V, et al: Final overall
survival data of sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum as
first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous
NSCLC in the phase 3 ORIENT-11 study. Lung Cancer. 171:56–60. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sezer A, Kilickap S, Gümüş M, Bondarenko
I, Özgüroğlu M, Gogishvili M, Turk HM, Cicin I, Bentsion D, Gladkov
O, et al: Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: A
multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled
trial. Lancet. 397:592–604. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rizvi NA, Cho BC, Reinmuth N, Lee KH, Luft
A, Ahn MJ, van den Heuvel MM, Cobo M, Vicente D, Smolin A, et al:
Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab vs standard chemotherapy in
first-line treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: The
MYSTIC phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 6:661–674.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carbone DP, Reck M, Paz-Ares L, Creelan B,
Horn L, Steins M, Felip E, van den Heuvel MM, Ciuleanu TE, Badin F,
et al: First-line nivolumab in stage IV or recurrent non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:2415–2426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herbst RS, Garon EB, Kim DW, Cho BC,
Gervais R, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, Majem M, Forster MD, Monnet I,
et al: Five year survival update from KEYNOTE-010: Pembrolizumab
versus docetaxel for previously treated, programmed death-ligand
1-positive advanced NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 16:1718–1732. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Castro G Jr, Kudaba I, Wu YL, Lopes G,
Kowalski DM, Turna HZ, Caglevic C, Zhang L, Karaszewska B,
Laktionov KK, et al: Five-year outcomes with pembrolizumab versus
chemotherapy as first-line therapy in patients with non-small-cell
lung cancer and programmed death ligand-1 tumor proportion score
≥1% in the KEYNOTE-042 study. J Clin Oncol. 41:1986–1991. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG,
Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe
S, et al: Five-year outcomes with pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy
for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor
proportion score ≥50. J Clin Oncol. 39:2339–2349. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren S, Feng J, Ma S, Chen H, Ma Z, Huang
C, Zhang L, He J, Wang C, Zhou J, et al: KEYNOTE-033: Randomized
phase 3 study of pembrolizumab vs docetaxel in previously treated,
PD-L1-positive, advanced NSCLC. Int J Cancer. 153:623–634. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu YL, Lu S, Cheng Y, Zhou C, Wang J, Mok
T, Zhang L, Tu HY, Wu L, Feng J, et al: Nivolumab versus docetaxel
in a predominantly chinese patient population with previously
treated advanced NSCLC: CheckMate 078 randomized phase III clinical
trial. J Thorac Oncol. 14:867–875. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crinò L,
Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes EE,
Holgado E, et al: Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced
squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
373:123–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou C, Huang D, Fan Y, Yu X, Liu Y, Shu
Y, Ma Z, Wang Z, Cheng Y, Wang J, et al: Tislelizumab versus
docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC
(RATIONALE-303): A phase 3, open-label, randomized controlled
trial. J Thorac Oncol. 18:93–105. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fehrenbacher L, von Pawel J, Park K,
Rittmeyer A, Gandara DR, Ponce Aix S, Han JY, Gadgeel SM, Hida T,
Cortinovis DL, et al: Updated efficacy analysis including secondary
population results for OAK: A randomized phase iii study of
atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1156–1170.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jassem J, de Marinis F, Giaccone G,
Vergnenegre A, Barrios CH, Morise M, Felip E, Oprean C, Kim YC,
Andric Z, et al: Updated overall survival analysis from IMpower110:
Atezolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy in treatment-naive
programmed death-ligand 1-selected NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol.
16:1872–1882. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou C, Wu L, Fan Y, Wang Z, Liu L, Chen
G, Zhang L, Huang D, Cang S, Yang Z, et al: Sintilimab plus
platinum and gemcitabine as first-line treatment for advanced or
metastatic squamous NSCLC: Results from a randomized, double-blind,
phase 3 trial (ORIENT-12). J Thorac Oncol. 16:1501–1511. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ren S, Chen J, Xu X, Jiang T, Cheng Y,
Chen G, Pan Y, Fang Y, Wang Q, Huang Y, et al: Camrelizumab plus
carboplatin and paclitaxel as first-line treatment for advanced
squamous NSCLC (CameL-Sq): A phase 3 trial. J Thorac Oncol.
17:544–557. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Makharadze T, Gogishvili M, Melkadze T,
Baramidze A, Giorgadze D, Penkov K, Laktionov K, Nemsadze G,
Nechaeva M, Rozhkova I, et al: Cemiplimab plus chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone in advanced NSCLC: 2-Year follow-up from the
phase 3 EMPOWER-lung 3 part 2 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 18:755–768.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang Y, Wang Z, Fang J, Yu Q, Han B, Cang
S, Chen G, Mei X, Yang Z, Ma R, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum as first-line treatment for
locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: A randomized,
double-blind, phase 3 study (Oncology pRogram by InnovENT
anti-PD-1-11). J Thorac Oncol. 15:1636–1646. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spigel DR, Faivre-Finn C, Gray JE, Vicente
D, Planchard D, Paz-Ares L, Vansteenkiste JF, Garassino MC, Hui R,
Quantin X, et al: Five-year survival outcomes from the PACIFIC
trial: Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage iii
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 40:1301–1311. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sugawara S, Lee JS, Kang JH, Kim HR, Inui
N, Hida T, Lee KH, Yoshida T, Tanaka H, Yang CT, et al: Nivolumab
with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line
treatment of advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann
Oncol. 32:1137–1147. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Novello S, Kowalski DM, Luft A, Gümüş M,
Vicente D, Mazières J, Rodríguez-Cid J, Tafreshi A, Cheng Y, Lee
KH, et al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in squamous
non-small-cell lung cancer: 5-year update of the phase III
KEYNOTE-407 study. J Clin Oncol. 41:1999–2006. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garassino MC, Gadgeel S, Speranza G, Felip
E, Esteban E, Dómine M, Hochmair MJ, Powell SF, Bischoff HG, Peled
N, et al: Pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed and platinum in nonsquamous
non-small-cell lung cancer: 5-Year outcomes from the phase 3
KEYNOTE-189 study. J Clin Oncol. 41:1992–1998. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou Q, Chen M, Jiang O, Pan Y, Hu D, Lin
Q, Wu G, Cui J, Chang J, Cheng Y, et al: Sugemalimab versus placebo
after concurrent or sequential chemoradiotherapy in patients with
locally advanced, unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung
cancer in China (GEMSTONE-301): Interim results of a randomised,
double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:209–219.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou C, Wang Z, Sun Y, Cao L, Ma Z, Wu R,
Yu Y, Yao W, Chang J, Chen J, et al: Sugemalimab versus placebo, in
combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, as first-line
treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (GEMSTONE-302):
Interim and final analyses of a double-blind, randomised, phase 3
clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:220–233. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Wu L, Li B, Cheng Y, Li X, Wang X,
Han L, Wu X, Fan Y, Yu Y, et al: Toripalimab plus chemotherapy for
patients with treatment-naive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer:
A multicenter randomized phase III trial (CHOICE-01). J Clin Oncol.
41:651–663. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jotte R, Cappuzzo F, Vynnychenko I,
Stroyakovskiy D, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Hussein M, Soo R, Conter HJ,
Kozuki T, Huang KC, et al: Atezolizumab in combination with
carboplatin and nab-paclitaxel in advanced squamous NSCLC
(IMpower131): Results from a randomized phase III trial. J Thorac
Oncol. 15:1351–1360. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
West H, McCleod M, Hussein M, Morabito A,
Rittmeyer A, Conter HJ, Kopp HG, Daniel D, McCune S, Mekhail T, et
al: Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus
nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as
first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell
lung cancer (IMpower130): A multicentre, randomised, open-label,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:924–937. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reck M, Mok TSK, Nishio M, Jotte RM,
Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodríguez-Abreu
D, Moro-Sibilot D, et al: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and
chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key
subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver
metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir
Med. 7:387–401. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nishio M, Barlesi F, West H, Ball S,
Bordoni R, Cobo M, Longeras PD, Goldschmidt J Jr, Novello S,
Orlandi F, et al: Atezolizumab plus chemotherapy for first-line
treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC: Results from the randomized phase 3
IMpower132 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 16:653–664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou C, Chen G, Huang Y, Zhou J, Lin L,
Feng J, Wang Z, Shu Y, Shi J, Hu Y, et al: Camrelizumab plus
carboplatin and pemetrexed as first-line treatment for advanced
nonsquamous NSCLC: Extended follow-up of CameL phase 3 trial. J
Thorac Oncol. 18:628–639. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Johnson ML, Cho BC, Luft A,
Alatorre-Alexander J, Geater SL, Laktionov K, Kim SW, Ursol G,
Hussein M, Lim FL, et al: Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab
in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy for
metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: The phase III POSEIDON
study. J Clin Oncol. 41:1213–1227. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, Provencio M,
Mitsudomi T, Awad MM, Felip E, Broderick SR, Brahmer JR, Swanson
SJ, et al: Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 386:1973–1985. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lu S, Wu L, Jian H, Chen Y, Wang Q, Fang
J, Wang Z, Hu Y, Sun M, Han L, et al: Sintilimab plus bevacizumab
biosimilar IBI305 and chemotherapy for patients with EGFR-mutated
non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on EGFR
tyrosine-kinase inhibitor therapy (ORIENT-31): First interim
results from a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:1167–1179. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lu S, Wang J, Yu Y, Yu X, Hu Y, Ai X, Ma
Z, Li X, Zhuang W, Liu Y, et al: Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as
first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous
NSCLC (RATIONALE 304): A randomized phase 3 trial. J Thorac Oncol.
16:1512–1522. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang J, Lu S, Yu X, Hu Y, Sun Y, Wang Z,
Zhao J, Yu Y, Hu C, Yang K, et al: Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy
vs chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for advanced squamous
non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 3 randomized clinical trial.
JAMA Oncol. 7:709–717. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang DD, Shaver LG, Shi FY, Wei JJ, Qin
TZ, Wang SZ and Kong YJ: Comparative efficacy and safety of
PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapies for non-small cell lung cancer: A
network meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:2866–2884.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang M, Liu C, Ding D, Tian H and Yu C:
Comparative efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 for the
treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis of
13 randomized controlled studies. Front Oncol. 12:8270502022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li H, Han H, Li C, Wu R, Wang Z, Wang Y,
Zhan P, Lv T, Zhang F, Song Y and Lu H: Efficacy and safety of
first-line PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor combinations for extensive-stage
small-cell lung cancer: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. Ther Adv
Med Oncol. 15:175883592311894302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee J, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K and
Ahn MJ: Are there any ethnic differences in the efficacy and safety
of immune checkpoint inhibitors for treatment of lung cancer? J
Thorac Dis. 12:3796–3803. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ayers KL, Mullaney T, Zhou X, Liu JJ, Lee
K, Ma M, Jones S, Li L, Redfern A, Jappe W, et al: Analysis of
real-world data to investigate the impact of race and ethnicity on
response to programmed cell death-1 and programmed cell
death-ligand 1 inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancers.
Oncologist. 26:e1226–e1239. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang J, He X, Lv Q, Jing J and Shi H:
Management of adverse events in cancer patients treated with
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Focus on Asian populations. Front Pharmacol.
10:7262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Peravali M, Gomes-Lima C, Tefera E, Baker
M, Sherchan M, Farid S, Burman K, Constantinescu F and Veytsman I:
Racial disparities in immune-related adverse events of immune
checkpoint inhibitors and association with survival based on
clinical and biochemical responses. World J Clin Oncol. 12:103–114.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lang W, Ai Q, He Y, Pan Y, Jiang Q, Ouyang
M and Sun T: Cost-effectiveness analysis of tislelizumab plus
chemotherapy versus standard chemotherapy in first-line treatment
for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: Perspectives from the
United States and China. Int J Clin Pharm. 46:1536–1545. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Peravali M, Ahn J, Chen K, Rao S, Veytsman
I, Liu SV and Kim C: Safety and efficacy of first-line
pembrolizumab in black patients with metastatic non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncologist. 26:694–700. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guo Y, Jia J, Hao Z and Yang J:
Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus pembrolizumab plus
chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of advanced non-small
cell lung cancer: Systematic review and indirect comparison of
randomized trials. Front Pharmacol. 14:11729692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hu J, Li M, Xie Z and Chen J: Comparison
of the efficacy and safety of domestically produced tislelizumab,
camrelizumab, and imported pembrolizumab in the treatment of
advanced NSCLC: A real-world retrospective study. Clin Transl
Oncol. Jun 27–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Paz-Ares L, Ciuleanu TE, Cobo M, Schenker
M, Zurawski B, Menezes J, Richardet E, Bennouna J, Felip E,
Juan-Vidal O, et al: First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined
with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell
lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): An international, randomised,
open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 22:198–211. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lei J, Zhao J, Gong L, Ni Y, Zhou Y, Tian
F, Liu H, Gu Z, Huang L, Lu Q, et al: Neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus
platinum-based chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone for chinese
patients with resectable stage IIIA or IIIB (T3N2) non-small cell
lung cancer: The TD-FOREKNOW randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol.
9:1348–1355. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Markham A and Keam SJ: Camrelizumab: First
global approval. Drugs. 79:1355–1361. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen P, Li Y, Jing X, Chen J, Chen S and
Yang Q: Cost-effectiveness analysis of sugemalimab in combination
with chemotherapy as first-line treatment in Chinese patients with
metastatic NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 174:157–164. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Blum SM, Rouhani SJ and Sullivan RJ:
Effects of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) and their
treatment on antitumor immune responses. Immunol Rev. 318:167–178.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kuchroo JR, Hafler DA, Sharpe AH and Lucca
LE: The double-edged sword: Harnessing PD-1 blockade in tumor and
autoimmunity. Sci Immunol. 6:eabf40342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Huang YT, Chen YP, Lin WC, Su WC and Sun
YT: Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced myasthenia gravis. Front
Neurol. 11:6342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Darnell EP, Mooradian MJ, Baruch EN,
Yilmaz M and Reynolds KL: Immune-related adverse events (irAEs):
Diagnosis, management, and clinical pearls. Curr Oncol Rep.
22:392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li Y, Liang X, Li H and Chen X: Efficacy
and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small
cell lung cancer with or without PD-L1 selection: A systematic
review and network meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 136:2156–2165.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen W, Chen J, Zhang L, Cheng S and Yu J:
Network meta-analysis of first-line immune checkpoint inhibitor
therapy in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer
patients with PD-L1 expression ≥ 50. BMC Cancer. 23:7912023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|