Introduction
Propofol (2,6-disopropylphenol) is a short-acting
drug, which has been extensively used as a sedative and anesthetic
induction drug prior to medical procedures, which could modulate
the different γ-aminobutyric acid receptors in the central nervous
system (1). It has been indicated
that the use of sedative techniques could affect long-term outcome
following cancer surgery, including propofol, which has potential
to impede metastasis and to activate apoptosis in cancer cells
(2). Besides, previous studies
demonstrated that propofol has antitumor effects inhibiting
invasion or proliferation in ovarian cancer cells and osteosarcoma
cells (3,4). A number of reports demonstrated that
propofol could induce apoptosis in different cancer cells,
including pancreatic cancer (5),
lung cancer (6,7), epithelial ovarian cancer (8) and hepatocarcinoma (9). Thus, propofol has the ability to be a
therapeutic drug for malignancies.
The control of cell number is important in tissue
homeostasis, and its dysregulation could give rise to the
occurrence of tumors, which could be regulated by cell death,
proliferation and differentiation (10). A previous study demonstrated that
cancer cells exhibit different characteristics progressing from
normal cells to tumor cells, which include tissue invasion and
metastasis, unlimited replicative capability, self-sufficiency in
growth signals, avoidance of apoptosis, continued angiogenesis, and
resistance to antigrowth signals (11), and the majority of anticancer
therapies are against these properties (10,11).
Notably, when cells experience environmental stresses or the
stimulation of intracellular signals, cell death may occur
(12). Cell death is classified in
three categories from morphological appearance, including
autophagy, necrosis and apoptosis (13). Apoptosis and autophagy are types of
programmed cell death (12,13). Autophagy is contradictory for cancer
cells with pro-survival or pro-death roles (14). Compared with apoptosis, necrosis is
a procedure of cell death in an unregulated manner resulting from
severe insults or adverse conditions (15). Therefore, the induction of apoptosis
could be a beneficial therapy for patients with cancer. Apoptosis
in cells consistently features cell shrinking, nuclear condensation
and then fragmentation, membrane blebbing and the formation of
apoptotic bodies from the separation of cellular components
(16).
There are two major pathways in apoptosis: Extrinsic
pathway and intrinsic pathways (17). Extrinsic pathways, also termed death
receptor pathways, begin with the activation of death receptors by
pro-apoptotic ligands, including Fas ligand, tumor necrosis
factor-α (TNF-α) and TNF superfamily member 10 (17,18).
Following ligand binding, intracellular death domains of these
receptors bind to Fas-associated death domain, which causes the
recruitment of death-induced signaling complex and the activation
of caspase-8 to trigger downstream effector caspases, including
caspase-3 and −7 (18). An
intrinsic pathway involves mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum
pathways. It has been demonstrated that the mitochondrial pathway
could be triggered by ultraviolet radiation, chemotherapeutic
agents and growth factor withdrawal, resulting in the release of
cytochrome c from mitochondrial intermembrane space to
cytosol (19). Cytochrome c
binds to apoptotic peptidase activating factor-1 to recruit
pro-caspase-9 forming apoptosome to cleave caspase-9, and then the
active caspase-9 activates caspase-3 to orchestrate apoptosis
(20). The intrinsic and extrinsic
pathways induce poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage
following activating downstream caspase effectors, and the
cleaved-PARP impedes DNA repair (17).
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway
serves key roles in cancer development, which also regulates cell
growth, proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis
(21). MAPKs, including
extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun
N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38, are protein-serine/threonine
kinases, which could be activated through a cascade of
phosphorylation events and regulate cell fate (22,23).
Akt signaling is a pro-survival pathway, which
inhibits apoptotic signal cascades and activates pro-survival
signal (24). Akt signaling
inhibits a number of pro-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) family
members, including Bcl-2 associated agonist of cell death,
Bcl-2-associated X and Bcl-2 like 11 (25). Akt also positively regulates
anti-apoptotic pathways to induce the nuclear factor-κB
transcription factor, promoting anti-apoptotic genes, including
Bcl-2 and Bcl-extra large (24,25).
Numerous studies demonstrated that the suppression of Akt prompts
apoptosis in human testicular germ tumor cells (24–26).
Testicular cancer is a cancer type that develops in
the testis, which is primarily classified into two categories: Germ
cell tumor; and stromal tumor (27). Leydig cell tumor types are the most
common form of stromal tumors with a significantly increasing
incidence, and ~10% of Leydig cell tumor cases are malignant;
however, this has not been clearly documented (28). Malignant Leydig cell tumors do not
respond to irradiation and chemotherapy (29). Thus, it's important to determine an
improved therapeutic method for Leydig cell tumors (29). The majority of the studies
demonstrated that propofol induces apoptosis resulting in
beneficial therapy for patients with different cancer types
(3–5). Therefore, whether propofol promotes
apoptosis in MA-10 cells to provide a potential antitumor therapy
was investigated.
Materials and methods
Chemicals
Propofol (cat. no. 1572503; 0.962 g/ml), MTT (cat.
no. M5655), penicillin-streptomycin, propidium iodide (PI; cat. no.
P4170), RNase A (cat. no. R6513), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
(EDTA; cat. no. E5134), Triton X-100 (cat. no. T8787), sodium
orthovanadate (cat. no. S6508), Waymouth MB 752/1 medium (cat. no.
W1625), monoclonal antibody against β-actin (cat. no. A5441;
1:8,000) and 30% acrylamide/Bis-acrylamide solution (cat. no.
A3574) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt,
Germany). DS (cat. no. 822050), EGTA (cat. no. L808635342),
Tween-20 (cat. no. 817072) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; cat. no.
102952) were purchased from Merck KGaA. Dulbecco's modified Eagle
medium/F12 (cat. no. 12400-024), trypsin-EDTA (cat. no. 15400-054)
and fetal bovine serum (FBS; cat. no. 10437-028) were purchased
from Gibco (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Tris
base (cat. no. 4019-06), potassium chloride (cat. no. 3040-01),
glycine (cat. no. 4059-06)
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (cat. no.
4018-04) and sodium chloride (NaCl; cat. no. 3624-05) were
purchased from J.T.Baker (Avantor Performance Materials, Center
Valley, PA, USA). An Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)
apoptosis detection kit (cat. no. AVK050) was purchased from Strong
Biotech Corporation (Taipei, Taiwan). A Micro BCA protein assay kit
(cat. no. 23235) was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
An Enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (cat. no. WBKLS050) was
purchased from EMD Millipore (Billerica, MA, USA). Donkey
anti-rabbit and anti-mouse IgG conjugated with horseradish
peroxidase (HRP) were purchased from PerkinElmer, Inc. (Waltham,
MA, USA). Polyclonal antibodies against cleaved caspase-8 (cat. no.
9429; 1:1,000), cleaved caspase-9 (cat. no. 9509; 1:1,000), cleaved
PARP (cat. no. 9544; 1:1,000), phospho-ERK1/2 (cat. no. 9101;
1:4,000), ERK1/2 (cat. no. 9102; 1:4,000), phospho-JNK (cat. no.
9251; 1:2,000), JNK (cat. no. 9252; 1:2,000), phospho-p38 MAPK
(cat. no. 9215; 1:4,000), p38 MAPK (cat. no. 9212; 1:4,000),
phospho-mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR; cat. no.
2971; 1:2,000), mTOR (cat. no. 2983; 1:2,000), phospho-Akt (cat.
no. 9271; 1:4,000) and Akt (cat. no. 9272; 1:4,000) were purchased
from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Danvers, MA, USA). Isoton II
(cat. no. 8546719) was purchased from Beckman Coulter, Inc. (Brea,
CA, USA). Monoclonal antibody against cleaved caspase-3 (cat. no.
9664; 1:1,000) was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology,
Inc.
Cell culture
The MA-10 cell line was provided by Dr. Mario Ascoli
(Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Iowa, Iowa
City, IA, USA), which is a mouse Leydig tumor cell line cultured in
the Waymouth medium containing 10% FBS. MA-10 cells were regularly
maintained in a humidified atmosphere incubator containing 5%
CO2 at 37°C.
Cellular morphological
examination
MA-10 cells were seeded at a concentration of
6×105 cells/ml in a 6 cm petri dish with 2 ml Waymouth
culture medium, and treated without or with different
concentrations of propofol (300, 350 and 400 µM) for 3 h at 37°C.
Propofol was diluted with DMSO. Cell morphology was observed under
Olympus CK40 light microscopy at ×100 magnification and the images
were recorded by Olympus DP20 digital camera (Olympus Corporation,
Tokyo, Japan).
MTT viability assay
An MTT assay is a colorimetric assay to detect cell
viability (30). MA-10 cells
(1.2×104 cells/well) were seeded in 96-well plates. When
cell density reached 70–80% confluence at 37°C, cells were treated
with different concentrations of propofol (0, 10, 50, 100, 300,
400, 500 and 600 µM) for 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 h. Subsequently, 0.5
mg/ml MTT was added in each well at different time points (1, 3, 6,
12 and 24 h) and incubated at 37°C for 4 h. The medium was then
discarded, and 50 µl DMSO was added into each well for dissolving
the crystals by shaking the plate with a shaker at 37°C for 20 min
in the dark. Cell viability was then detected at λ=570 nm using a
VersaMax ELISA reader (Molecular Devices, LLC, Sunnyvale, CA, USA)
for the MTT assay (31).
Cell cycle analysis assay
To further investigate if propofol induces MA-10
cell death through apoptosis, the DNA contents were examined by PI
staining through a flow cytometric analysis assay. The
6×105 MA-10 cells were seeded in a 6 cm petri dish with
2 ml Waymouth culture medium, and treated with different
concentrations of propofol (0, 100, 300 and 400 µM) for 3, 6, 12
and 24 h. Cells were then harvested through trypsin digestion and
centrifugation (400 × g at 25°C for 10 min), and washed by isoton
II (1:4,000 dilution) and fixed with 70% ethanol for 2 h at −20°C.
Following fixation, MA-10 cells were washed with cold isoton II
(1:4,000 dilution) and collected by centrifugation (400 × g at 25°C
for 10 min). Cell suspensions were then mixed with 100 µg/ml RNase
A and stained with 40 µg/ml PI solution for 30 min at 25°C. The
stained cells were further analyzed for PI detection at λ=488 nm
with the BD FACScan flow cytometer (Becton-Dickinson and Company,
Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Cells in sub-G1 phase contained reduced
DNA contents in cell cycle distribution, which is considered as DNA
fragmentation, a consequence of cell apoptosis (32). The percentages of cells in sub-G1, S
and G2/M phases were calculated and analyzed using FACStation v6.1×
and Modfit LT v3.3 software (Becton-Dickinson and Company).
Annexin V and PI double staining
assay
After MA-10 cells were harvested by trypsin, which
was rinsed with 2 ml Waymouth culture medium, cell suspensions were
centrifuged (400 × g at 25°C for 10 min). The pellets were then
resuspended by cold isoton II (1:4,000 dilution) and centrifuged
again (400 × g at 25°C for 10 min). The pellets were mixed with 100
µl staining solution for 15 min at 25°C according to manufacturer's
protocols of the Annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis detection kit. The
stained cells were analyzed at λ=488 nm excitation using 515 nm
band pass filter for FITC detection and >600 nm band pass filter
for PI detection with the BD FACScan flow cytometer
(Becton-Dickinson and Company). The double-negative cells (viable),
Annexin V single positive cells (early apoptotic), PI single
positive cells (necrotic) and double positive cells (late
apoptotic) can be depicted in four quadrants (33). The percentage of cells in four
quadrants were calculated using FACStation v6.1× software.
Protein extraction and western blot
assay
Following propofol (0, 100, 300 and 400 µM)
treatment for 3, 6, 12 and 24 h, the medium was removed and cells
were washed 3 times with cold PBS. Attached cells were then lysed
by 20 µl lysis buffer (20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1
mM EGTA, 1% Triton X-100, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate and 1 mM
sodium orthovanadate) with proteinase inhibitor cocktail
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA; cat. no. P5655). The cell pellets were
resuspended with 10 µl lysis buffer and mixed with cell lysates,
and it was centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 12 min at 4°C. The
supernatants were then collected and stored at −80°C. Cell lysate
protein concentrations were determined with a Lowry assay (34).
For western blot assay, 30 µg total protein were
separated by 12% SDS-PAGE gel with standard running buffer (25 mM
Tris, 0.1% SDS and 192 mM glycine; pH 8.3) at 25°C, and
electrophoretically transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride
membrane at 4°C. After 1% milk at 25°C for 3 h blocking of the
membranes, the membranes were incubated with primary antibodies
overnight at 4°C, the membrane was washed 3 times and then
incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies at 25°C for 1 h,
which was detected with an enhanced chemiluminescence kit through
UVP EC3 BioImaging Systems (UVP; LLC, Phoenix, AZ, USA).
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as mean ± standard error of
the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical significance
of differences between control and propofol treated groups were
analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and then least
significance difference comparison. Statistical analysis was
performed by using GraphPad Prism 6 software (GraphPad Software,
Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Propofol induces morphological changes
in MA-10 cells
MA-10 cells were treated with different
concentrations of propofol (0, 300, 350 and 400 µM; Fig. 1). The morphology of cells was
observed with light microscopy. Without propofol treatment, MA-10
cells firmly attached with polygonal shapes (Fig. 1). Following treatment with 400 µΜ
propofol for 3 h (Fig. 1), cells
transformed to round shape and possessed apparent blebbing in the
plasma membrane. These results demonstrated that propofol causes
membrane blebbing in MA-10 cells, indicating that propofol may
induce cell death through apoptosis in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor
cells.
Propofol decreases MA-10 cell
viability with time- and dose-dependent associations
For investigating the effect of propofol upon MA-10
cell viability, an MTT viability test was conducted on MA-10 cells
with 0, 10, 50, 100, 300, 400, 500 and 600 µM propofol for 1, 3, 6,
12 and 24 h treatments (Fig. 2).
The results demonstrated that cell viability was significantly
reduced by propofol from 300–600 µM for 24 h (P<0.05; Fig. 2). The results indicated that
propofol induces cell death in MA-10 cells.
 | Figure 2.Propofol decreases MA-10 cell
viability with time- and dose-dependent associations. MA-10 cells
were treated with 0, 10, 50, 100, 300, 400, 500 and 600 µM propofol
for 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 h. Cell viabilities were examined with an
MTT viability assay. Results are depicted as the percentages of
cell growth relative to control groups. **P<0.01 and
***P<0.005, compared with control. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. |
Propofol regulates the cell cycle in
MA-10 cells
To investigate whether propofol could influence the
cell cycle and result in apoptosis, MA-10 cells were treated with
propofol, and their DNA contents were determined with flow
cytometry. Different dosages of propofol were used to treat cells
examining the impacts on cell cycle progression. The results
demonstrated that increased sub-G1 phase cells were significantly
increased at 400 µM propofol for 3–24 h in MA-10 cells (P<0.05;
Fig. 3A). Additionally, the
significant increases of G2/M phase cells were observed at 300 µM
propofol at 6 and 12 h in MA-10 cells (P<0.05; Fig. 3B). These results demonstrated that
propofol regulated the cell cycle to increase sub-G1 phase cells
and then induced apoptosis in MA-10 cells. Furthermore, propofol
reduced the cell population of MA-10 cells in the G2/M phase.
Propofol induces cell apoptosis in
MA-10 cells
It was observed that propofol stimulated cell death,
causing DNA fragmentation and membrane blebbing. To confirm that
propofol could induce MA-10 cell apoptosis, the Annexin V and PI
double staining method followed by flow cytometry were conducted.
It is well known that percentages of double-negative cells
(viable), Annexin V single positive cells (early apoptotic), PI
single positive cells (necrotic) and double positive cells (late
apoptotic) are observed in four quadrants by double staining, to
demonstrate the cell apoptotic phenomenon (35). The results demonstrated that the
number of Annexin V-positive cells was significantly increased by
propofol at 350 and 400 µM for 3 h in MA-10 cells (P<0.05;
Fig. 4). These results indicated
that propofol induces apoptosis in MA-10 cells.
 | Figure 4.Propofol induces cell apoptosis in
MA-10 cells. MA-10 cells were treated with 0, 300, 350 and 400 µM
propofol for 3 h. (A) The apoptotic status of propofol-treated
cells was detected by Annexin V and PI double staining assay. The
double-negative cells (viable cells), Annexin V single positive
cells (early apoptotic cells), PI single positive cells (necrotic
cells) and Annexin V and PI double positive cells (late apoptotic
cells) were depicted. (B) The various percentages of late apoptotic
cells, early apoptotic cells, necrotic cells, and normal cells in
each treatment. (C) The difference of Annexin V positive cells
(early apoptotic and late apoptotic status) was then analyzed with
propofol treatment. ***P<0.005, compared with control. PI,
propidium iodide; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate. |
Propofol activates the caspase cascade
to induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells
The caspase cascade is an essential inducer of
apoptosis, which is involved with extrinsic and intrinsic pathways
(17–19,36).
According to previous experiments, propofol promotes apoptosis in
MA-10 cells (Figs. 3 and 4); therefore whether propofol induced
apoptosis through apoptotic extrinsic and intrinsic pathways,
inducing cleavages of caspase-8, −9 and −3, and PARP, was
investigated. The present data demonstrated that propofol at 400 µM
for 3 h significantly induces cleaved caspase-8, −9 and −3, and
PARP expression levels in MA-10 cells (P<0.05; Fig. 5A-E). Furthermore, 350 µM propofol
for 6 h also significantly induced cleaved caspase-8 and −3, and
PARP expression levels in MA-10 cells (P<0.05; Fig. 5A, B, D and E).
 | Figure 5.Propofol activates the caspase
cascade to induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells. MA-10 cells were
treated with different concentrations of propofol (0, 300, 350 and
400 µM) for 3, 6, 12 and 24 h. (A) A western blot assay was used to
determine cleaved caspase-8 (43/18 kDa), −9 (39/37 kDa) and −3
(17/19 kDa), and PARP (85–90 kDa). Integrated optical densities of
(B) cleaved caspase-8, (C) −9 and (D) −3, and (E) PARP proteins
were normalized by β-actin (43 kDa) in each lane. *P<0.05,
**P<0.01 and ***P<0.005, compared with control. PARP,
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. |
Propofol activates MAPK pathways to
induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells
Previous studies demonstrated that MAPK pathways
regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis and growth (21,32).
Therefore, whether propofol-induced MA-10 cell apoptosis is
modulated by MAPK pathways was examined by determining the
expression levels of MAPK proteins with a western blot assay. The
data demonstrated that propofol at 400 µM for 3 h significantly
induced the expression levels of phospho-JNK, phospho-ERK and
phospho-p38 (P<0.05; Fig. 6A-D),
and the expression of phospho-p38 was prolonged to 6 h by 400 µM
propofol in MA-10 cells (P<0.05; Fig. 6A and D). Dosage at 350 µM of
propofol for 3 and 6 h significantly induced the expression levels
of phospho-JNK and phospho-ERK (P<0.05; Fig. 6A-C). Notably, a reduced dosage of
propofol at 300 µM for 3 h also significantly induced the
expression of phospho-ERK in MA-10 cells (P<0.05; Fig. 6A and C). These results demonstrated
that propofol at different dosages and temporal durations
significantly induce MAPK signal pathways, implying that propofol
may activate MAPK pathways to induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells.
 | Figure 6.Propofol activates MAPK pathways to
induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells. MA-10 cells were treated with
different concentrations of propofol (0, 300, 350 and 400 µM) for
3, 6, 12 and 24 h. (A) p-JNK (54/46 kDa), JNK, p-ERK (44/42 kDa),
ERK, p-p38 (43 kDa) and p38 were detected by western blot analysis.
The integrated optical densities of (B) p-JNK, (C) p-ERK and (D)
phospho-p38 proteins were normalized by β-actin (43 kDa) in each
lane. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.005, compared with
control. ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun
N-terminal kinase; p-, phospho-. |
In fact, the stimulation of MAPKs, caspases and the
cleavage of PARP occurred at 3 h of propofol treatment in MA-10
(400 µM) cells, indicating that propofol could induce the caspase
cascade and MAPK pathways within a similar time frame.
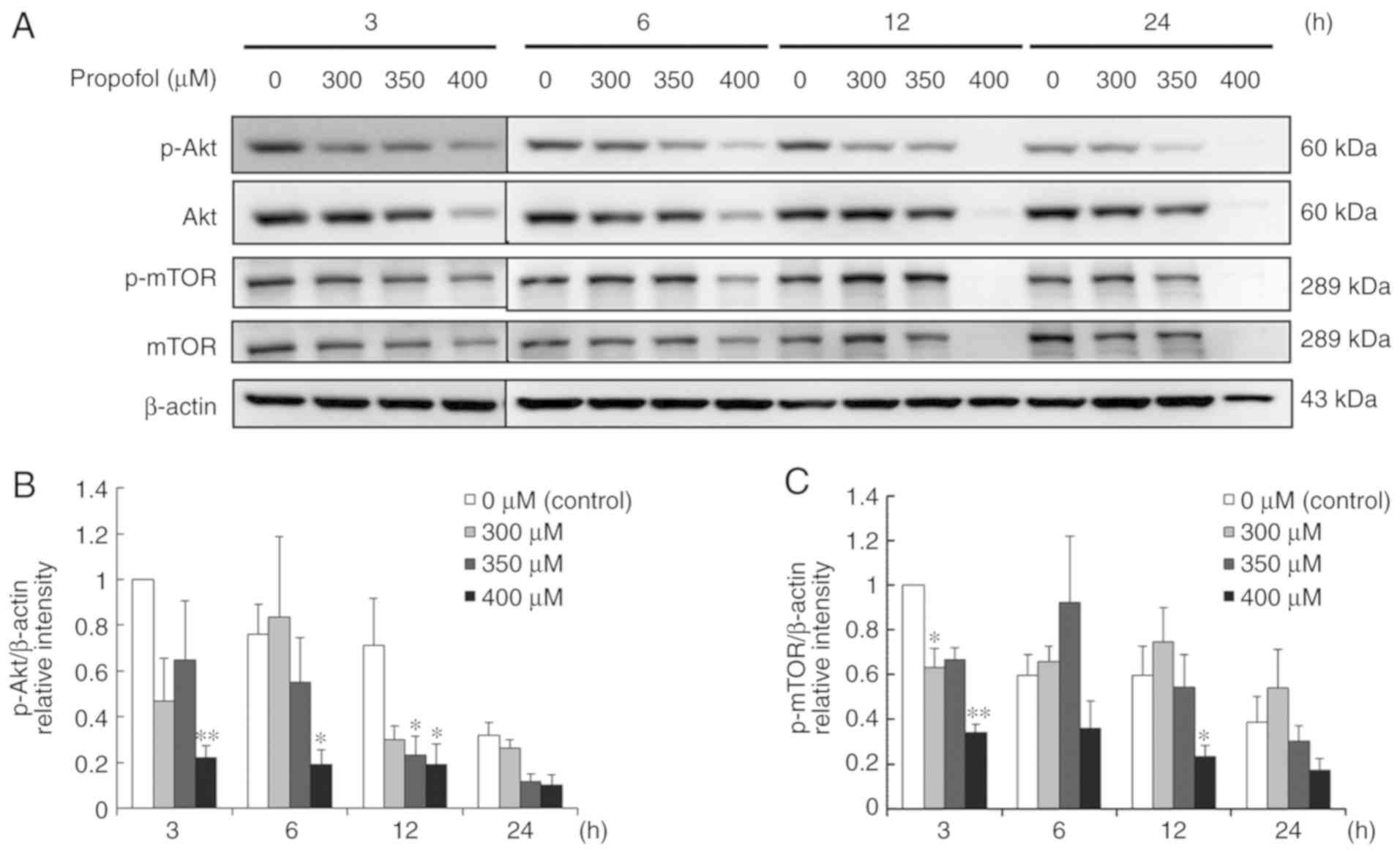
Propofol suppresses the Akt pathway to
induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells
Studies demonstrated that Akt pathway is a
pro-survival pathway, which can inhibit apoptotic signal cascades
and activate pro-survival signal cascades (24,25).
To further determine whether propofol would induce apoptosis in
MA-10 cells through inhibiting the Akt pathway, the expression
levels of Akt, phospho-Akt, mTOR and phospho-mTOR were investigated
with a western blot assay. The results demonstrated that 400 µM
propofol for 3–12 h significantly reduced the expression levels of
phospho-Akt and phospho-mTOR,, but not at 6 h for phospho-mTOR, in
MA-10 cells (P<0.05; Fig. 7A-C).
A reduced concentration of propofol (350 µM) downregulated the
expression levels of phospho-Akt at 12 h, and 300 µM reduced the
expression of phospho-mTOR at 3 h (P<0.05; Fig. 7A-C). These results demonstrated that
propofol at different dosages and temporal durations significantly
inhibits the Akt pathway, implying that propofol decreases the Akt
pathway to induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells.
Discussion
Numerous studies regarding sedative drug effects
have focused on the clinical dosages and their side effects
(37,38), and a number of researches
demonstrated that propofol induces neurotoxicity (38,39). A
previous study indicated that sedative drugs, including propofol,
induce apoptosis in various cancer cells (8). Additionally, it has been demonstrated
that propofol has anticancer ability on numerous cancer types,
including pancreatic (5), lung
(6) and epithelial ovarian cancer
(8). Nevertheless, whether propofol
could serve as anticancer drug for Leydig tumor cases and the
involved mechanisms are not clear. Therefore, whether propofol
induces apoptosis in MA-10 cells and the mechanism was investigated
in the present study.
Intense transformations in cellular architecture are
essential characterizations in apoptosis, and the activation of
caspases regulates the weakening of the cell cytoskeleton,
triggering morphological changes, including membrane blebbing and
cell shrinkage (40). The present
results demonstrated that propofol induces membrane blebbing and
cell shrinkage, indicating that propofol influences the
cytoskeleton and morphological changes to induce apoptosis in MA-10
cells. In the present study, the effects of propofol in MA-10 cell
viability were investigated.
Propofol significantly increased MA-10 cell in the
sub-G1 phase, indicating that propofol causes DNA fragmentation and
induces MA-10 cell apoptosis. Notably, propofol did not induce
increased MA-10 cells in the G2/M phase. Previous studies
demonstrated that sub-G1 phase increase and/or G2/M phase arrest
could induce cell death through apoptosis (41,42).
Therefore, the present results advocated that propofol-induced
apoptosis is associated with cell cycle regulation, and the
detailed mechanisms require further investigation. Additionally,
the Annexin V and PI double staining assay also demonstrated that
propofol induces MA-10 cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner,
indicating that propofol induces cell apoptosis.
Apoptosis is primarily started by extrinsic and
intrinsic signals to activate caspase cascades (17). The present data demonstrated that
propofol activates extrinsic and intrinsic pathways to induce MA-10
cell apoptosis. Previous studies reported that propofol has the
same effects in murine hepatocellular carcinoma (9,43).
Thus, the present observations are in line with other studies.
Apoptotic pathways are controlled by numerous
pathways, and the MAPK pathways, including JNK, ERK1/2 and p38
MAPK, may respond to cellular stress regulating cell survival
and/or apoptosis (21). Studies
demonstrated that JNKs can be stimulated by numerous different
stimuli, including stress factors, growth factors and cytokines
(44,45). Additionally, studies indicated that
the JNK pathway results in a switch from apoptosis to autophagy to
survival in choriocarcinoma cells (46), and inhibit apoptosis in acute
myeloid leukemia cells (47).
However, it was reported that JNK triggers apoptosis by activating
c-Jun and mitochondria apoptotic pathways, which are induced by
irradiation, DNA damage and oxidative stress (48). Studies demonstrated that ERK may
induce apoptosis by mediating cell cycle arrest due to DNA damage
(49). Similar to the JNK pathway,
the role of p38 in apoptosis is diverse, which could inhibit
caspase-3 activity in neuronal cells (50), which may enhance the expression of
TNF-α, and then result in cell apoptosis (51). Numerous studies reported that
propofol inhibits MAPK pathways in different cells to inhibit
migration (9,52) or inflammation (53,54).
In the present data, propofol increased the expression levels of
phospho-JNK, phospho-ERK and phospho-p38 in MA-10 mouse Leydig
tumor cells, indicating that propofol induces MAPK pathways and as
a result apoptosis in MA-10 cells. Notably, propofol reduced the
total protein expression levels of JNK, ERK and p38, indicating
that propofol may rapidly stimulate phosphorylation of MAPKs and
result in MAPK instability, and then result in MAPK
degradation.
It has been demonstrated that Akt signaling is a
pro-survival pathway, which can inhibit apoptotic signal cascades
and activate pro-survival signals (24). It is known that activation of the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway is observed in the formation
of a number of cancer types, including breast, endometrial and
gastric cancer (55–57). In fact, the role of propofol in the
Akt pathway is diverse, which may inhibit Akt activity in
macrophages to induce cell apoptosis (58), while propofol may also keep rat
cardiomyocytes alive whilst avoiding doxorubicin-induced toxicity
through activation of the Akt pathway (59). The present data demonstrated that
propofol decreases the expression levels of phospho-Akt and
phospho-mTOR in MA-10 cells. Thus, propofol attenuates Akt activity
to induce apoptosis in MA-10 cells.
A previous study demonstrated that patients treated
with propofol would receive total doses ranging between 90–600 mg
with an initial bolus dose, depending on patient age and body
weight, followed by intermittent intravenous bolus infusion to
maintain the appropriate level of sedation (60). The dosages of propofol ranging from
90–600 mg are approximately equal to 500–3,000 µM. In the present
study, propofol doses ranging from 300–400 µM had a significant
inhibitory effect on cell viability and induced apoptosis in MA-10
cells, implying that a low dosage of propofol would have an
effective potency to exterminate tumor cells.
In conclusion, propofol induces cell apoptosis
through the stimulation of caspase and MAPK pathways, and the
inhibition of the Akt pathway in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor
cells.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Chi Mei-NCKU hospital
grant CMNCKU10705 (FCK and BMH) and Ministry of Science and
Technology MOST 105-2320-B-006-028 (BMH), Taiwan, Republic of
China.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
FCK and SCW contributed to conducting the
experiments and statistical analysis. ECS and MMC designed the
experiment and wrote the manuscript. KLW and KSC contributed to
statistical analysis and the writing of the manuscript. YCC and BMH
contributed to experimental designs, data interpretation, writing
of the manuscript, and ensuring the accuracy and the integrity of
whole work. All authors read and approved the final version of the
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Busettini C and Frolich MA: Effects of
mild to moderate sedation on saccadic eye movements. Behav Brain
Res. 272:286–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cassinello F, Prieto I, Del Olmo M, Rivas
S and Strichartz GR: Cancer surgery: How may anesthesia influence
outcome? J Clin Anesth. 27:262–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang P, Chen J, Mu LH, Du QH, Niu XH and
Zhang MY: Propofol inhibits invasion and enhances paclitaxel-
induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through the suppression
of the transcription factor slug. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
17:1722–1729. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ye Z, Jingzhong L, Yangbo L, Lei C and
Jiandong Y: Propofol inhibits proliferation and invasion of
osteosarcoma cells by regulation of microRNA-143 expression. Oncol
Res. 21:201–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Du QH, Xu YB, Zhang MY, Yun P and He CY:
Propofol induces apoptosis and increases gemcitabine sensitivity in
pancreatic cancer cells in vitro by inhibition of nuclear
factor-kappaB activity. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5485–5492. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cui WY, Liu Y, Zhu YQ, Song T and Wang QS:
Propofol induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and apoptosis in
lung cancer cell H460. Tumour Biol. 35:5213–5217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xing SG, Zhang KJ, Qu JH, Ren YD and Luan
Q: Propofol induces apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells
via ERK1/2-dependent upregulation of PUMA. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 22:4341–4349. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su Z, Hou XK and Wen QP: Propofol induces
apoptosis of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by upregulation of
microRNA let-7i expression. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 35:688–691.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu SQ, Zhang JL, Li ZW, Hu ZH, Liu Z and
Li Y: Propofol inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and
promotes apoptosis through down-regulating miR-374a in
hepatocarcinoma cell lines. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:2099–2110.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu FX and Guan KL: The Hippo pathway:
Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 27:355–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuwabara M, Asanuma T, Niwa K and Inanami
O: Regulation of cell survival and death signals induced by
oxidative stress. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 43:51–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Classification of cell death:
Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2009.
Cell Death Differ. 16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Long JS and Ryan KM: New frontiers in
promoting tumour cell death: Targeting apoptosis, necroptosis and
autophagy. Oncogene. 31:5045–5060. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oliveira JB and Gupta S: Disorders of
apoptosis: Mechanisms for autoimmunity in primary immunodeficiency
diseases. J Clin Immunol. 28 (Suppl 1):S20–S28. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lewis-Wambi JS and Jordan VC: Estrogen
regulation of apoptosis: How can one hormone stimulate and inhibit?
Breast Cancer Res. 11:2062009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cossarizza A, Baccarani-Contri M,
Kalashnikova G and Franceschi C: A new method for the
cytofluorimetric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using
the J-aggregate forming lipophilic cation
5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolcarbocyanine
iodide (JC-1). Biochemical and biophysical research communications
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 197:40–45. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang
DG and Pae HO: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive
oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal
Transduct. 2011:7926392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rauch N, Rukhlenko OS, Kolch W and
Kholodenko BN: MAPK kinase signalling dynamics regulate cell fate
decisions and drug resistance. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 41:151–158.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Markman B, Dienstmann R and Tabernero J:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway-beyond rapalogs. Oncotarget.
1:530–543. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hein AL, Ouellette MM and Yan Y:
Radiation-induced signaling pathways that promote cancer cell
survival (review). Int J Oncol. 45:1813–1819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou C, Zhao XM, Li XF, Wang C, Zhang XT,
Liu XZ, Ding XF, Xiang SL and Zhang J: Curcumin inhibits
AP-2γ-induced apoptosis in the human malignant testicular germ
cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:1192–1200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pang S, Zhang L, Shi Y and Liu Y:
Unclassified mixed germ cell-sex cord-stromal tumor with multiple
malignant cellular elements in a young woman: A case report and
review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5259–5266.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Olivier P, Simoneau-Roy J, Francoeur D,
Sartelet H, Parma J, Vassart G and Van Vliet G: Leydig cell tumors
in children: Contrasting clinical, hormonal, anatomical, and
molecular characteristics in boys and girls. J Pediatr.
161:1147–1152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gheorghisan-Galateanu AA: Leydig cell
tumors of the testis: A case report. BMC Res Notes. 7:6562014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Green LM, Reade JL and Ware CF: Rapid
colorimetric assay for cell viability: Application to the
quantitation of cytotoxic and growth inhibitory lymphokines. J
Immunol Methods. 70:257–268. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
So EC, Chen YC, Wang SC, Wu CC, Huang MC,
Lai MS, Pan BS, Kang FC and Huang BM: Midazolam regulated caspase
pathway, endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and cell cycle to
induce apoptosis in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Onco Targets
Ther. 9:2519–2533. 2017.
|
|
32
|
Chang MM, Lai MS, Hong SY, Pan BS, Huang
H, Yang SH, Wu CC, Sunny Sun H, Chuang JI, Wang CY and Huang BM:
FGF9/FGFR2 increase cell proliferation by activating ERK1/2,
Rb/E2F1 and cell cycle pathways in mouse Leydig tumor cells. Cancer
Sci. 109:3503–3518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang FC, Wang SC, Chang MM, Pan BS, Wong
KL, Cheng KS, So EC and Huang BM: Midazolam activates caspase,
MAPKs and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways, and inhibits cell
cycle and Akt pathway, to induce apoptosis in TM3 mouse Leydig
progenitor cells. Onco Targets Ther. 11:1475–1490. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B
and Reutelingsperger CP: A novel assay to measure loss of plasma
membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent cells in culture.
Cytometry. 24:131–139. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Creagh EM and Martin SJ: Caspases:
Cellular demolition experts. Biochem Soc Trans. 29:696–702. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harris CE, Grounds RM, Murray AM, Lumley
J, Royston D and Morgan M: Propofol for long-term sedation in the
intensive care unit. A comparison with papaveretum and midazolam.
Anaesthesia. 45:366–372. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Radke J: Analgesia and sedation in
intensive care patients. Der Anaesthesist (German). 41:793–808.
1992.
|
|
39
|
Yu D, Jiang Y, Gao J, Liu B and Chen P:
Repeated exposure to propofol potentiates neuroapoptosis and
long-term behavioral deficits in neonatal rats. Neurosci Lett.
534:41–46. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taylor RC, Cullen SP and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis: Controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Paul-Samojedny M, Suchanek R, Borkowska P,
Pudelko A, Owczarek A, Kowalczyk M, Machnik G, Fila-Danilow A and
Kowalski J: Knockdown of AKT3 (PKBgamma) and PI3KCA suppresses cell
viability and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of
glioblastoma multiforme T98G cells. Biomed Res Int.
2014:7681812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang C, Chen Z, Zhou X, Xu W, Wang G,
Tang X, Luo L, Tu J, Zhu Y, Hu W, et al: Cantharidin induces G/M
phase arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 and
BGC-823 cells. Oncol Lett. 8:2721–2726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Khan AA, Jabeen M, Khan AA and Owais M:
Anticancer efficacy of a novel propofol-linoleic acid-loaded
escheriosomal formulation against murine hepatocellular carcinoma.
Nanomedicine (London). 8:1281–1294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A and Karin
M: Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein
kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain.
Genes Dev. 7:2135–2148. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cano E, Hazzalin CA and Mahadevan LC:
Anisomycin-activated protein kinases p45 and p55 but not
mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK-1 and −2 are implicated in
the induction of c-fos and c-jun. Mol Cell Biol. 14:7352–7362.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shen Y, Yang J, Zhao J, Xiao C, Xu C and
Xiang Y: The switch from ER stress-induced apoptosis to autophagy
via ROS-mediated JNK/p62 signals: A survival mechanism in
methotrexate-resistant choriocarcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res.
334:207–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lin X, Fang Q, Chen S, Zhe N, Chai Q, Yu
M, Zhang Y, Wang Z and Wang J: Heme oxygenase-1 suppresses the
apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells via the JNK/c-JUN
signaling pathway. Leuk Res. 39:544–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dhanasekaran DN and Reddy EP: JNK
signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:6245–6251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L,
Mazza B, Kidd VJ, Mak TW and Ingram AJ: ERK activation mediates
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of
p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee JM, Lee JM, Kim KR, Im H and Kim YH:
Zinc preconditioning protects against neuronal apoptosis through
the mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated induction of heat
shock protein 70. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:220–226. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang B, Wu T, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Wang J,
Yang B, Zhao Y, Rao Z and Gao J: p38MAPK activation mediates tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Mol Med
Rep. 11:3101–3107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu KC, Yang ST, Hsia TC, Yang JS, Chiou
SM, Lu CC, Wu RS and Chung JG: Suppression of cell invasion and
migration by propofol are involved in down-regulating matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and p38 MAPK signaling in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. Anticancer Res. 32:4833–4842.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li D, Wang C, Li N and Zhang L: Propofol
selectively inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activity by suppressing
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in human EA.hy926
endothelial cells during intermittent hypoxia/reoxygenation. Mol
Med Rep. 9:1460–1466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hsu CP, Lin CH and Kuo CY:
Endothelial-cell inflammation and damage by reactive oxygen species
are prevented by propofol via ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux.
Int J Med Sci. 15:978–985. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen L, Yang G and Dong H: Everolimus
reverses palbociclib resistance in ER+ human breast cancer cells by
inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase(PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target
of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:77–86. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Barra F, Evangelisti G, Ferro Desideri L,
Di Domenico S, Ferraioli D, Vellone VG, De Cian F and Ferrero S:
Investigational PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in development for
endometrial cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 28:131–142. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hu M, Zhu SX, Xiong SW, Xue XX and Zhou
XD: MicroRNAs and the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway in gastric cancer
(Review). Oncol Rep. 43:1439–1454. 2019.
|
|
58
|
Hsing CH, Chen YH, Chen CL, Huang WC, Lin
MC, Tseng PC, Wang CY, Tsai CC, Choi PC and Lin CF: Anesthetic
propofol causes glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-regulated
lysosomal/mitochondrial apoptosis in macrophages. Anesthesiology.
116:868–881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sun X, Gu J, Chi M, Li M, Lei S and Wang
G: Activation of PI3K-Akt through taurine is critical for propofol
to protect rat cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced toxicity.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 92:155–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Padmanabhan A, Frangopoulos C and Shaffer
LET: Patient satisfaction with propofol for outpatient colonoscopy:
A prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Dis Colon Rectum.
60:1102–1108. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|