Introduction
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common type of
cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer-associated mortality
among women worldwide (1). In
addition, cervical cancer is the second leading cause of
cancer-associated mortality in women aged 20–39 years in the USA,
and it was estimated that there may be 13,800 new cases and 4,290
mortalities in 2020 (2). Radical
hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy is the standard
recommended surgical therapy for patients with early-stage cervical
cancer (3). However, this method also
increases the number of circulating tumor cells, and promotes
cancer progression and metastasis (4). In addition to surgical therapy,
molecular-targeted strategies have recently received attention in
the field of cancer treatment. However, molecular-targeted
strategies have not shown significant benefit in the majority of
patients with cervical cancer, as these precision drugs are
available for only 3–13% of patients (5,6). Thus,
alternative treatments for patients with cervical cancer are
needed.
Molecular hydrogen (H2) biology and
H2 therapy are novel and rapidly developing areas of
research (7–9). H2 has been shown to exert
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (10), and to protect neurons from oxidative
stress injury during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (11). Importantly, since the tumorigenesis
and progression of cancer are closely associated with the levels of
peroxidation and inflammation, H2 may play a role in
tumor regulation in endometrial (12), lung (13) and breast cancer (14). A prospective follow-up study of 82
patients with stage III and IV cancer, including lung, pancreatic
and gynecological cancer (including cervical cancer), revealed
significant improvements in fatigue, insomnia, anorexia, pain and
physical status after 4 weeks of H2 inhalation (15). However, the potential antitumor
mechanism of H2 intervention in cervical cancer is
currently unknown.
High-throughput RNA sequencing is a powerful method
for revealing transcriptional and non-transcriptional signatures in
cells and animals (16). It maximizes
the identification of the regulatory effects of different
treatments at the genetic level. The human cervical adenocarcinoma
HeLa cell line expresses over 10,000 proteins and is considered the
most commonly analyzed cells in cervical cancer research (17,18).
Previous studies reported that HeLa cells can be used in
vitro (19) and in in vivo
xenotransplant models (20) to
simulate the process of cervical cancer. In addition, HeLa cells
have been used to investigate the regulatory role of H2
in Wnt/β-catenin signaling (21). But
the tumor inhibitory effect of H2 and its related
mechanism in HeLa cells remain unknown. Thus, RNA sequencing of
control and H2-treated HeLa cells may be helpful for
identifying the potential antitumor mechanism of H2 in
cervical cancer.
The present study demonstrated that treatment with
66.7% H2 significantly elevated the apoptosis rate, and
reduced the cell proliferation and oxidative stress of HeLa cells
in vitro. Furthermore, tumor growth and cell death were also
observed in H2-treated HeLa tumors. Decreased hypoxia
inducible factor (HIF)1A and RELA proto-oncogene, NF-κB
subunit (RelA) expression levels were detected in the
H2 group through RNA sequencing. The expression of
HIF1A and RelA and their encoded protein expression
were further confirmed by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR), western blotting, and immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Materials and methods
Cell line and cell experiments
The human cervical cancer HeLa cell line and
nontumor HaCaT keratinocytes were purchased from the American Type
Culture Collection. Cells were cultured in DMEM (Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with 10% filtered FBS (Gibco;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at 37°C in a humidified 5%
CO2/95% air environment. For H2 intervention,
H2 gas was produced by a H2-O2
nebulizer (AMS-H-01; Asclepius), and HeLa and HaCaT cells were
incubated at 37°C in a mixture of 33.3% H2/33.3%
N2/33.4% O2 or 66.7% H2/33.3%
O2 environment for 1 h every 12 h. Cisplatin was
obtained from APeXBIO Technology LLC (cat. no. A8321). Our
preliminary results suggested that the IC50 of cisplatin
treatment of HeLa cells for 24 h is 12 µg/ml, which is consistent
with previously reported results (22). Cisplatin was used in the present study
at a concentration of 5 µg/ml. After 7 days of H2
treatment, cells were evaluated for their viability, apoptosis,
reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide
dismutase (SOD) levels. In addition, RNA was isolated for RNA
sequencing. Cells cultured under a normal environment were used as
control.
Animal experiments
A total of 22 female athymic BALB/c nude mice (age,
5–6 weeks old; weight, 20–25 g) were obtained from Jackson
Laboratory and housed in a pathogen-free facility with temperature
of 18–29°C, relative humidity of 40–70%, 12-h light/dark cycle, and
free access to food and water. HeLa cells (1×107 cells
in 200 µl PBS) were subcutaneously injected into the left armpit of
nude mice. Tumor-bearing mice were monitored by body condition
scoring index and clinical evaluations every day, and were
euthanized by administration of an overdose of pentobarbital sodium
(100 mg/kg) if they exhibited either a >10% decrease in body
weight compared with pre-injection body weight or if their activity
level declined due to tumor burden. In total, 4 tumor-bearing mice
were euthanized who reached the aforementioned humane endpoints. At
7 days post-injection, the remaining tumor-bearing mice were
randomly divided into two groups: The group housed under normal
conditions (control group, n=9) and the H2 intervention
group (H2 group, n=9). To establish a H2
intervention model, mice were kept in a mixture of 66.7%
H2/33.3% O2 environment for 30 min per day
(11), and after 27 days, the mice
were sacrificed with 100 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium as evidenced by
the disappearance of breathing and heartbeat to collect the tumors.
Tumor volumes were estimated as the length × width2 ×
0.5 every 3 days starting from 7 days after cell injection. The
maximum tumor volume observed in the present study was 1,582
mm3. All animal experiments were performed in accordance
with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and
Use of Laboratory Animals, and were approved by the Ethics
Committee for Animal Studies of Naval Medical University (approval
no. 202027).
Cellular apoptosis and proliferation
assay
TUNEL assay by immunofluorescence staining was
performed to determine the cellular apoptosis rate. Briefly,
2×104 HeLa or HaCaT cells were seeded into 48-well
plates and, after H2 intervention, the cells were fixed
with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature. After
permeabilization with 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA)
for 10 min at room temperature, the cells were blocked with 5% BSA
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 10 min at room temperature.
Furthermore, the In situ Cell Death Detection kit (cat. no.
11684809910; Roche Diagnostics) was used according to the
manufacturer's protocol, and cells were then counterstained with
DAPI (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for nuclear staining and observed
through a fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corporation). The
percentage of TUNEL-positive cells was calculated as the ratio of
the number of TUNEL-positive nuclei/total number of nuclei, which
were counted in three different random fields of view. Cell
proliferation was evaluated using a Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assay
(cat. no. C0037; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) following the
manufacturer's instructions. The absorbance at 450 nm was detected
using a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc.).
Cellular oxidative stress
detection
The level of ROS was determined using the Cellular
ROS Assay kit (cat. no. ab113851; Abcam) according to the
manufacturer's instructions. The ROS level was calculated as ROS
positive area/total area × 100%. In addition, MDA and SOD levels
were detected using the commercially available test kits Lipid
Peroxidation (MDA) Assay kit (cat. no. ab118970; Abcam) and SOD
Colorimetric Activity kit (cat. no. EIASODC; Invitrogen; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's
protocol.
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)
staining and immuno-histochemistry (IHC)
HeLa tumors fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde were
dehydrated and then embedded in paraffin. Next, samples were
sectioned at 5-µm thickness and stained with hematoxylin and eosin
(H&E). Tumor histopathological changes were captured with an
optical microscope (Olympus Corporation).
For IHC, the sections were deparaffinized, hydrated
at 70°C in xylene and microwaved at full power for 20 min for
antigen retrieval using sodium citrate (pH 6.0). In addition, 5%
BSA was used as the blocking reagent overnight at 4°C. Next, the
slides were incubated with anti-HIF-1α primary antibody (1:100;
cat. no. ab51608; Abcam), anti-NF-κB p65 primary antibody (1:200;
cat. no. ab16502; Abcam) or anti-Ki67 primary antibody (1:200; cat.
no. ab15580; Abcam) overnight at 4°C. The next day, the slides were
washed three times with PBS and incubated with a goat anti-rabbit
polyclonal HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (1:50; cat. no. 32260;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) for 2 h at room temperature. After
diaminobenzidine staining (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.), images were captured with an optical microscope and analyzed
using ImageJ 1.53 software (NIH). TUNEL assay by IHC was performed
with DeadEnd™ Colorimetric TUNEL system (cat. no. G7360; Promega
Corporation) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
RNA sequencing
cDNA libraries were constructed in a strand-specific
manner from 4 µg DNase-treated RNA using TruSeq Stranded Total RNA
Library Prep kit (cat. no. 20020597; Illumina, Inc.). Total RNA,
including mRNA and small RNA (circRNA, lncRNA, and miRNA) was then
fragmented, subjected to two rounds of cDNA synthesis, and adapters
were then ligated to double-strand cDNA. All libraries were
sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq 6000 and HiSeq X Ten platforms
(Illumina, Inc.), generating 100-bp paired-end reads. High-quality
reads were obtained by trimming adapter sequences, invalid and
low-quality reads from the raw reads (quality control). The clean
reads were then mapped to the human genome by HISAT2 software (v
2.1.0) using default parameters. Next, transcript assemblies were
constructed using StringTie software (v 1.3.6; The Center for
Computational Biology at Johns Hopkins University) to merge
transcripts, and DESeq2 software (v 2.11.40.2; Bioconductor, Inc.)
was used to compute differential expression.
Bioinformatic analyses
Multivariate analysis and principal component
analysis were performed by ClustVis online tool (https://github.com/fw1121/ClustVis) (23). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis
was carried out using DAVID bioinformatics tool (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/tools.jsp) (24). A hypergeometric test (Fisher's exact
test) was used to calculate the statistical significance of gene
overrepresentation, followed by a Bonferroni correction for
multiple comparisons to estimate the proportion of enriched genes
that may occur by chance for the given set of genes. Heatmaps and
volcano plots were generated using TBtools (v 1.055; programmed by
C.J. Chen). Fold-change (FC) was calculated as the mean value of
RNA reads in H2 groups/mean value in controls.
Western blotting
Protein samples from HeLa cells in the control and
H2 treatment groups were lysed with Tissue or Cell Total
Protein Extraction kit (cat. no. C510003; Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd.)
following the manufacturer's protocol. Protein concentration was
determined using a BCA Protein Assay kit (cat. no. P0010; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology). Equal quantities of protein (20 µg per
lane) from the lysate of control or H2 treatment groups
were subjected to SDS-PAGE. After transferring to a PVDF membrane
and blocking with 5% skimmed milk for 2 h at room temperature, the
membrane was incubated overnight at 4°C with specific primary
antibodies against HIF-1α (cat. no. ab51608), GAPDH (cat. no.
ab8245), NF-κB (cat. no. ab16502) or lamin B1 (cat. no. ab16048)
(all from Abcam) at a 1:1,000 dilution. After washing three times,
the membrane was incubated with HRP-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (H
+ L) or HRP-labeled goat anti-nouse IgG (H + L) secondary antibody
(1:2,000 both; cat. nos. A0208 and A0216, respectively; both from
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) for 2 h at room temperature,
and then developed with an ECL solution (cat. no. P0018; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology). For semi-quantitative analysis, the
bands were semi-quantified using ImageJ software (v 1.53; National
Institutes of Health, USA), and the data were normalized relative
to the cytoplasmic control GAPDH or the nuclear control lamin B1 as
the integral optical density ratio.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from tumors or cultured HeLa
cells with TRIzol® (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.), and its quality and quantity were assessed using
NanoDrop2000c (NanoDrop Technologies; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). RNA was then reverse transcribed with random hexamers (cat.
no. N8080127; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and
SuperScript II kit (cat. no. 18064014; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.). qPCR was performed with specific primers and
SYBR-Green PCR Master Mix kit (cat. no. 4368702; Applied
Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the
manufacturer's protocol. An 8-µl (final volume) reaction system was
established, which contained 300 nM primers. The thermocycling
conditions were as follows: Initial denaturation start cycle at
95°C for 3 min, followed by 32 cycles at 95°C for 10 sec and then
59°C for 30 sec. The expression levels of HIF1A and
RelA were calculated by the 2−ΔΔCq method
(25), normalized to that of GAPDH
and converted to FC values. The following pairs of primers were
used: HIF1A forward, 5′-GCACAGTTTGACTTGACTGGAC-3′ and
reverse, 5′-TTCTTGGAGCCTGTTCTGTGG-3′; RelA forward,
5′-ACGAGCAGATGGTCAAGGAG-3′ and reverse, 5′-CTTCCATGGTCAGTGCCTTT-3′;
and GAPDH forward, 5′-GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG-3′.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of
mean. Differences between two groups were compared using unpaired
Student's t-test, while multiple comparisons were performed with
one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. In addition,
multiple comparisons in two independent variables were performed
with two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v 23.0 (IBM Corp.).
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
H2 intervention reduces
HeLa cell proliferation, and promotes cellular apoptosis and
oxidative stress in a selective and dose-dependent manner
Firstly, the effects of H2 treatment in
HeLa cells were explored in vitro. As shown in Fig. 1A and B, the ratio of TUNEL-positive
cells among all H2-treated Hela cells was significantly
increased compared with that of the controls (P<0.01). Treatment
with 66.7% H2 markedly increased the apoptosis rate.
Importantly, the increase in HeLa cell apoptotic rate induced by 5
µg/ml cisplatin treatment (IC50=12 µg/ml) was consistent
with the effect of 66.7% H2 treatment. Notably, no
significant differences in apoptosis rate were observed in HaCaT
cells treated with or without H2 gas. The CCK-8 assay
revealed that cell proliferation was reduced after 33.3%
H2 treatment progressively, and 66.7% H2
further decreased the proliferation of HeLa cells over time but not
of HaCaT cells (Fig. 1C). In
addition, the effect of time was significant associated with the
cell proliferation in both Hela cells and HaCaT cells. These
results suggest that H2 has a specific
concentration-dependent inhibitory effect on HeLa cells rather than
on non-tumor HaCaT cells. Thus, H2 at a concentration of
66.7% was then used for the further experiments.
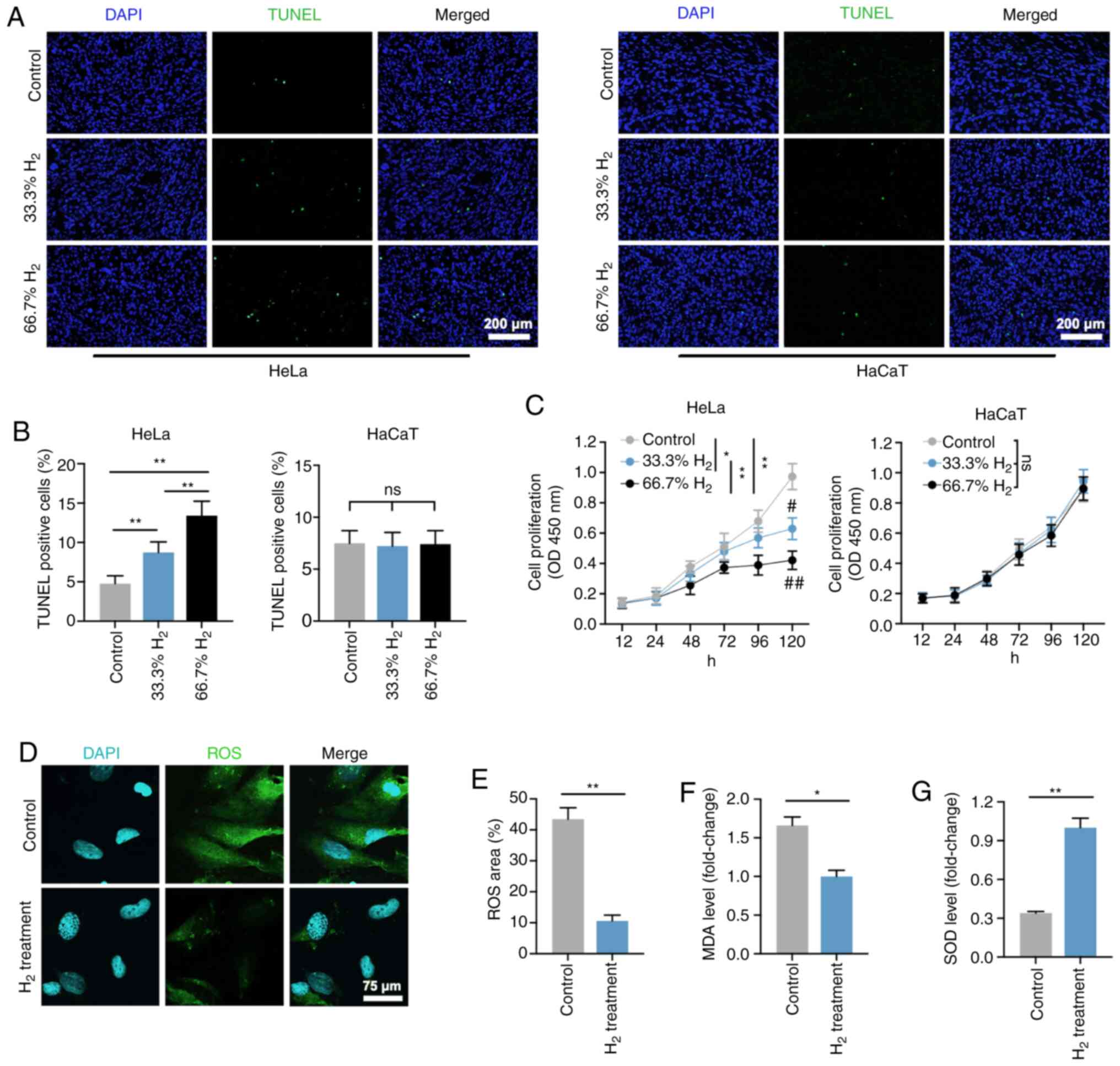 | Figure 1.Decreased cell proliferation, and
increased cell death and oxidative stress level in
H2-treated HeLa cervical cancer cells. (A) TUNEL
staining of HeLa and HaCaT cells in the control, 33% H2
and 66.7% H2 groups. Furthermore, 5 µg/ml cisplatin
treatment was used as a positive control (scale bar, 200 µm). (B)
Statistical results of TUNEL-positive HeLa and HaCaT cells in the
control, 33% H2 and 66.7% H2 groups (n=4 per
group). **P<0.01, ns indicates no significant difference. (C)
Cell proliferation curves of the control, 33% H2 and
66.7% H2 groups in HeLa and HaCaT cells during different
time periods (n=3 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. indicated
group, and #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs.
control group at day 5, ns indicates no significant difference. (D)
Fluorescent staining of ROS in control and 66.7%
H2-treated HeLa cells (scale bar, 75 µm). (E)
Statistical results of ROS area (%) in the control and 66.7%
H2 groups (n=4 per group). **P<0.01. Statistical
results of (F) malondialdehyde (MDA) and (G) superoxide dismutase
(SOD) levels in the control and 66.7% H2 treatment
groups (n=5 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01. H2,
hydrogen; ROS, reactive oxygen species. |
ROS are generated by ageing mitochondria due to
overproduction of free radicals and reduced antioxidant defenses
(26,27). The present study demonstrated that the
ROS level in the H2-treated HeLa cells was markedly
reduced compared with that of the control group (P<0.01;
Fig. 1D and E), which is consistent
with the previously reported anti-oxidative stress activity of
H2 gas (10). In addition,
the level of MDA, an indicator of lipid peroxidation, was also
decreased in HeLa cells treated with H2 (Fig. 1F), whereas an increased level in SOD,
an important representative of antioxidant enzymes, was observed in
the H2 group compared with that of the controls
(P<0.01; Fig. 1G). These results
suggested that H2 intervention induced HeLa cell
apoptosis, inhibited cell proliferation and reduced the oxidative
stress level.
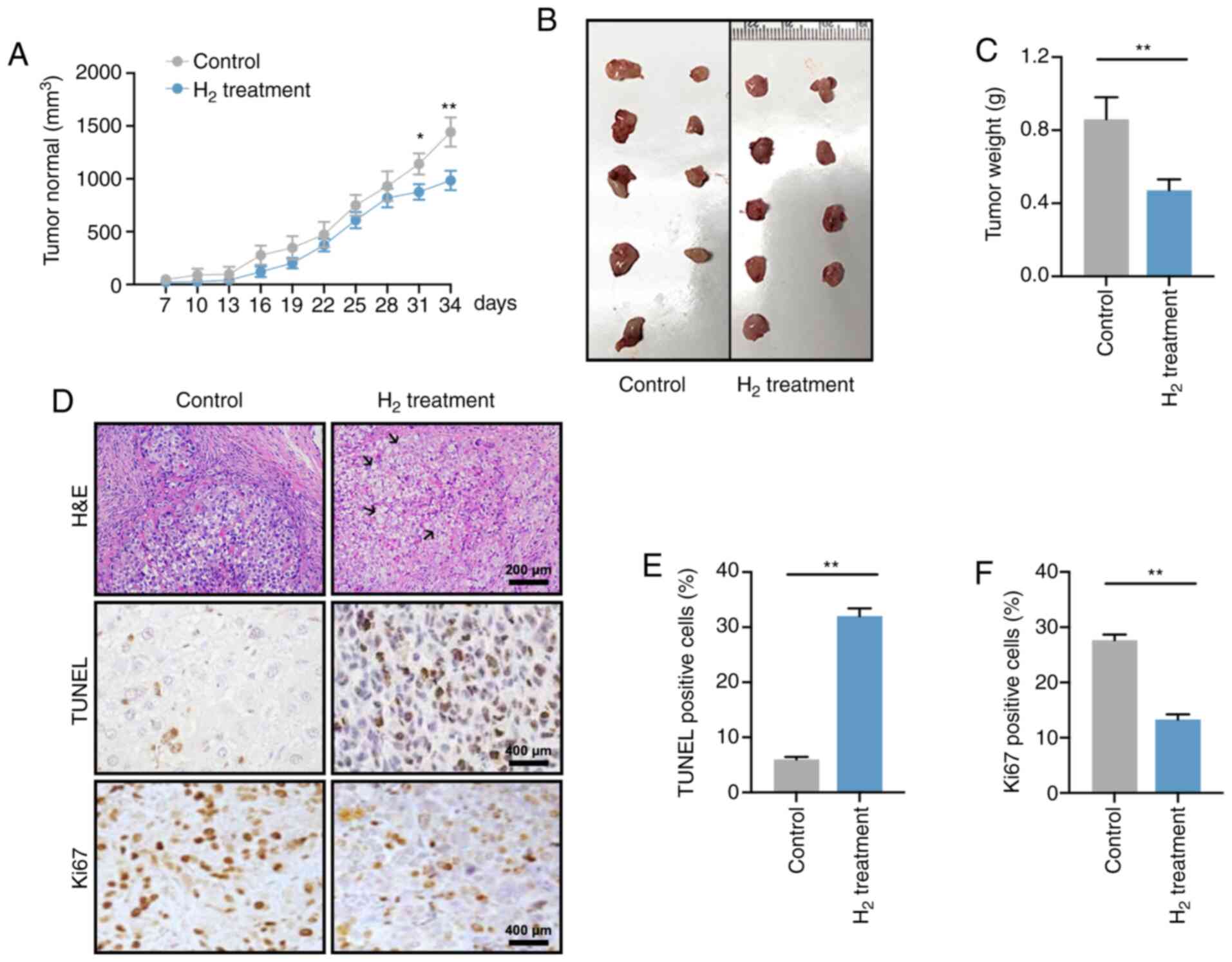
Reduced tumor growth is observed in a
H2-induced xenograft in vivo model
A total of 1×107 HeLa cells were
subcutaneously injected into the left armpit of nude mice, and the
tumor volume was recorded every 3 days starting 7 days
post-injection (Fig. 2A). At days 31
and 34, the tumor volume in mice under high H2
environment was significantly smaller than that that in the control
group (P<0.05 at day 31 and P<0.01 at day 34), which was
consistent with the change in tumor weight on day 34 (P<0.01;
Fig. 2B and C).
H&E staining revealed that the tumor cell death
rate in the H2 xenograft group was elevated, and was
accompanied by cell swelling as well as nuclear fragmentation and
disintegration (Fig. 2D; black
arrows). In addition, H2 treatment significantly
increased the apoptosis rate and reduced the cell proliferation of
HeLa cells (Fig. 2E and F). Taken
together, these data suggested that a high-H2
environment inhibited tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice.
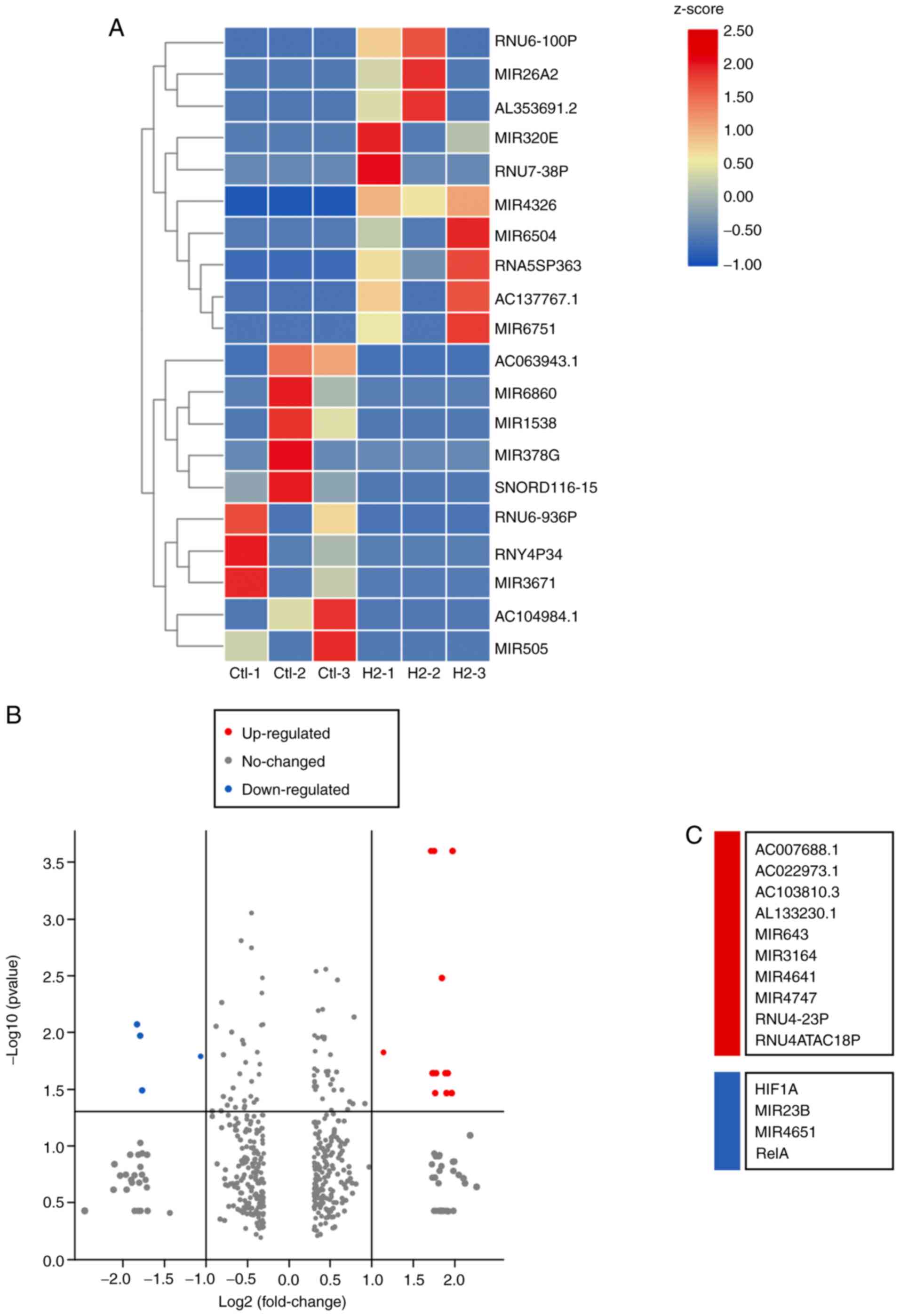
Bulk RNA sequencing of
H2-treated HeLa cells and control cells
To investigate the potential mechanism by which
H2 inhibits tumor cell growth, whole-genome sequencing
was performed (Fig. 3). As shown in
Fig. S1A-C, 11 upregulated and 16
downregulated circular RNAs (circRNAs) were determined in
H2-treated HeLa cells through the HiSeq4000 platform. In
addition, 2 long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were detected to be
upregulated, while 6 lncRNAs were downregulated in
H2-treated HeLa cells (Fig.
S2A-C). A total of 12 hsa-microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) were found
to be upregulated, and 2 miRNAs to be downregulated, including
hsa-miR-431-5p and hsa-miR-762 (Fig.
S3A-C). Importantly, mRNA sequencing revealed that 10 mRNAs
were upregulated in HeLa cells subjected to H2
treatment, and 4 mRNAs were downregulated, including HIF1A,
miR23B, miR4651 and RelA (Fig.
4A-C). miR23B and miR4651 are non-coding RNAs,
whereas HIF1A and RelA are the coding genes for
HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 subunit, respectively. These results suggested
that the mRNA levels of HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 subunit were reduced
in H2-treated HeLa cells compared with those of the
controls.
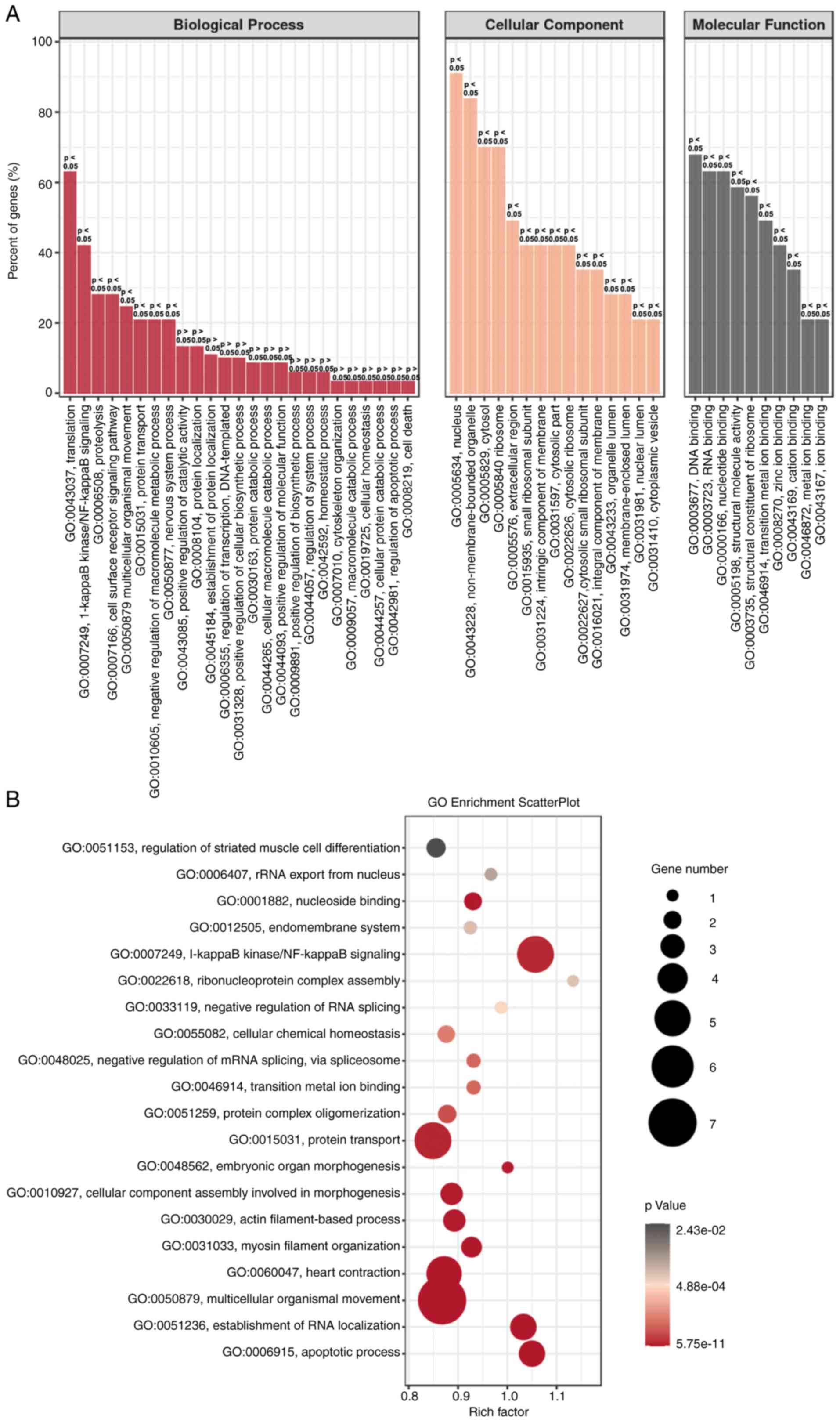
GO enrichment analysis for HeLa cells
with H2 intervention
To further confirm the aforementioned gene
regulation in H2-treated HeLa cells, GO enrichment
analysis was performed. As shown in Fig.
5A, the biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and
molecular function (MF) were analyzed. ‘Translation’ and ‘NF-κB
signaling’ were the two most dominant processes in BP, and gene
regulation mainly occurs in the nucleus and non-membrane-bounded
organelles. MF analysis revealed that ‘DNA and RNA binding’ were
dominant. GO enrichment scatter plot further indicated that the
processes of ‘NF-κB signaling’, ‘protein transport’ and
‘multicellular organismal movement’ are enriched in
H2-treated HeLa cells (Fig.
5B). These results suggested that downregulation of the NF-κB
signaling pathway may be an important target for H2
intervention in HeLa cells.
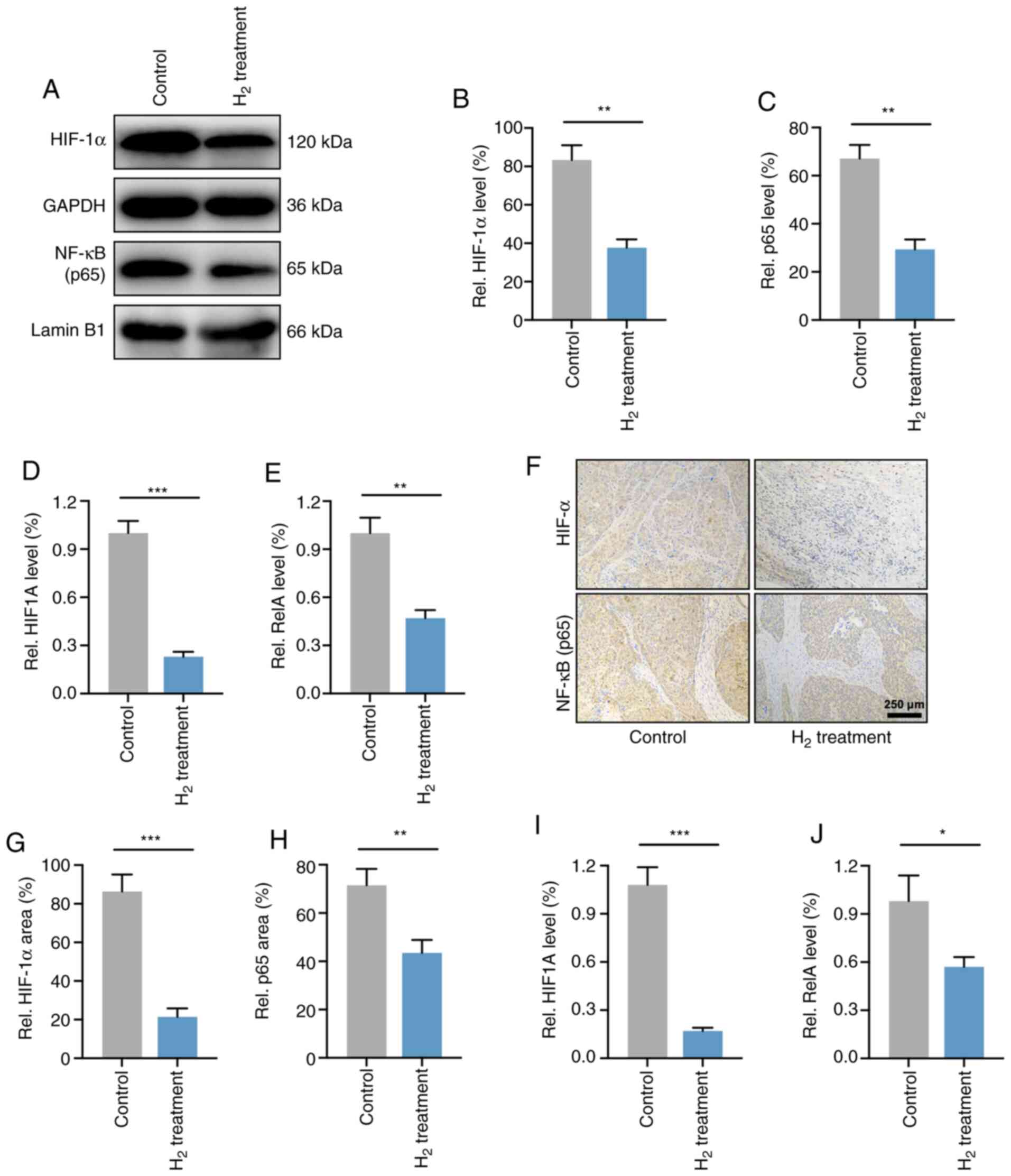
HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 expression levels
are downregulated in H2-treated HeLa cells in vivo and
in vitro
As the p65 subunit is a classic active type of the
NF-κB family (28), the present study
verified the expression levels of NF-κB p65 and HIF-1α in HeLa
cells. As expected, western blot analysis demonstrated that the
HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 protein levels were significantly reduced in
H2-treated HeLa cells compared with those in control
HeLa cells (Fig. 6A-C). RT-qPCR
analysis revealed that the mRNA expression levels of HIF-1α and
NF-κB p65 (HIF1A and RelA) were elevated in HeLa
cells (Fig. 6D and E).
The levels of HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 were then
determined in HeLa cell-derived tumors. As shown in Fig. 6F-H, IHC demonstrated that the
expression of HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 in H2-treated HeLa
tumors was significantly reduced compared with that of the
controls. Furthermore, the mRNA levels in vivo were also
investigated, and the results revealed a significant decrease in
HIF1A and RelA expression in H2-treated
tumors compared with that of control tumors (Fig. 6I and J). These results indicated that
the expression levels of HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 were downregulated
both in HeLa cells and in HeLa tumors.
Discussion
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common type of
cancer in women worldwide, and ~70% of cervical cancer cases are
caused by human papilloma virus (HPV)16 and 18 infections (29). HPVs are diverse at the level of
genotype and pathogenicity, and can be classified into mucosal or
cutaneous according to their epithelial tropism (30). The mucosal high-risk HPV16 and HPV18
are primarily associated with squamous intraepithelial lesions,
which may progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma such as
cervical cancer (31). The pathogenic
effects of HPV can be avoided by preventive measures, mainly
vaccination. Although the currently available immunization methods
have been shown to be effective in decreasing cervical cancer,
genital warts and anogenital dysplasia, the global vaccination
rates remain low, and more effective alternative medical treatments
are therefore needed (32).
The present study first determined the pro-apoptotic
and anti-proliferative effects of H2 treatment in HeLa
cells. A H2 concentration of 33.3% significantly
increased the cell apoptosis and reduced the cell proliferation of
HeLa cells but not those of non-tumor HaCaT cells. Furthermore, a
high concentration of H2 further inhibited HeLa cell
proliferation and promoted cell apoptosis. These data reveal that
H2 has a dose-dependent role on cervical cancer HeLa
cell suppression. Importantly, the increase in HeLa cell apoptotic
rate induced by 5 µg/ml cisplatin treatment (IC50=12
µg/ml) is similar to the effect of 66.7% H2 treatment,
suggesting that H2 therapy may be a novel therapy for
cervical cancer with less toxicity and efficacy comparable to
chemotherapy.
Unexpectedly, H2 intervention reduced the
oxidative stress levels, including decreased ROS and MDA
concentrations, and increased SOD levels, which appeared to have
the opposite effect on tumor cell suppression. The tumor inhibitory
effect of H2 was then verified in HeLa tumor-bearing
mice. The tumor volume at days 31 and 34 post-injection in
tumor-bearing mice with continuous H2 treatment was
significantly reduced compared with that of controls, and decreased
tumor weight and cell proliferation as well as increased tumor cell
apoptosis were also observed at day 34 post-injection. To explore
the specific mechanisms of H2 on HeLa cell suppression,
high-throughput RNA sequencing, including cirRNA, lncRNA, miRNA and
mRNA sequencing, was performed. In cervical cancer, as well as in
multiple other cancer types, short, non-coding single strands of
RNAs, including circRNA, lncRNA and miRNA, play a vital role, since
their deregulation has been widely reported (33–35). For
example, miRNA may modulate oncogenic viral gene expression, as
well as the gene expression of the host (36). Specifically, miRNA genes may be
located at the susceptible sites in the amplified or deleted
genome/regions in human tumors (37).
Furthermore, as miRNAs are associated with the regulation of cell
proliferation and apoptosis, changes in their expression may be
responsible for proliferative disease, including cancer (38). The present study revealed that 11
circRNAs, 2 lncRNAs and 12 miRNAs were upregulated, and 16
circRNAs, 6 lncRNAs and 2 miRNAs were downregulated in
H2-treated HeLa cells. These observations suggest that
non-coding RNAs may account for the tumor inhibitory roles of
H2 on HeLa cervical cancer cells, but the specific
mechanism needs to be further explored.
In addition, RNA sequencing demonstrated the changes
in expression of several genes closely associated with tumor
development, such as HIF1A and RelA, which encode
HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 subunit, respectively. GO analysis further
indicated that NF-κB signaling was involved in the inhibitory
mechanism of H2-treated HeLa cells. Declined expression
of HIF1A and RelA and their translated HIF-1α and
NF-κB p65 proteins was then confirmed by RT-qPCR, western blotting
and IHC both in vitro and in vivo. p65 subunit is a
classic active type of the NF-κB family (28). It has been reported that NF-κB p65 is
a molecular lynchpin that links chronic infection and inflammation
with elevated cancer risk (39).
NF-κB is persistently activated in multiple types of cancer and
exerts a variety of pro-tumorigenic functions. For example, NF-κB
activation in cancer cells usually leads to the elevation of
anti-apoptotic genes to provide a cell survival mechanism for
resisting the physiological stress that induces inflammation
(40). Furthermore, NF-κB stimulates
cytokines that regulate the immune response and inflammation,
including TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6 and IL-8, as well as adhesion
molecules, which result in the recruitment of leukocytes to
inflammatory sites (28,40). In addition, NF-κB signaling was shown
to modulate various other conserved cellular processes, including
cell proliferation (41,42) and apoptosis (43). H2 intervention in HeLa
cells and tumors was demonstrated to reduce both NF-κB p65 protein
and mRNA levels in the RNA-sequencing and molecular biology
experiments of the present study, suggesting a decrease in
inflammatory response and tumor growth.
In cancer, hypoxia is considered as a vital
characteristic of the tumor microenvironment that drives tumor
progression (44,45). Hypoxic adaptation is largely modulated
by a group of transcriptional regulators named hypoxia-inducible
factors (HIFs) (46). HIF is a
heterotrimeric complex consisting of an O2-regulated
α-subunit and an O2-independent β-subunit (also called
aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator) (47). There are three HIF-α proteins
recognized in humans: HIF-1α, −2α and −3α. Under normal
O2 conditions, HIF-α subunits are tightly modulated by a
series of enzymes called HIF prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs). PHD is a
non-heme Fe (II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase that
hydroxylates HIF-α subunits at specific prolyl residues. The
hydroxylated HIF-α subunits are identified by the von-Hippel Lindau
tumor-suppressor E3 ligase and degraded via the proteasome pathway
(46,47). Intratumoral hypoxia induces both HIF-1
and HIF-2 activation, and overexpression of HIF-1α is strongly
associated with elevated metastasis and mortality in numerous human
cancer types (45,48), including cervical cancer (49). Upregulated HIF-1α in these cancer
types results in a series of regulatory processes leading to tumor
progression, including migration, invasion, angiogenesis, glucose
metabolism and pH regulation (44,45,50,51).
The present study demonstrated that both
HIF1A (HIF-1α gene) and HIF-1α protein levels were reduced
in H2-treated HeLa cells and HeLa tumors, which is
important for elucidating the potential mechanisms of H2
gas on cervical cancer treatment. Notably, the reduced oxidative
stress observed in HeLa cells may contradict the antitumor effects
of H2. However, since ROS are essential in the
stabilization of HIF that maintains the transcription of genes
involved in tumor development (52),
this downward trend of oxidative stress may be considered as an
antitumor effect in general. Additionally, since HeLa cells are
infected by HPV18 and its mechanism is associated with the
regulation of oxidative stress (53),
it could be hypothesized that H2 intervention may also
regulate the HPV18 genome in HeLa cells, thereby exerting a
tumor-suppressor effect. Future research on this topic needs to be
conducted.
The present study also has several limitations. As
one of numerous cervical cancer cell lines, experiments solely on
HeLa cell cells cannot determine whether all types of cervical
cancer cells exhibit a consistent effect after H2
intervention, and therefore additional cell types need to be
further evaluated. Furthermore, the growth characteristics of
cervical cancer cells is affected in a subcutaneous tumor model in
the present study, therefore the effects of H2 treatment
are different from what would be seen in human cervical cancer. The
establishment of an in situ cervical cancer model in
follow-up experiments is therefore needed. In addition, the
specific mechanism of the inhibitory effect of H2 on
HIF-1α and NF-κB (such as the regulation of the transcriptional
levels of HIF1A and RelA) needs to be verified in
further research. Also, the lack of negative and positive controls
in this study may lead to a deviation in IHC results to a certain
extent.
In conclusion, the present study suggests a novel
H2-induced tumor suppression target towards HIF-1α and
NF-κB. Inhibition of HIF-1α and NF-κB reduces cervical cancer HeLa
cell proliferation and oxidative stress level, and decreases tumor
growth, which makes H2 therapy a potential target in the
treatment of cervical cancer.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the
National Military Health Care Project (2016CGGS03).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the
current study are available in the Sequence Read Archive repository
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/?term=PRJNA718006),
with accession number: PRJNA718006.
Authors' contributions
JC, XL, and ZJ conceived and designed the research.
JC, JG, JW, LL and GC performed the in vitro and in
vivo experiments. JD and ZW performed the RNA sequencing and
analyzed the data. JC, JG, and XL were responsible for data
analysis and writing of the manuscript. All the authors listed have
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
All animal experiments were performed in accordance
with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and
Use of Laboratory Animals, and were approved by the Ethics
Committee for Animal Studies of Naval Medical University (approval
number: 202027).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Landoni F, Maneo A, Colombo A, Placa F,
Milani R, Perego P, Favini G, Ferri L and Mangioni C: Randomised
study of radical surgery versus radiotherapy for stage Ib-IIa
cervical cancer. Lancet. 350:535–540. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neeman E and Ben-Eliyahu S: Surgery and
stress promote cancer metastasis: New outlooks on perioperative
mediating mechanisms and immune involvement. Brain Behav Immun. 30
(Suppl 1):S32–S40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hodson R: Precision medicine. Nature.
537:S492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tannock IF and Hickman JA: Limits to
personalized cancer medicine. N Engl J Med. 375:1289–1294. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sano M, Suzuki M, Homma K, Hayashida K,
Tamura T, Matsuoka T, Katsumata Y, Onuki S and Sasaki J: Promising
novel therapy with hydrogen gas for emergency and critical care
medicine. Acute Med Surg. 5:113–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ge L, Yang M, Yang NN, Yin XX and Song WG:
Molecular hydrogen: A preventive and therapeutic medical gas for
various diseases. Oncotarget. 8:102653–102673. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ohta S: Molecular hydrogen as a preventive
and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential
of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol Ther. 144:1–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tamura T, Suzuki M, Hayashida K, Kobayashi
Y, Yoshizawa J, Shibusawa T, Sano M, Hori S and Sasaki J: Hydrogen
gas inhalation alleviates oxidative stress in patients with
post-cardiac arrest syndrome. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 67:214–221.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Chao Y, Cheng P, Li N, Zheng H and
Yang Y: UPLC-QTOF/MS-based metabolomics reveals the protective
mechanism of hydrogen on mice with ischemic stroke. Neurochem Res.
44:1950–1963. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Liu PY, Bao W, Chen SJ, Wu FS and
Zhu PY: Hydrogen inhibits endometrial cancer growth via a
ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptotic pathway. BMC Cancer.
20:282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang D, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhao Y and Chen
G: Hydrogen gas inhibits lung cancer progression through targeting
SMC3. Biomed Pharmacother. 104:788–797. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harguindey S, Alfarouk K, Orozco JP,
Hardonniere K, Stanciu D, Fais S and Devesa J: A new and integral
approach to the etiopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer
based upon its hydrogen ion dynamics. Int J Mol Sci. 21:11102020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen JB, Kong XF, Lv YY, Qin SC, Sun XJ,
Mu F, Lu TY and Xu KC: ‘Real world survey’ of hydrogen-controlled
cancer: A follow-up report of 82 advanced cancer patients. Med Gas
Res. 9:115–121. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andrews KR, Good JM, Miller MR, Luikart G
and Hohenlohe PA: Harnessing the power of RADseq for ecological and
evolutionary genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 17:81–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Masters JR: HeLa cells 50 years on: The
good, the bad and the ugly. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:315–319. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagaraj N, Wisniewski JR, Geiger T, Cox J,
Kircher M, Kelso J, Pääbo S and Mann M: Deep proteome and
transcriptome mapping of a human cancer cell line. Mol Syst Biol.
7:5482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tavakolian S, Goudarzi H, Eslami G and
Faghihloo E: Transcriptional regulation of epithelial to
mesenchymal transition related genes by lipopolysaccharide in human
cervical cancer cell line HeLa. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
20:2455–2461. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johrens K, Lazzerini L, Barinoff J,
Sehouli J and Cichon G: Mesothelin as a target for cervical cancer
therapy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 299:211–216. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin Y, Ohkawara B, Ito M, Misawa N,
Miyamoto K, Takegami Y, Masuda A, Toyokuni S and Ohno K: Molecular
hydrogen suppresses activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Sci Rep.
6:319862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kamalipooya S, Abdolmaleki P, Salemi Z,
Javani Jouni F, Zafari J and Soleimani H: Simultaneous application
of cisplatin and static magnetic field enhances oxidative stress in
HeLa cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 53:783–790. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Metsalu T and Vilo J: ClustVis: A web tool
for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using principal
component analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:W566–W570.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2^(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Costa V and Moradas-Ferreira P: Oxidative
stress and signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae:
Insights into ageing, apoptosis and diseases. Mol Aspects Med.
22:217–246. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F and Karin M: NF-κB
and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev.
246:379–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Trottier H and Burchell AN: Epidemiology
of mucosal human papillomavirus infection and associated diseases.
Public Health Genomics. 12:291–307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McBride AA: Oncogenic human
papillomaviruses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
372:201602732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Viarisio D, Gissmann L and Tommasino M:
Human papillomaviruses and carcinogenesis: Well-established and
novel models. Curr Opin Virol. 26:56–62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
St Laurent J, Luckett R and Feldman S: HPV
vaccination and the effects on rates of HPV-related cancers. Curr
Probl Cancer. 42:493–506. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tornesello ML, Faraonio R, Buonaguro L,
Annunziata C, Starita N, Cerasuolo A, Pezzuto F, Tornesello AL and
Buonaguro FM: The role of microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and
circular RNAs in cervical cancer. Front Oncol. 10:1502020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Casarotto M, Fanetti G, Guerrieri R,
Palazzari E, Lupato V, Steffan A, Polesel J, Boscolo-Rizzo P and
Fratta E: Beyond microRNAs: Emerging role of other non-coding RNAs
in HPV-driven cancers. Cancers (Basel). 12:12462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wen X, Liu S, Sheng J and Cui M: Recent
advances in the contribution of noncoding RNAs to cisplatin
resistance in cervical cancer. PeerJ. 8:e92342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vojtechova Z and Tachezy R: The role of
miRNAs in virus-mediated oncogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:12172018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gaur A, Jewell DA, Liang Y, Ridzon D,
Moore JH, Chen C, Ambros VR and Israel MA: Characterization of
microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human
cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 67:2456–2468. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY,
Pestell RG and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB controls cell growth and
differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:5785–5799. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
La Rosa FA, Pierce JW and Sonenshein GE:
Differential regulation of the c-myc oncogene promoter by the
NF-kappa B rel family of transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol.
14:1039–1044. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Perkins ND: Achieving transcriptional
specificity with NF-kappa B. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 29:1433–1448.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vaupel P and Mayer A: Hypoxia in tumors:
Pathogenesis-related classification, characterization of hypoxia
subtypes, and associated biological and clinical implications. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 812:19–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou J, Schmid T, Schnitzer S and Brune B:
Tumor hypoxia and cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 237:10–21. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Semenza GL: Oxygen sensing,
hypoxia-inducible factors, and disease pathophysiology. Annu Rev
Pathol. 9:47–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wenger RH, Stiehl DP and Camenisch G:
Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci STKE.
2005:re122015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Seeber LM, Horree N, Vooijs MA, Heintz AP,
van der Wall E, Verheijen RH and van Diest PJ: The role of hypoxia
inducible factor-1alpha in gynecological cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 78:173–184. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Keith B, Johnson RS and Simon MC: HIF1α
and HIF2α: Sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and
progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Scholz CC and Taylor CT: Targeting the HIF
pathway in inflammation and immunity. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
13:646–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hervouet E, Cizkova A, Demont J,
Vojtiskova A, Pecina P, Franssen-van Hal NL, Keijer J, Simonnet H,
Ivanek R, Kmoch S, et al: HIF and reactive oxygen species regulate
oxidative phosphorylation in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 29:1528–1537.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hao Y, Yan Z, Zhang A, Hu S, Wang N, Luo
XG, Ma W, Zhang TC and He H: IL-6/STAT3 mediates the HPV18 E6/E7
stimulated upregulation of MALAT1 gene in cervical cancer HeLa
cells. Virus Res. 281:1979072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|