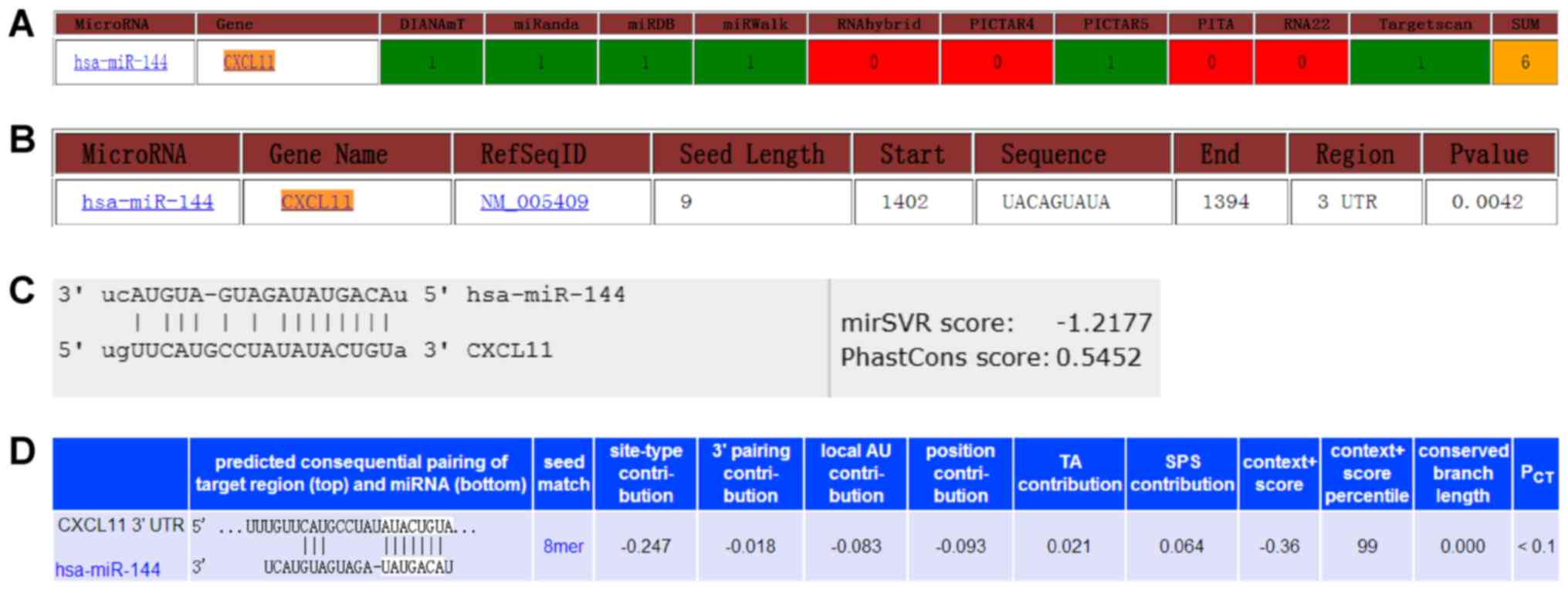
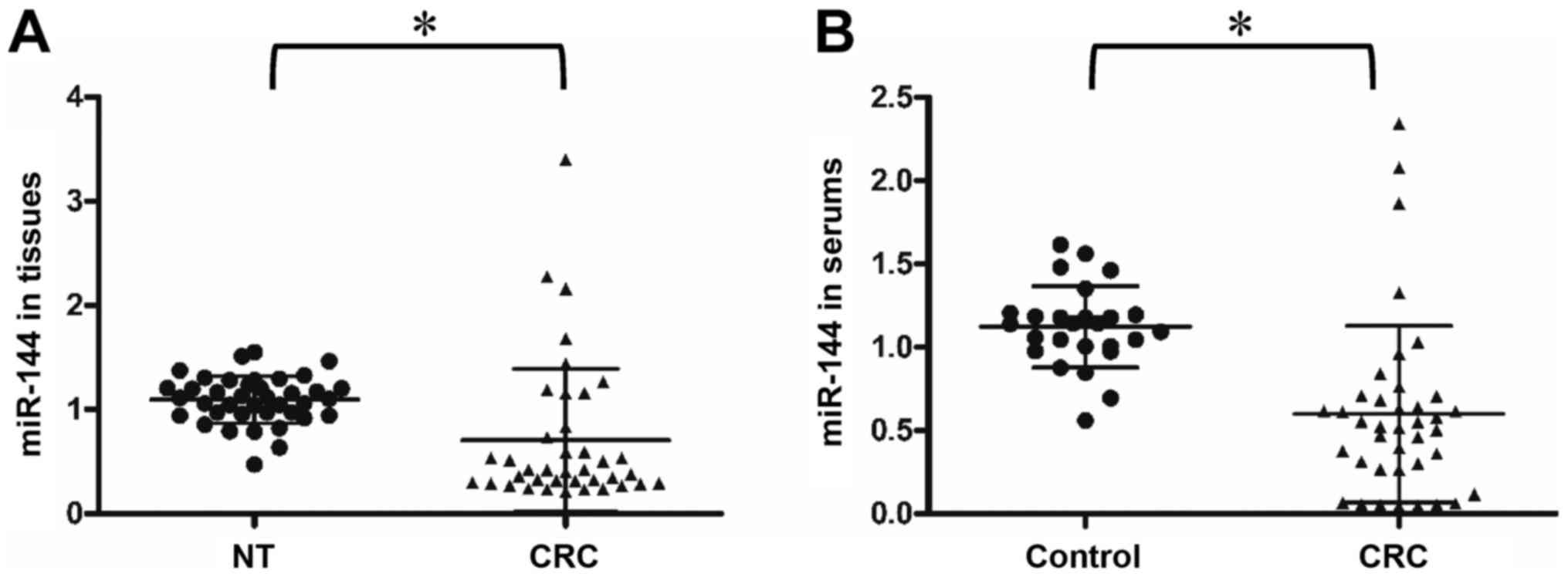
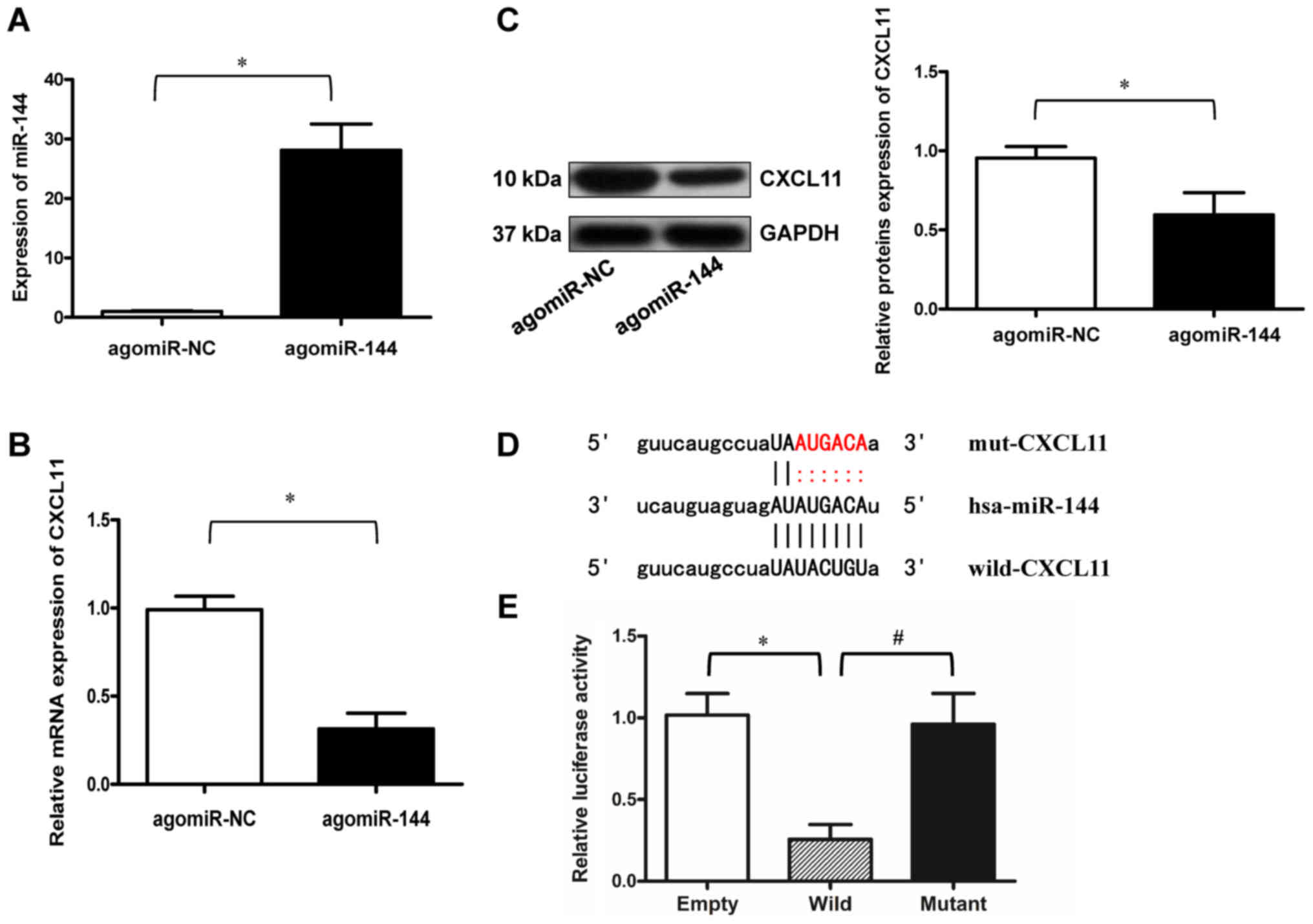
|
1
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu T, Li LF, Shen J, Zhang L and Cho CH:
Chronic inflammation and colorectal cancer: The role of vascular
endothelial growth factor. Curr Pharm Des. 21:2960–2967. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rupertus K, Sinistra J, Scheuer C, Nickels
RM, Schilling MK, Menger MD and Kollmar O: Interaction of the
chemokines I-TAC (CXCL11) and SDF-1 (CXCL12) in the regulation of
tumor angiogenesis of colorectal cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis.
31:447–459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kerr JS, Jacques RO, Cardaba Moyano C, Tse
T, Sexton D and Mueller A: Differential regulation of chemotaxis:
Role of Gβγ in chemokine receptor-induced cell migration. Cell
Signal. 25:729–735. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng YJ, Lai W, Wu H, Liu L, Xu HY, Wang J
and Chu ZH: Neuroendocrine-like cells-derived CXCL10 and CXCL11
induce the infiltration of tumor-associated macrophage leading to
the poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:27394–27407.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cole KE, Strick CA, Paradis TJ, Ogborne
KT, Loetscher M, Gladue RP, Lin W, Boyd JG, Moser B, Wood DE, et
al: Interferon-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant (I-TAC): A
novel non-ELR CXC chemokine with potent activity on activated T
cells through selective high affinity binding to CXCR3. J Exp Med.
187:2009–2021. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schneiderova M, Naccarati A, Pardini B,
Rosa F, Gaetano CD, Jiraskova K, Opattova A, Levy M, Veskrna K,
Veskrnova V, et al: MicroRNA-binding site polymorphisms in genes
involved in colorectal cancer etiopathogenesis and their impact on
disease prognosis. Mutagenesis. 32:533–542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Keller A, Leidinger P, Vogel B, Backes C,
El Sharawy A, Galata V, Mueller SC, Marquart S, Schrauder MG,
Strick R, et al: miRNAs can be generally associated with human
pathologies as exemplified for miR-144. BMC Med. 12:2242014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gaedcke J, Grade M, Camps J, Søkilde R,
Kaczkowski B, Schetter AJ, Difilippantonio MJ, Harris CC, Ghadimi
BM, Møller S, et al: The rectal cancer microRNAome-microRNA
expression in rectal cancer and matched normal mucosa. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:4919–4930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang W, Peng B, Wang D, Ma X, Jiang D,
Zhao J and Yu L: Human tumor microRNA signatures derived from
large-scale oligonucleotide microarray datasets. Int J Cancer.
129:1624–1634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ren K, Liu QQ, An ZF, Zhang DP and Chen
XH: MiR-144 functions as tumor suppressor by targeting PIM1 in
gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3028–3037.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iwaya T, Yokobori T, Nishida N, Kogo R,
Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Sawada G, Takahashi Y, Ishibashi M, et
al: Downregulation of miR-144 is associated with colorectal cancer
progression via activation of mTOR signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 33:2391–2397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khamas A, Ishikawa T, Shimokawa K, Mogushi
K, Iida S, Ishiguro M, Mizushima H, Tanaka H, Uetake H and Sugihara
K: Screening for epigenetically masked genes in colorectal cancer
Using 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine, microarray and gene expression
profile. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:67–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alhopuro P, Sammalkorpi H, Niittymäki I,
Biström M, Raitila A, Saharinen J, Nousiainen K, Lehtonen HJ,
Heliövaara E, Puhakka J, et al: Candidate driver genes in
microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
130:1558–1566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Snipstad K, Fenton CG, Kjaeve J, Cui G,
Anderssen E and Paulssen RH: New specific molecular targets for
radio-chemotherapy of rectal cancer. Mol Oncol. 4:52–64. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sabates-Bellver J, Van der Flier LG, de
Palo M, Cattaneo E, Maake C, Rehrauer H, Laczko E, Kurowski MA,
Bujnicki JM, Menigatti M, et al: Transcriptome profile of human
colorectal adenomas. Mol Cancer Res. 5:1263–1275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu Y and Wu F: A new miRNA regulator,
miR-672, reduces cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting JUN expression.
Gene. 648:21–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F,
Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP and Odenthal M: MicroRNA gene
expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:1223–1232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Yu X, Xu Y and Shen H:
Identification of dysregulated lncRNAs profiling and
metastasis-associated lncRNAs in colorectal cancer by genome-wide
analysis. Cancer Med. 6:2321–2330. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zong S, Li W, Li H, Han S, Liu S, Shi Q
and Hou F: Identification of hypoxia-regulated angiogenic genes in
colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 493:461–467. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Fallahi P,
Frascerra S, Piaggi S, Gelmini S, Lupi C, Minuto M, Berti P,
Benvenga S, et al: Dysregulation of secretion of CXC
alpha-chemokine CXCL10 in papillary thyroid cancer: Modulation by
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 16:1299–1311. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kistner L, Doll D, Holtorf A, Nitsche U
and Janssen KP: Interferon-inducible CXC-chemokines are crucial
immune modulators and survival predictors in colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:89998–90012. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Keeley EC, Mehrad B and Strieter RM: CXC
chemokines in cancer angiogenesis and metastases. Adv Cancer Res.
106:91–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin YH, Friederichs J, Black MA, Mages J,
Rosenberg R, Guilford PJ, Phillips V, Thompson-Fawcett M, Kasabov
N, Toro T, et al: Multiple gene expression classifiers from
different array platforms predict poor prognosis of colorectal
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:498–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rahmani F, Avan A, Hashemy SI and
Hassanian SM: Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulatory microRNAs
in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol.
233:811–817. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moridikia A, Mirzaei H, Sahebkar A and
Salimian J: MicroRNAs: Potential candidates for diagnosis and
treatment of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol. 233:901–913. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai SD, Chen JS, Xi ZW, Zhang LJ, Niu ML
and Gao ZY: MicroRNA-144 inhibits migration and proliferation in
rectal cancer by downregulating ROCK-1. Mol Med Rep. 12:7396–7402.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sureban SM, May R, Mondalek FG, Qu D,
Ponnurangam S, Pantazis P, Anant S, Ramanujam RP and Houchen CW:
Nanoparticle-based delivery of siDCAMKL-1 increases microRNA-144
and inhibits colorectal cancer tumor growth via a Notch-1 dependent
mechanism. J Nanobiotechnology. 9:402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Afaloniati H, Karagiannis GS, Hardas A,
Poutahidis T and Angelopoulou K: Inflammation-driven colon
neoplasmatogenesis in uPA-deficient mice is associated with an
increased expression of Runx transcriptional regulators. Exp Cell
Res. 361:257–264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mandal P: Molecular mechanistic pathway of
colo-rectal carcinogenesis associated with intestinal microbiota.
Anaerobe. 49:63–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Verbeke H, Geboes K, Van Damme J and
Struyf S: The role of CXC chemokines in the transition of chronic
inflammation to esophageal and gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1825:117–129. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miekus K, Jarocha D, Trzyna E and Majka M:
Role of I-TAC-binding receptors CXCR3 and CXCR7 in proliferation,
activation of intracellular signaling pathways and migration of
various tumor cell lines. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 48:104–111.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Li G, Stanco A, Long JE, Crawford
D, Potter GB, Pleasure SJ, Behrens T and Rubenstein JL: CXCR4 and
CXCR7 have distinct functions in regulating interneuron migration.
Neuron. 69:61–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bolomsky A, Schreder M, Hübl W, Zojer N,
Hilbe W and Ludwig H: Monokine induced by interferon gamma
(MIG/CXCL9) is an independent prognostic factor in newly diagnosed
myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 57:2516–2525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|