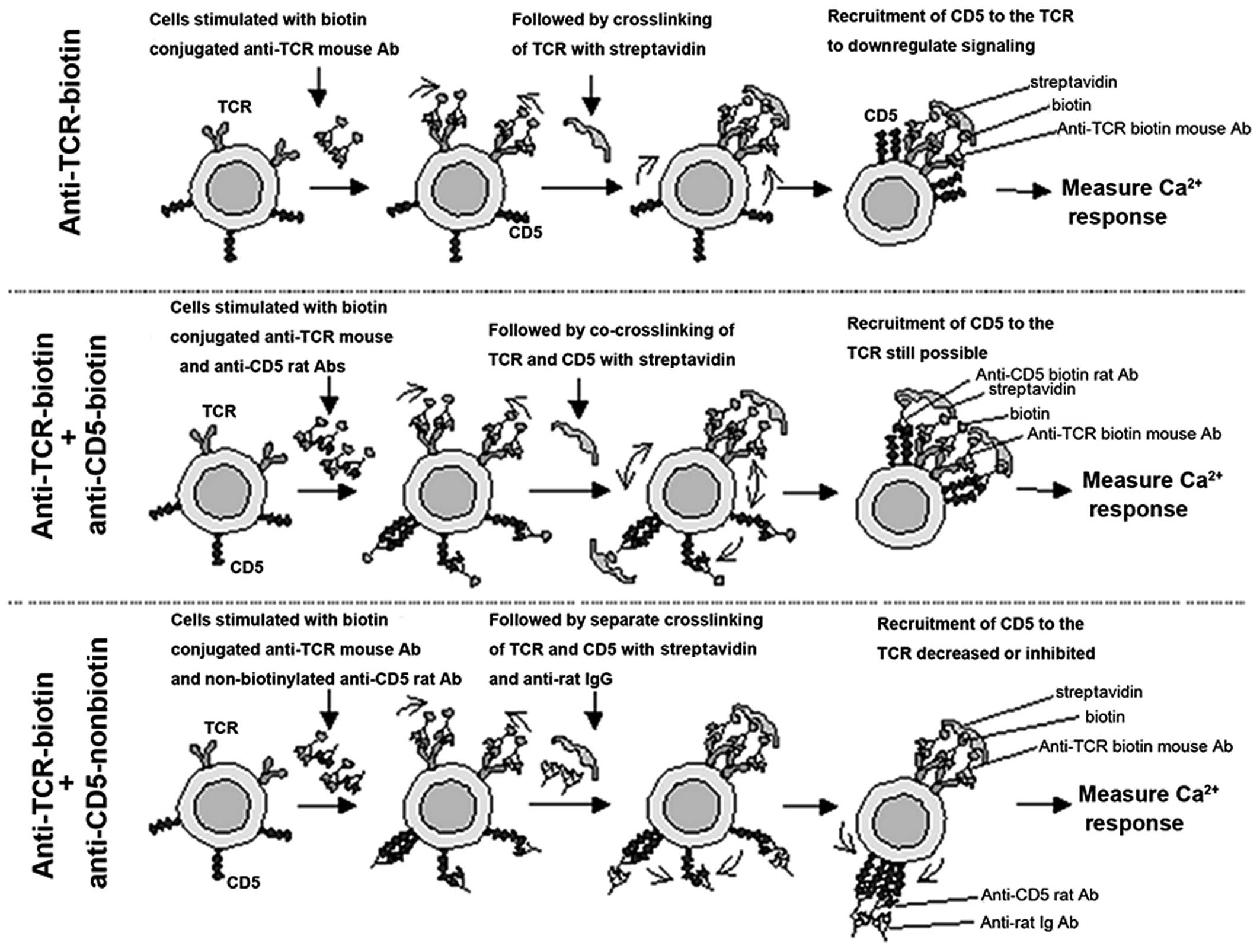
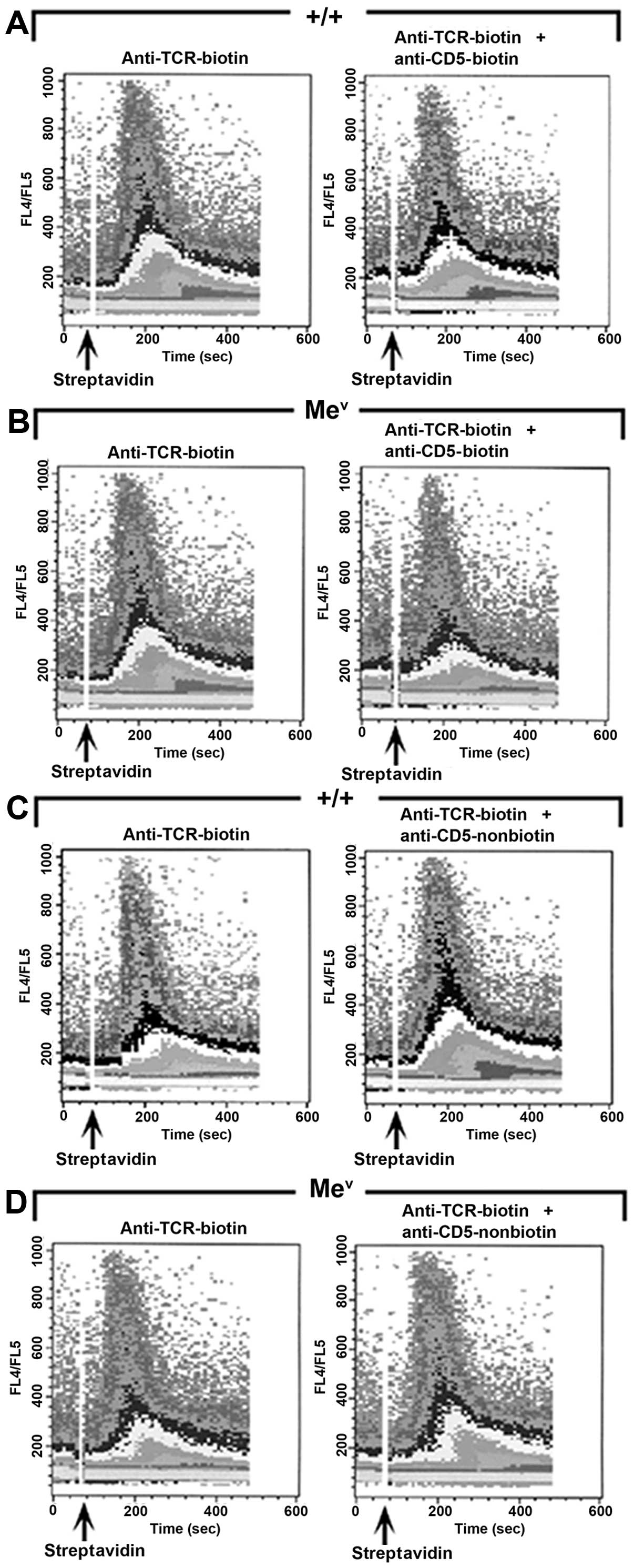
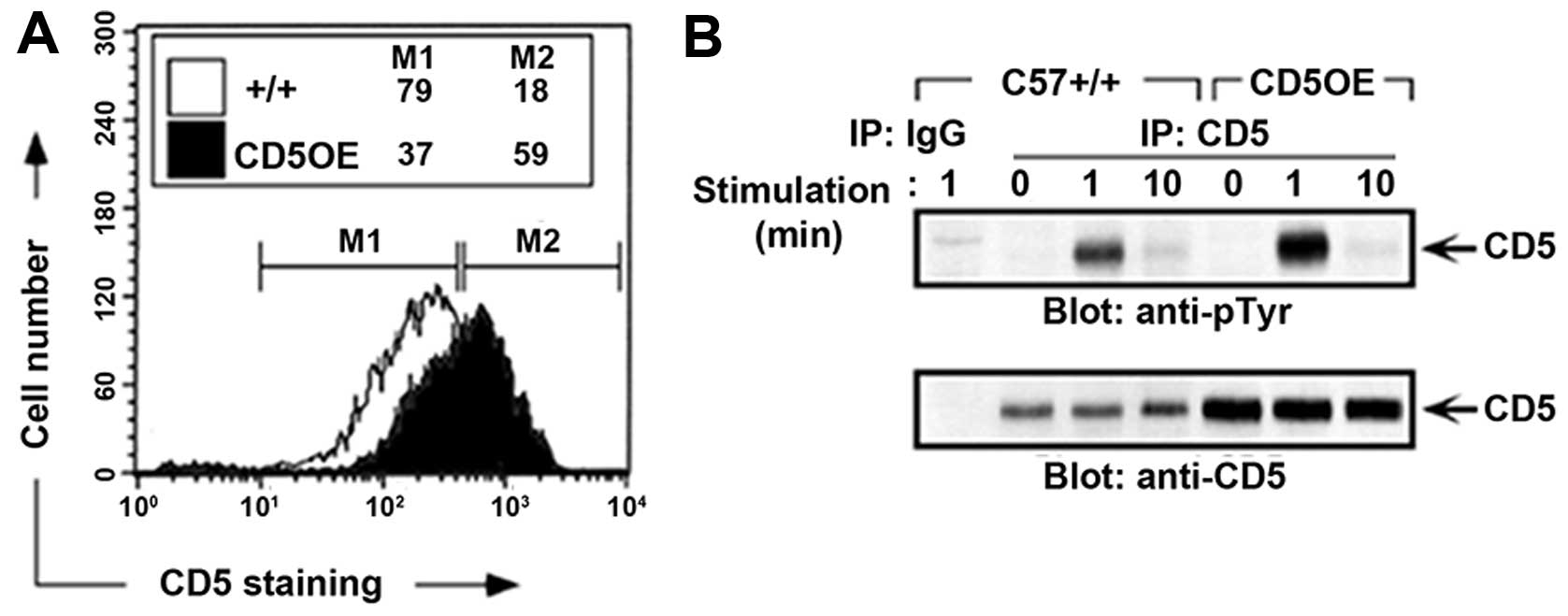
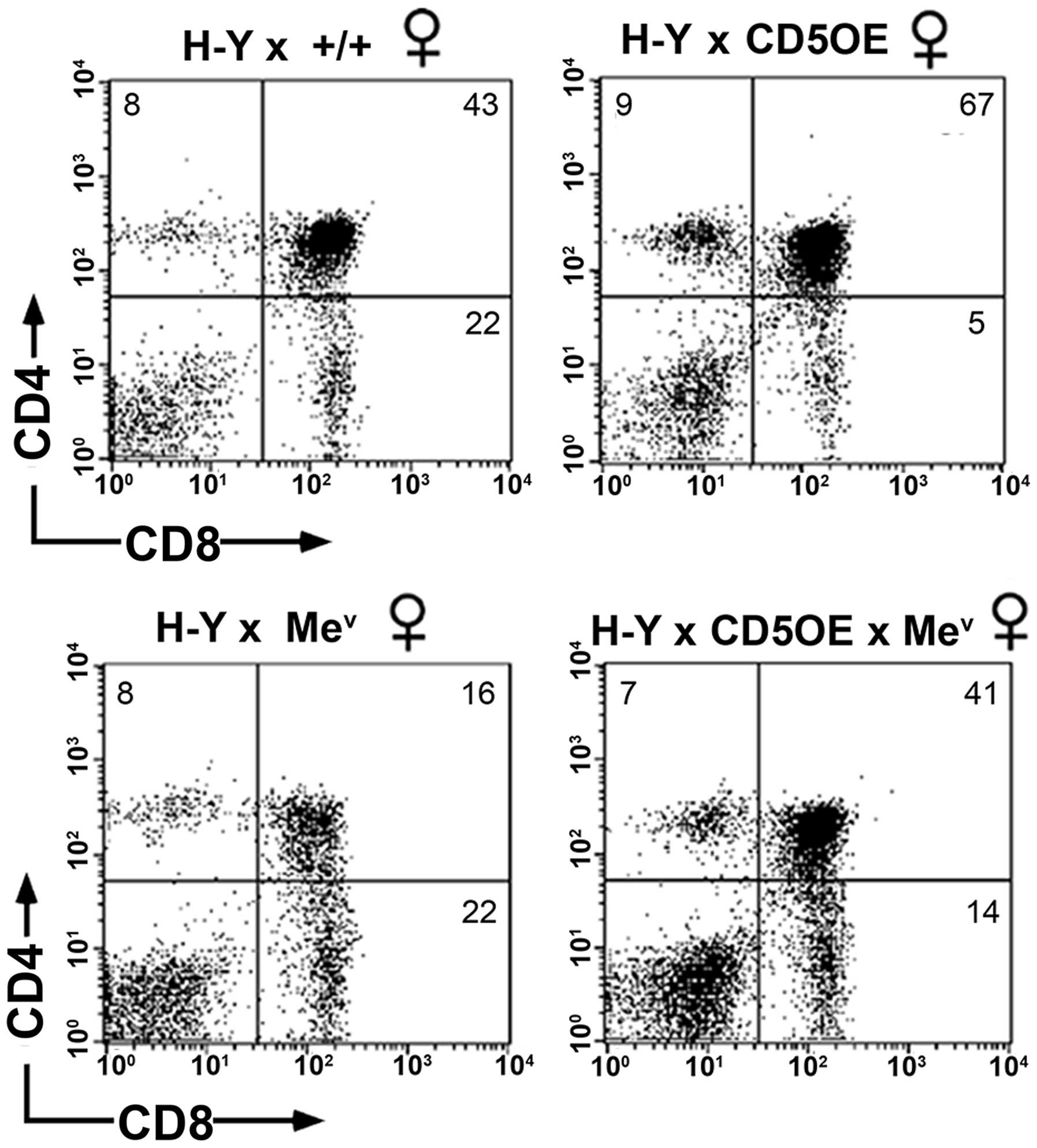
|
1
|
Martínez VG, Moestrup SK, Holmskov U,
Mollenhauer J and Lozano F: The conserved scavenger receptor
cysteine-rich super-family in therapy and diagnosis. Pharmacol Rev.
63:967–1000. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mandl JN, Monteiro JP, Vrisekoop N and
Germain RN: T cell-positive selection uses self-ligand binding
strength to optimize repertoire recognition of foreign antigens.
Immunity. 38:263–274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Azzam HS, Grinberg A, Lui K, Shen H,
Shores EW and Love PE: CD5 expression is developmentally regulated
by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and TCR avidity. J Exp Med.
188:2301–2311. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stamou P, de Jersey J, Carmignac D,
Mamalaki C, Kioussis D and Stockinger B: Chronic exposure to low
levels of antigen in the periphery causes reversible functional
impairment correlating with changes in CD5 levels in monoclonal CD8
T cells. J Immunol. 171:1278–1284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raman C: CD5, an important regulator of
lymphocyte selection and immune tolerance. Immunol Res. 26:255–263.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klinker MW and Lundy SK: Multiple
mechanisms of immune suppression by B lymphocytes. Mol Med.
18:123–137. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Mage RG and Pospisil R: CD5 and other
superantigens may select and maintain rabbit self-renewing
B-lymphocytes and human B-CLL cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
252:87–96. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mamonkin M, Rouce RH, Tashiro H and
Brenner MK: A T-cell-directed chimeric antigen receptor for the
selective treatment of T-cell malignancies. Blood. 126:983–992.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sheng JR, Quan S and Soliven B:
CD1d(hi)CD5+ B cells expanded by GM-CSF in vivo suppress
experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. J Immunol.
193:2669–2677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beaudette-Zlatanova BC, Le PT, Knight KL,
Zhang S, Zakrzewski S, Parthasarathy M and Stiff PJ: A potential
role for B cells in suppressed immune responses in cord blood
transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 48:85–93. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Spertini F, Stohl W, Ramesh N, Moody C and
Geha RS: Induction of human T cell proliferation by a monoclonal
antibody to CD5. J Immunol. 146:47–52. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alberola-Ila J, Places L, Cantrell DA,
Vives J and Lozano F: Intracellular events involved in CD5-induced
human T cell activation and proliferation. J Immunol.
148:1287–1293. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ochi H and Watanabe T: Negative regulation
of B cell receptor-mediated signaling in B-1 cells through CD5 and
Ly49 co-receptors via Lyn kinase activity. Int Immunol.
12:1417–1423. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fenutría R, Martinez VG, Simões I, Postigo
J, Gil V, Martínez-Florensa M, Sintes J, Naves R, Cashman KS,
Alberola-Ila J, et al: Transgenic expression of soluble human CD5
enhances experimentally-induced autoimmune and anti-tumoral immune
responses. PLoS One. 9:e848952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tarakhovsky A, Kanner SB, Hombach J,
Ledbetter JA, Müller W, Killeen N and Rajewsky K: A role for CD5 in
TCR-mediated signal transduction and thymocyte selection. Science.
269:535–537. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peña-Rossi C, Zuckerman LA, Strong J, Kwan
J, Ferris W, Chan S, Tarakhovsky A, Beyers AD and Killeen N:
Negative regulation of CD4 lineage development and responses by
CD5. J Immunol. 163:6494–6501. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dennehy KM, Ferris WF, Veenstra H,
Zuckerman LA, Killeen N and Beyers AD: Determination of the
tyrosine phosphorylation sites in the T cell transmembrane
glycoprotein CD5. Int Immunol. 13:149–156. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iwai LK, Benoist C, Mathis D and White FM:
Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of T cell receptor signaling
in diabetes prone and resistant mice. J Proteome Res. 9:3135–3145.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beyers AD, Spruyt LL and Williams AF:
Molecular associations between the T-lymphocyte antigen receptor
complex and the surface antigens CD2, CD4, or CD8 and CD5. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:2945–2949. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Unkeless JC and Jin J: Inhibitory
receptors, ITIM sequences and phosphatases. Curr Opin Immunol.
9:338–343. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Perez-Villar JJ, Whitney GS, Bowen MA,
Hewgill DH, Aruffo AA and Kanner SB: CD5 negatively regulates the
T-cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathway: Involvement of
SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Mol Cell Biol.
19:2903–2912. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carmo AM, Castro MA and Arosa FA: CD2 and
CD3 associate independently with CD5 and differentially regulate
signaling through CD5 in Jurkat T cells. J Immunol. 163:4238–4245.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tibaldi E, Brunati AM, Zonta F, Frezzato
F, Gattazzo C, Zambello R, Gringeri E, Semenzato G, Pagano MA and
Trentin L: Lyn-mediated SHP-1 recruitment to CD5 contributes to
resistance to apoptosis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
cells. Leukemia. 25:1768–1781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kisielow P, Blüthmann H, Staerz UD,
Steinmetz M and von Boehmer H: Tolerance in T-cell-receptor
transgenic mice involves deletion of nonmature
CD4+8+ thymocytes. Nature. 333:742–746. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Love PE, Shores EW, Lee EJ, Grinberg A,
Munitz TI, Westphal H and Singer A: Differential effects of zeta
and eta transgenes on early alpha/beta T cell development. J Exp
Med. 179:1485–1494. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Somani AK, Yuen D, Yang Y, Love
PE and Siminovitch KA: Involvement of the SHP-1 tyrosine
phosphatase in regulation of T cell selection. J Immunol.
163:3012–3021. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kozlowski M, Mlinaric-Rascan I, Feng GS,
Shen R, Pawson T and Siminovitch KA: Expression and catalytic
activity of the tyrosine phosphatase PTP1C is severely impaired in
motheaten and viable motheaten mice. J Exp Med. 178:2157–2163.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pani G, Fischer KD, Mlinaric-Rascan I and
Siminovitch KA: Signaling capacity of the T cell antigen receptor
is negatively regulated by the PTP1C tyrosine phosphatase. J Exp
Med. 184:839–852. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bikah G, Carey J, Ciallella JR,
Tarakhovsky A and Bondada S: CD5-mediated negative regulation of
antigen receptor-induced growth signals in B-1 B cells. Science.
274:1906–1909. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sen G, Bikah G, Venkataraman C and Bondada
S: Negative regulation of antigen receptor-mediated signaling by
constitutive association of CD5 with the SHP-1 protein tyrosine
phosphatase in B-1 B cells. Eur J Immunol. 29:3319–3328. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gary-Gouy H, Bruhns P, Schmitt C, Dalloul
A, Daëron M and Bismuth G: The pseudo-immunoreceptor tyrosine-based
activation motif of CD5 mediates its inhibitory action on B-cell
receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 275:548–556. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dennehy KM, Broszeit R, Ferris WF and
Beyers AD: Thymocyte activation induces the association of the
proto-oncoprotein c-cbl and ras GTPase-activating protein with CD5.
Eur J Immunol. 28:1617–1625. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weiss A, Dazin PF, Shields R, Fu SM and
Lanier LL: Functional competency of T cell antigen receptors in
human thymus. J Immunol. 139:3245–3250. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Johnson KG, LeRoy FG, Borysiewicz LK and
Matthews RJ: TCR signaling thresholds regulating T cell development
and activation are dependent upon SHP-1. J Immunol. 162:3802–3813.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Imboden JB, Weiss A and Stobo JD: The
antigen receptor on a human T cell line initiates activation by
increasing cytoplasmic free calcium. J Immunol. 134:663–665.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Imboden JB and Stobo JD: Transmembrane
signalling by the T cell antigen receptor. Perturbation of the
T3-antigen receptor complex generates inositol phosphates and
releases calcium ions from intracellular stores. J Exp Med.
161:446–456. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ledbetter JA, June CH, Martin PJ, Spooner
CE, Hansen JA and Meier KE: Valency of CD3 binding and
internalization of the CD3 cell-surface complex control T cell
responses to second signals: Distinction between effects on protein
kinase C, cytoplasmic free calcium, and proliferation. J Immunol.
136:3945–3952. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Altman A, Coggeshall KM and Mustelin T:
Molecular events mediating T cell activation. Adv Immunol.
48:227–360. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hardy RR and Hayakawa K: Development and
physiology of Ly-1 B and its human homolog, Leu-1 B. Immunol Rev.
93:53–79. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
June CH, Rabinovitch PS and Ledbetter JA:
CD5 antibodies increase intracellular ionized calcium concentration
in T cells. J Immunol. 138:2782–2792. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupta S: Mechanisms of transmembrane
signalling in human T cell activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 91:45–50.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vandenberghe P, Verwilghen J, Van Vaeck F
and Ceuppens JL: Ligation of the CD5 or CD28 molecules on resting
human T cells induces expression of the early activation antigen
CD69 by a calcium- and tyrosine kinase-dependent mechanism.
Immunology. 78:210–217. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Simarro M, Calvo J, Vilà JM, Places L,
Padilla O, Alberola-Ila J, Vives J and Lozano F: Signaling through
CD5 involves acidic sphingomyelinase, protein kinase C-zeta,
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, and c-Jun NH2-terminal
kinase. J Immunol. 162:5149–5155. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Osman N, Ley SC and Crumpton MJ: Evidence
for an association between the T cell receptor/CD3 antigen complex
and the CD5 antigen in human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol.
22:2995–3000. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Page DM: Cutting edge: Thymic selection
and autoreactivity are regulated by multiple coreceptors involved
in T cell activation. J Immunol. 163:3577–3581. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mageed RA, Garaud S, Taher TE, Parikh K,
Pers JO, Jamin C, Renaudineau Y and Youinou P: CD5 expression
promotes multiple intracellular signaling pathways in B lymphocyte.
Autoimmun Rev. 11:795–798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Amantini C, Mosca M, Lucciarini R, Perfumi
MC and Santoni G: Thiorphan-induced survival and proliferation of
rat thymocytes by activation of Akt/survivin pathway and inhibition
of caspase-3 activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 327:215–225. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dennehy KM, Broszeit R, Garnett D,
Durrheim GA, Spruyt LL and Beyers AD: Thymocyte activation induces
the association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and pp120 with
CD5. Eur J Immunol. 27:679–686. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cuevas B, Lu Y, Watt S, Kumar R, Zhang J,
Siminovitch KA and Mills GB: SHP-1 regulates Lck-induced
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase phosphorylation and activity. J Biol
Chem. 274:27583–27589. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Imani F, Rager KJ, Catipovic B and Marsh
DG: Interleukin-4 (IL-4) induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
(p85) dephosphorylation. Implications for the role of SHP-1 in the
IL-4-induced signals in human B cells. J Biol Chem. 272:7927–7931.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Antony P, Petro JB, Carlesso G, Shinners
NP, Lowe J and Khan WN: B cell receptor directs the activation of
NFAT and NF-kappaB via distinct molecular mechanisms. Exp Cell Res.
291:11–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kishimoto H and Sprent J: Several
differenT cell surface molecules control negative selection of
medullary thymocytes. J Exp Med. 190:65–73. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sanjurjo L, Amézaga N, Aran G,
Naranjo-Gómez M, Arias L, Armengol C, Borràs FE and Sarrias MR: The
human CD5L/AIM-CD36 axis: A novel autophagy inducer in macrophages
that modulates inflammatory responses. Autophagy. 11:487–502. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Turner M, Mee PJ, Walters AE, Quinn ME,
Mellor AL, Zamoyska R and Tybulewicz VL: A requirement for the
Rho-family GTP exchange factor Vav in positive and negative
selection of thymocytes. Immunity. 7:451–460. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tanaka Y, So T, Lebedeva S, Croft M and
Altman A: Impaired IL-4 and c-Maf expression and enhanced Th1-cell
development in Vav1-deficient mice. Blood. 106:1286–1295. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|