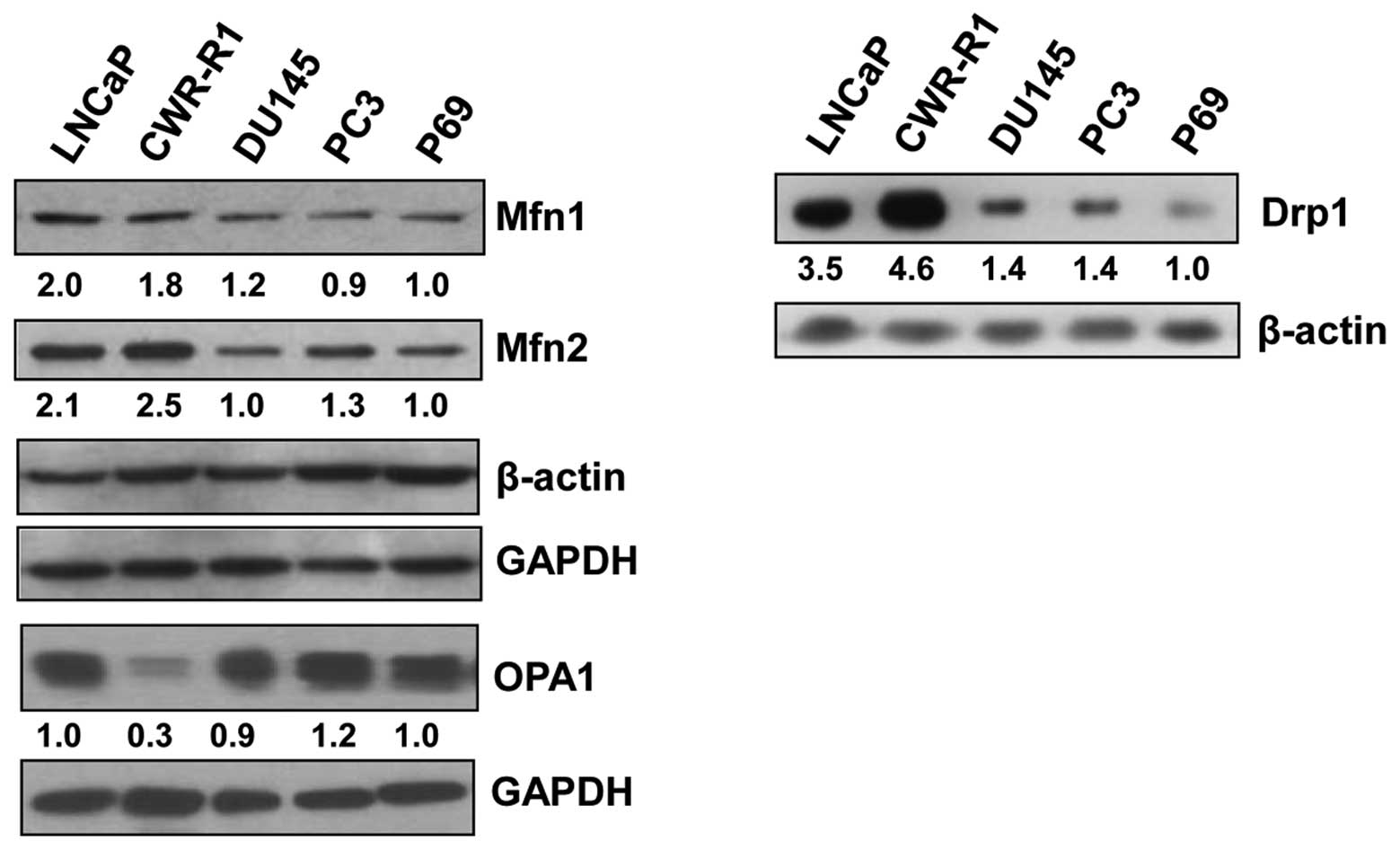
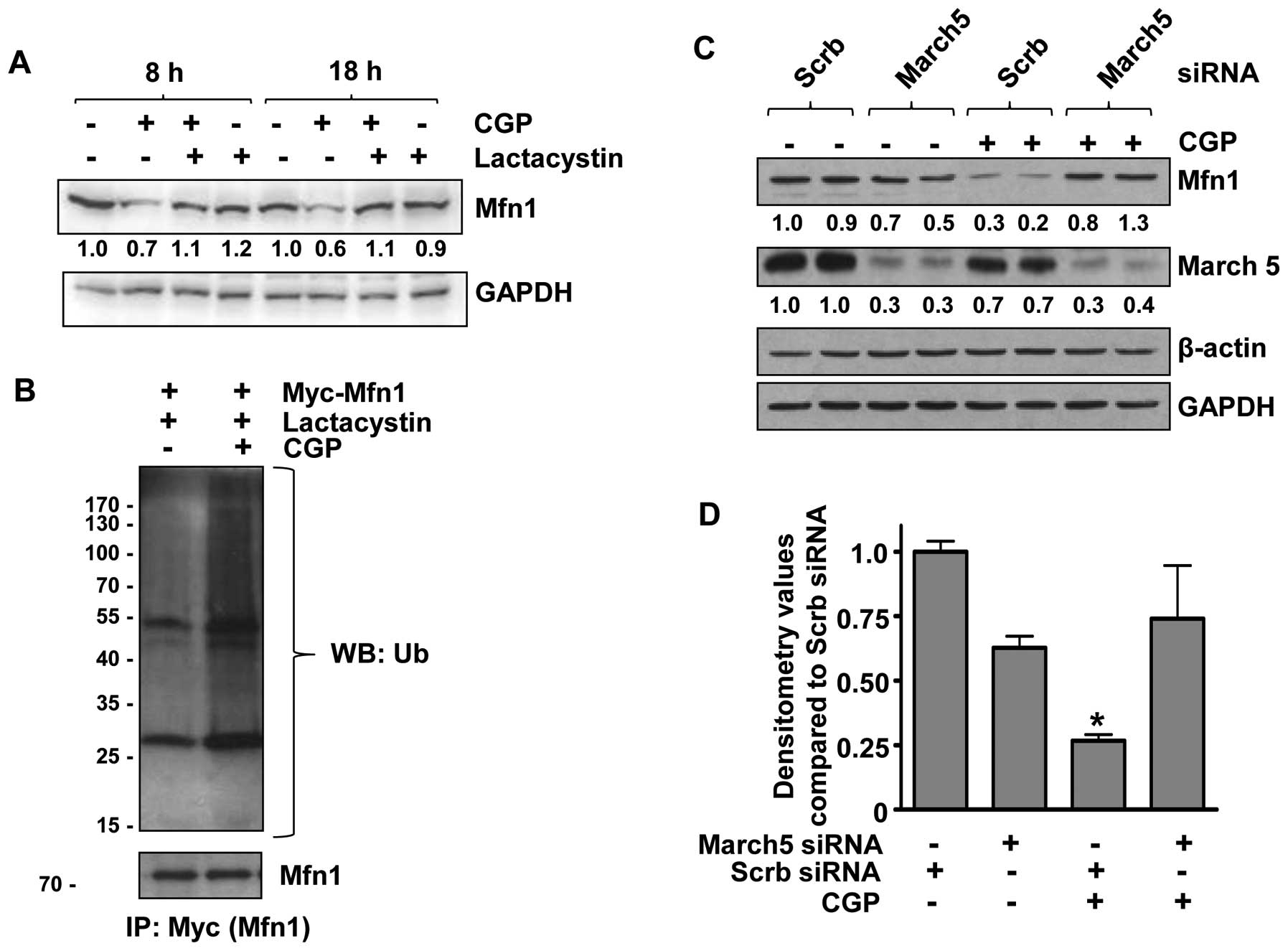
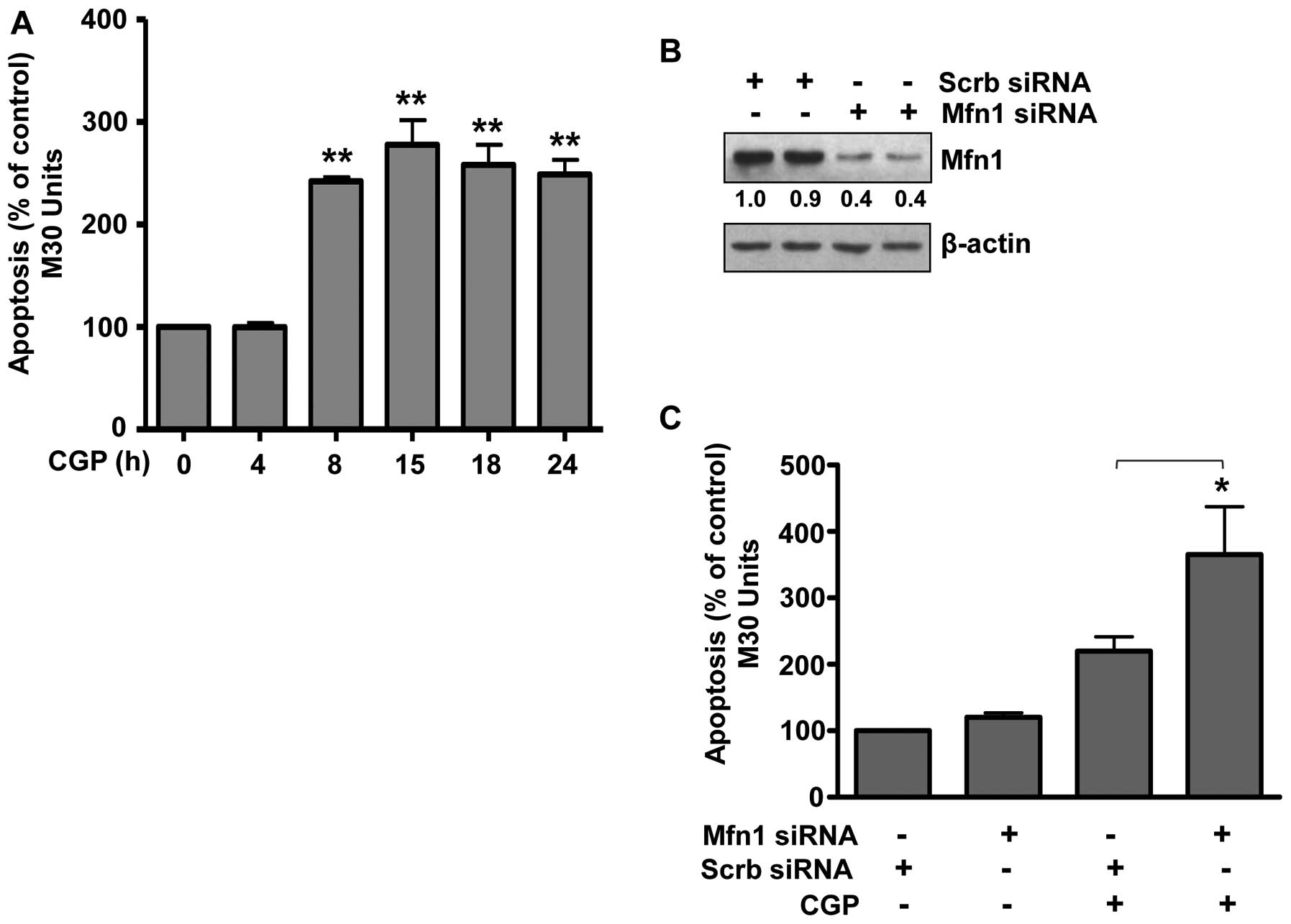
|
1.
|
Chen G, Wang F, Trachootham D and Huang P:
Preferential killing of cancer cells with mitochondrial dysfunction
by natural compounds. Mitochondrion. 10:614–625. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Frezza C, Pollard PJ and Gottlieb E:
Inborn and acquired metabolic defects in cancer. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:213–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kuznetsov AV, Margreiter R, Amberger A,
Saks V and Grimm M: Changes in mitochondrial redox state, membrane
potential and calcium precede mitochondrial dysfunction in
doxorubicin-induced cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1813:1144–1152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Willers IM and Cuezva JM:
Post-transcriptional regulation of the mitochondrial H(+)-ATP
synthase: a key regulator of the metabolic phenotype in cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:543–551. 2010.
|
|
5.
|
McBride HM, Neuspiel M and Wasiak S:
Mitochondria: more than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol. 16:R551–R560.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Bereiter-Hahn J and Voth M: Dynamics of
mitochondria in living cells: shape changes, dislocations, fusion,
and fission of mitochondria. Microsc Res Tech. 27:198–219. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Griparic L and van der Bliek AM: The many
shapes of mitochondrial membranes. Traffic. 2:235–244. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bossy-Wetzel E, Barsoum MJ, Godzik A,
Schwarzenbacher R and Lipton SA: Mitochondrial fission in
apoptosis, neurodegeneration and aging. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
15:706–716. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Skulachev VP: Mitochondrial filaments and
clusters as intra-cellular power-transmitting cables. Trends
Biochem Sci. 26:23–29. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Brooks C, Wei Q, Cho SG and Dong Z:
Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in acute kidney injury in cell
culture and rodent models. J Clin Invest. 119:1275–1285. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Choudhary V, Kaddour-Djebbar I,
Lakshmikanthan V, et al: Novel role of androgens in mitochondrial
fission and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1067–1077. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Frank S, Gaume B, Bergmann-Leitner ES, et
al: The role of dynamin-related protein 1, a mediator of
mitochondrial fission, in apoptosis. Dev Cell. 1:515–525. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Gomez-Lazaro M, Bonekamp NA, Galindo MF,
Jordan J and Schrader M: 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induces
Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation in SH-SY5Y cells. Free
Radic Biol Med. 44:1960–1969. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Kaddour-Djebbar I, Choudhary V, Brooks C,
et al: Specific mitochondrial calcium overload induces
mitochondrial fission in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
36:1437–1444. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Gandre-Babbe S and van der Bliek AM: The
novel tail-anchored membrane protein Mff controls mitochondrial and
peroxisomal fission in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Cell.
19:2402–2412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Loson OC, Song Z, Chen H and Chan DC:
Fis1, Mff, MiD49, and MiD51 mediate Drp1 recruitment in
mitochondrial fission. Mol Biol Cell. 24:659–667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Otera H, Wang C, Cleland MM, et al: Mff is
an essential factor for mitochondrial recruitment of Drp1 during
mitochondrial fission in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol.
191:1141–1158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Palmer CS, Osellame LD, Laine D,
Koutsopoulos OS, Frazier AE and Ryan MT: MiD49 and MiD51, new
components of the mitochondrial fission machinery. EMBO Rep.
12:565–573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Zhao J, Liu T, Jin S, et al: Human MIEF1
recruits Drp1 to mitochondrial outer membranes and promotes
mitochondrial fusion rather than fission. EMBO J. 30:2762–2778.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Cipolat S, Martins de Brito O, Dal Zilio B
and Scorrano L: OPA1 requires mitofusin 1 to promote mitochondrial
fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15927–15932. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Song Z, Ghochani M, McCaffery JM, Frey TG
and Chan DC: Mitofusins and OPA1 mediate sequential steps in
mitochondrial membrane fusion. Mol Biol Cell. 20:3525–3532. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Ishihara N, Eura Y and Mihara K: Mitofusin
1 and 2 play distinct roles in mitochondrial fusion reactions via
GTPase activity. J Cell Sci. 117:6535–6546. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Rojo M, Legros F, Chateau D and Lombes A:
Membrane topology and mitochondrial targeting of mitofusins,
ubiquitous mammalian homologs of the transmembrane GTPase Fzo. J
Cell Sci. 115:1663–1674. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Santel A, Frank S, Gaume B, Herrler M,
Youle RJ and Fuller MT: Mitofusin-1 protein is a generally
expressed mediator of mitochondrial fusion in mammalian cells. J
Cell Sci. 116:2763–2774. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Santel A and Fuller MT: Control of
mitochondrial morphology by a human mitofusin. J Cell Sci.
114:867–874. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Eura Y, Ishihara N, Yokota S and Mihara K:
Two mitofusin proteins, mammalian homologues of FZO, with distinct
functions are both required for mitochondrial fusion. J Biochem.
134:333–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Honda S, Aihara T, Hontani M, Okubo K and
Hirose S: Mutational analysis of action of mitochondrial fusion
factor mitofusin-2. J Cell Sci. 118:3153–3161. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Yuan H, Gerencser AA, Liot G, et al:
Mitochondrial fission is an upstream and required event for bax
foci formation in response to nitric oxide in cortical neurons.
Cell Death Differ. 14:462–471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Barsoum MJ, Yuan H, Gerencser AA, et al:
Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial fission is regulated by
dynamin-related GTPases in neurons. EMBO J. 25:3900–3911. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Cohen MM, Amiott EA, Day AR, et al:
Sequential requirements for the GTPase domain of the mitofusin Fzo1
and the ubiquitin ligase SCF Mdm30 in mitochondrial outer membrane
fusion. J Cell Sci. 124:1403–1410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Cohen MM, Leboucher GP, Livnat-Levanon N,
Glickman MH and Weissman AM: Ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent
degradation of a mitofusin, a critical regulator of mitochondrial
fusion. Mol Biol Cell. 19:2457–2464. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Park YY, Lee S, Karbowski M, Neutzner A,
Youle RJ and Cho H: Loss of MARCH5 mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin
ligase induces cellular senescence through dynamin-related protein
1 and mitofusin 1. J Cell Sci. 123:619–626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kaddour-Djebbar I, Lakshmikanthan V,
Shirley RB, Ma Y, Lewis RW and Kumar MV: Therapeutic advantage of
combining calcium channel blockers and TRAIL in prostate cancer.
Mol Cancer Ther. 5:1958–1966. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Jiang S, Zu Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y and Fu Y:
Involvement of mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening
in 7-xylosyl-10-deacetylpaclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Planta Med.
77:1005–1012. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Karbowski M and Youle RJ: Dynamics of
mitochondrial morphology in healthy cells and during apoptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 10:870–880. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Yingkun N, Lvsong Z and Huimin Y: Shikonin
inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of human HepG2
cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 88:1138–1146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Knott AB and Bossy-Wetzel E: Impairing the
mitochondrial fission and fusion balance: a new mechanism of
neurodegeneration. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1147:283–292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Wasilewski M and Scorrano L: The changing
shape of mitochondrial apoptosis. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
20:287–294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39.
|
Chang CR and Blackstone C: Cyclic
AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of Drp1 regulates its
GTPase activity and mitochondrial morphology. J Biol Chem.
282:21583–21587. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Cribbs JT and Strack S: Reversible
phosphorylation of Drp1 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and
calcineurin regulates mitochondrial fission and cell death. EMBO
Rep. 8:939–944. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Taguchi N, Ishihara N, Jofuku A, Oka T and
Mihara K: Mitotic phosphorylation of dynamin-related GTPase Drp1
participates in mitochondrial fission. J Biol Chem.
282:11521–11529. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Escobar-Henriques M, Westermann B and
Langer T: Regulation of mitochondrial fusion by the F-box protein
Mdm30 involves proteasome-independent turnover of Fzo1. J Cell
Biol. 173:645–650. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Chan NC, Salazar AM, Pham AH, et al: Broad
activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by Parkin is critical
for mitophagy. Hum Mol Genet. 20:1726–1737. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Rakovic A, Grunewald A, Kottwitz J, et al:
Mutations in PINK1 and Parkin impair ubiquitination of Mitofusins
in human fibroblasts. PLoS One. 6:e167462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Nakamura N, Kimura Y, Tokuda M, Honda S
and Hirose S: MARCH-V is a novel mitofusin 2- and Drp1-binding
protein able to change mitochondrial morphology. EMBO Rep.
7:1019–1022. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Chiche J, Rouleau M, Gounon P,
Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxic enlarged
mitochondria protect cancer cells from apoptotic stimuli. J Cell
Physiol. 222:648–657. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Ong SB, Subrayan S, Lim SY, Yellon DM,
Davidson SM and Hausenloy DJ: Inhibiting mitochondrial fission
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Circulation. 121:2012–2022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|