Introduction
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) comprises
more than 90% of all pancreatic cancer cases and remains one of the
most deadly malignancies (1).
Approximately 80% of patients already have metastases at the time
of diagnosis due to the lack of early symptoms. Furthermore,
potentially curative surgical resection is limited to only a few
patients. Among other chemotherapeutic drugs, the deoxycytidine
analog gemcitabine is used for palliative purposes to treat PDA
after surgical resection (2).
Glucocorticoids (GCs) have become the cornerstone of
lymphoid cancer treatment, though not all patients respond to this
treatment (3). Dexamethasone
(DEX), a potent synthetic GC, is often prescribed for lymphoid
cancer, and is also a co-treatment for PDA and other types of
epithelial tumors. Furthermore, GCs may limit the side effects of
chemotherapy and cancer growth, reduce inflammation in
pancreatitis, which is often associated with PDA, and inhibit tumor
cachexia and pain (4). However,
for epithelial tumors such as PDA, accumulating evidence indicates
that GCs have anti-apoptotic effects and induce cancer progression
and therapy resistance (5,6). In 2003, we reported the first in
vivo evidence of induction of chemotherapy resistance due to
pharmacological doses of DEX in a lung and cervical cancer cell
line (7), and these data have been
confirmed by several experimental studies (4-6,8).
Additionally, clinical studies have indicated an increased
likelihood of drug resistance, disease progression and metastasis
in patients with glioblastoma, oral squamous cell carcinoma and
cancers of the ovary, breast, prostate or lung due to GCs (8-15).
Similarly, an increased risk for skin and bladder cancer as well as
non-Hodgkin lymphoma has been observed among systemic GC users
(16,17). Our latest data based on PDA cells
demonstrate that DEX treatment mediates cancer progression and
metastasis by inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT),
and cancer stem cell (CSC) signaling through the activation of
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/c-Jun and transforming growth
factor-β (TGF-β) pathways (4).
Although GCs interfere with many signaling pathways
and affect the regulation of many target genes, the entire spectrum
of their molecular, cell type-specific activity is still not
completely understood. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are potential key players
because these highly conserved, small, 19-25-nucleotide-long,
single-stranded, endogenous, non-coding RNAs act as cell
context-dependent transcriptional regulators (18-20).
miRNAs bind to the 3′-untranslated region (3′UTR) of a target
messenger RNA (mRNA) and induce translational suppression or mRNA
degradation. A growing body of evidence indicates that GCs modulate
the expression of miRNAs; for example, cortisol treatment of HeLa
cells was shown to mediate the downregulation of miR-145, and
thereby the invasion and therapy resistance (21).
Nonetheless, the involvement of miRNA signaling in
GC-induced CSC and EMT signaling pathways in PDA has not yet been
studied. Through miRNA microarray analysis, bioinformatics
evaluation and RT-qPCR, we detected the significant deregulation of
several miRNAs in PDA cells after treatment with DEX, and we
selected miR-132 as the most important candidate. Herein, we
demonstrate that DEX regulates the expression of miR-132 through
promoter methylation. Consequently, miR-132 mimics transfected into
cells activate TGF-β2 expression via directly binding to its 3′UTR,
which in turn causes enhanced clonogenicity, migration and
EMT-associated expression.
Materials and methods
Human primary and established cell
lines
AsPC-1 and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell lines were
obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA,
USA). The established cell lines were recently authenticated by a
commercial service (Multiplexion GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany). The
human primary pancreatic cancer cell line ASAN-PaCa, which has been
described previously, was kindly provided by Dr N. Giese (22). To maintain the authenticity of the
cell lines, we prepared frozen stocks from the initial stocks, and
a new thawed stock was used every three months for experiments.
Monthly testing ensured mycoplasma-negative cultures. Cells were
cultured under standard conditions in DMEM (PAA Laboratories GmbH;
GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Little Chalfont, UK) supplemented with
10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck
KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and 25 mmol/l HEPES (PAA).
Patient tissues
Tissue specimens were obtained from patients who had
undergone surgery at the Department of General, Visceral and
Transplant Surgery, University of Heidelberg, from January 2014 to
December 2016. The Ethics Committee of the University of Heidelberg
approved the study after receiving written informed consent from
the patients. Clinical diagnoses were established by conventional
clinical and histological criteria. Surgical resection was
performed as indicated by the principles and practice of
oncological therapy.
Reagents and treatment of cells
Stock solutions of DEX (25 mM, ≥98% pure),
Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) were prepared in ethanol. A solution of
5′AZA-2′-deoxycytidine was freshly diluted with the cell culture
medium to prepare a 10 µM stock solution (23).
miRNA microarray profiling and
analysis
Total RNA was extracted with the use of a Qiagen
miRNeasy Mini Isolation Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Agilent
Human miRNA Microarray (Release 19.0) covering 2006 human microRNAs
was used for microRNA profiling. The raw array data were analyzed
by the Linear Regression Model for Microarrays (LIMMA) software
version 3.24.15. The Benjamini and Hochberg (BH) algorithm was used
to correct for multiple testing and false discovery rates (FDRs).
Gene Ontology analysis was used to detect associations between the
identified set of miRNA candidates and the associated specific
biological processes and molecular functions. The microarray data
were uploaded to Array Express (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/help/accession_codes.html)
under the accession number E-MTAB-4718.
In silico analysis and target
prediction
Gene Ontology (www.geneontology.org) was used to analyze the miRNA
array data for identification of a set of significantly and
differentially regulated miRNAs with similar functions. The 100
most significantly deregulated miRNAs after 96 h of DEX treatment
were uploaded, and the keywords EMT, Wnt and SMAD were entered. The
commercially available Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) database
(Qiagen) was used for identifying targets of the top differentially
regulated miRNAs. In addition, the databases miRanda (http://www.microrna.org) (24), TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org) (25), miRwalk (http://mirwalk.uni-hd.de/) (26) and PicTar (http://www.pictar.org) http://www.pictar.org (27) were used for miRNA target gene
prediction. Potential candidates with mirSVR scores <−0.1 were
considered. We then chose the most common predictions of the
different databases; the results from miRwalk and IPA were
preferred as their data were the most up-to-date. The binding site
of miR-132 in the 3′UTR of TGF-β2 was identified with
TargetScan.
TaqMan miR real-time qPCR
cDNA was synthesized from 500 ng total RNA using
TaqMan® Reverse Transcription Reagents (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and
1 µl cDNA was used for quantitative PCR. Quantitative PCR
was performed using a TaqMan Assay with specific primers. RNU6
served as an internal control for hsa-miR-132-3p expression, and
GAPDH was the internal control for vimentin and E-cadherin
expression (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The PCR was performed
using a StepOne Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.), and changes in relative concentration were calculated with
the second derivative maximum method 2−ΔΔCq
(28). The ΔCT value was
calculated by subtracting the CT of the housekeeping gene from the
CT of the gene of interest [ΔCT = Ct (gene of interest) - Ct
(housekeeping gene)]. Fold change data were generated using the
equation ΔΔCT = ΔCT (treated sample) - ΔCT (untreated sample).
Global DNA methylation analysis
An ELISA-based MethylFlash Methylated DNA 5-mC
Quantification Kit (Colorimetric; Epigentek, distributed by BioCat,
Heidelberg, Germany) was used for quantification of total
5-methylcytosine (5-mC). This assay detects the methylated fraction
of DNA with antibodies followed by quantification through an
ELISA-like reaction using the absorbance at 450 nm measured by a
micro-plate spectrophotometer. After genomic DNA was prepared by
the DNeasy® blood and tissue kit (Qiagen), 100 ng DNA
was bound to each well of the assay plates in biological and
technical duplicates (n=4). After the plates were washed, the
capture antibody was added; after another wash, the detection
antibody and an enhancer solution were added. A color-developing
solution was then added, and absorbance was measured at 450 nm. A
standard curve was generated for absolute 5-mC quantification.
Methylation-specific PCR
A methylation-specific PCR analysis of the miR-132
promoter CpG island located on chromosome 17, between base pairs
497 and 545 upstream of the transcriptional start site, was
performed as described (29).
Genomic DNA was extracted from PDA cells using a QIAamp DNA Mini
Kit (Qiagen), and a 100-ng sample of DNA was modified with
bisulfite using EZ DNA Methylation™ Kit following the
manufacturer’s instructions (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). PCR
was performed with 20 ng bisulfite-modified DNA using the HotStar
Polymerase Kit (Qiagen). The PCR primers were as follows:
methylated miR-132 forward, 5′-TTTTTTGGGATATTTTTGACGTTAC-3′,
methylated miR-132 reverse, 5′-CCGACTAAAAACTCTACTACTCCG-3′,
amplifying a 122-bp fragment; unmethylated miR-132 forward,
5′-TTTTTGGGATATTTTTGATGTTATG-3′, unmethylated miR-132 reverse,
5′-CCAACTAAAAACTCTACTACTCCAC-3′, amplifying a 121-bp fragment. PCR
settings were 95°C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 94°C for 30
sec, 62°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 60 sec, with a final extension
step at 72°C for 7 min.
Site-directed mutagenesis of the TGF-β2
3′UTR miR-132 binding site
A Renilla luciferase reporter construct
expressing the wild-type (wt) 3′UTR TGF-β2 was purchased from
BioCat. The complete putative 3′UTR binding region for miR-132 was
exchanged using QuikChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit to create
a mutated (mt) site (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). The
following primer sequences were created with the QuikChange Primer
Design Program (Agilent Technologies) and ordered from Eurofins
GATC Biotech GmbH (Konstanz, Germany): TGF-β-M1-3′UTR forward,
5′-GCC TAA GGA AGC TTC TTG TAA GGT CCA AAA ACT AAA ATC TGA CAT AAT
AAA AGA AAA CTT TCA GTC AGA ATA AGT CTG TAA G-3′; TGF-β2-M1-3′UTR
reverse, 5′-CTT ACA GAC TTA TTC TGA CTG AAA GTT TCT TTT ATT ATG TCA
GAT TTT AGT TTT GGA CCT TAC AAG AAG CTT CCT TAG GC-3′. The
sequences of the generated wt and mt miR-132 3′UTR plasmids were
confirmed by sequencing (Eurofins GATC Biotech GmbH).
miRNA transfection
MirVana™ mimics [miR-132-3p and non-coding miRNA
(miR-NC)] at 50 nM each were transfected into cells using
Lipofectamine 2000 (both from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) using
the reverse transfection method described in the manufacturer’s
instructions.
Dual-Luciferase® reporter
assay
Cells were seeded at a density of 1×104
cells per well into a 96-well plate and co-transfected with 50 nM
miR mimics, 25 ng/well Firefly luciferase plasmid and 50 ng/well
Renilla luciferase reporter construct expressing TGF-β2
3′UTR (BioCat). The cells were lysed in Passive Lysis Buffer of the
Dual-Luciferase® Assay System (Promega Corporation,
Mannheim, Germany) at 48 h post-transfection. Renilla and
Firefly luciferase activities were measured using the FLUOstar
OPTIMA instrument (BMG Labtech GmbH, Ortenberg, Germany).
Wound-healing assay
Cells were harvested 24 h after transfection and at
12 h after DEX treatment, resuspended in DMEM supplemented with 10%
FCS and plated at a density of 5×105 cells/ml in
ready-to-use culture-inserts in a µ-Dish (ibdiTreat, item
#80241; ibidi GmbH, Martinsried, Germany). At 100% cell confluence,
the inserts were removed, leaving a 500-µm gap in each dish;
fresh medium was added. After 24 and 48 h, images were taken with a
Nikon Eclipse TS 100-F inverted microscope equipped with a camera.
Images (5 per treatment condition) were obtained, and analysis was
performed with the WimScratch Quantitative Wound-Healing Image
Analysis Software version 1 (item #30002; ibidi GmbH).
Western blot analysis
Western blot analysis was performed as previously
described (30). Rabbit monoclonal
antibodies against TGF-β2 (#710276; ABfinity™; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA USA), E-cadherin (#3195-S; Cell
Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA), and vimentin
(#EPR3255; Abcam, Cambridge, UK) and a mouse monoclonal antibody
against β-actin (#A1978; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) were used. All
primary antibodies were diluted 1:1,000 and secondary antibodies
1:5,000; the incubations were all performed at room
temperature.
Colony-forming assay
AsPC-1, PANC-1 and ASAN-PaCa cells were transfected
with 50 nM miR-132 mimics or a negative miR control (NC). At 8 h
later, the cells were treated with 1 µM DEX in the presence
or absence of miR-132. After 48 h, the cells were resuspended in
DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS and plated at a density of 400
(AsPC-1 and PANC-1) or 1,000 cells/well (ASAN-PaCa) in 6-well
tissue culture plates. The cultures were maintained under standard
culture conditions for 14 days, followed by an evaluation of those
fixed and Coomassie-stained colonies consisting of ≥50 cells. The
plating efficiency was calculated as a percentage: (number of
colonies/number of seeded cells) ×100, as previously described
(30).
Immunohistochemistry and
immunofluorescence staining
Immunofluorescence staining was performed on
6-µm-thick frozen or paraffin-embedded tissue sections, as
previously described (31). The
following antibodies were used: Mouse monoclonal antibodies against
TGF-β2 (#ab36495), vimentin (#ab8059) and 5-methylcytosine
(#ab10805) (all from Abcam), and rabbit monoclonal antibodies
against E-cadherin (#3195s; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.) and
Ki-67 (#ab92742; Abcam). Primary antibodies were diluted 1:50 and
secondary antibodies 1:400; the incubations were all performed at
room temperature. Signals were detected with a Leica DMRB
fluorescence microscope (Leica Microsystems Ltd., Milton Keynes,
UK). Images of representative fields were captured using a SPOTTM
FLEX 15.2 64-Mp shifting pixel digital color camera and analyzed
with SPOT Basic/Advanced 4.6 software (both from Diagnostic
Instruments, Sterling Heights, Michigan, USA).
In situ hybridization of miR-132
Detection of miR-132 expression in tissue sections
was achieved using miRCURY LNA™ microRNA Detection Kit (Exiqon,
Vedbaek, Denmark) as described (32). Staining was performed on
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded patient tissues. Briefly,
sections were dewaxed in Roti-Histol (Carl Roth GmbH & Co. KG,
Karlsruhe, Germany), rehydrated in 2-propanol, treated with
proteinase K (15 µg/ml) and air-dried. Hybridization was
performed for 2 h at 58°C using a miR-132-specific,
digoxigenin-labeled locked nucleic acid (LNA) detection probe and a
scrambled miR as a negative control. After stringent washes, the
bound LNA probes were detected with an alkaline phosphatase-coupled
digoxigenin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) and NBT/BCIP
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) as the substrate. The sections
were mounted using Roti-Mount FluorCare (Carl Roth GmbH& Co.
KG) containing 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylin-dole (DAPI) as a
counterstain.
Tumor xenotransplantation into fertilized
chick eggs and in ovo treatment
ASAN-PaCa cells were transfected with 50 nM mirVana™
mimics of hsa-miR-132 or miR-NC using the Lipofectamine
2000® reagent (both from Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). At 8 h later, the cells were treated with DEX or left
untreated. At 48 h later, the cells were transplanted to the
chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) of fertilized chicken eggs on day 9
of embryonic development (n=25). On developmental day 14, 50
µl miR-Lipofectamine mixture containing 50 nM hsa-miR-132
mimics or saline as a control were injected into the CAM vessels
supplying the tumor xenografts. Fertilized eggs from genetically
identical hybrid Lohman Brown (LB) chickens were obtained from a
local ecological hatchery (Geflügelzucht Hockenberger, Eppingen,
Germany), and tumor xenotransplantation, treatment, and evaluations
of tumor take, tumor growth and metastasis were performed as
described recently (33).
Statistical analysis
Quantitative data are presented as the mean ± SD of
experiments performed in triplicate. The data were analyzed using
Student’s t-test for statistical significance. The data were
evaluated by the Mann-Whitney test and by the Kruskal-Wallis test
followed by Mann-Whitney and Bonferroni-Holm tests. The in
vivo tumor growth data were evaluated by the Kruskal-Wallis
test followed by the Mann-Whitney and Bonferroni-Holm tests.
Statistical significance was considered to be indicated by values
of P<0.05.
Results
Dexamethasone regulates miRNA
expression
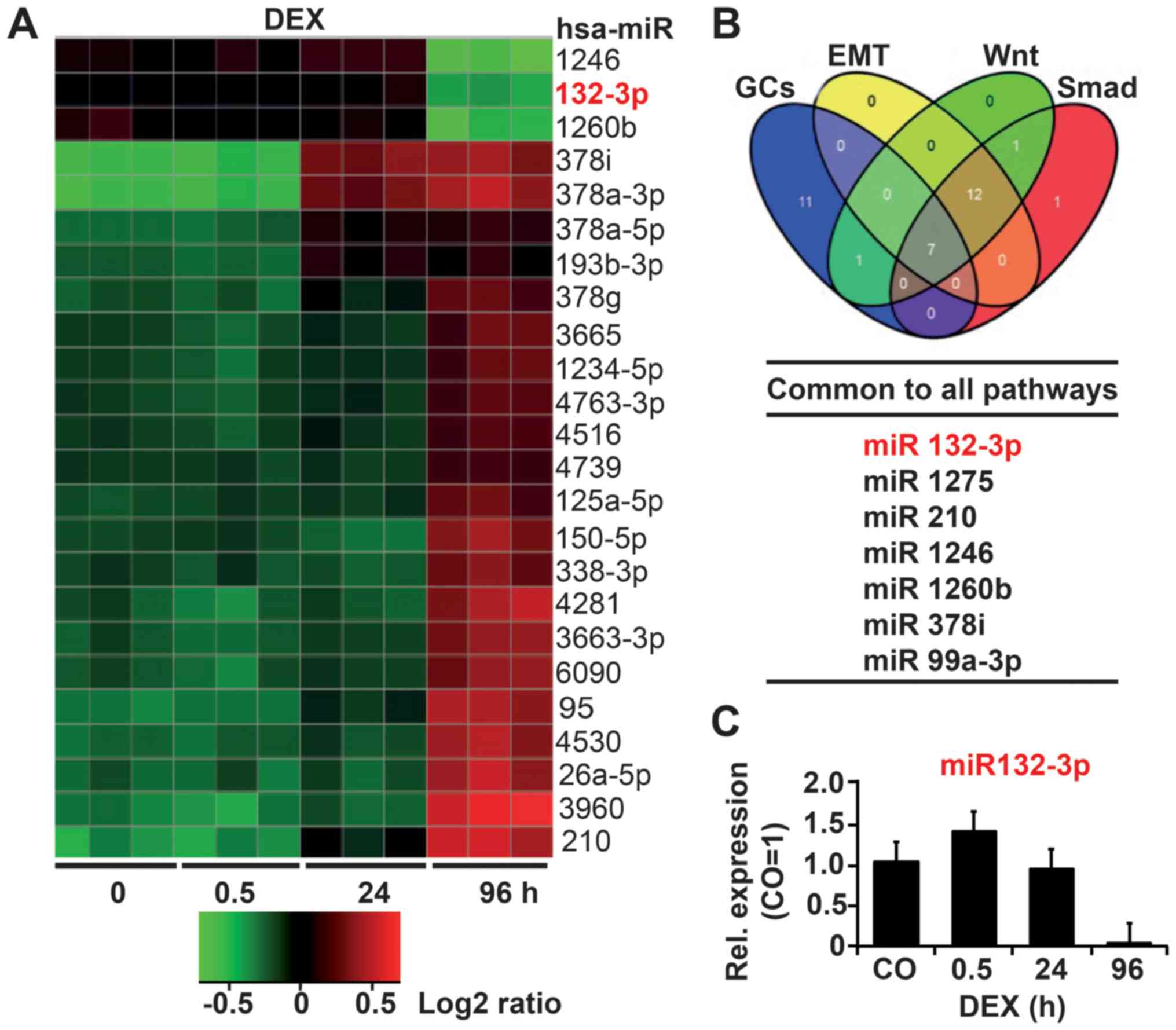
To evaluate potential GC-regulated miRNAs, we
treated the established PDA cell line AsPC-1 with DEX for 0.5, 24
or 96 h, or left the cells untreated as a control. Total RNA was
isolated and examined by Agilent Human miRNA Microarray analysis
(Release 19.0). Based on bioinformatics evaluation, 268 miRNAs were
significantly (P<0.05) differentially regulated at 96 h, more
than at any other time-point. Among these 268 miRNAs, 112 were
upregulated and 85 downregulated. The 24 top deregulated miRNAs
with the lowest standard deviations are shown as a heatmap in
Fig. 1A. We performed Gene
Ontology analysis to elucidate which pathways are regulated by the
most significantly regulated miRNAs and used keywords ‘EMT’, ‘DEX’,
‘Wnt’ and ‘Smad’ to determine miRNAs associated with DEX-induced
EMT. In total, 7 of the 100 deregulated miRNAs were found to share
all of these pathways, as shown in a Venn diagram (Fig. 1B; Table I). Finally, TargetScan, miRanda,
miRwalk and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) tools were applied,
resulting in the selection of miR-132-3p with its predicted target
gene TGF-β2 as the most relevant miRNA candidate. Via RT-qPCR we
confirmed that DEX induced differential regulation of miR-132-3p,
the expression of which was upregulated at 0.5 h after DEX
treatment but downregulated at 24 h and completely inhibited at 96
h (Fig. 1C).
 | Table IPrediction of miRNA candidates by
in silico gene ontology analysis. |
Table I
Prediction of miRNA candidates by
in silico gene ontology analysis.
| miRNA | Confidence | Gene | Key pathways |
|---|
| 132-3p | High | SMAD2 | TGFβ, EMT |
| 132-3p | High | SMAD5 | TGFβ, EMT |
| 132-3p | High | GSK3β | TGFβ, Wnt, EMT |
| 132-3pa | Moderatea | TGF-β2a | TGFβ, EMTa |
| 132-3p | High | KRAS | PDA, EMT |
| 132-3p | High | MAPK1 | MAPK, EMT |
| 132-3p | High | FOXO3 | GCs |
| 1275 | Moderate | SMAD3 | SMAD, EMT |
| 1275 | Moderate | SMAD9 | SMAD, EMT |
| 210 | High | INHBB | TGFβ, EMT |
| 210 | High | ACVR1B | Wnt, EMT |
| 210 | Moderate | SOX15 | Wnt, EMT |
| 1246 | High | GSK3β | TGFβ, Wnt, EMT |
| 1246 | High | CDH2 | Cell-cell
junctions |
| 1246 | High | AXIN2 | Wnt, EMT |
| 1260b | High | Bcl2 | Apoptosis |
| 1260b | High | Akt2 | MAPK, PI3K |
| 378i | High | BMP2 | TGFβ, EMT |
| 378i | High | MAPK1/9 | MAPKs |
| 99a-5p | High | BMPR2 | Wnt, TGFβ |
DEX inhibits miR-132 expression by
promoter hypermethylation
We hypothesized that promoter hypermethylation may
play a role in the observed DEX-induced downregulation of miR-132.
Because cytosines in CpG dinucleotides are methylated to form 5-mC,
we searched for the presence of CpG islands in the miR-132 promoter
using the UCSC genome browser (https://genome.ucsc.edu) and found several upstream of
the miR-132 transcription start site (data not shown). To evaluate
the ability of DEX to induce DNA methylation, we quantified the
amount of total 5-mC using a highly sensitive, colorimetric
ELISA-based assay. PDA cells were treated or not with DEX, followed
by isolation of genomic DNA after 96 h. After DNA capture and
detection with specific antibodies, signal enhancement and color
development, absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate
spectrophotometer. With the 5-mC level in the controls set to 1,
DEX significantly enhanced 5-mC levels to ~2 in AsPC-1 and PANC-1
cells, and to 2.5 in ASAN-PaCa cells (Fig. 2A). The presence of 5-mC was also
detected by IHC in the tissues of patients with PDA (Fig. 2B and C; Table II) who had taken GCs prior to
surgery via inhalation (n=8) or oral (n=6) methods, and in the
tissues of patients with PDA who had not taken GCs (n=18). A
greater level of methylation was present in tissues from patients
who were treated with GCs relative to in tissues from patients who
did not receive GC therapy, with the highest level appearing with
oral intake, confirming the in vitro results.
 | Figure 2DEX inhibits miR-132 expression via
promoter hypermethylation. (A) AsPC-1, PANC-1 and ASAN-PaCa cells
were treated with 1 µM DEX or left untreated (CO) for 96 h.
Genomic DNA was extracted, and 5-mC levels were detected using a
5-mC DNA Elisa kit. (B) Representative paraffin sections from the
tissues of patients with documented pre-operative inhaled or oral
intake of GCs (+GC, n=14; inhaled n=8, oral n=6) or without GC
treatment (−GC, n=18) were evaluated by IHC to detect expression of
5-mC. The number of positive cells was quantified in 10 visual
fields for each group at ×400 magnification. (C) Representative
staining of tissues from patients in each group is shown. The scale
indicates 50 µm. (D) AsPC-1 and PANC-1 cells were left
untreated or treated with 1 µM DEX, 10 µM of the
demethylating agent Aza, or both. At 72 h later, genomic DNA was
extracted followed by bisulfite conversion of non-methylated
cytokine residues to uracil. PCR was performed with two primer
pairs targeting the CpG island located at 497-540 bp of the miR-132
promoter. The first primer pair detected a band 120 bp in size in
the presence of methylcytosine residues (+), whereas the second
primer pair amplified this region only in the presence of uracil
residues (−). The amplified DNA was separated by agarose gel
electrophoresis, and the bands were visualized by ethidium bromide
staining, UV-transillumination and photography. The results from
parts A and B are shown as the means ± SD. *P<0.05.
DEX, dexamethasone; miR, microRNA; CO, control/untreated; Aza,
5′-AZA-2-deoxycytidine; GC, glucocorticoids. |
 | Table IIPDA patient tissues: Expression
levels and medication. |
Table II
PDA patient tissues: Expression
levels and medication.
| Patient no. | GC | Intake | Dose/d | 5-mC (%) | TGF-β2 |
|---|
| 1 | − | − | − | / | ++ |
| 2 | − | − | − | / | +++ |
| 3 | − | − | − | 3.4 | + |
| 4 | − | − | − | 11.3 | ++ |
| 5 | − | − | − | 5.2 | ++ |
| 6 | − | − | − | 8.3 | + |
| 7 | − | − | − | 3.7 | +++ |
| 8 | − | − | − | 9.8 | + |
| 9 | − | − | − | / | ++ |
| 10 | − | − | − | 6.4 | + |
| 11 | − | − | − | 6.1 | + |
| 12 | − | − | − | 6.88 | + |
| 13 | − | − | − | 8.75 | ++ |
| 14 | − | − | − | 18.45 | +++ |
| 15 | − | − | − | 8.61 | + |
| 16 | − | − | − | 8.34 | ++ |
| 17 | − | − | − | 6.54 | ++ |
| 18 | − | − | − | 3.92 | +++ |
| 19 | − | − | − | 8.51 | − |
| 20 | − | − | − | 5.41 | − |
| 21 | − | − | − | 5.44 | + |
| | | | 7.50 | ++ |
| 22 |
Beclometasonedipropionate | Inhalation | 100 µg | | |
|
Fluticasonefuroate | Inhalation | 27.5 µg | 5.81 | ++ |
| 23 | Budesonide | Inhalation | 3 mg | 14.95 | +++ |
| 24 |
Beclometasonedipropionate | Inhalation | 100 µg | | |
|
Fluticasonefuroate | Inhalation | 27.5 µg | 12.26 | ++ |
| 25 | Fluticasone | Inhalation | 250 µg | 20.43 | ++ |
| 26 | Budesonide | Inhalation | 200 µg | 8.46 | ++ |
| 27 |
Fluticasonefuroate | Inhalation | 100 µg | 4.8 | +++ |
| 28 | Budesonide | Inhalation | 400 µg | 2.37 | + |
| 29 |
Beclometasonepropionate | Inhalation | 100 µg | 7.44 | + |
| | | | 9.57 | ++ |
| 30 | Prednisone | Oral | 40 mg | 9.06 | ++ |
| 31 | Prednisolone | Oral | 5 mg | 15.43 | +++ |
| 32 | Prednisolone | Oral | 3 mg | 16.24 | +++ |
| 33 | Prednisolone | Oral | 6 mg | 10.07 | ++ |
| 34 | Prednisolone | Oral | 50 mg | 31.49 | +++ |
| 35 | Prednisolone | Oral | 5 mg | 10.03 | +++ |
| | | | 15.49 | +++ |
To examine whether DEX methylates the miR-132
promoter, we performed methylation-specific PCR using primers for
the CpG-rich portion upstream of the miR-132 promoter located at
497-540 bp. Cells were treated with DEX or left untreated, followed
by total DNA isolation 96 h later. The extracted DNA was treated
with bisulfite to convert the cytokine residues to uracil, leaving
5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. For the PCR reaction, we used
a specific methylation primer pair that selectively amplifies the
CpG-rich region containing methylated cytosine residues. In
parallel, an unmethylated primer pair was used to amplify this
region only if the non-methylated cytokine residues were reverted
to uracil residues by bisulfite. The PCR products were separated by
agarose gel electrophoresis, and representative results are shown
(Fig. 2D). Although untreated
AsPC-1 and PANC-1 cells yielded a band when using the unmethylated
primer pair, cells treated with DEX yielded a strong band when
using the methylated primer pair, which was suggestive of
DEX-induced hypermethylation of the miR-132 promoter. These data
indicate that methylation of the miR-132 promoter plays a role in
decreased miR-132 expression.
miR-132 targets TGF-β2
To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms by
which miR-132 regulates TGF-β2 expression, we examined whether
miR-132 directly binds to the TGF-β2 3′UTR region (Fig. 3A), which contains a putative
binding site for miR-132, as identified by TargetScan. Based on a
wt pLightSwitch™- TGF-β2-3′UTR luciferase vector, we mutated the
target site of the TGF-β2-3′UTR region to create the mt
pLightSwitch™-TGF-β2-3′UTR luciferase plasmid. AsPC-1, PANC-1 and
ASAN-PaCa cells were transfected with the wt and mt pLightSwitch-
TGF-β2-3′UTR constructs in the presence of miR-132 mimics. At 48 h
after transfection, a luciferase reaction was performed, and
luciferase activity was quantified using a luminescence microplate
reader. We found that in all cell lines, miR-132 markedly reduced
the luciferase reporter activity of the wt- but not the mt-TGF-β2
3′UTR construct (Fig. 3B).
Furthermore, miR-132 significantly inhibited expression of the
TGF-β2 protein in PANC-1 cells, as shown by western blot analysis
(Fig. 3C). To evaluate clinical
significance, expression of TGF-β2 was examined in tissue samples
from patients with PDA who had received inhaled (n=8) or oral (n=6)
GCs prior to surgery, and in tissues from patients with PDA who had
not received GCs (n=20). With the use of a semi-quantitative
scoring system, we detected higher expression of TGF-β2 in the
tissues of patients who had received GCs compared with tissues from
those who had not. There was a slight though insignificant increase
in expression in tissues from those who had received oral GCs
compared with those who had received inhaled GCs (Fig. 3D; Table II). We also assessed the
expression of miR-132 in patient tissues by in situ
hybridization. Although expression of miR-132 was detectable in
both groups (Fig. 3E), we were
unable to perform a quantitative analysis. Due to a lack of
suitable patient tissue, we could not evaluate miR-132 expression
by RT-qPCR. Nevertheless, expression of miR-132 and TGF-β2 in
patient tissue underlines the potential clinical significance of
our in vitro data.
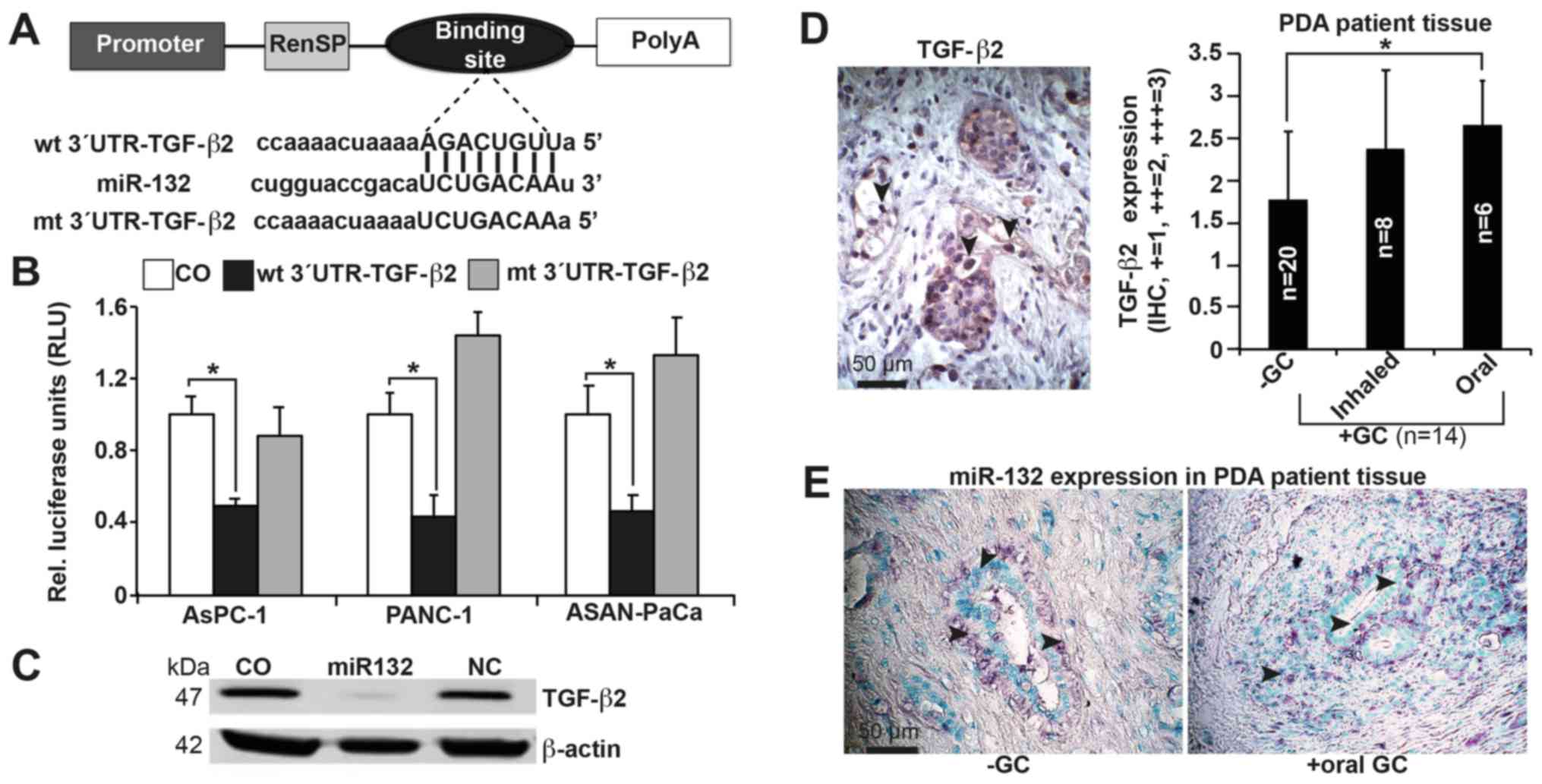 | Figure 3miR-132 binds to the 3′UTR of TGF-β2
to inhibit its expression. (A) Schematic of the miR-132 binding
site in the TGF-β2 3′UTR at position 746-753 and its sequence
homology to miR-132. The mutant version of the TGF-β2 3′UTR is
shown. (B) The wt and mt TGF-β2 3′UTRs were cloned into a
pLightSwitch Renilla plasmid and transfected into AsPC-1,
PANC-1 and ASAN-PaCa cells in the presence or absence of 50 nM
miR-132 mimics. Negative mimics served as a control.
Co-transfection with Firefly luciferase (0.25 ng/µl) served
as a normalization control. At 48 h after transfection, the
expression of Renilla and Firefly luciferases was detected
using a FLUOstar Omega microplate reader. Renilla luciferase
activities were normalized to Firefly luciferase activities. (C)
PANC-1 cells were transfected with miR-132 or non-coding miRNA
(NC), or mock-treated without miRNA (CO). Proteins were harvested
48 h later and analyzed by western blotting. β-actin served as the
normalization control. (D) Representative paraffin-embedded PDA
tissue sections from patients with documented pre-operative intake
of inhaled (n=8) or oral (n=6) GCs (+GC, n=14) and from those
without GC intake (−GC, n=20) were evaluated by IHC to detect the
expression of TGF-β2. A semi-quantitative scoring system was used
to evaluate expression levels based on visual determination of the
percentage of positive cells. The sections were analyzed at ×400
magnification, and representative images are shown. (E) In
situ hybridization of miR-132 expression in patient tissues.
The arrows indicate positive cells. Representative results for part
B are shown as the means ± SD. *P<0.05. UTR,
untranslated region; wt, wild-type; mt, mutant/mutated; miR,
microRNA; CO, control/untreated; GC, glucocorticoids. |
miR-132 reverses DEX-induced
clonogenicity, migration and proliferation
To examine the role of miR-132 and its target gene
TGF-β2 in DEX-induced EMT and CSC signaling, we performed
colony-forming assays, which allowed us to evaluate the influence
of miR-132 on clonogenicity as a typical stem cell feature. Cells
were transfected with miR-132 mimics or non-coding control mimics,
and then either treated with DEX 8 h later or left untreated. At 48
h after DEX treatment, the cells were seeded at a clonogenic
concentration, followed by evaluation of colony formation 14 days
later. Untreated control cells and cells treated with control
mimics formed colonies, and DEX enhanced the colony number.
However, miR-132 mimics strongly inhibited both basal and
DEX-induced colony formation (Fig.
4A). Similar results were obtained in wound-healing assays,
wherein miR-132 completely inhibited basal and DEX-induced PANC-1
cell migration into the wounded region (Fig. 4B). Similarly, miR-132 attenuated
basal and DEX-enhanced cell viability and cell number, as measured
by a luminescence-based viability assay (Fig. 4C) and the quantification of cell
numbers with a Coulter counter (Fig.
4D), respectively.
 | Figure 4Cancer progression features are
inhibited by miR-132. (A) AsPC-1, PANC-1 and ASAN-PaCa cells were
transfected with 50 nM miR-132 mimics or a negative miR control
(NC). At 8 h later, the cells were treated with 1 µM DEX in
the presence or absence of miR-132. After 48 h, the cells were
resuspended in complete medium and plated at a low clonogenic
density in 6-well tissue culture plates. After 14 days,
colony-forming assays were performed and evaluated as described in
the materials and methods. (B) PANC-1 cells were transfected as
aforementioned. At 48 h after transfection, the cells were seeded
at a high density in ibidi culture insert 24-well plates. After 24
h, once the cells had attached and reached ~90% confluency, the
inserts were removed to leave a defined 500-µm-thick
scratch. Images of the cell-free gap were obtained immediately (0
h), and at 24 and 48 h after removal of the inserts. (C) PANC-1
cells were treated as afore-described, and cell viability was
measured using a RealTime-Glo™ MT Cell Viability Assay. (D) The
number of PANC-1 cells was determined by the use of a Coulter
counter after 24, 48 and 72 h of treatment. Data are presented as
the means ± SD. *P<0.05. DEX, dexamethasone; NC,
negative miR control. |
These results were also reflected by the expression
patterns of EMT markers, as assessed by RT-qPCR. miR-132 mimics
significantly inhibited DEX-induced expression of the mesenchymal
marker vimentin and significantly activated basal and DEX-inhibited
expression of the epithelial marker E-cadherin (Fig. 5A). By contrast, transfection with
antisense mimics targeting miR-132 upregulated E-cadherin and
downregulated vimentin expression, regardless of the presence of
DEX. These results were confirmed by western blot analysis
(Fig. 5B).
miR-132 inhibits tumor growth in
vivo
For in vivo evaluation, we used the CAM
xenotransplantation model. Prior to xenotransplantation, ASAN-PaCa
cells were transfected with miR-132 or negative control mimics,
followed by the application of DEX 24 h later, which was added to
both untreated and miR-132-transfected cells. At 48 h
post-transfection, 5×105 cells per egg were transplanted
onto the CAM at day 8 of chick development (n=25 eggs per group).
On day 14 of embryonic development, 50 nM miR-132 mimics, negative
control mimics, DEX in saline or saline alone was injected into the
CAM vessels supplying the tumor xenografts. On day 18, the chick
embryos were humanely euthanized, followed by resection of the
tumor xenografts and determination of their volume by calipers.
Large tumor xenografts developed in the groups treated with the
negative control mimics or DEX alone, whereas the tumor sizes in
the miR-132 groups were significantly smaller (Fig. 6A). Notably, the mean weight of the
chick embryos in the DEX-treated group was ~10 g and thus one-third
lower than that of the control embryos (15 g) (Fig. 6B). This change in embryo weight
suggests that DEX interferes with embryonic development, as already
shown in humans (34). It may be
assumed that the tumor volumes of the DEX-treated group would have
been much higher when relative to a normal body weight. However,
in vivo treatment with miR-132 normalized the body weight
despite the presence of DEX. To highlight these results, we
examined the xenograft sections by IHC. DEX treatment was
associated with increased proliferation, as indicated by Ki-67
expression and enhanced TGF-β2 expression (Fig. 6C). Both the basal and DEX-induced
expression patterns of Ki-67 and TGF-β2 were strongly suppressed in
the presence of miR-132. Similarly, the low expression of
E-cadherin was restored in the presence of miR-132, and the high
expression of vimentin was inhibited. Nonetheless, the effect of
DEX on the basal expression levels of E-cadherin and vimentin was
difficult to quantify in vivo.
 | Figure 6miR-132 suppresses cancer features
in vivo. (A) ASAN-PaCa cells were treated as described in
Fig. 4A. At 48 h later,
5×105 viable cells were transplanted to the CAM of
fertilized chicken eggs at day 8 of embryonic development. After 10
days, the tumors were resected, and the volumes were determined
using calipers; the results are presented as single dots in the
diagram. The means of each group are presented as a line.
Representative images of xenografts are shown above the diagrams;
*P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (B)
Representative images of the chicks from each group and the mean
weights are shown. (C) IHC staining of the human proliferation
marker Ki-67 in frozen xenograft sections. Positive cells appear
red-dark red. Similarly, expression of TGF-β2 (green), E-cadherin
(green), and vimentin (red) was detected by immunofluorescence
staining and counterstaining of cell nuclei with DAPI (blue).
Sections were analyzed under ×400 magnification, and representative
images are shown. CAM, chorioallantoismembrane; IHC,
immunohistochemistry; TGF, transforming growth factor. |
Discussion
The present study is based on our recent finding
that DEX meditates PDA progression through its actions on the GC
receptor, TGF-β and JNK/AP1 (4)
Here, we evaluate the mechanism underlying DEX-induced upregulation
of TGF-β. Because a number of studies have suggested that miRNAs
are important mediators of GC signaling (35,36),
we performed miRNA microarray analysis and identified several
significantly DEX-deregulated miRNAs, with miR-132 as the top
down-regulated candidate. Through in silico analysis and
luciferase reporter assays, we identified TGF-β2 as a target gene
and demonstrated the direct binding of miR-132 to the TGF-β2 3′UTR
region, which was responsible for the observed inhibition of TGF-β2
expression. Consequently, inhibition of miR-132 by DEX led to the
upregulation of TGF-β2 expression. This DEX-induced regulation of
TGF-β2 is an important finding because TGF-β2 is a main component
of the TGF-β signaling cascade and mediator of EMT and cancer
progression (37,38).
In general, TGF-β acts as a tumor suppressor in
normal and pre-malignant cells; during progression, however, cancer
cells lose the suppressive effect of TGF-β, which then increases
expression of growth factors and thereby promotes differentiation,
invasion and metastasis (37,39).
We presume that dysregulation of miR-132 and its target gene TGF-β
might begin early in cancer development with the upregulation of
miR-132-3p and downregulation of TGF, based on our RT-qPCR results
after 0.5 h of DEX treatment. miR-132-3p might be gradually
downregulated during cancer progression until its complete
inhibition in the advanced stages, as suggested by our RT-qPCR
results after 24 and 96 h of DEX treatment. This conclusion is
underlined by our observation that miR-132 overexpression led to
strong inhibition of DEX-induced clonogenicity, migration, and
proliferation as well as modulation of E-cadherin and vimentin
expression patterns. These in vitro data were confirmed
in vivo, whereby overexpression of miR-132 inhibited tumor
xenograft growth and normalized expression of TGF-β2, vimentin, and
E-cadherin. Most importantly, miR-132 abolished the observed
DEX-induced reduction in chick embryo weight and body size. Birth
weight reduction caused by administration of synthetic GCs during
pregnancy to improve fetal lung maturity in threatened preterm
birth is a well-known problem (40), which may be overcome by
co-application with miR-132 as a future treatment option.
Although GC-induced miRNA signaling in PDA has not
been well studied to date, the idea that miRNA signaling may be
regulated by GCs is not new. For example, Zhao et al
(35) demonstrated the importance
of the miR-221-222 family in DEX-induced drug resistance in
multiple myeloma, and Kim et al (36) reported that miR-124 is an
attractive therapeutic target for overcoming GC resistance in
lymphoma. Nevertheless, the effect of DEX on global miRNA
expression and the phenotype resulting from this deregulation in
PDA has never been evaluated, to the best of our knowledge. Thus,
our study provides pioneer data. Our genome-wide microarray
analysis of miRNA changes in response to DEX identified 268
significant candidates. The top deregulated miRNAs, including
miR-210, miR-378i, miR-125a-5p, miR-132 and miR-1260b, have all
been reported to have important roles in regulating such processes
as cell growth, angiogenesis, migration, invasion, proliferation,
and apoptosis in different human tumor models (41-45).
Among the significant candidates identified, we validated
miR-132-3p as the most significantly downregulated miRNA, because,
according to bioinformatics target prediction algorithms,
miR-132-3p is a target for key genes in important signaling
pathways. This miRNA is produced from the miR-212/132 cluster, and
miR-132-3p has been reported to be deregulated in several
malignancies. Its function appears to be complicated: miR-132-3p
has been described as oncogenic in pancreatic, breast, and
colorectal cancers (46), but as
tumor suppressive in osteosarcoma, prostate, non-small cell lung,
and ovarian cancers (47). In PDA,
overexpression of miR-132 has been suggested to play a role in
tumor progression by targeting the patched 1 (PTCH1) receptor in
the Hedgehog pathway (48). In
accordance with our findings, Kawashima et al (49) previously showed that DEX inhibits
miR-132 expression in the brain, which was considered to lead to
the suppression of invasion and metastasis. In agreement with our
results, Zheng et al (50)
showed that miR-132 regulates EMT in colorectal cancer via direct
binding to the 3′UTR region of ZEB2, a transcriptional suppressor
of E-cadherin, which has a role in EMT.
Overall, only a limited number of studies have
attempted to explain the mechanisms of miRNA differential
regulation by GCs. In this regard, Smith et al (51) reported that Dicer repression in
response to GCs was responsible for the reduced expression of
certain miRNA candidates. We found a high-density CpG island in the
miR-132 promoter region and observed a 2-fold global increase in
DNA methylation in response to DEX, indicating the widespread
silencing of several genes, as described previously (7). Specific analysis of the miR-132
promoter region revealed hypermethylation after DEX treatment;
indeed, miR-132 expression was restored by a demethylating agent.
Correspondingly, another study on prostate cancer showed that the
miR-132 promoter is regulated by hypermethylation, which results in
reduced expression (52).
In conclusion, the present study identified
DEX-induced inhibition of miR-132 as a novel mediator of EMT and
cancer progression in PDA, suggesting that the overexpression of
miR-132 is a potential novel treatment option for basal and
DEX-induced PDA progression.
Abbreviations:
|
DEX
|
dexamethasone
|
|
GC
|
glucocorticoid
|
|
JNK
|
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
|
|
PDA
|
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
|
|
TGF-β2
|
transforming growth factor-β2,3′UTR,
3′ untranslated region
|
Acknowledgments
We thank the microarray unit of the Genomics and
Proteomics Core Facility of the German Cancer Research Center
(DKFZ) Heidelberg for providing Illumina Whole-Genome Expression
BeadChips and associated services. We are also grateful to Dr W.
Gross for providing Histo 3.0 customized image analysis software
and to Heiner Sähr, Jutta Mohr and Sebastian Faus for excellent
technical assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the German
Cancer Aid (grant no. Deutsche Krebshilfe 111299), the German
Research Council (grant no. DFG HE 3186/15-1), the Federal Ministry
of Education and Research (grant no. BMBF 031A213), the
Heidelberger Stiftung Chirurgie, Dietmar Hopp-Stiftung, and the
Hanns (A) Pielenz-Stiftung. The tissue bank of our clinic
(PancoBank) was funded by the Heidelberger Stiftung Chirurgie, the
Federal Ministry of Education and Research (grant no. BMBF
01GS08114) and the Biomaterial Bank Heidelberg/BMBH (grant no. BMBF
01EY1101).
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to submit this publication. This
manuscript has not been published, and it is not under
consideration for publication elsewhere.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this
article are included within the article; data not shown are
available from the corresponding author upon reasonable
request.
Authors’ contributions
IH, AA, OS: Concept and design. AA, CN, NB, ZZ, JF,
JG: Development of the methodology. AA, JG: Acquisition of the
data. AA, AB, WG, LL: Analysis and interpretation of the data. AA,
IH: Writing, review and/or revision of the manuscript.
Ethical approval and consent to
participate
Patient materials were obtained with the approval of
the Ethical Committee of the University of Heidelberg after
receiving written informed consent from each patient. Diagnoses
were established according to conventional clinical and
histological criteria set by the World Health Organization (WHO).
All surgical resections were conducted as indicated by the
principles and practice of oncological therapy.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ryan DP, Hong TS and Bardeesy N:
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 371:2140–2141. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pufall MA: Glucocorticoids and cancer. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 872:315–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu L, Aleksandrowicz E, Schönsiegel F,
Gröner D, Bauer N, Nwaeburu CC, Zhao Z, Gladkich J, Hoppe-Tichy T,
Yefenof E, et al: Dexamethasone mediates pancreatic cancer
progression by glucocorticoid receptor, TGFβ and JNK/AP-1. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e30642017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Herr I and Pfitzenmaier J: Glucocorticoid
use in prostate cancer and other solid tumours: Implications for
effectiveness of cytotoxic treatment and metastases. Lancet Oncol.
7:425–430. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Volden PA and Conzen SD: The influence of
glucocorticoid signaling on tumor progression. Brain Behav Immun.
30(Suppl): S26–S31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Herr I, Ucur E, Herzer K, Okouoyo S,
Ridder R, Krammer PH, von Knebel Doeberitz M and Debatin KM:
Glucocorticoid cotreatment induces apoptosis resistance toward
cancer therapy in carcinomas. Cancer Res. 63:3112–3120.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Puhr M, Hoefer J, Eigentler A, Ploner C,
Handle F, Schaefer G, Kroon J, Leo A, Heidegger I, Eder I, et al:
The glucocorticoid receptor is a key player for prostate cancer
cell survival and a target for improved antiandrogen Therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:927–938. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Iversen HG and Hjort GH: The influence of
corticoid steroids on the frequency of spleen metastases in
patients with breast cancer. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand.
44:205–212. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sherlock P and Hartmann WH: Adrenal
steroids and the pattern of metastases of breast cancer. JAMA.
181:313–317. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Melhem A, Yamada SD, Fleming GF, Delgado
B, Brickley DR, Wu W, Kocherginsky M and Conzen SD: Administration
of glucocorticoids to ovarian cancer patients is associated with
expression of the anti-apoptotic genes SGK1 and MKP1/DUSP1 in
ovarian tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3196–3204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan D, Kocherginsky M and Conzen SD:
Activation of the gluco-corticoid receptor is associated with poor
prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res.
71:6360–6370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong ET, Lok E, Gautam S and Swanson KD:
Dexamethasone exerts profound immunologic interference on treatment
efficacy for recurrent glioblastoma. Br J Cancer. 113:16422015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hirai H, Tomioka H, Mochizuki Y, Oikawa Y,
Tsushima F and Harada H: Clinical course of oral squamous cell
carcinoma in patients on immunosuppressant and glucocorticoid
therapy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 75:1980–1986. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang HY, Chang YL, Cheng CC, Chao MW, Lin
SI, Pan SL, Hsu CC, Liu TW, Cheng HC, Tseng CP, et al:
Glucocorticoids may compromise the effect of gefitinib in non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:85917–85928. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sørensen HT, Mellemkjaer L, Nielsen GL,
Baron JA, Olsen JH and Karagas MR: Skin cancers and non-hodgkin
lymphoma among users of systemic glucocorticoids: A
population-based cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:709–711.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dietrich K, Schned A, Fortuny J, Heaney J,
Marsit C, Kelsey KT and Karagas MR: Glucocorticoid therapy and risk
of bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 101:1316–1320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu M, Xu Z, Wang K, Wang N and Li Y:
microRNA and gene networks in human pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett.
6:1133–1139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi M, Du L, Liu D, Qian L, Hu M, Yu M,
Yang Z, Zhao M, Chen C, Guo L, et al: Glucocorticoid regulation of
a novel HPV-E6-p53-miR-145 pathway modulates invasion and therapy
resistance of cervical cancer cells. J Pathol. 228:148–157. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heller A, Angelova AL, Bauer S, Grekova
SP, Aprahamian M, Rommelaere J, Volkmar M, Janssen JW, Bauer N,
Herr I, et al: Establishment and characterization of a novel cell
line, ASAN- PaCa, derived from human adenocarcinoma arising in
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Pancreas.
45:1452–1460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang S, Hao J, Xie F, Hu X, Liu C, Tong
J, Zhou J, Wu J and Shao C: Downregulation of miR-132 by promoter
methylation contributes to pancreatic cancer development.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1183–1189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M,
et al: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet.
37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myöhänen S, Nelkin BD
and Baylin SB: Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for
methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:9821–9826. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kallifatidis G, Rausch V, Baumann B, Apel
A, Beckermann BM, Groth A, Mattern J, Li Z, Kolb A, Moldenhauer G,
et al: Sulforaphane targets pancreatic tumour-initiating cells by
NF-kappaB-induced antiapoptotic signalling. Gut. 58:949–963. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Liu L, Fan P, Bauer N, Gladkich
J, Ryschich E, Bazhin AV, Giese NA, Strobel O, Hackert T, et al:
Aspirin counteracts cancer stem cell features, desmoplasia and
gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget.
6:9999–10015. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jørgensen S, Baker A, Møller S and Nielsen
BS: Robust one-day in situ hybridization protocol for detection of
microRNAs in paraffin samples using LNA probes. Methods.
52:375–381. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amponsah PS, Fan P, Bauer N, Zhao Z,
Gladkich J, Fellenberg J and Herr I: microRNA-210 overexpression
inhibits tumor growth and potentially reverses gemcitabine
resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 388:107–117. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fan P, Zhang Y, Liu L, Zhao Z, Yin Y, Xiao
X, Bauer N, Gladkich J, Mattern J, Gao C, et al: Continuous
exposure of pancreatic cancer cells to dietary bioactive agents
does not induce drug resistance unlike chemotherapy. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e22462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao JJ, Chu ZB, Hu Y, Lin J, Wang Z,
Jiang M, Chen M, Wang X, Kang Y, Zhou Y, et al: Targeting the
miR-221-222/PUMA/BAK/BAX pathway abrogates dexamethasone resistance
in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 75:4384–4397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim J, Jeong D, Nam J, Aung TN, Gim JA,
Park KU and Kim SW: MicroRNA-124 regulates glucocorticoid
sensitivity by targeting phosphodiesterase 4B in diffuse large B
cell lymphoma. Gene. 558:173–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Butz H, Rácz K, Hunyady L and Patócs A:
Crosstalk between TGF-β signaling and the microRNA machinery.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 33:382–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zaravinos A: The Regulatory Role of
MicroRNAs in EMT and Cancer. J Oncol. 2015.865816:2015.
|
|
39
|
Brabletz T: EMT and MET in metastasis:
Where are the cancer stem cells? Cancer Cell. 22:699–701. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Painter RC, Roseboom TJ and de Rooij SR:
Long-term effects of prenatal stress and glucocorticoid exposure.
Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 96:315–324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Tang L, Shen H, Li X, Li Z, Liu Z, Xu J,
Ma S, Zhao X, Bai X, Li M, et al: MiR-125a-5p decreases after long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR knockdown to promote cancer cell apoptosis by
releasing caspase 2. Cell Death Dis. 7:e21372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hong L, Han Y, Zhang H, Zhao Q and Qiao Y:
miR-210: A therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
17:21–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen QG, Zhou W, Han T, Du SQ, Li ZH,
Zhang Z, Shan GY and Kong CZ: MiR-378 suppresses prostate cancer
cell growth through downregulation of MAPK1 in vitro and in vivo.
Tumour Biol. 37:2095–2103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li S, Meng H, Zhou F, Zhai L, Zhang L, Gu
F, Fan Y, Lang R, Fu L, Gu L, et al: MicroRNA-132 is frequently
downregulated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of breast and acts
as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Pathol Res
Pract. 209:179–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Shahryari V, Deng G,
Tanaka Y, Tabatabai ZL and Dahiya R: Genistein downregulates
onco-miR-1260b and upregulates sFRP1 and Smad4 via demethylation
and histone modification in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
110:1645–1654. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Formosa A, Lena AM, Markert EK, Cortelli
S, Miano R, Mauriello A, Croce N, Vandesompele J, Mestdagh P,
Finazzi-Agrò E, et al: DNA methylation silences miR-132 in prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 32:127–134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fu W, Tao T, Qi M, Wang L, Hu J, Li X,
Xing N, Du R and Han B: MicroRNA-132/212 upregulation inhibits
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer
cells by targeting SOX4. Prostate. 76:1560–1570. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ma C, Nong K, Wu B, Dong B, Bai Y, Zhu H,
Wang W, Huang X, Yuan Z and Ai K: miR-212 promotes pancreatic
cancer cell growth and invasion by targeting the hedgehog signaling
pathway receptor patched-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:542014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kawashima H, Numakawa T, Kumamaru E,
Adachi N, Mizuno H, Ninomiya M, Kunugi H and Hashido K:
Glucocorticoid attenuates brain-derived neurotrophic
factor-dependent upregulation of glutamate receptors via the
suppression of microRNA-132 expression. Neuroscience.
165:1301–1311. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y,
Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC and Tong SL: miR-132 inhibits colorectal
cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6515–6522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Smith LK, Shah RR and Cidlowski JA:
Glucocorticoids modulate microRNA expression and processing during
lymphocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 285:36698–36708. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Qin J, Ke J, Xu J, Wang F, Zhou Y, Jiang Y
and Wang Z: Downregulation of microRNA-132 by DNA hypermethylation
is associated with cell invasion in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 8:3639–3648. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|