Introduction
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most
common type of mesenchymal tumor of the gastrointestinal tract
(1). The majority of GISTs test
positive for mutations in the v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline
sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KIT) gene. This leads to the
expression of CD34 or the protein marker CD117, which is also known
as the mast/stem cell growth factor receptor (SCFR) and c-Kit
(2). Approximately 60, 30 and 1–2%
of GIST cases occur in the stomach, small intestine and the colon
or rectum, respectively. GISTs of the esophagus are rare (3).
The most common presentation of GIST is bleeding of
the upper gastrointestinal tract, which may be either acute or
chronic, and results in anemia (4).
Complete surgical resection remains the best treatment option.
Unlike carcinomas, GIST does not widely infiltrate at the
microscopic level and rarely metastasizes to the lymph nodes;
therefore, local excision may be appropriate when technically
feasible.
GISTs of the duodenum occur in less than 4% of all
cases and frequently involve the descending portion (5). As the GIST grows, the central portion
becomes necrotic and forms a deeply penetrating ulcer, which may
result in hematemesis. Under the gastroscope, the tumor may appear
similar to a papilla; therefore, it is difficult to distinguish
between a patient with hemobilia and a patient with a small
duodenal GIST. In the present study, we report 2 cases of small
duodenal GIST (less than 2 cm in size), which at first were
misdiagnosed as hemobilia. The study was approved by the ethics
committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical
University. Patient consent was obtained both from the patient and
the patient’s families.
Case report
Patient 1
A 66-year-old male was admitted to The Second
Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University (Dalian, China)
with syncope. The patient presented with heartburn and melena for
17 days. There was no associated fever, dyspeptic symptoms or
localized abdominal pain and the hemoglobin level upon admission
was 29 g/l. Due to the patient’s poor condition, a blood
transfusion and a high ligation of the great saphenous vein were
conducted.
Emergent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed
bleeding from a duodenal papilla (Fig.
1), which was diagnosed as hemobilia; however, further
angiography did not support this result. Although the blood
transfusion level was increased to 12,000 ml, the hemoglobin level
remained at 41 g/l (reference range, 120–160 g/l). There was no
time to conduct other accessory examinations. To save the patient’s
life, an exploratory laparotomy was conducted. During the surgery,
numerous blood clots were identified in the second part of the
duodenum, and no bleeding was identified in the duodenal papilla. A
submucosal tumor (<2 cm) with signs of ulceration and oozing at
the upper end was revealed on the descending section of the
duodenum (Fig. 2A and B). The tumor
was <2 cm in diameter, and 1 cm from the papilla. Peritoneal
dissemination and liver metastasis were not observed.
On the basis of these observations, and since the
patient was elderly and weakening, a wedge resection was conducted.
The histopathological examination of the resected lesion revealed a
GIST. The patient did not undergo chemotherapy following surgery
and, to date, has been free from recurrence.
Patient 2
A 71-year-old female with no previous medical
history presented with a 2-month history of melena. The patient
felt nauseated, suddenly vomited ∼50 ml of blood and was
immediately taken to a local hospital.
An upper gastrointestinal endoscopy resulted in a
diagnosis of hemobilia. The patient was then transferred to The
Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University for further
treatment. From our previous experience with patient 1, we
understood that endoscopic diagnosis comprises certain limitations.
Therefore, the patient underwent barium swallow and a
contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan, which revealed a
high-density area in the descending duodenum (Fig. 3A and B).
An endoscopy was then conducted by an experienced
practitioner, who identified a tumor <2 cm in diameter following
sufficient washing of the bleeding site. The tumor revealed an area
of necrosis and ulceration, which had a similar appearance to a
duodenal papilla (Fig. 4). We
temporarily controlled the bleeding by sclerotherapy, then a wedge
resection was conducted to permanently terminate the bleeding.
During the procedure, we identified that the tumor was notably
small and located ∼1 cm from the papilla. Peritoneal dissemination
and liver metastasis were not observed.
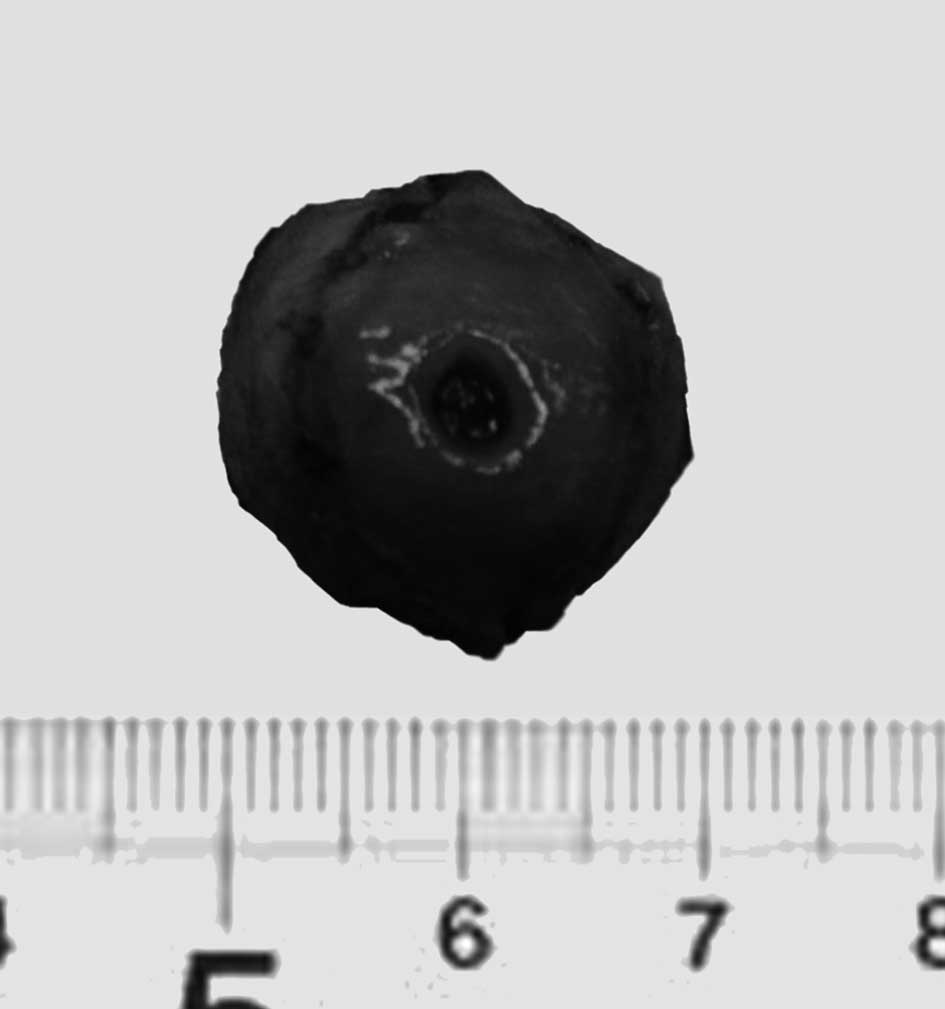
Gross examination revealed a 1.5x2.0-cm submucosal
tumor covered with blood and containing a central ulceration
(Fig. 5). Upon histopathological
examination, the resected lesion was identified as a GIST. The
patient did not undergo chemotherapy following surgery, and to
date, has been free from recurrence.
Discussion
GIST is the most common type of mesenchymal tumor,
which appears to originate from the gastrointestinal wall,
mesentery, omentum or retroperitoneum. GISTs usually occur on the
stomach or small bowel, and only 1–4% are located in the duodenum.
Depending on their size, location and the presence of mucosal
ulceration, GISTs most often present with gastrointestinal
bleeding, abdominal pain and obstructive jaundice (6).
The most typical feature of a duodenal GIST is the
formation of a deep ulceration in the mucosa or an intramural mass
with a centrally ulcerated umbilication (7). Therefore, bleeding is the most common
symptom at presentation. Bleeding may cause acute abdominal pain
and severe anemia, which may require emergency surgery. In the
presented cases, the most common symptom was anemia, and in
previous studies, anemia and gastrointestinal bleeding were
observed in 48% of cases with ulcerated lesions (8).
The gross ulceration of a GIST in the duodenum
facilitates the detection of the tumor under endoscopic
examination; however, a small duodenal tumor (less than 2 cm in
size) is easily confused with a duodenal papilla. In the presented
cases, the endoscopic diagnosis for both patients was hemobilia. In
hemobilia, acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding is one of the most
common life-threatening conditions; therefore, the sooner the cause
of bleeding is identified, the sooner the patients are out of
danger. For this reason, a complete examination should be conducted
during upper gastrointestinal bleeding to prevent misdiagnosis.
To date, there are no recognized specific
radiological examinations for duodenal GIST diagnosis; however, a
gastroscopy may be a useful procedure. Under the endoscope, it is
possible to observe the hemorrhagic area, arrest the bleeding and
conduct a biopsy. More attention should be paid to the bleeding
from the descending part of the duodenum. When there is deep
ulceration of the tumor, the endoscopic appearance may be confused
with hemobilia by an insufficiently observant gastroscopy operator,
particularly when the tumor diameter is less than 2 cm and markedly
accompanied with blood clots. The barium swallow examination may be
complementary to gastroscopy in the differential diagnosis of
hemobilia and tumor bleeding.
Contrast-enhanced CT is the standard preoperative
imaging technique. It usually exposes a mass originating from the
digestive tract wall and reveals the tumor size and presence of
secondary localizations (e.g., hepatic metastases). In patient 2,
the barium swallow examination demonstrated a filling defect,
indicating the presence of a mass causing a mucosal irregularity. A
contrast-enhanced CT scan revealed a high density lesion in the
descending part of the duodenum. Utilizing the barium swallow
examination and contrast-enhanced CT scan may help prevent a
misdiagnosis of hemobilia. Thus, a gastroscopy, contrast-enhanced
CT scan and barium swallow examination are recommended to increase
the preoperative diagnostic rate for small duodenal GISTs.
In conclusion, the two duodenal GIST (less than 2 cm
in size) cases presented were initially misdiagnosed as hemobilia.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first published
acknowledgment that such a misdiagnosis may be likely. To avoid
misdiagnosis, a gastroscopy, contrast-enhanced CT scan and barium
swallow examination should be routinely conducted.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants
from the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation Projects
(30870550) and the Chinese State Key Program in Basic Research
(2012CB822103).
References
|
1.
|
I JudsonG DemetriAdvances in the treatment
of gastrointestinal stromal tumoursAnn Oncol18Suppl
10x20x24200710.1093/annonc/mdm41017761719
|
|
2.
|
H YoshidaY MamadaN TaniaiY MizuguchiY
NakamuraT NomuraT OkudaE UchidaY FukudaM WatanabeT TajiriSpurt
bleeding from a calcificated gastrointestinal stromal tumor in the
stomachJ Nihon Med Sch72304307200510.1272/jnms.72.30416247232
|
|
3.
|
M StamatakosE DouzinasC StefanakiP
SafioleasE PolyzouG LevidouM SafioleasGastrointestinal stromal
tumorWorld J Surg Oncol761200910.1186/1477-7819-7-61
|
|
4.
|
M MiettinenJ LasotaGastrointestinal
stromal tumors: review on morphology, molecular pathology,
prognosis, and differential diagnosisArch Pathol Lab
Med130146614782009
|
|
5.
|
JC ChungCW ChuGS ChoEJ ShinCW LimHC KimOP
SongManagement and outcome of gastrointestinal stromal tumors of
the duodenumJ Gastrointest
Surg14880883201010.1007/s11605-010-1170-620140534
|
|
6.
|
R MennigenHH WoltersB SchulteFW
PelsterSegmental resection of the duodenum for gastrointestinal
stromal tumour (GIST)World J Surg
Oncol6105200810.1186/1477-7819-6-10518826622
|
|
7.
|
P GervazO HuberP MorelSurgical management
of gastrointestinal stromal tumoursBr J
Surg96567578200910.1002/bjs.660119434705
|
|
8.
|
YW NovitskyKW KercherRF SingBT
HenifordLong-term outcomes of laparoscopic resection of gastric
gastrointestinal stromal tumorsAnn
Surg243738744200610.1097/01.sla.0000219739.11758.2716772777
|