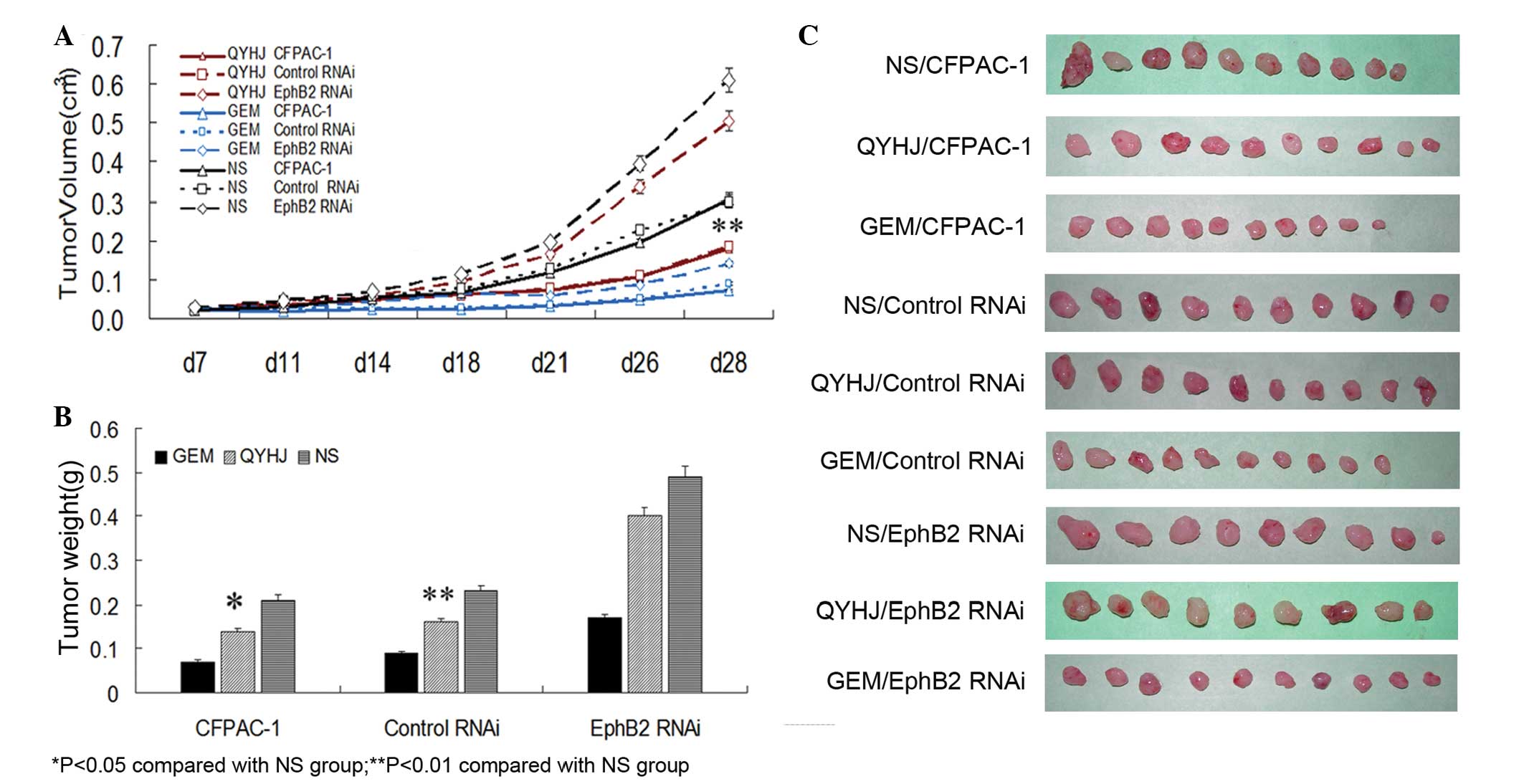
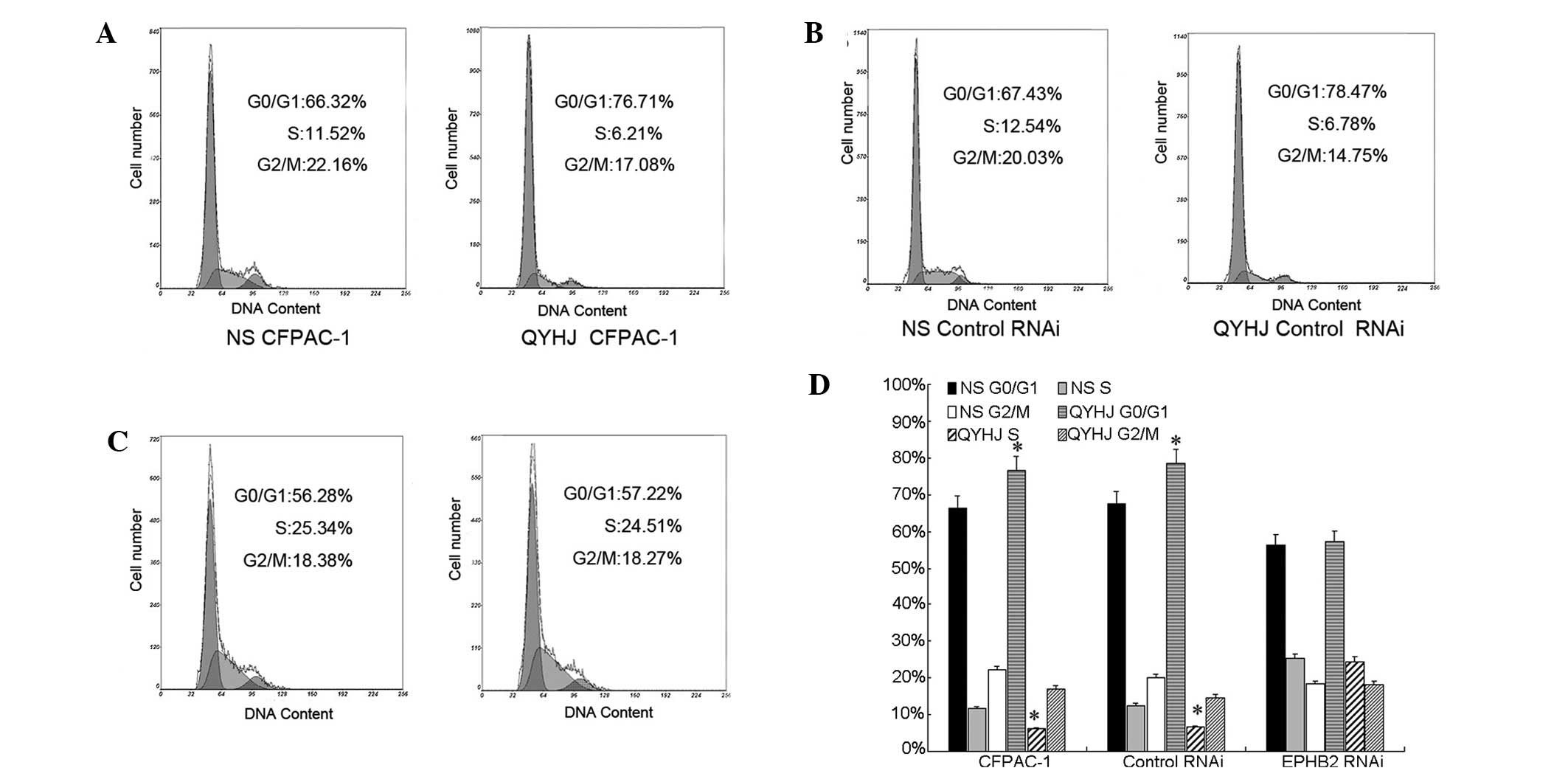
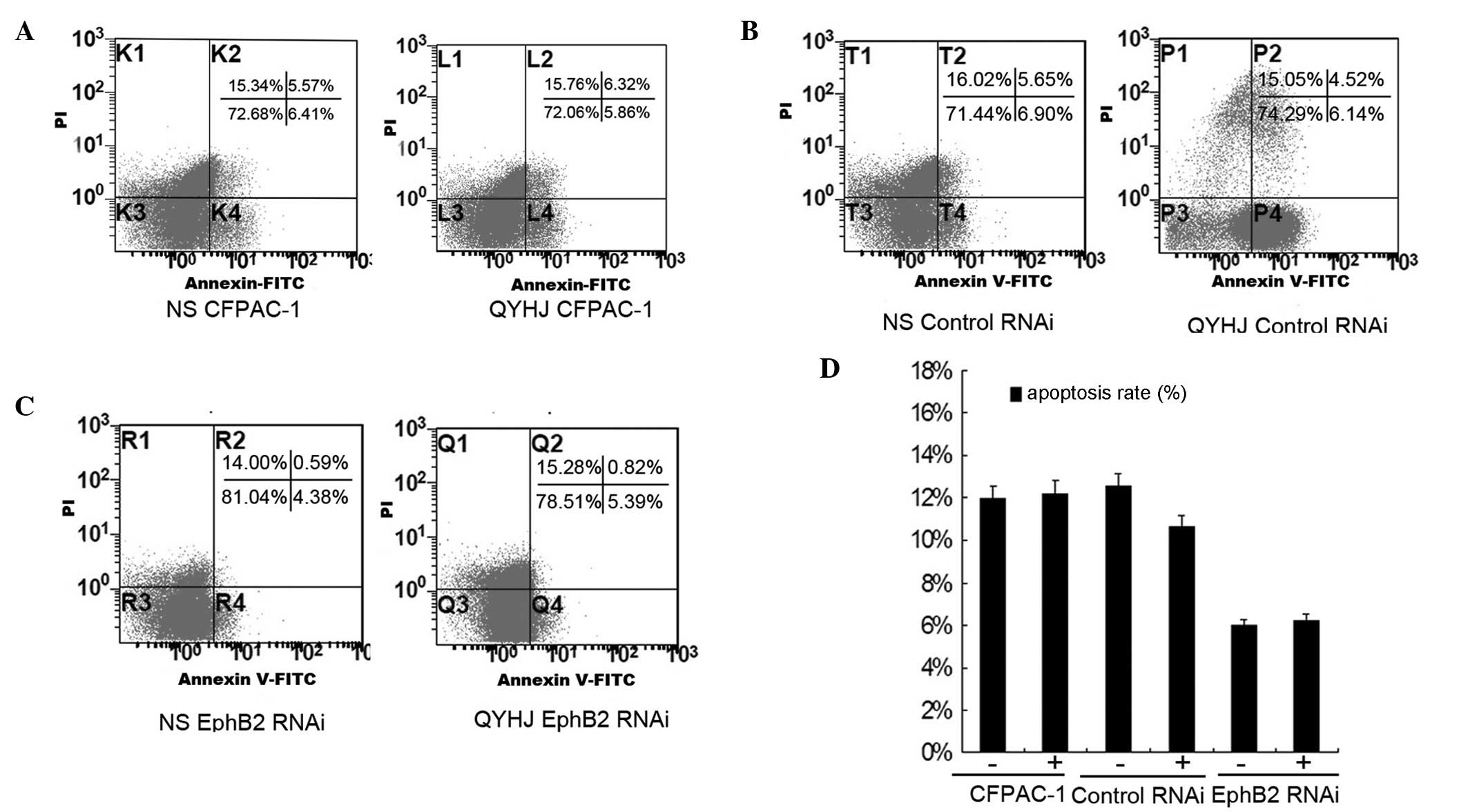
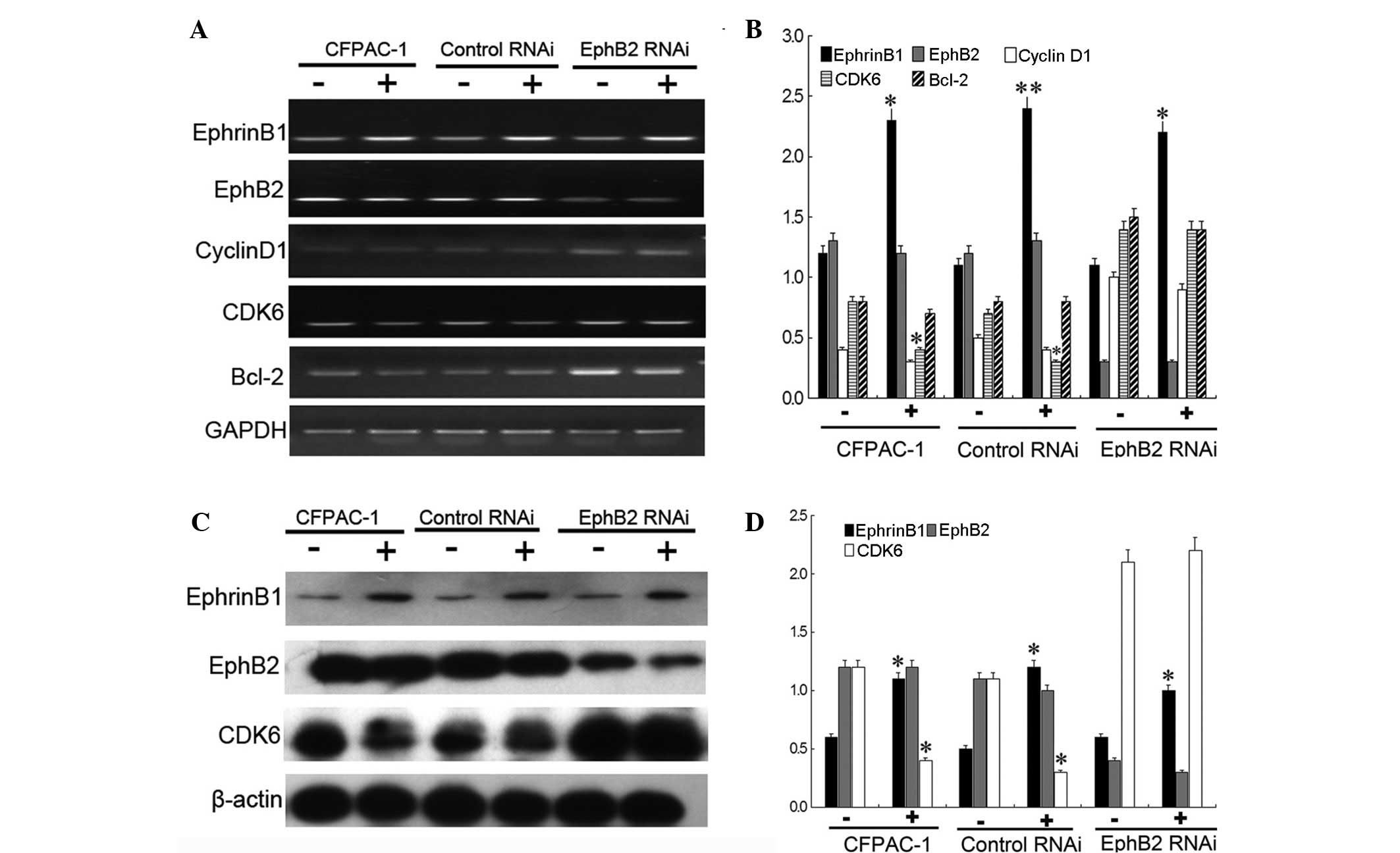
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Dai M, Ren JS, Li N, Li Q, Yang L and Chen
YH: Estimation and prediction on cancer related incidence and
mortality in China, 2008. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi.
33:57–61. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Ouyang H, Wang P, Meng Z, et al:
Multimodality treatment of pancreatic cancer with liver metastases
using chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or Chinese herbal
medicine. Pancreas. 40:120–125. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Shen YH, Liu LM, Chen Z, et al: Study on
Chinese medicine combined with chemotherapy for treatment of 32
cases of advanced pancreatic cancer. Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 47:115–117.
2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Shen YH, Liu LM, Meng ZQ, et al: Survival
analysis on 64 cases of advanced pancreatic cancer treated by
integrated Western and traditional Chinese medicine mainly with
Qingyi Huaji formula. Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 50:39–42. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Shen YH, Liu LM, Lu Y, et al: Impact of
Qingyi Xiaoji Decoction on gene expression of experimental
pancreatic cancer in vivo. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Za Zhi. 15:454–457.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Kataoka H, Tanaka M, Kanamori M, et al:
Expression profile of EFNB1, EFNB2, two ligands of EPHB2 in human
gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 128:343–348. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Wu Q, Suo Z, Risberg B, Karlsson MG,
Villman K and Nesland JM: Expression of Ephb2 and Ephb4 in breast
carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 10:26–33. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Guo DL, Zhang J, Yuen ST, et al: Reduced
expression of EphB2 that parallels invasion and metastasis in
colorectal tumours. Carcinogenesis. 27:454–464. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, et al:
Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign
human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem. 50:490–499. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Jubb AM, Zhong F, Bheddah S, et al: EphB2
is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:5181–5187. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Genander M, Halford MM, Xu NJ, et al:
Dissociation of EphB2 signaling pathways mediating progenitor cell
proliferation and tumor suppression. Cell. 139:679–692. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Batlle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, et al: EphB
receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer progression. Nature.
435:1126–1130. 2005.
|
|
14
|
Huusko P, Ponciano-Jackson D, Wolf M, et
al: Nonsense-mediated decay microarray analysis identifies
mutations of EPHB2 in human prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 36:979–983.
2004.
|
|
15
|
Yu G, Gao Y, Ni C, et al: Reduced
expression of EphB2 is significantly associated with nodal
metastasis in Chinese patients with gastric cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 137:73–80. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Hua YQ, Ouyang HQ, Chen Z, et al: Promoted
cancer growth by stimulating cell proliferation and decreasing
apoptosis using a lentivirus-based EphB2 RNAi in pancreatic
carcinoma CFPAC-1 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 65:123–131. 2011.
|
|
17
|
McCulloch M, See C, Shu XJ, et al:
Astragalus-based Chinese herbs and platinum-based chemotherapy for
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: meta-analysis of randomized
trials. J Clin Oncol. 24:419–430. 2006.
|
|
18
|
Guo H, Liu JX, Xu L, Madebo T and Baak
JPA: Traditional Chinese medicine herbal treatment may have a
relevant impact on the prognosis of patients with stage IV
adenocarcinoma of the lung treated with platinum-based chemotherapy
or combined targeted therapy and chemotherapy. Integr Cancer Ther.
10:127–137. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Schoumacher RA, Ram J, Iannuzzi MC, et al:
A cystic fibrosis pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 87:4012–4016. 1990.
|
|
20
|
Pasquale EB: Eph-ephrin bidirectional
signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 133:38–52. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Noberini R and Pasquale EB: Proliferation
and tumor suppression: not mutually exclusive for Eph receptors.
Cancer Cell. 16:452–454. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Nakada M, Niska JA, Tran NL, McDonough WS
and Berens ME: EphB2/R-Ras signaling regulates glioma cell
adhesion, growth, and invasion. Am J Pathol. 167:565–576. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Wade TP, Halaby IA, Stapleton DR, Virgo KS
and Johnson FE: Population-based analysis of treatment of
pancreatic cancer and Whipple resection: Department of Defense
hospitals, 1989–1994. Surgery. 120:680–687. 1996.
|
|
24
|
Masui T, Hosotani R, Ito D, et al: Bcl-XL
antisense oligonucleotides coupled with antennapedia enhances
radiation-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. Surgery.
140:149–160. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Reni M, Pasetto L, Aprile G, et al:
Raltitrexed-eloxatin salvage chemotherapy in gemcitabine-resistant
metastatic pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 94:785–791. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Lemke G: A coherent nomenclature for Eph
receptors and their ligands. Mol Cell Neurosci. 9:331–332.
1997.
|
|
27
|
Himanen JP and Nikolov DB: Eph signaling:
a structural view. Trends Neurosci. 26:46–51. 2003.
|
|
28
|
Gale NW, Holland SJ, Valenzuela DM, et al:
Eph receptors and ligands comprise two major specificity subclasses
and are reciprocally compartmentalized during embryogenesis.
Neuron. 17:9–19. 1996.
|
|
29
|
Lugli A, Spichtin H, Maurer R, et al:
EphB2 expression across 138 human tumor types in a tissue
microarray: high levels of expression in gastrointestinal cancers.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:6450–6458. 2005.
|
|
30
|
Li X, Yang G, Zhang Y, et al: Traditional
Chinese medicine in cancer care: a review of controlled clinical
studies published in chinese. PLoS One. 8:e603382013.
|
|
31
|
DeWitt J, Yu M, Al-Haddad MA, Sherman S,
McHenry L and Leblanc JK: Survival in patients with pancreatic
cancer after the diagnosis of malignant ascites or liver metastases
by EUS-FNA. Gastrointest Endosc. 71:260–265. 2010.
|
|
32
|
Jiang T, Kambadakone A, Kulkarni NM, Zhu
AX and Sahani DV: Monitoring response to antiangiogenic treatment
and predicting outcomes in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma using
image biomarkers, CT perfusion, tumor density, and tumor size
(RECIST). Invest Radiol. 47:11–17. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Manuyakorn A, Paulus R, Farrell J, et al:
Cellular histone modification patterns predict prognosis and
treatment response in resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: results
from RTOG 9704. J Clin Oncol. 28:1358–1365. 2010.
|
|
34
|
Lundin KB, Henningson M, Hietala M, Ingvar
C, Rose C and Jernström H: Androgen receptor genotypes predict
response to endocrine treatment in breast cancer patients. Br J
Cancer. 105:1676–1683. 2011.
|
|
35
|
Krause DS and Van Etten RA: Tyrosine
kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 353:172–187.
2005.
|
|
36
|
Shawver LK, Slamon D and Ullrich A: Smart
drugs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Cell.
1:117–123. 2002.
|
|
37
|
Chow LQ and Eckhardt SG: Sunitinib: from
rational design to clinical efficacy. J Clin Oncol. 25:884–896.
2007.
|
|
38
|
Bell DW, Lynch TJ, Haserlat SM, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and gene amplification
in non-small-cell lung cancer: molecular analysis of the
IDEAL/INTACT gefitinib trials. J Clin Oncol. 23:8081–8092.
2005.
|
|
39
|
Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Boige V, et al: KRAS
mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with
advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol.
26:374–379. 2008.
|
|
40
|
Senior PV, Zhang BX and Chan ST: Loss of
cell-surface receptor EphB2 is important for the growth, migration,
and invasiveness of a colon cancer cell line. Int J Colorectal Dis.
25:687–694. 2010.
|
|
41
|
Kandouz M, Haidara K, Zhao J, Brisson ML
and Batist G: The EphB2 tumor suppressor induces autophagic cell
death via concomitant activation of the ERK1/2 and PI3K pathways.
Cell Cycle. 9:398–407. 2010.
|