Introduction
Onychomycosis is the most common nail disease
worldwide, accounting for ~90% of all toenail infections (1). Onychomycosis can occur at any age and
is mostly common among older adults; the number of affected nails
and prevalence rate continue to increase (2). Onychomycosis is a type of disease
caused by fungal infection. Although dermatophytes are the most
common pathogen of onychomycosis, non-dermatophyte infections are
also prevalent. The transmission of onychomycosis can be caused by
direct or indirect contact, and this disease can lead to
finger/toenail discoloration, thickening, peeling, deformity, and
pain or other discomfort in patients. Therefore, it can have a
negative impact on the psychological wellbeing and the social
interactions of the patient. Currently, the treatment of this
disease remains a challenge, considering its high recurrence rate
(2). Since onychomycosis is a
chronic disease that is difficult to treat, it is important to
develop new therapeutic methods for its treatment.
Non-coding small molecule RNAs, including microRNAs
(miRNAs or miRs), are the key regulators of the gene expression
pathways and systems in various different cells (3). Previous research has shown that miRNAs
are associated with various diseases (4-7).
Circulating and exosome-derived miRNAs have been considered as
biomarkers for a number of diseases, including viral infections,
neurological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes
(7). As key regulatory factors of
gene expression, miRNA-related studies in various diseases have
been increasing and these molecules are expected to become
candidates for the development of certain biomarkers. Moreover,
miRNA mimics and miRNA inhibitors have been proven as promising
therapeutic drugs in preliminary clinical studies (8). However, it has not been determined
whether miRNAs are associated with onychomycosis and whether they
can also be used as drug targets for the treatment of
onychomycosis.
Therefore, after obtaining study approval from the
Ethics Committee of Shanghai Skin Disease Hospital (approval no.
2022-68; Shanghai, China) for the present study, the potential role
and relationship of miRNAs in onychomycosis were investigated. A
small molecule RNA-related study on patients with onychomycosis was
subsequently conducted, for the first time, to the best of the
authors' knowledge, which provides insights for future studies.
Patients and methods
Ethics statement and clinical
specimens
The present study was approved (approval no.
2022-68) by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Skin Disease Hospital
(Shanghai, China) on February 15, 2022, and was performed in
accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All samples including
those of healthy controls were obtained from patients at Shanghai
Skin Disease Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine from
February 20, 2022 to December 31, 2022 (Shanghai, China). Written
informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to the study.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were as follows: The affected
nail samples were obtained from patients with onychomycosis who
were diagnosed by clinical features and positive mycological
examination. Normal control nail samples were obtained from healthy
individuals without onychomycosis and other systemic or immune
diseases. All subjects were required to have no history of
systematic medication, 3 months prior to commencement of the sample
collection, and no history of drugs or other chemical agents
applied to the surface of the nail, 1 month prior to commencement
of the sample collection. A total of 33 affected nail samples from
onychomycosis and 18 normal nail samples from healthy individuals
were obtained. Each nail sample was stored in a separate tissue box
in a refrigerator at a temperature of -80˚C. The clinical
information of the onychomycosis and control groups are shown in
Table I. The patient cohort median
age was 47 years, and the age range was 21-72 years.
 | Table IClinical features of subjects in the
onychomycosis and control groups. |
Table I
Clinical features of subjects in the
onychomycosis and control groups.
| Feature | Affected group
(n=33) | Control group
(n=18) |
|---|
| Age (years) | 46.87±11.53 | 35.64±10.1 |
| Sex
(female/male) | 15/18 | 10/8 |
| Position
(fingernail/toenail) | 11/22 | 8/10 |
| Positive mycological
examination | 33 | - |
Nail sample preparation and RNA
extraction
The nail samples were obtained by scissors, put into
tissue boxes, and stored at a temperature of -80˚C. Moreover, the
nail clippings were further pulverized and stored at a temperature
of -80˚C. The total RNAs from the pulverized nails were extracted
using TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.), and their quality and quantity were measured
using the NanoDrop ND1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.).
Small RNA library construction and
miRNA sequencing
Purified RNA was sent to Shanghai Yingbai
Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for the construction of the small RNA
library. Nail-derived RNAs from three affected nails in
onychomycosis and three normal nails from the control group were
used for miRNA sequencing. The small RNA library was constructed
using the NEBNext Multiplex Small RNA Library Prep kit (cat. no.
E7560S; New England Biolabs, Inc.). In brief, the total RNA was
combined with 3' and 5' adapters, and complementary DNA (cDNA) was
synthesized by reverse transcription quantitative PCR. The
fragments from 135-150 bp adapters, including 120 bp adapters, were
extracted using the QIAquick gel extraction kit (cat. no. 28704;
Qiagen China Co., Ltd.). The small RNAs and the purified library
were sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencing system
(Illumina, Inc.). The loading concentration of the library was 4.71
pM and concentrations were measured using Qubit™ 3 Fluorometer
Invitrogen™ (cat. no. Q33216; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
Data analysis for miRNA
sequencing
At first, the raw sequencing data needed to be
filtered, their low-quality reads and short reads (<15 nt) were
removed, and they were subjected to quality control by fast-QC
(v0.12.1) (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/).
All clean reads were aligned to the miRbase database (http://www.mirbase.org/) to determine the known
miRNAs. The clean data was screened using EBSeq (9) to identify the differentially expressed
miRNAs between the onychomycosis and control groups in accordance
with the following criteria: Log2 fold change >1 and
false discovery rate <0.05. miRanda (https://regendbase.org/tools/miranda; selection
criteria, score ≥150 and energy <-20) and RNAhybrid (https://omictools.com/rnahybrid-tool;
selection criteria, energy <-25) (10) were used to predict the target genes
of the screened miRNAs showing significant differences. The
overlapping genes between these two databases were considered as
the final target genes. Gene Ontology (GO; http://www.geneontology.org/) and Kyoto Encyclopedia
of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg) were used to classify the
functions and pathways of the predicted target genes.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
In order to further screen miRNAs and further
confirm the association between miRNAs and onychomycosis, firstly,
six differentially expressed miRNAs, including downregulated
hsa-miR-1-3p hsa-miR-34c-5p and hsa-miR-361-3p and upregulated
hsa-miR-766-5p, hsa-miR-6767-5p, and hsa-miR-4253, were selected
for RT-qPCR in nails from 5 patients with onychomycosis and 5
healthy controls. The identified miRNAs with differences were then
further verified in another 10 controls and 25 cases. The RNAs were
reverse transcribed into cDNA using the RevertAid First Strand cDNA
Synthesis kit (cat no. K1691; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) in
accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. RT-qPCR was
conducted using the SYBR Green PCR kit (cat. no. 208054; Qiagen
China Co., Ltd.) on an ABI Q6 detection system (Applied Biosystems;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The PCR thermocycling conditions
were as follows: 95˚C for 10 min, 45 cycles of 15 sec at 95˚C and
60 sec at 60˚C. The relative calculations and quantification were
conducted with the quantitative threshold (Cq) cycle method,
2-ΔΔCq (11). U6 served
as the internal control for miRNA.
Principle for the design of stem-loop
primers
In the reverse transcription process, a stem-loop
primer that can bind to the miRNA sequence and extend the length of
miRNA had to be designed. The stem-loop primer is a primer that is
~45 bp in length and can self-loop. Every miRNA has its own
specific stem-loop primer, the most important reason for this is
that the designed stem-loop primer includes a section that is
related to the complementary sequence of the miRNA: Stem-loop
reverse transcription primer=5' end stem-loop sequence + 3' end
specific complementary sequence of miRNA.
Features of the design of stem-loop
primers
Initially, the mature miRNA sequences (5 '-3') were
found in the miRBase database, using the substitution function in
excel to replace all U in the sequence with T, in a general
universal sequence of stem ring primers such as
5'-CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGC-3' or
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGAC-3';
the italicized part of the sequence can form its own cyclization.
In addition, stem-loop primers were designed for specific miRNA.
The reverse complementary sequence of 6-8 bases (6 in general) was
added to the -3' end of the universal stem-loop primer, after the U
in the mature sequence of miRNA was replaced by T in the -3' end of
the universal stem-loop primer, so as to obtain the stem-loop
primer of a certain miRNA. The specific primer sequences are shown
in Table II.
 | Table IISequences of primers for
microRNAs. |
Table II
Sequences of primers for
microRNAs.
| Primers | Sequences |
|---|
| hsa-miR-1-3p | R:
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGATACGACATACATA-3' |
| | F:
CGCAGTGGAATGTAAAGAAG-3' |
| hsa-miR-361-3p | R:
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGATACGACAAATCAG-3' |
| | F:
5'-TCCCCCAGGTGTGATTC-3' |
| hsa-miR-766-5p | R:
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGATACGACAAGACCA-3' |
| | F: 5'-CAGAGG
AGGAATTGGTGCT-3' |
| hsa-miR-34c-5p | R:
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGATACGACGCAATCA-3' |
| | F:
5'-GCAGAGGCAGTGTAGTTAG-3' |
| hsa-miR-4253 | R:
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGATACGACACCCCCT-3' |
| | F:
5'-GCAGAGGGCATGTCCAG-3' |
| hsa-miR-6767-5p | R:
5'-GTCGTATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGATACGACTCTCCAT-3' |
| | F:
5'-CGCAGACAGGGACACA-3' |
| U6 | F:
5'-CGATACAGAGAAGATTAGCATGGC-3' |
| | R:
5'-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3' |
| IRI (Downstream
universal primer) | R:
5'-AGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCG-3' |
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS
version 12.0 statistical software (SPSS, Inc.). The quantitative
data was presented as the mean ± standard deviation and compared
via the two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. Statistical
significance was set at a P-value of <0.05. The experimental
data was obtained from at least three independent experiments.
Results
Sequencing of miRNAs from the nails of
patients with onychomycosis
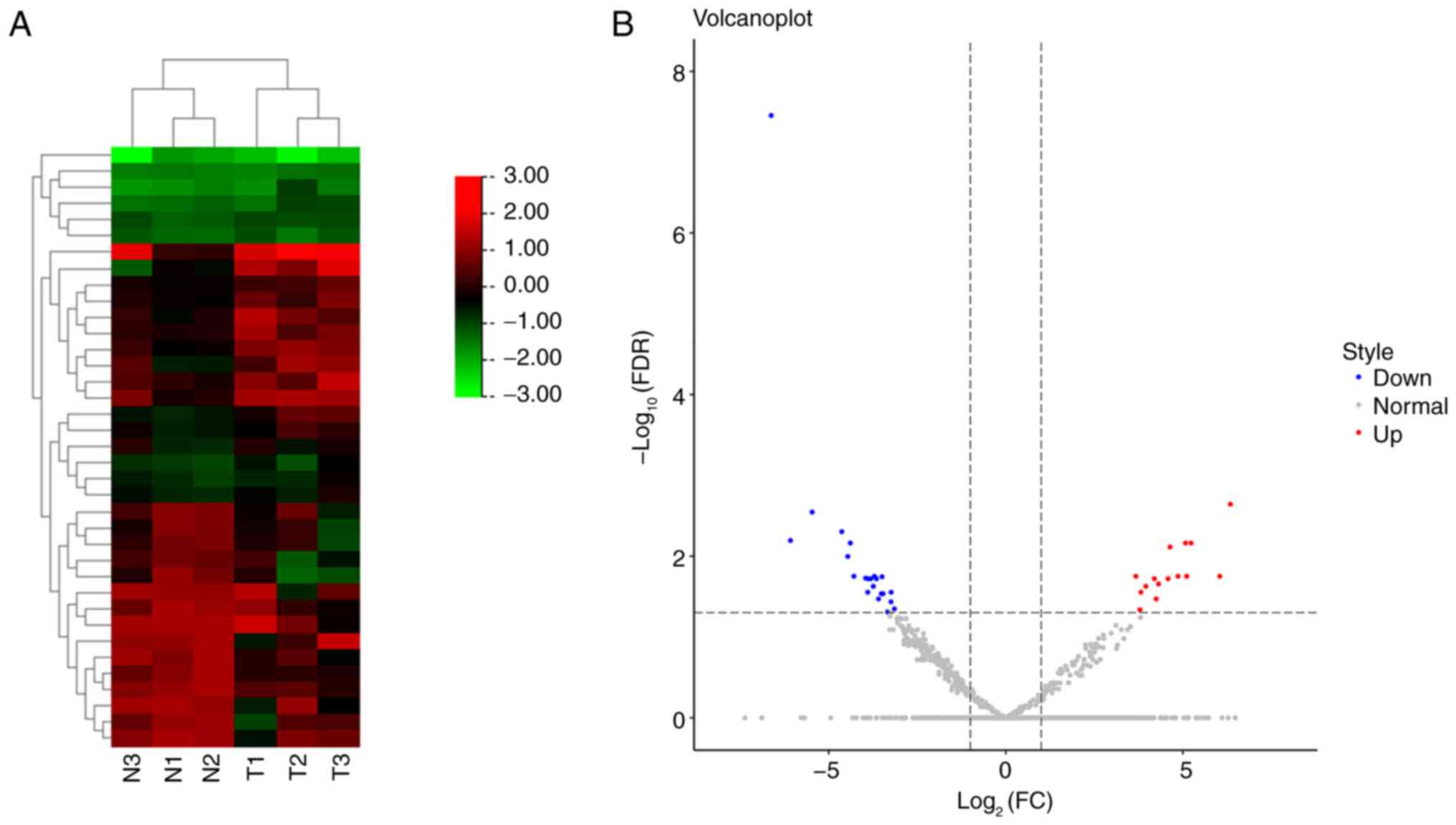
A total of 2,136 miRNAs were identified between 3
patients with onychomycosis and 3 controls, of which, 37
differentially expressed miRNAs were considered statistically
significant after screening (Fig.
1A), including 15 upregulated and 22 downregulated miRNAs, in
the onychomycosis group compared with the control group (Fig. 1B). The detailed differentially
expressed miRNAs are revealed in Table III.
 | Table IIIDifferentially expressed miRNAs
identified in onychomycosis. |
Table III
Differentially expressed miRNAs
identified in onychomycosis.
| miRNAs | log2
FC | FDR | Expression | P-value |
|---|
| hsa-miR-1-3p | -6.62285 | 3.51E-08 | Down |
7.89x10-11 |
| hsa-miR-4253 | 6.340101 | 0.002272 | Up | 0.0000102 |
| hsa-miR-34c-5p | -5.46533 | 0.00285 | Down | 0.0000192 |
| hsa-miR-361-3p | -4.62943 | 0.004969 | Down | 0.0000447 |
| hsa-miR-1248 | -6.07778 | 0.006409 | Down | 0.0000720 |
| hsa-miR-135b-5p | -4.38787 | 0.006887 | Down | 0.000101 |
| hsa-miR-6767-5p | 5.231031 | 0.006887 | Up | 0.000112 |
| hsa-miR-766-5p | 5.077687 | 0.006887 | Up | 0.000124 |
| hsa-miR-1911-3p | 4.635966 | 0.007694 | Up | 0.000156 |
| hsa-miR-10395-3p | -4.45961 | 0.010072 | Down | 0.000226 |
| hsa-miR-125a-5p | -3.70702 | 0.017771 | Down | 0.000488 |
| hsa-miR-26a-5p | -4.28808 | 0.017771 | Down | 0.000505 |
| hsa-miR-634 | 4.863213 | 0.017771 | Up | 0.000524 |
|
hsa-miR-6843-3p | 5.109063 | 0.017771 | Up | 0.000602 |
|
hsa-miR-4755-5p | 6.043341 | 0.017771 | Up | 0.000628 |
|
hsa-miR-1911-5p | 3.672735 | 0.017771 | Up | 0.000639 |
| hsa-miR-1246 | -3.49335 | 0.017979 | Down | 0.000687 |
| hsa-miR-152-3p | -3.9556 | 0.018725 | Down | 0.000757 |
|
hsa-miR-200a-3p | -3.87371 | 0.019056 | Down | 0.000855 |
|
hsa-miR-6763-5p | 4.195021 | 0.019056 | Up | 0.000864 |
| hsa-miR-101-3p | -3.80914 | 0.019056 | Down | 0.000946 |
| hsa-miR-99b-5p | -3.64934 | 0.019056 | Down | 0.000985 |
|
hsa-miR-6823-3p | 4.581339 | 0.019056 | Up | 0.000985 |
|
hsa-miR-7154-3p | 4.312293 | 0.022085 | Up | 0.001191 |
|
hsa-miR-5196-5p | 3.954891 | 0.023612 | Up | 0.00137 |
| hsa-miR-182-5p | -3.73798 | 0.023612 | Down | 0.00138 |
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | -3.23665 | 0.02792 | Down | 0.001722 |
|
hsa-miR-514a-3p | -3.89711 | 0.02792 | Down | 0.001807 |
|
hsa-miR-1234-3p | 3.816317 | 0.02792 | Up | 0.001819 |
|
hsa-miR-148a-5p | -3.51467 | 0.029162 | Down | 0.002017 |
| hsa-miR-186-5p | -3.46579 | 0.029162 | Down | 0.002032 |
| hsa-miR-769-5p | -3.59224 | 0.033852 | Down | 0.002494 |
| hsa-miR-873-3p | 4.245054 | 0.033852 | Up | 0.00251 |
| hsa-miR-28-3p | -3.2411 | 0.036765 | Down | 0.002809 |
|
hsa-miR-5585-5p | -3.14452 | 0.044994 | Down | 0.003539 |
|
hsa-miR-6800-5p | 3.787112 | 0.046003 | Up | 0.003722 |
| hsa-miR-141-3p | -3.33558 | 0.04909 | Down | 0.004082 |
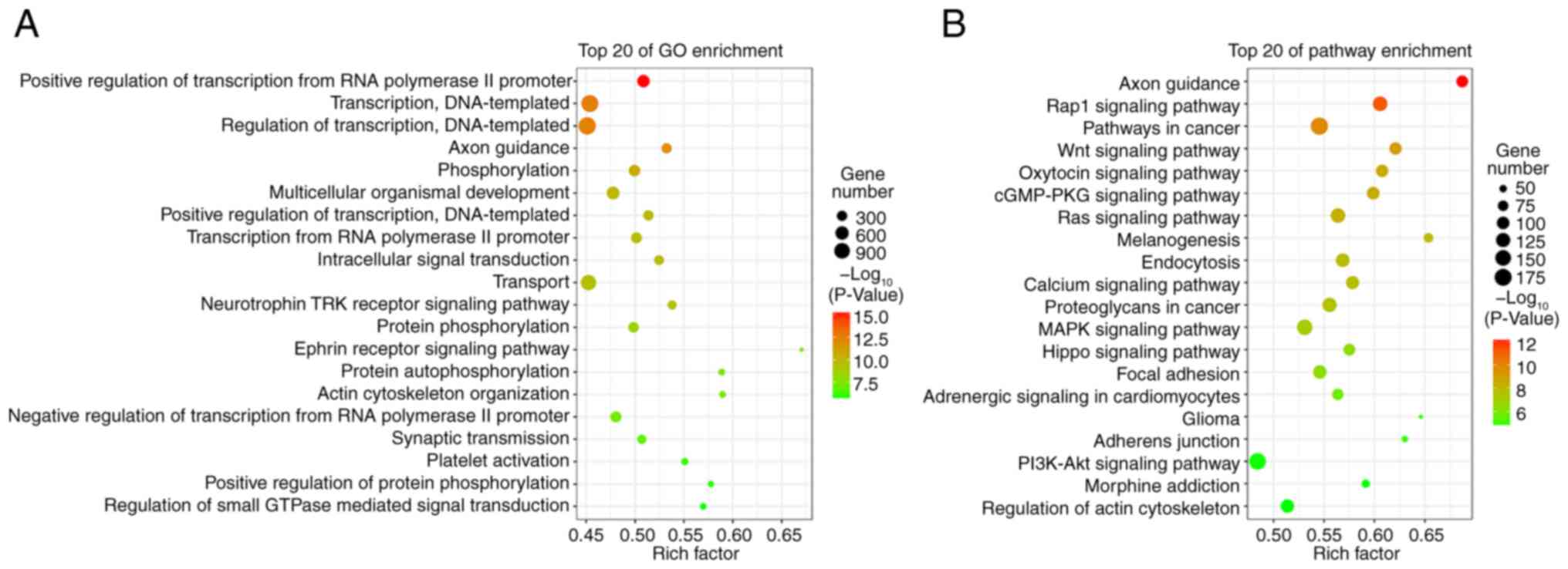
Target gene prediction and functional
analysis of differentially expressed microRNAs
A total of 14,511 target genes from 37
differentially expressed microRNAs were predicted using the miRanda
and RNAhybrid databases. The GO analysis indicated that these
target genes were enriched in the ‘positive regulation of
transcription from the RNA polymerase II promoter’, ‘transcription,
DNA-templated’, and ‘regulation of transcription, DNA-templated’
(Fig. 2A). The KEGG pathway
analysis revealed that these target genes were enriched in the
‘Rap1 signaling pathway’, ‘Wnt signaling pathway’, ‘Ras signaling
pathway’, ‘calcium signaling pathway’, and ‘MARK signaling pathway’
(Fig. 2B).
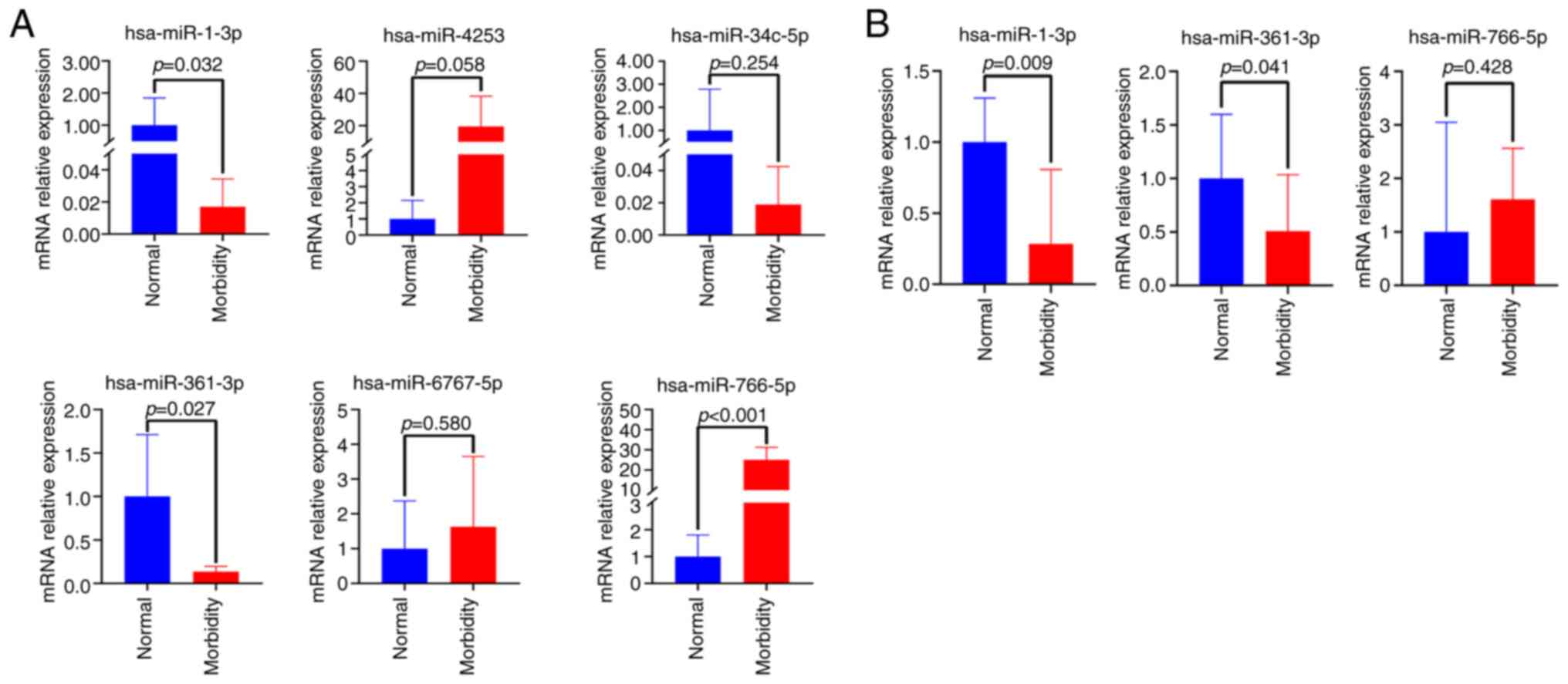
Validation of differentially expressed
miRNAs
To further screen miRNAs, six differentially
expressed miRNAs, including downregulated hsa-miR-1-3p
hsa-miR-34c-5p and hsa-miR-361-3p, and upregulated hsa-miR-766-5p,
hsa-miR-6767-5p and hsa-miR-4253, were subjected to RT-qPCR
analysis in nails from 5 patients with onychomycosis and 5 healthy
controls. As a result, three of them including hsa-miR-1-3p,
hsa-miR-361-3p and hsa-miR-766-5p exhibited significant differences
(P=0.032, P=0.027 and P<0.001, respectively; Fig. 3A). In further verification of larger
samples from 25 patients with onychomycosis and 10 healthy
controls, no differentially expressed miRNAs were detected.
However, after the removal of these samples, including the three
repetitions of the same sample, there were significant variations
among the experimental data, with some samples showing excessively
large or small deviations, while others remained indeterminate.
Notably, downregulated hsa-miR-1-3p and hsa-miR-361-3p exhibited
significant differences in expression (P=0.009 and P=0.041,
respectively; Fig. 3B). These
results indicated that the expression of hsa-miR-1-3p and
hsa-miR-361-3p in onychomycosis might be downregulated compared
with control group.
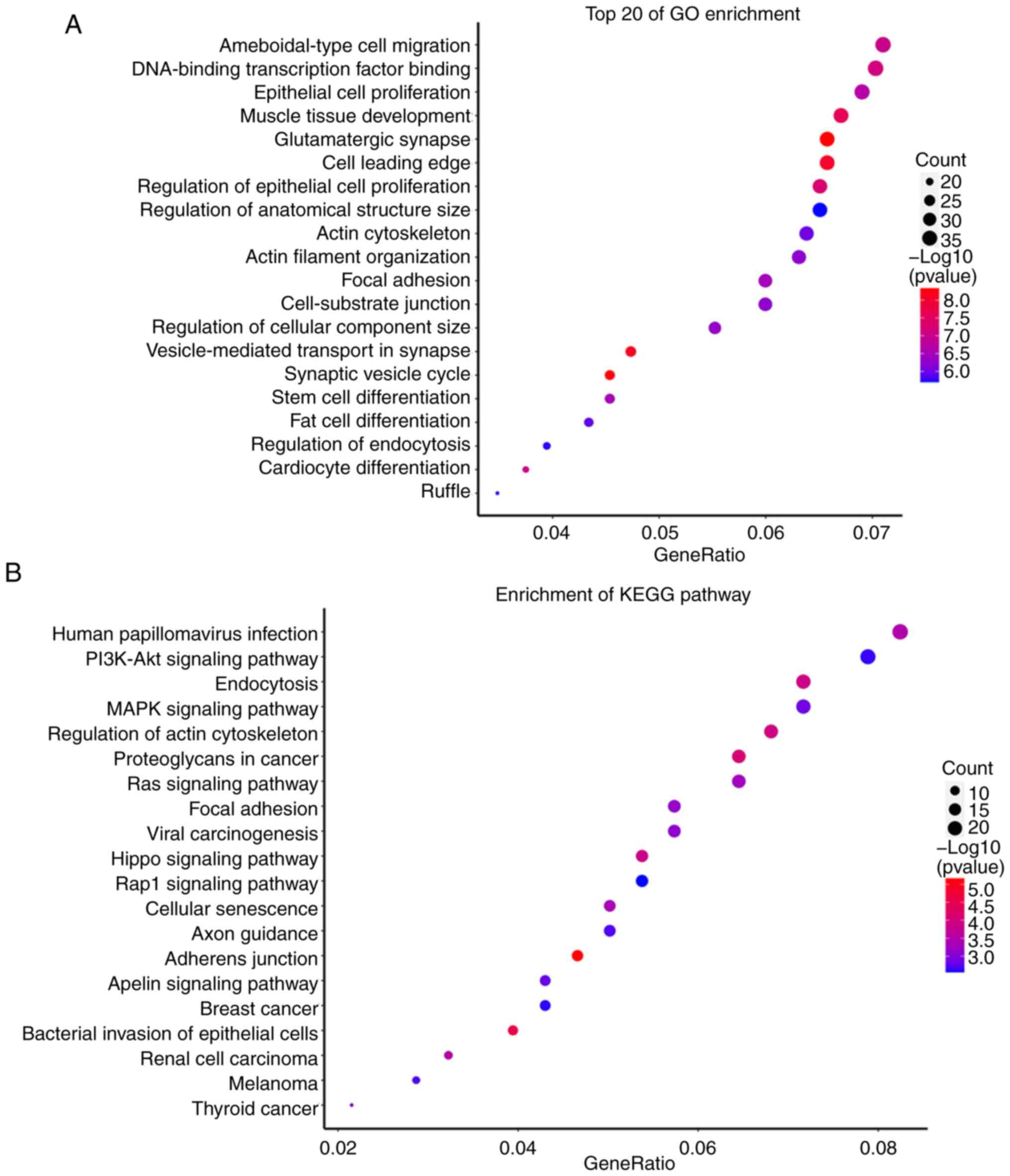
Target gene prediction and functional
analysis of hsa-miR-1-3p and hsa-miR-361-3p
A total of 544 target genes from hsa-miR-1-3p and
604 target genes from hsa-miR-361-3p were predicted by the miRanda
and RNAhybrid databases. The GO and KEGG analyses showed that these
target genes were enriched in multiple signaling pathways as shown
in Figs. 4 and 5.
Discussion
Onychomycosis is commonly caused by fungal
infections and has a high prevalence. Since its treatment remains a
challenge, new treatment methods need to be developed. miRNAs are
small non-coding RNAs that usually bind with mRNA targeting their
3-UTR and regulating gene expression at the pre-transcription
level. The dysregulation of miRNAs ultimately leads to
differentially expressed profiles of other miRNAs and their target
genes. Moreover, miRNAs have been suggested to be involved in
various functions, such as impact on the immune system, apoptosis,
cellular proliferation and differentiation, and the cellular stress
response (12). In the last decade,
previous research (4-7)
has shown that miRNAs might be involved in multiple biological and
pathological processes in various diseases, and can be considered
as potential biomarkers for a number of diseases and targets in the
treatment of various diseases. miRNAs may also be used as a
treatment option or can be implemented in the treatment strategies
for onychomycosis. Therefore, studies that focus on miRNAs are
required to determine their potential contribution to the treatment
of onychomycosis.
The is the first RNA-related study on patients with
onychomycosis that has been conducted, to the best of the authors'
knowledge, and 37 differentially expressed miRNAs from nail
clippings were identified. Thus, an initial miRNA panel of
onychomycosis is presented, which may aid in future research. GO
and KEGG analyses revealed that the targets of these 37 miRNAs were
enriched in multiple functional pathways, including ‘axon
guidance’, ‘Wnt signaling pathway’, ‘calcium signaling pathway’,
‘Rap1 signaling pathway’, and the ‘ephrin receptor signaling
pathway’ (Fig. 2), suggesting the
potential role of miRNAs in the treatment of onychomycosis. Further
RT-qPCR verification results showed that the expression of
hsa-miR-1-3p and hsa-miR-361-3p in onychomycosis was downregulated
compared with the control group. However, further studies with
larger sample sizes are needed, to confirm these results.
Research has shown that has-miR-1-3p and T-synthase
mRNA could be considered as independent risk factors for the
patients with intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction with severe
acute pancreatitis, and can facilitate the diagnosis of intestinal
mucosal barrier dysfunction in patients with severe acute
pancreatitis (13). In addition, a
number of studies have reported the role of has-miR-1-3p in various
cancers, such as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (14), breast cancer (15), and lung adenocarcinoma (16). In the present study, GO and KEGG
analyses suggested that the targets of has-miR-1-3p were enriched
in ‘human papillomavirus infection’, ‘bacterial invasion of
epithelial cells’, ‘breast cancer’, and ‘thyroid cancer’ (Fig. 4). The results of the present
analysis were consistent with those of the previous studies
aforementioned and also suggested that has-miR-1-3p may have a
potential role in the pathogenesis of the fungal infection of
onychomycosis, and might be a potential biomarker for
onychomycosis. However, further research is required to confirm the
potential role of has-miR-1-3p in onychomycosis.
hsa-miR-361-3p has been revealed to inhibit the
progression of lymphoma via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
(17), and to promote colorectal
cancer progression by targeting the TRAF3-mediated noncanonical
NF-κB pathway (18) as well as
human breast cancer cell viability by suppressing the E2F1/P73
signaling pathway (19). Moreover,
hsa-miR-361-3p was overexpressed in the oral squamous cell
carcinoma tissues, and targeting hsa-miR-361-3p may be a useful
therapeutic approach for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
(20). In the present study, GO and
KEGG analyses showed that the targets of has-miR-361-3p were
enriched in ‘pathogenic Escherichia coli infection’ and
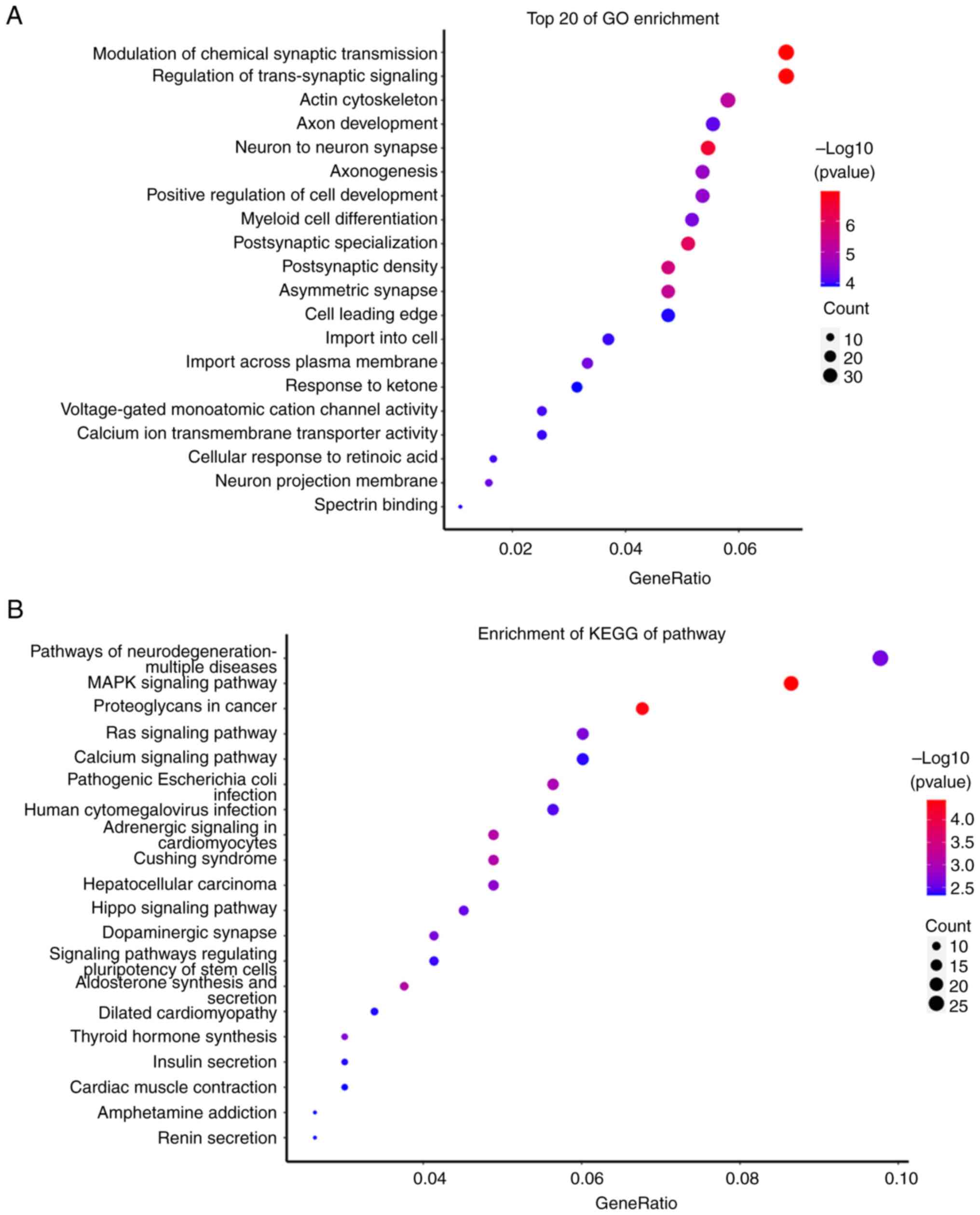
‘human cytomegalovirus infection’ (Fig.
5). It is known that onychomycosis is a disease caused by
fungal infections. Therefore, the results of the present study
indicated that hsa-miR-361-3p may be a potential biomarker for
patients with onychomycosis and could be involved in
infection-related pathways in onychomycosis. Considering the
limitations of the present study, further research is still needed
to determine the potential role of hsa-miR-361-3p in patients with
onychomycosis.
Of note, the current study has several limitations.
Firstly, the sample size was relatively small. Therefore, in the
interpretation of the results, the possibility of a beta error may
exist and lead to the lack of significance. Thus, future studies
with larger sample sizes are needed. Secondly, some differences in
the weight of each sample were observed between the patient and the
control groups, potentially introducing data bias in the data
analysis, although the concentration which was detected, was not
influenced by the weight of the sample. Moreover, the samples used
in the present study were obtained from the nail clippings of
affected nails and healthy nails. For the most part, affected nails
tend to be relatively thick, rendering it easy to acquire a large
weight of nail clipping sample. However, normal healthy nails are
relatively thin, and a low weight of nail clipping was obtained.
Thirdly, the nail clippings obtained from individuals were used to
only perform RNA sequencing and RT-qPCR. Therefore, more
experiments and testing methods are needed to further confirm and
clarify the potential role of miRNAs in patients with
onychomycosis. Finally, the present study was just an initial
investigation, the experimental design was relatively simple, and
no other in-depth functional pathway studies were conducted.
Regardless of the limitations, a differential
expression miRNA panel of onychomycosis was provided in the present
study, and it was revealed that hsa-miR-1-3p and hsa-miR-361-3p
were downregulated in the onychomycosis group compared with the
control group, which suggested that hsa-miR-1-3p and hsa-miR-361-3p
might be potential biomarkers for onychomycosis. The present study
was an initial investigation of potential miRNAs in onychomycosis,
and a larger sample size and additional functional analyses are
required, to further provide a more comprehensive and accurate
understanding of this topic.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be found
in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession nos. SUB14485829
(Submission ID) and PRJNA1117633 (BioProject ID) or at the
following URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/1117633.
Authors' contributions
LM and QC were involved with the conception and
design of the study, as well as manuscript writing, editing, and
acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. LM and QC confirm
the authenticity of all the raw data. HZ and ZG were involved with
the collection of clinical data. LY was involved with study
conception, supervision and manuscript revision. All authors read
and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of Shanghai Skin Disease Hospital (approval no. 2022-68;
Shanghai, China), and all subjects have signed the written informed
consent.
Patient consent for publication
All subjects have provided written informed consent
for the publication of any associated data and accompanying
images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Vlahovic TC: Onychomycosis: Evaluation,
treatment options, managing recurrence, and patient outcomes. Clin
Podiatr Med Surg. 33:305–318. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gupta AK, Stec N, Summerbell RC, Shear NH,
Piguet V, Tosti A and Piraccini BM: Onychomycosis: A review. J Eur
Acad Dermatol Venereol. 34:1972–1990. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hombach S and Kretz M: Non-coding RNAs:
Classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol.
937:3–17. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: Diagnostic,
functional, and therapeutic roles of microRNA in allergic diseases.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 132:3–13. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Miranda KC, Bond DT, McKee M, Skog J,
Paunescu TG, Da Silva N, Brown D and Russo LM: Nucleic acids within
urinary exosomes/microvesicles are potential biomarkers for renal
disease. Kidney Int. 78:191–199. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mendt M, Kamerkar S, Sugimoto H, McAndrews
KM, Wu CC, Gagea M, Yang S, Blanko EVR, Peng Q, Ma X, et al:
Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic
cancer. JCI Insight. 3(e99263)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Chen J and Sen S: MicroRNA as
Biomarkers and Diagnostics. J Cell Physiol. 231:25–30.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Leng N, Dawson JA, Thomson JA, Ruotti V,
Rissman AI, Smits BM, Haag JD, Gould MN, Stewart RM and Kendziorski
C: EBSeq: An empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in
RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics. 29:1035–1043. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kruger J and Rehmsmeier M: RNAhybrid:
MicroRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34:W451–W454. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rozalski M, Rudnicka L and Samochocki Z:
MiRNA in atopic dermatitis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 33:157–162.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu WB, Jiang XF and Chen MQ: microRNA-1-3p
and T-synthase mRNA have high diagnostic efficacy on intestinal
mucosal barrier dysfunction in patients with severe acute
pancreatitis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 39:732–739. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Liu M, Jin H, Peng B, Dai L, Wang
S, Xing H, Wang B and Wu Z: Synthetic evaluation of MicroRNA-1-3p
expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on
microarray chips and MicroRNA Sequencing. Biomed Res Int.
2021(6529255)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tao S, Li H, Ma X, Ma Y, He J, Gao Y and
Li J: Elevating microRNA-1-3p shuttled by cancer-associated
fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles suppresses breast cancer
progression and metastasis by inhibiting GLIS1. Cancer Gene Ther.
28:634–648. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lin Q: MicroRNA-1-3p affects lung
adenocarcinoma progression through E2F8 and regulating NF-кB
pathwayy. Cytokine. 156(155922)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhou H, Tang H, Li N, Chen H, Chen X, Gu
L, Zhang L, Tian G and Tao D: MicroRNA-361-3p inhibit the
progression of lymphoma by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Cancer Manag Res. 12:12375–12384. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li J, Yang P, Chen F, Tan Y, Huang C, Shen
H, Peng C, Feng Y and Sun Y: Hypoxic colorectal cancer-derived
extracellular vesicles deliver microRNA-361-3p to facilitate cell
proliferation by targeting TRAF3 via the noncanonical NF-κB
pathways. Clin Transl Med. 11(e349)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hua B, Li Y, Yang X, Niu X, Zhao Y and Zhu
X: MicroRNA-361-3p promotes human breast cancer cell viability by
inhibiting the E2F1/P73 signalling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
125(109994)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ogawa H, Nakashiro KI, Tokuzen N,
Kuribayashi N, Goda H and Uchida D: MicroRNA-361-3p is a potent
therapeutic target for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
111:1645–1651. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|