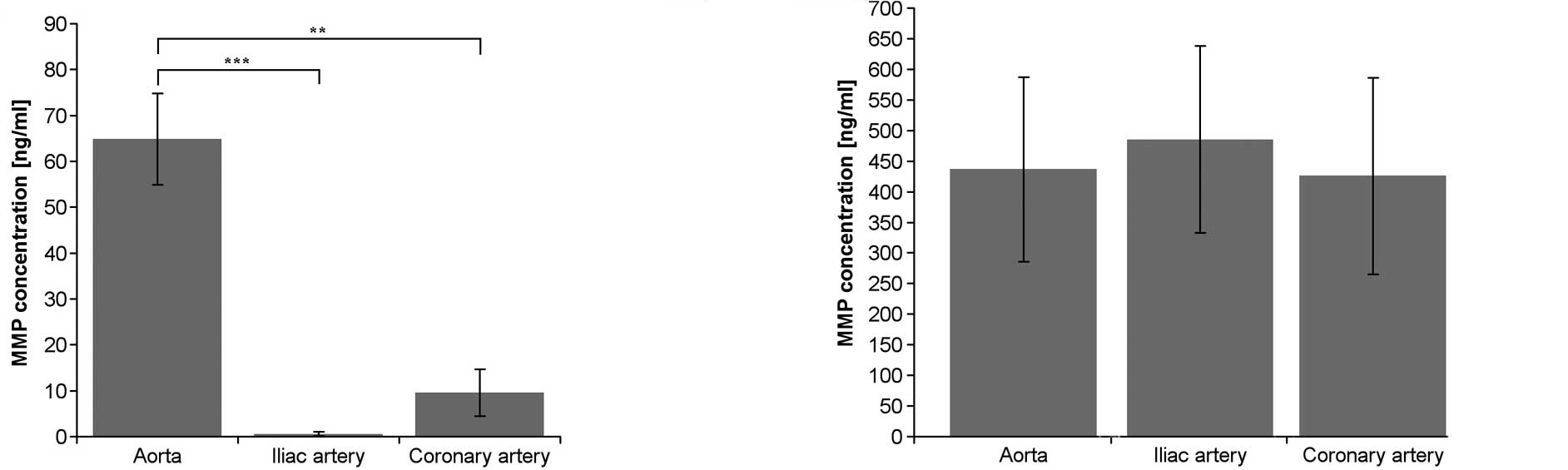
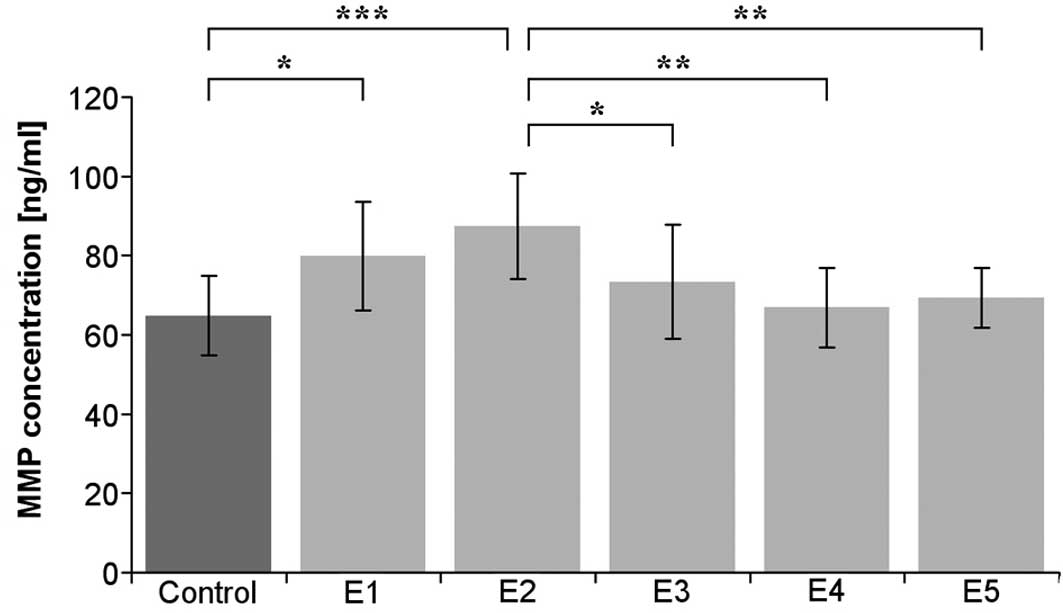
|
1.
|
Visse R and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases:
structure, function and biochemistry. Circ Res. 92:827–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Nagase H and Woessner JF: Matrix
metalloproteases. J Biol Chem. 274:21491–21494. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis – an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999.
|
|
4.
|
Palombo D, Maione M, Cifiello BI, Udini M,
Maggio D and Lupo M: Matrix metalloproteinases. Their role in
degenerative chronic diseases of abdominal aorta. J Cardiovasc
Surg. 40:257–260. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Pearce WH and Shively VP: Abdominal aortic
aneurysm as a complex multifactorial disease: interactions of
polymorphisms of inflammatory genes, features of autoimmunity, and
current status of MMPs. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1085:117–132. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Nishimura K, Ikebuchi M, Kanaoka Y, Ohgi
S, Ueta E, Nanba E and Ito H: Relationships between matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in
the wall of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Int Angiol. 22:229–238.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ishii T and Asuwa N: Collagen and elastin
degradation by matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of
matrix metalloproteinases in aortic dissection. Hum Pathol.
31:640–646. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Annabi B, Shedid D, Ghosm P, Kenigsberg
RL, Desrosiers RR, Bojanowski MW, Beaulieu E, Nassif E, Moumdjian R
and Béliveau R: Differential regulation of matrix metalloproteinase
activities in abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 35:539–546.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CNB, Brewer
HB, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC and Stone NJ;
for the Coordinating Committee of the National Cholesterol
Education Program: Implications of recent clinical trials for the
National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III
Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:720–732. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Hornebeck W and Robert L: Elastase-like
enzymes in aortas and human breast carcinomas: quantitative
variations with age and pathology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 79:145–156.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Gminski J and Drozdz M: Succinyl
trialanine p-nitroanilide hydrolytic activities in plasma and the
aorta of rabbits experimentally immunized with soluble elastin. Exp
Pathol. 43:37–40. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Faury G, Ristori MT, Verdetti J, Jacob MP
and Robert L: Effect of elastin peptides on vascular tone. J Vasc
Res. 32:112–119. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Faury G, Garnier S, Weiss AS, Wallach J,
Fülöp T Jr, Jacob MP, Mecham RP, Robert L and Verdetti J: Action of
tropoelastin and synthetic elastin sequences on vascular tone and
on free Ca2+ level in human vascular endothelial cells.
Circ Res. 82:328–336. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Robert L, Labat-Robert J and Robert AM:
Genetic, epigenetic and posttranslational mechanisms of aging.
Biogerontology. 11:387–399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Jackson CJ and Nguyen M: Human
microvascular endothelial cells differ from macrovascular
endothelial cells in their expression of matrix metalloproteinases.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 29:1167–1177. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Basu P, Sen U, Tyagi N and Tyagi SC: Blood
flow interplays with elastin: collagen and MMP: TIMP ratios to
maintain healthy vascular structure and function. Vasc Health Risk
Manag. 6:215–228. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Burridge KA and Friedman MH: Environment
and vascular bed origin influence differences in endothelial
transcriptional profiles of coronary and iliac arteries. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 299:H837–H846. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Aboyans V, Lacroix P and Criqui MH: Large
and small vessel atherosclerosis: similarities and differences.
Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 50:112–125. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Galis ZS, Sukhova GK, Lark MW and Libby P:
Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases and matrix
degrading activity in vulnerable regions of of human
atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest. 94:2493–2503. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Feldman LJ, Mazighi M, Scheuble A, Deux
JF, De Benedetti E, Badier-Comander C, Brambilla E, Henin D, Steg
PG and Jacob MP: Differential expression of matrix
metalloproteinases after stent implantation and balloon angioplasty
in the hypercholesterolemic rabbit. Circulation. 103:3117–3122.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Tummers AM, Mountain DJ, Mix JW,
Kirkpatric SS, Cassada DC, Stevens SL, Freeman MB, Goldman MH and
Grandas OH: Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2 as a marker
of intimal hyperplasia. J Surg Res. 160:9–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Yasmin, McEniery CM, Wallace S, Dakham Z,
Pulsalkar P, Maki-Petaja K, Ashby MJ, Cockcroft JR and Wilkinson
IB: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), MMP-2, and serum elastase
activity are associated with systolic hypertension and arterial
stiffness. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:3722005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Friese RS, Rao F, Khandrika S, Thomas B,
Zielgler MG, Schmid-Schönbein GW and O'Connor DT: Matrix
metalloproteinases: discrete elevations in essential hypertension
and hypertensive end-stage renal disease. Clin Exp Hypertens.
31:521–533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Qin X, Corriere MA, Matrisian LM and
Guzman RJ: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition attenuates aortic
calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:1510–1516. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Kieffer P, Giummelly P, Schjoth B,
Carteaux JP, Villemot JP, Hornebeck W and Atkinson J: Activation of
metalloproteinase-2, loss of matrix scleroprotein content and
coronary artery calcification. Atherosclerosis. 157:251–254. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Pauly RR, Passaniti A, Bilato C, et al:
Migration of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells through a
basement membrane barrier requires type IV collagenase activity and
is inhibited by cellular differentiation. Circ Res. 75:41–54. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Reeps C, Pelisek J, Seidl S, Schuster T,
Zimmermann A, Kuehnl A and Eckstein HH: Inflammatory infiltrates
and neovessels are relevant sources of MMPs in abdominal aortic
aneurysm wall. Pathobiology. 76:243–252. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|