|
1.
|
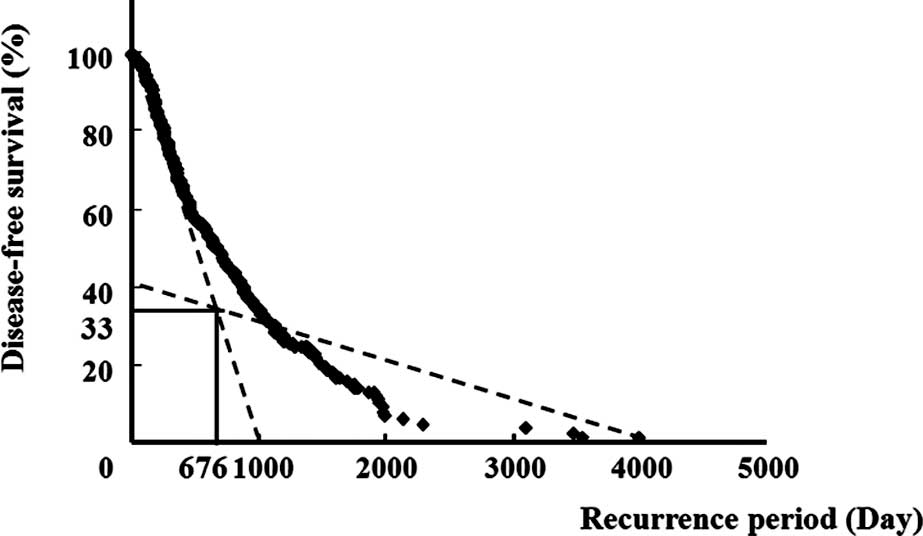
Ikai I, Arii S, Okazaki M, et al: Report
of the 17th Nationwide follow-up survey of primary liver cancer in
Japan. Hepatol Res. 37:676–691. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Makuuchi M, Takayama T, Kubota K, et al:
Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma – Japanese
experience. Hepatogastroenterology. 45(Suppl 3): 1267–1274.
1998.
|
|
3.
|
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, et al:
Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J
Hepatol. 38:200–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Lo CM, Liu CL and
Wong J: Different risk factors and prognosis for early and late
intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer. 89:500–507. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Honda M, Kaneko S, Kawai H, Sirota Y and
Kobayashi K: Differential gene expression between chronic hepatitis
B and C hepatic lesion. Gastroenterology. 120:955–966. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Okabe H, Satoh S, Kato T, et al:
Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in human hepatocellular
carcinomas using cDNA microarray: identification of genes involved
in viral carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Cancer Res.
61:2129–2137. 2001.
|
|
7.
|
Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, et al:
Differential gene expression in distinct virologic types of
hepatocellular carcinoma: association with liver cirrhosis.
Oncogene. 22:3007–3014. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumours (UICC). 6th edition.
Wiley-Liss; New York: pp. 81–83. 2002
|
|
9.
|
Hosida Y, Villanueva A, Kobayashi M, et
al: Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:2045–2047. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Tsuchiya M, Parker JS, Kono H, Matsuda M,
Fujii H and Rusyn I: Gene expression in nontumoral liver tissue and
recurrence-free survival in hepatitis C virus-positive
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 9:742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ko S, Kanehiro H, Hisanaga M, Nagao M,
Ikeda N and Nakajima Y: Liver fibrosis increases the risk of
intrahepatic recurrence after hepatectomy for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Br J Surg. 89:57–62. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Wakai T, Shirai Y, Yokoyama N, Nagakura S
and Hatakeyama K: Hepatitis virus status affects the pattern of
intrahepatic recurrence after resection for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 29:266–271. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Shah SA, Cleary SP, Wei AC, et al:
Recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: risk
factors, treatment, and outcomes. Surgery. 141:330–339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Regimbeau JM, Abdalla EK, Vauthey JN, et
al: Risk factors for early death due to recurrence after liver
resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a multicenter
study. J Surg Oncol. 85:36–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ijichi M, Takayama T, Matsumura M,
Shiratori Y, Omata M and Makuuchi M: α-fetoprotein mRNA in the
circulation as a predictor of postsurgical recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study. Hepatology.
35:853–860. 2002.
|
|
16.
|
Chen JY, Chau GY, Lui WY, Tsay SH, King KL
and Wu CW: Clinicopathologic features and factors related to
survival of patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma after
hepatic resection. World J Surg. 27:294–298. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Shirabe K, Kanematsu T, Matsumata T,
Adachi E, Akazawa K and Sugimachi K: Factors linked to early
recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy:
univariate and multivariate analyses. Hepatology. 14:802–805. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Guenzi E, Töpolt K, Lubeseder-Martellato
C, et al: The guanylate binding protein-1 GTPase controls the
invasive and angiogenic capability of endothelial cells through
inhibition of MMP-1 expression. EMBO J. 15:3772–3782. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Guenzi E, Töpolt K, Cornali E, et al: The
helical domain of GBP-1 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell
proliferation by inflammatory cytokines. EMBO J. 20:5568–5577.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Llovet JM, Chen Y, Wurmbach E, et al: A
molecular signature to discriminate dysplastic nodules from early
hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV cirrhosis. Gastroenterology.
131:1758–1767. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Smith MW, Yue ZN, Geiss GK, et al:
Identification of novel tumor markers in hepatitis C
virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63:859–864.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Itsui Y, Sakamoto N, Kurosaki M, et al:
Expressional screening of interferon-stimulated genes for antiviral
activity against hepatitis C virus replication. J Viral Hepat.
13:690–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Naschberger E, Croner RS, Merkel S, et al:
Angiostatic immune reaction in colorectal carcinoma: impact on
survival and perspectives for antiangiogenic therapy. Int J Cancer.
123:2120–2129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Redjimi N, Gaudin F, Touboul C, et al:
Identification of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper as a key
regulator of tumor cell proliferation in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Mol Cancer. 8:832009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Wu XZ, Xie GR and Chen D: Hypoxia and
hepatocellular carcinoma: the therapeutic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroen Hepatol. 22:1178–1182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Yasui M, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY, et al:
Antisense to cyclin D1 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor
– stimulated growth of vascular endothelial cells: implication of
tumor vascularization. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4720–4729. 2006.
|