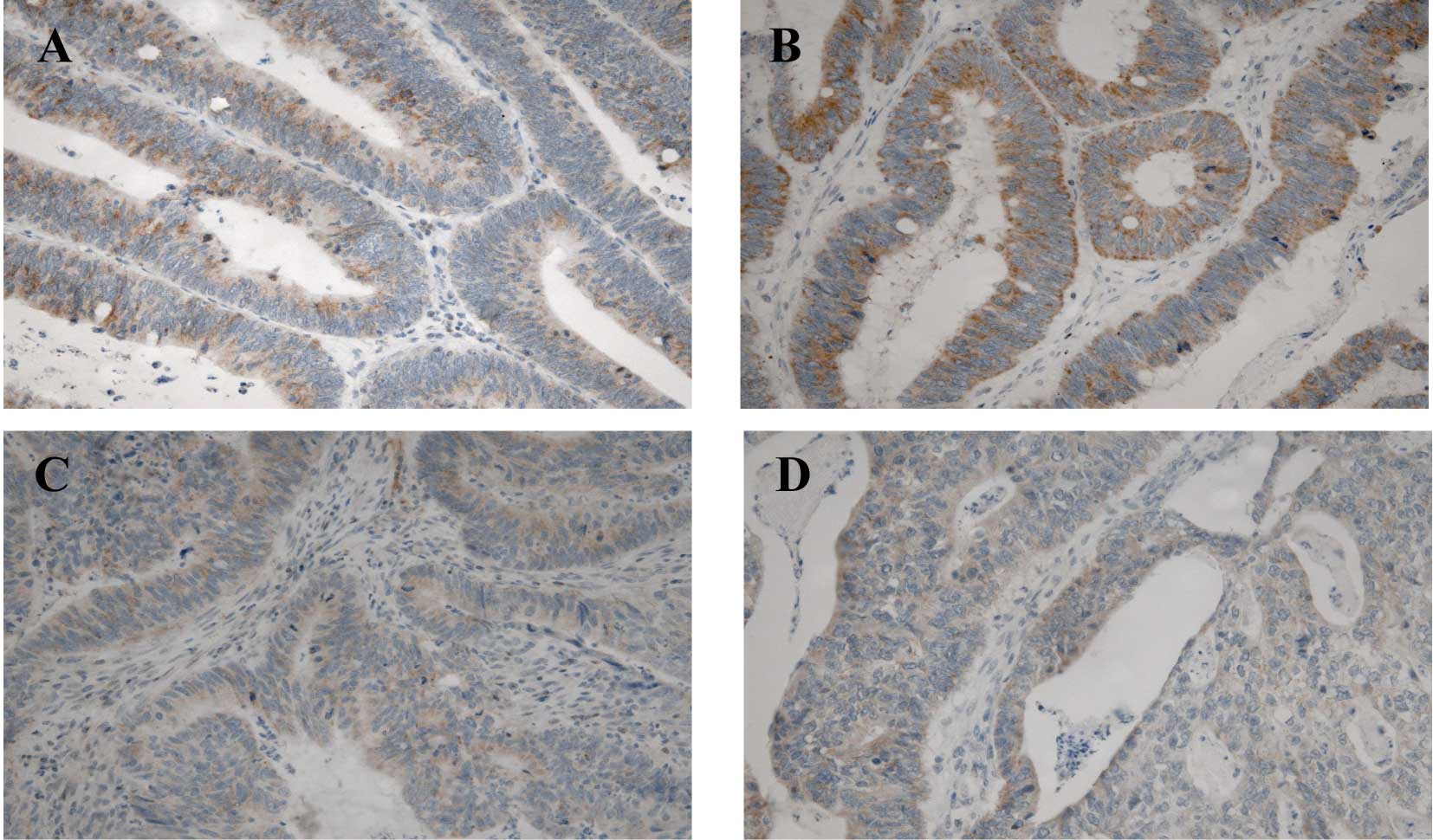
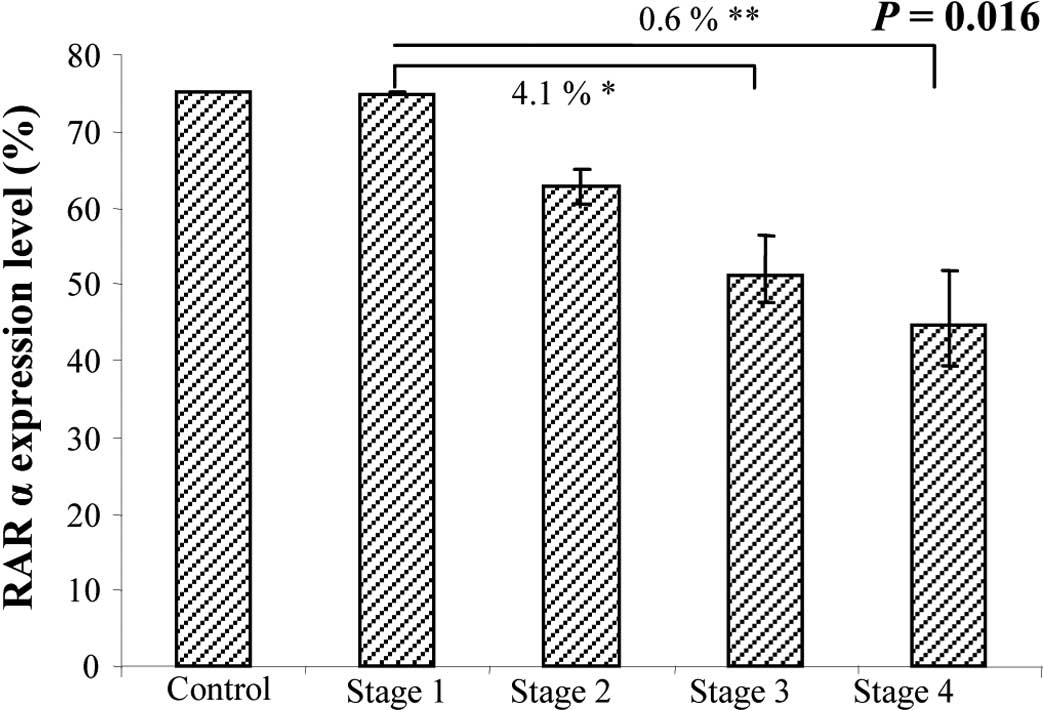
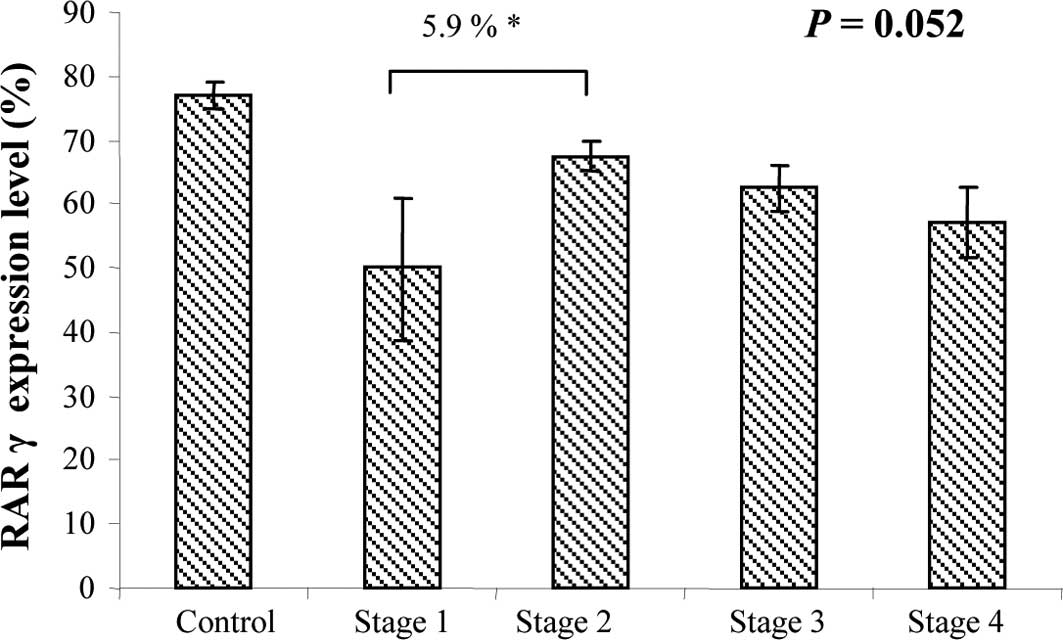
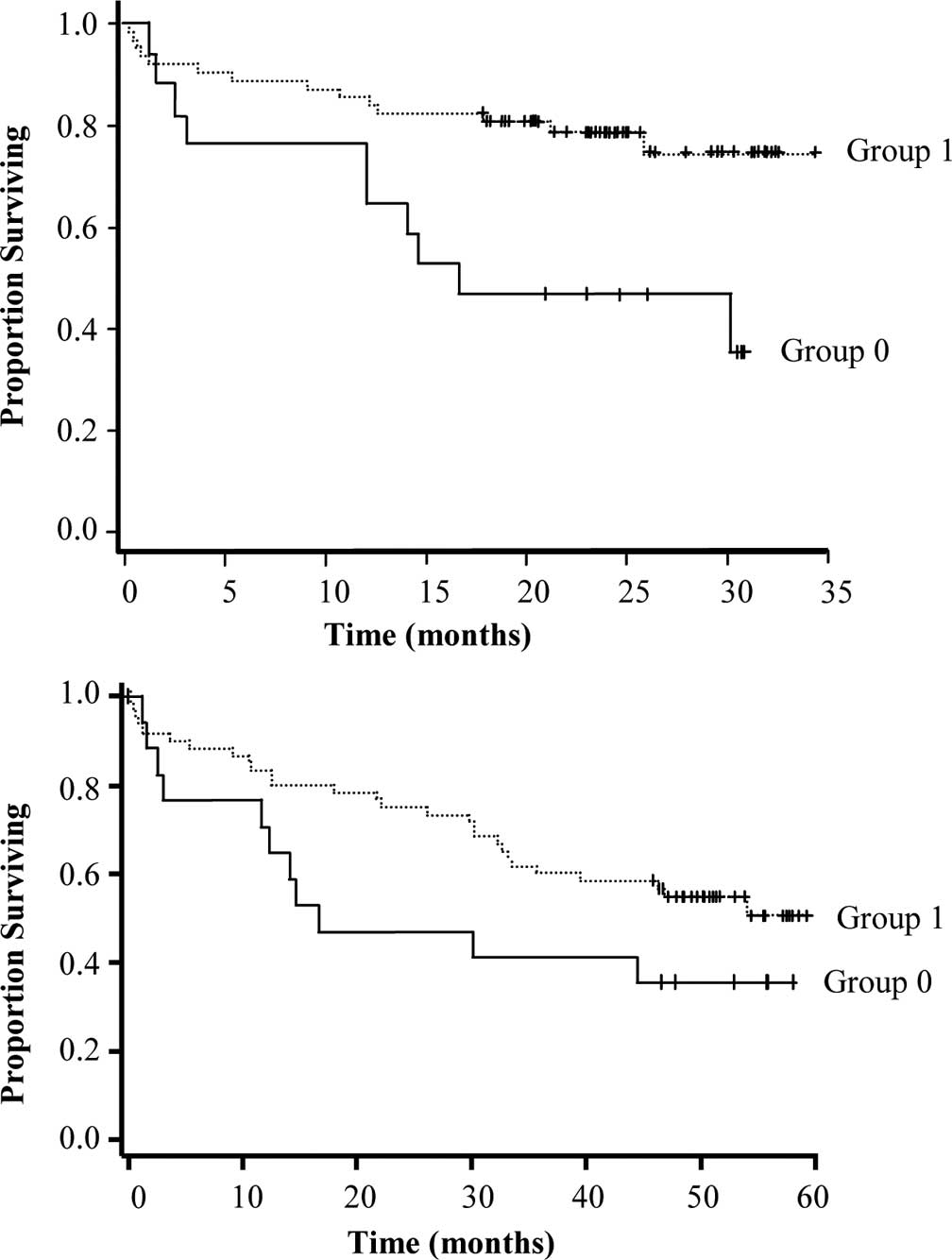
|
1.
|
Wolbach B and Howe PR: Tissue changes
following deprivation of fat soluble A vitamin. J Exp Med.
42:753–777. 1925. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
De Luca LM: Retinoids and their receptors
in differentiation, embryogenesis, and neoplasia. FASEB J.
5:2924–2933. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Altucci L and Gronemeyer H: The promise of
retinoids to fight against cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:181–193. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Mongan NP and Gudas LJ: Diverse actions of
retinoid receptors in cancer prevention and treatment.
Differentiation. 75:853–870. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Asou N: All-trans retinoic acid in the
treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Intern Med. 46:91–93.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Degos L and Wang ZY: All trans retinoic
acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene. 20:7140–7145. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Nagy L, Thomazy VA, Shipley GL, et al:
Activation of retinoid X receptors induces apoptosis in HL-60 cell
lines. Mol Cell Biol. 15:3540–3551. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Germain P, Staels B, Dacquet C, Spedding M
and Laudet V: Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors.
Pharmacol Rev. 58:685–704. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Germain P, Chambon P, Eichele G, et al:
International Union of Pharmacology. LX Retinoic acid receptors.
Pharmacol Rev. 58:712–725. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Germain P, Chambon P, Eichele G, et al:
International Union of Pharmacology. LXIII Retinoid X receptors.
Pharmacol Rev. 58:760–772. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Sun SY: Retinoic acid receptor beta and
colon cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:87–88. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Li R, Saito T, Tanaka R, et al:
Hypermethylation in promoter region of retinoic acid receptor-beta
gene and immunohistochemical findings on retinoic acid receptors in
carcinogenesis of endometrium. Cancer Lett. 219:33–40. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Xu XC, Ro JY, Lee JS, Shin DM, Hong WK and
Lotan R: Differential expression of nuclear retinoid receptors in
normal, premalignant, and malignant head and neck tissues. Cancer
Res. 54:3580–3587. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kamradt J and Reichrath J: Expression of
retinoic acid receptor proteins in basal cell carcinomas: an
immunohistochemical analysis. J Histochem Cytochem. 44:1415–1420.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Widschwendter M, Berger J, Daxenbichler G,
et al: Loss of retinoic acid receptor beta expression in breast
cancer and morphologically normal adjacent tissue but not in the
normal breast tissue distant from the cancer. Cancer Res.
57:4158–4161. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Picard E, Seguin C, Monhoven N, et al:
Expression of retinoid receptor genes and proteins in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:1059–1066. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Zhang W, Rashid A, Wu H and Xu XC:
Differential expression of retinoic acid receptors and p53 protein
in normal, premalignant, and malignant esophageal tissues. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 127:237–242. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Richter F, Joyce A, Fromowitz F, et al:
Immunohistochemical localization of the retinoic acid receptors in
human prostate. J Androl. 23:830–838. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Haugen BR, Larson LL, Pugazhenthi U, et
al: Retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors are differentially
expressed in thyroid cancer and thyroid carcinoma cell lines and
predict response to treatment with retinoids. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 89:272–280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Karamouzis MV, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G,
Vandoros G, Varakis I and Papavassiliou AG: Differential expression
of retinoic acid receptor beta (RARβ) and the AP-1 transcription
factor in normal, premalignant and malignant human laryngeal
tissues. Eur J Cancer. 40:761–773. 2004.
|
|
21.
|
Ralhan R, Chakravarti N, Kaur J, et al:
Clinical significance of altered expression of retinoid receptors
in oral precancerous and cancerous lesions: Relationship with cell
cycle regulators. Int J Cancer. 118:1077–1089. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Alvarez S, Germain P, Alvarez R,
Rodriguez-Barrios F, Gronemeyer H and de Lera AR: Structure,
function and modulation of retinoic acid receptor beta, a tumor
suppressor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:1406–1415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Bossard N, Veltenc M, Remonteta L, et al:
Survival of cancer patients in France: A population-based study
from The Association of the French Cancer Registries (FRANCIM). Eur
J Cancer. 43:149–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming I, et al: AJCC
(American Joint Committee on Cancer) Cancer Staging Manual. 6th
edition. Springer-Verlag; New York: pp. 1132002
|
|
25.
|
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH,
Schwab U and Stein H: Cell cycle analysis of a cell
proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the
monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 133:1710–1715.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Du L, Wang H, He L, et al: CD44 is of
functional importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:6751–6760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT and Ryan PD: PAST:
Paleontological statistics software package for education and data
analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica. 4:92001.
|
|
28.
|
Gyftopoulos K, Perimenis P,
Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Sakellaropoulos G, Varakis I and Barbalias
GA: Immunohistochemical detection of retinoic acid receptor-alpha
in prostate carcinoma: correlation with proliferative activity and
tumor grade. Int Urol Nephrol. 32:263–269. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Xu XC: Tumor-suppressive activity of
retinoic acid receptor-beta in cancer. Cancer Lett. 253:14–24.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Van der Leede BM, Geertzema J, Vroom TM,
et al: Immunohistochemical analysis of retinoic acid receptor-alpha
in human breast tumors: retinoic acid receptor-alpha expression
correlates with proliferative activity. Am J Pathol. 148:1905–1914.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Lee MO, Han SY, Jiang S, Park JH and Kim
SJ: Differential effects of retinoic acid on growth and apoptosis
in human colon cancer cell lines associated with the induction of
retinoic acid receptor beta. Biochem Pharmacol. 59:485–496. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Nicke B, Kaiser A, Wiedenmann B, Riecken
EO and Rosewicz S: Retinoic acid receptor alpha mediates growth
inhibition by retinoids in human colon carcinoma HT29 cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 261:572–577. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kim EJ, Kang YH, Schaffer BS, Bach LA,
MacDonald RG and Park JH: Inhibition of Caco-2 cell proliferation
by all-trans retinoic acid: role of insulin-like growth factor
binding protein-6. J Cell Physiol. 190:92–100. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Freemantle SJ, Spinella MJ and Dmitrovsky
E: Retinoids in cancer therapy and chemoprevention: promise meets
resistance. Oncogene. 22:7305–7315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|