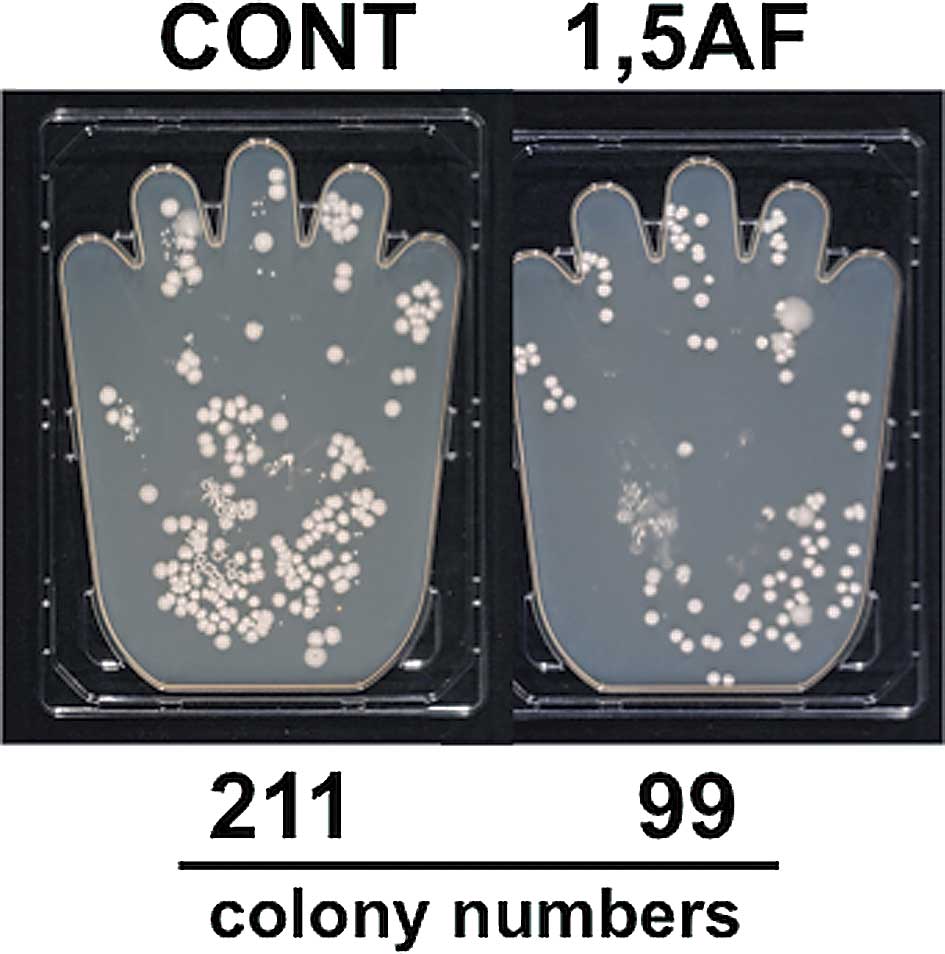
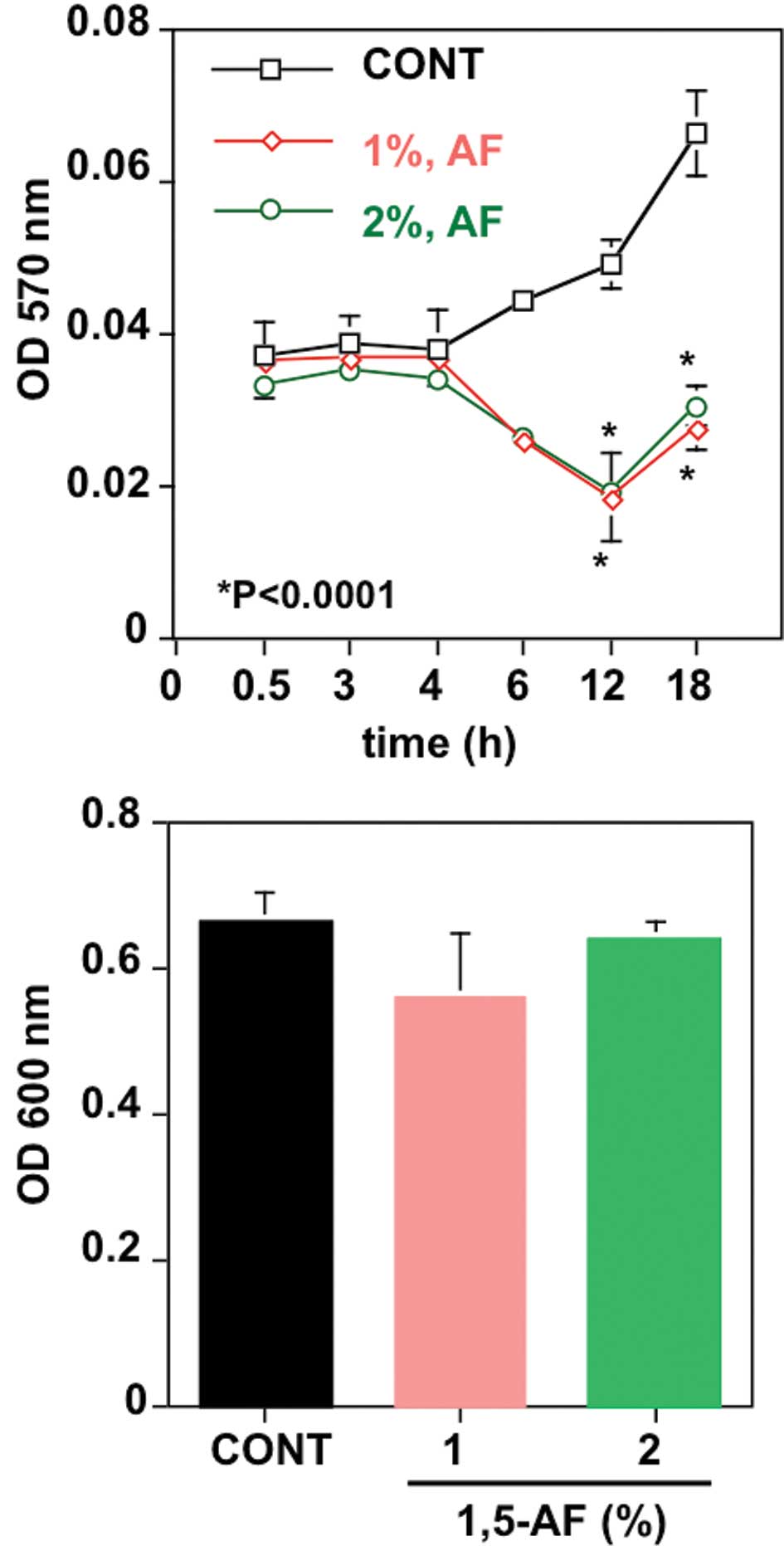
Spandidos Publications style
Meng X, Kawahara K, Miyanohara H, Yoshimoto Y, Yoshinaga K, Noma S, Kikuchi K, Morimoto Y, Ito T, Oyama Y, Oyama Y, et al: 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose: A natural antibiotic that inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria and microbial biofilm formation to prevent nosocomial infection. Exp Ther Med 2: 625-628, 2011.
APA
Meng, X., Kawahara, K., Miyanohara, H., Yoshimoto, Y., Yoshinaga, K., Noma, S. ... Maruyama, I. (2011). 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose: A natural antibiotic that inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria and microbial biofilm formation to prevent nosocomial infection. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 2, 625-628. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2011.245
MLA
Meng, X., Kawahara, K., Miyanohara, H., Yoshimoto, Y., Yoshinaga, K., Noma, S., Kikuchi, K., Morimoto, Y., Ito, T., Oyama, Y., Yoshinaga, N., Shrestha, B., Chandan, B., Mera, K., Tada, K., Miura, N., Ono, Y., Takenouchi, K., Maenosono, R., Nagasato, T., Hashiguchi, T., Maruyama, I."1,5-anhydro-D-fructose: A natural antibiotic that inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria and microbial biofilm formation to prevent nosocomial infection". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2.4 (2011): 625-628.
Chicago
Meng, X., Kawahara, K., Miyanohara, H., Yoshimoto, Y., Yoshinaga, K., Noma, S., Kikuchi, K., Morimoto, Y., Ito, T., Oyama, Y., Yoshinaga, N., Shrestha, B., Chandan, B., Mera, K., Tada, K., Miura, N., Ono, Y., Takenouchi, K., Maenosono, R., Nagasato, T., Hashiguchi, T., Maruyama, I."1,5-anhydro-D-fructose: A natural antibiotic that inhibits the growth of gram-positive bacteria and microbial biofilm formation to prevent nosocomial infection". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2, no. 4 (2011): 625-628. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2011.245