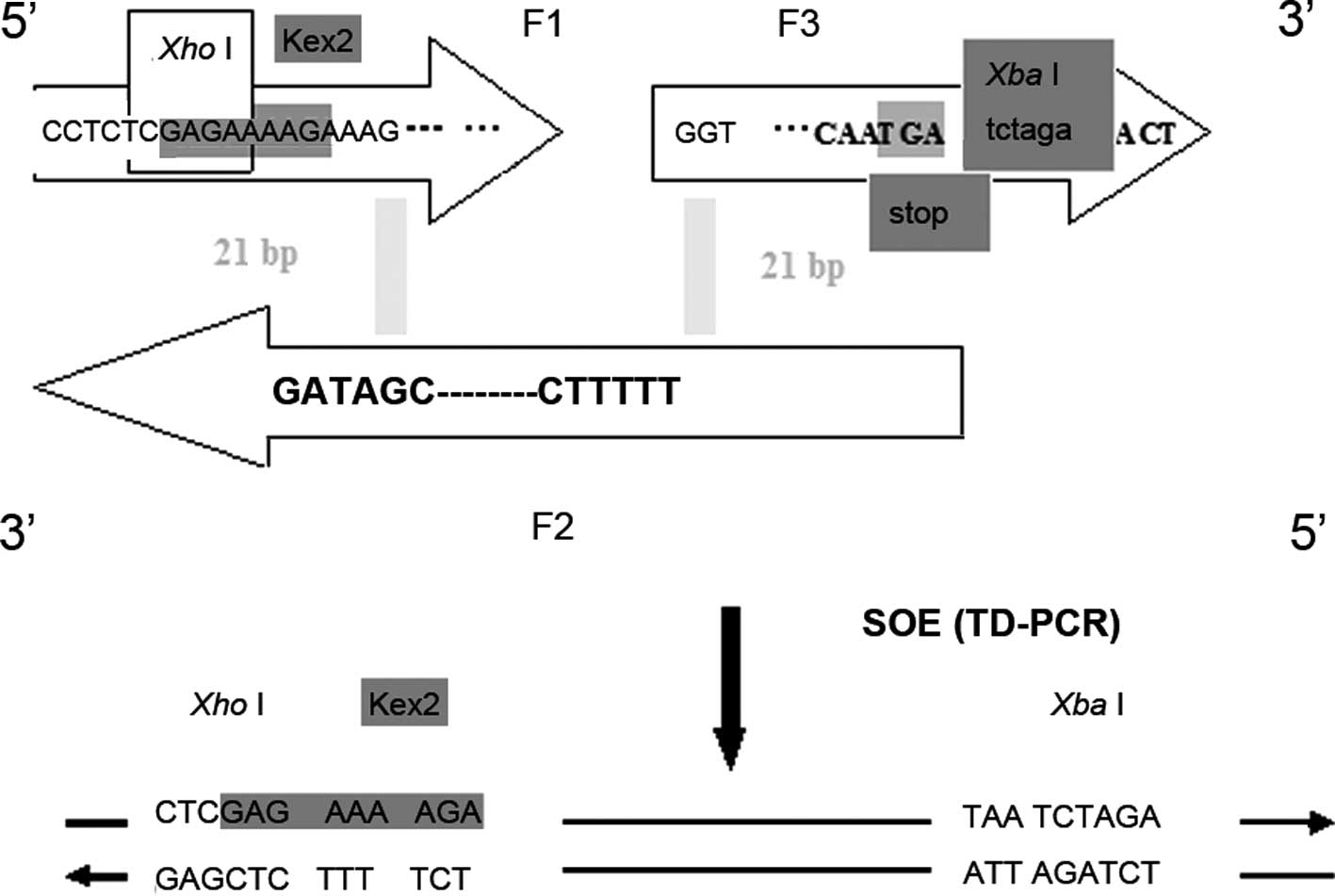
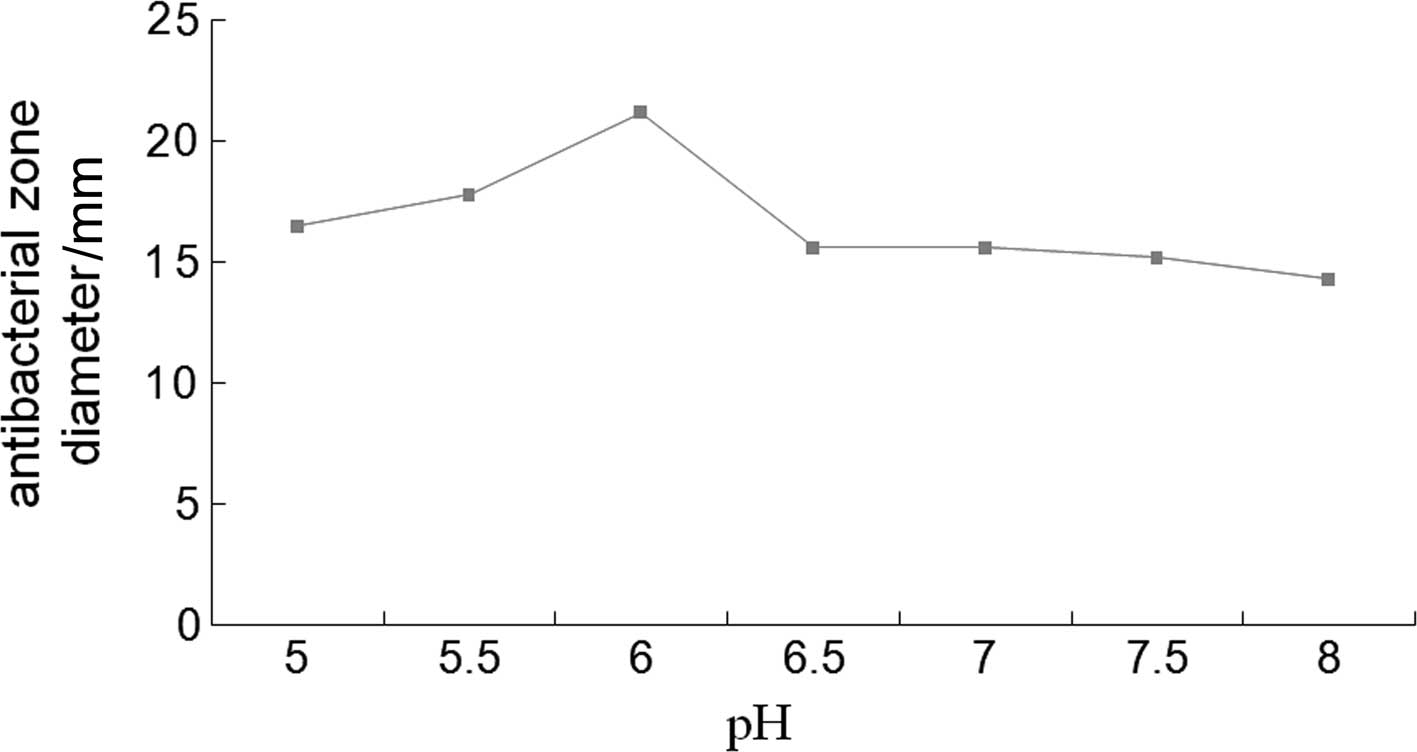
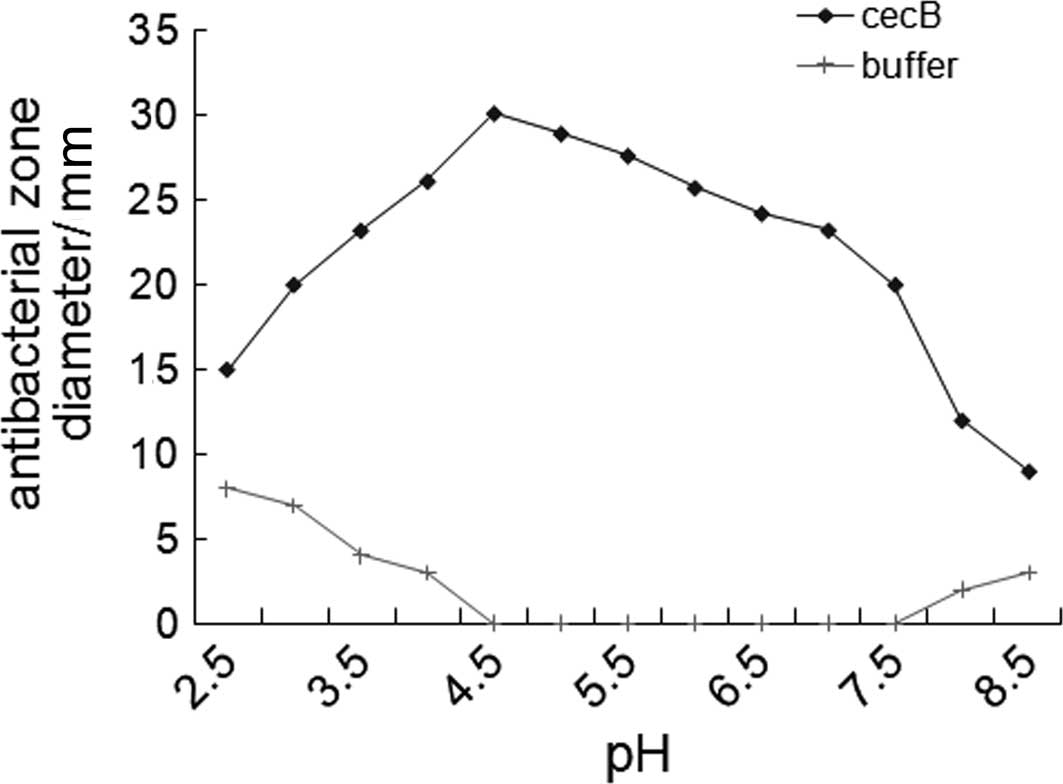
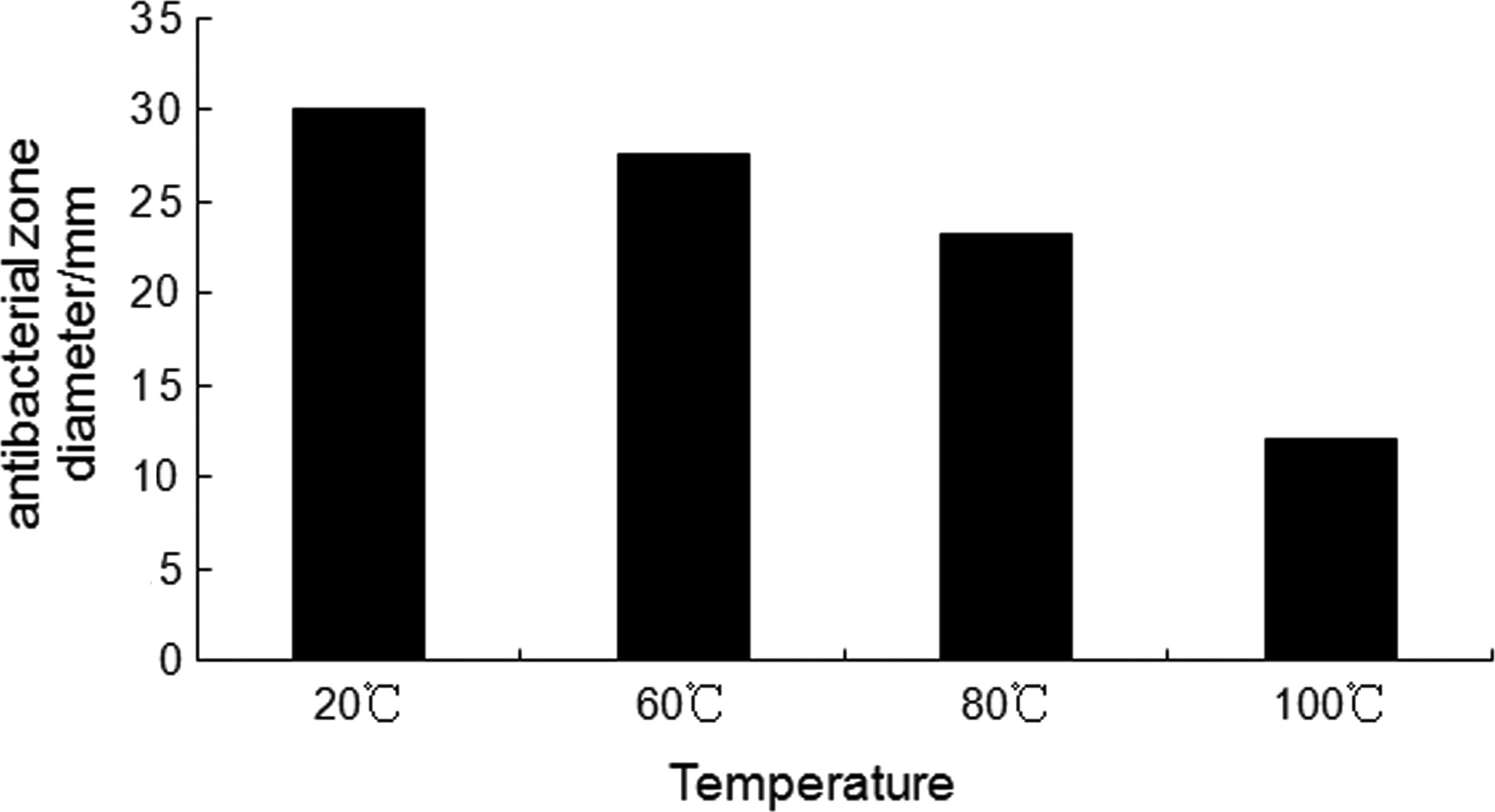
|
1.
|
Devine DA and Hancock RE: Cationic
peptides: distribution and mechanisms of resistance. Curr Pharm
Des. 8:703–714. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Ganz T: Defensins: antimicrobial peptides
of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:710–720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Segrest JP, De Loof H, Dohlman JG,
Brouillette CG and Anantharamaiah GM: Amphipathic helix motif:
classes and properties. Proteins. 8:103–117. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Zasloff M: Antimicrobial peptides of
multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Boman HG: Peptide antibiotics and their
role in innate immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 13:61–92. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Noga EJ and Silphaduang U: Piscidins: a
novel family of peptide antibiotics from fish. Drug News Perspect.
16:87–92. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Steiner H, Hultmark D, Engstrom A, Bennich
H and Boman HG: Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial
proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. 292:246–248. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Boman HG and Hultmark D: Cell-free
immunity in insects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 41:103–126. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lee JY, Boman A, Sun CX, Andersson M,
Jornvall H, Mutt V and Boman HG: Antibacterial peptides from pig
intestine: isolation of a mammalian cecropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 86:9159–9162. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Hultmark D, Engstrom A, Bennich H, Kapur R
and Boman HG: Insect immunity: isolation and structure of cecropin
D and four minor antibacterial components from Cecropia
pupae. Eur J Biochem. 127:207–217. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Boman HG, Wade D, Boman IA, Wahlin B and
Merrifield RB: Antibacterial and antimalarial properties of
peptides that are cecropin-melittin hybrids. FEBS Lett.
259:103–106. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Moore AJ, Devine DA and Bibby MC:
Preliminary experimental anticancer activity of cecropins. Pept
Res. 7:265–269. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hancock RE and Lehrer R: Cationic
peptides: a new source of antibiotics. Trends Biotechnol. 16:82–88.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hancock RE and Patrzykat A: Clinical
development of cationic antimicrobial peptides: from natural to
novel antibiotics. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2:79–83. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Diamond G: Natures antibiotics: the
potential of antimicrobial peptides as new drugs. Biologist.
48:209–212. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Andres E and Dimarcq JL: Cationic
antimicrobial peptides: from innate immunity study to drug
development. Med Mal Infect. 37:194–199. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Cereghino JL and Cregg JM: Heterologous
protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia
pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 24:45–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Sreekrishna K, Brankamp RG, Kropp KE,
Blankenship DT, Tsay JT, Smith PL, Wierschke JD, Subramaniam A and
Birkenberger LA: Strategies for optimal synthesis and secretion of
heterologous proteins in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia
pastoris. Gene. 190:55–62. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Cregg JM, Cereghino JL, Shi J and Higgins
DR: Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Mol
Biotechnol. 16:23–52. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Boze H, Celine L, Patrick C, Fabien R,
Christine V, Yves C and Guy M: High-level secretory production of
recombinant porcine follicle-stimulating hormone by Pichia
pastoris. Process Biochem. 36:907–913. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Lee CY, Lee SJ, Jung KH, Katoh S and Lee
K: High dissolved oxygen tension enhances heterologous protein
expression by recombinant Pichia pastoris. Process Biochem.
38:1147–1154. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Almeida MS, Cabral KS, de Medeiros LN,
Valente AP, Almeida FC and Kurtenbach E: cDNA cloning and
heterologous expression of functional cysteine-rich antifungal
protein Psd1 in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 395:199–207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Ausubel FM, Brent R and Kingston RE:
Protocols in molecular biology. Trends Cell Biol. 6:366–367.
1996.
|
|
24.
|
Lehrer RI, Rosenman M, Harwig SS, Jackson
R and Eisenhauer P: Ultrasensitive assays for endogenous peptides.
J Immunol Methods. 137:167–173. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Cipakova I, Hostinova E, Gasperik J and
Velebny V: High-level expression and purification of a recombinant
hBD-1 fused to LMM protein in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr
Purif. 37:207–212. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Shi X, Karkut T, Chamankhah M, Alting-Mees
M, Hemmingsen SM and Hegedus D: Optimal conditions for the
expression of a single-chain antibody (scFv) gene in Pichia
pastoris. Protein Express Purif. 28:321–330. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Jahic M, Gustavsson M, Jansen AK,
Martinelle M and Enfors SO: Analysis and control of proteolysis of
a fusion protein in Pichia pastoris fed-batch processes. J
Biotechnol. 102:45–53. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Li SZ, Xiong F and Lin Q: Low-temperature
increases the yield of biologically active herring antifreeze
protein in Pichia pastoris. Protein Express Purif.
21:438–445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Bencurova M, Rendic D, Fabini G, Kopecky
EM, Altmann F and Wilson IB: Expression of eukaryotic
glycosyltransferases in the yeast Pichia pastoris.
Biochimie. 85:413–422. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Skosyrev VS, Kulesskiy EA, Yakhnin AV,
Temirov YV and Vinokurov LM: Expression of the recombinant
antibacterial peptide sarcotoxin IA in Escherichia coli
cells. Protein Expr Purif. 28:350–356. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Aly R, Granot D, Mahler-Slasky Y, Halpern
N, Nir D and Galun E: Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells
harboring the gene encoding sarcotoxin IA secrete a peptide that is
toxic to plant pathogenic bacteria. Protein Expr Purif. 16:120–124.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Yamada K, Nakajima Y and Nator S:
Production of recombinant sarcotoxin IA in Bombyx mori
cells. Biochem J. 272:633–636. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Rao XC, Li S, Hu JC, Jin XL, Hu XM, Huang
JJ, Chen ZJ, Zhu JM and Hu FQ: A novel carrier molecule for
high-level expression of peptide antibiotics in Escherichia
coli. Protein Expr Purif. 36:11–18. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Cabral KM, Almeida MS, Valente AP, Almeida
FC and Kurtenbach E: Production of the active antifungal Pisum
sativum defensin 1 (Psd1) in Pichia pastoris: overcoming
the inefficiency of the STE13 protease. Protein Expr Purif.
31:115–122. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Sarmasik A and Chen TT: Bactericidal
activity of cecropin B and cecropin P1 expressed in fish cells
(CHSE-214): application in controlling fish bacterial pathogens.
Aquaculture. 220:183–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Sessitsch A, Kan FY and Pfeifer U:
Diversity and community structure of culturable Bacillus
spp. populations in the rhizospheres of transgenic potatoes
expressing the lytic peptide cecropin B. Appl Soil Ecol.
22:149–158. 2003.
|
|
37.
|
Sharma A, Sharma R, Imamura M, Yamakawa M
and Machii H: Transgenic expression of cecropin B, an antibacterial
peptide from Bombyx mori, confers enhanced resistance to
bacterial leaf blight in rice. FEBS Lett. 484:7–11. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|