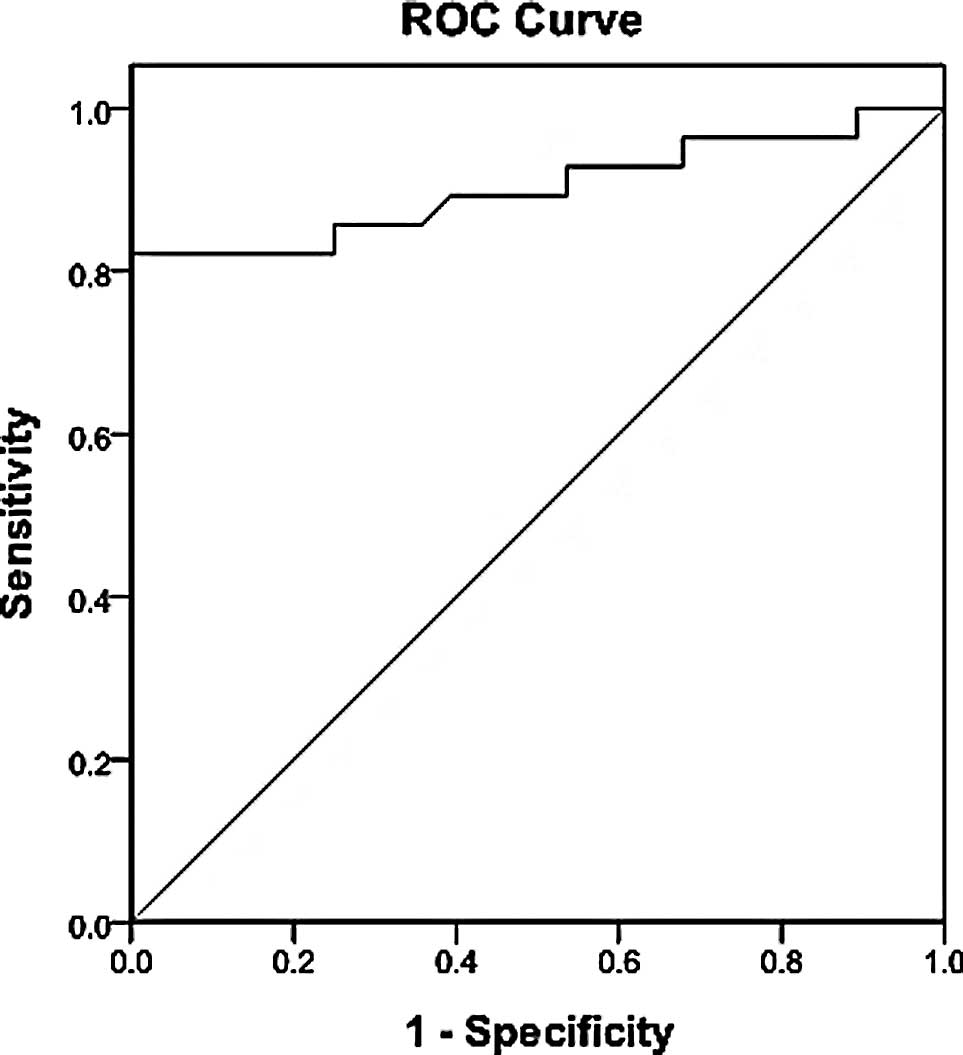
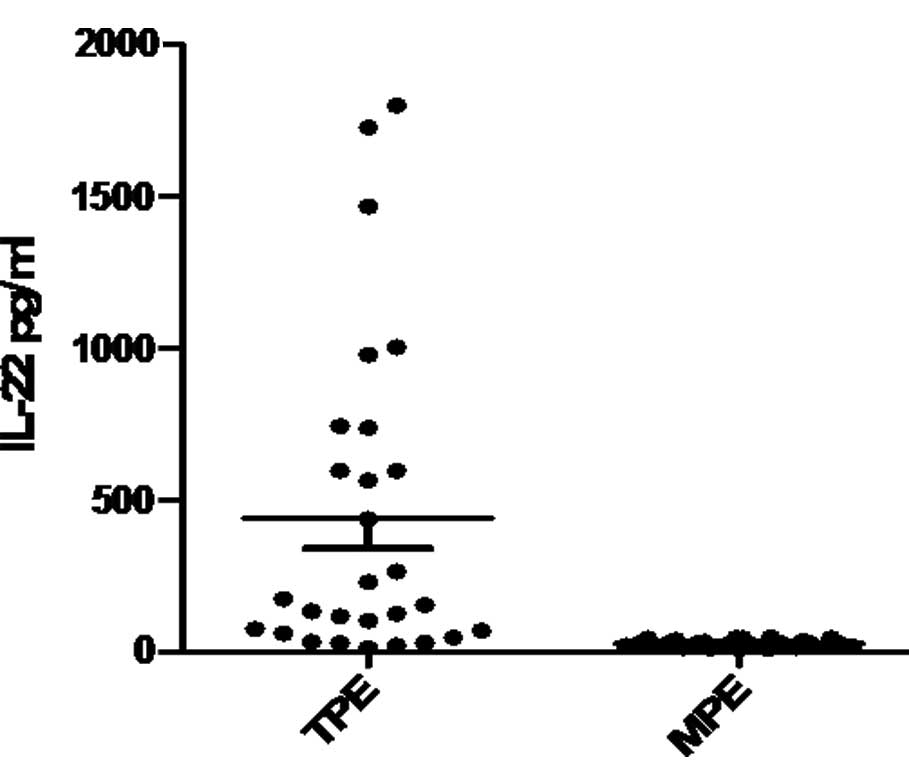
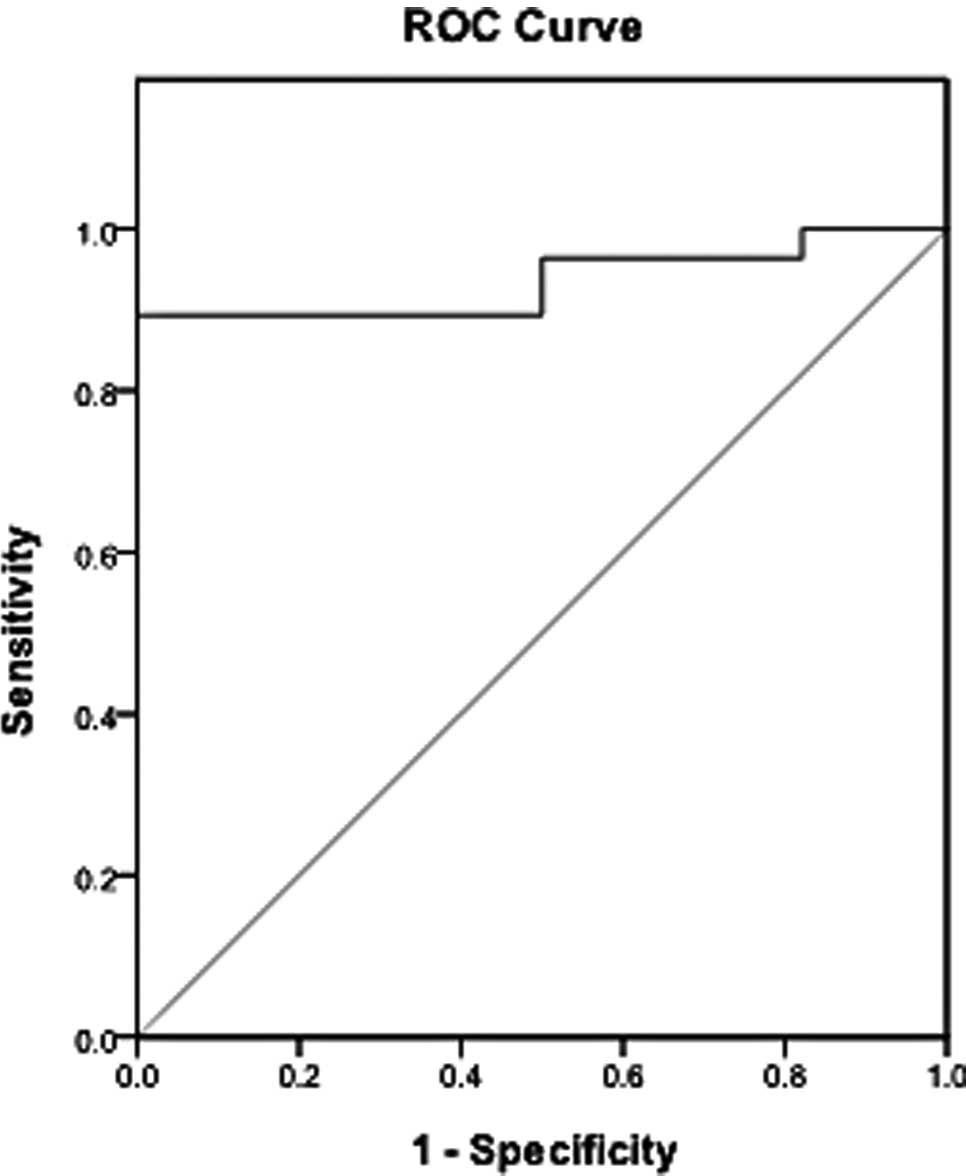
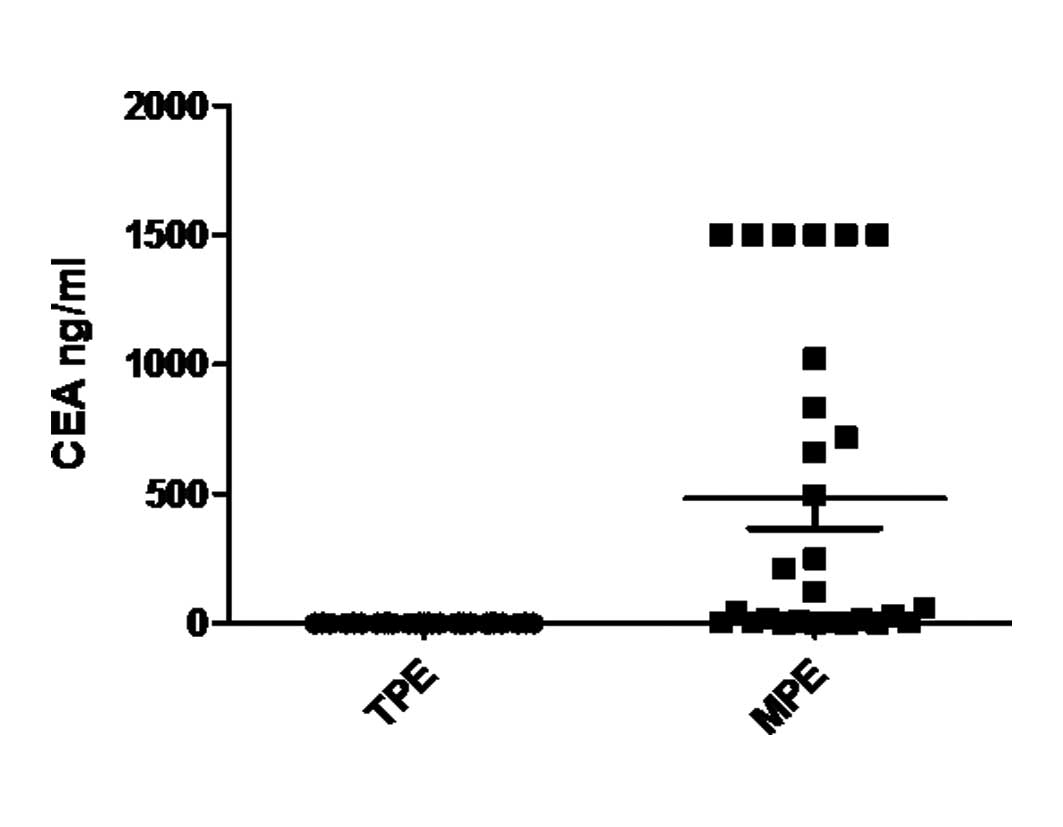
|
1
|
Doelken P: Clinical implications of
unexplainable lung due to pleural disease. Am J Med Sci. 335:21–25.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Khaleeq G and Musani AI: Emerging
paradigms in the management of malignant pleural effusions. Respir
Med. 102:939–948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Musani AI: Treatment options for malignant
pleural effusion. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 15:380–387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Spector M and Pollak JS: Management of
malignant pleural effusions. Semin Respir Crit Care Med.
29:405–413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heffner JE: Diagnosis and management of
malignant pleural effusions. Respirology. 13:5–20. 2008.
|
|
6
|
Yang HB and Shi HZ: T lymphocytes in
pleural effusion. Chin Med J (Engl). 121:579–580. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qin XJ, Shi HZ, Liang QL, Huang LY and
Yang HB: CD4+CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes
in tuberculous pleural effusion. Chin Med J (Engl). 121:581–586.
2008.
|
|
8
|
Infante-Duarte C, Horton HF, Byrne MC and
Kamradt T: Microbial lipopeptides induce the production of IL17 in
Th cells. J Immunol. 165:6107–6115. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva
R, Wang YH, Wang Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q and Dong C: A distinct
lineage of CD4+ T cells regulates tissue inflammation by
producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 6:1133–1141. 2005.
|
|
10
|
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR,
Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM and Weaver CT:
Interleukin17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop
via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat
Immunol. 6:1123–1133. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harrington LE, Mangan PR and Weaver CT:
Expanding the effector CD4 T-cell repertoire: the Th17 lineage.
Curr Opin Immunol. 18:349–356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weaver CT, Harrington LE, Mangan PR,
Gavrieli M and Murphy KM: Th17: an effector CD4 T cell lineage with
regulatory T cell ties. Immunity. 24:677–688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang T, Lv M, Qian Q, Nie Y, Yu L and Hou
Y: Increased frequencies of T helper type 17 cells in tuberculous
pleural effusion. Tuberculosis. 91:231–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wolk K, Witte E, Witte K, Warszawska K and
Sabat R: Biology of interleukin-22. Semin Immunopathol. 32:17–31.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dumoutier L, Lejeune D, Colau D and
Renauld JC: Cloning and characterization of IL-22 binding protein,
a natural antagonist of IL-10-related T cell-derived inducible
factor/IL-22. J Immunol. 166:7090–7095. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wolk K and Sabat R: Interleukin-22: a
novel T and NK cell-derived cytokine that regulates the biology of
tissue cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:367–380. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aggarwal S, Xie MH, Maruoka M, Foster J
and Gurney AL: Acinar cells of the pancreas are a target of
interleukin-22. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 21:1047–1053. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wolk K, Witte E, Wallace E, Döcke WD, Kunz
S, Asadullah K, Volk HD, Sterry W and Sabat R: IL-22 regulates the
expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular
differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: a potential role in
psoriasis. Eur J Immunol. 36:1309–1323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmechel S, Konrad A, Diegelmann J, Glas
J, Wetzke M, Paschos E, Lohse P, Göke B and Brand S: Linking
genetic susceptibility to Crohn's disease with Th17 cell function:
IL-22 serum levels are increased in Crohn's disease and correlate
with disease activity and IL23R genotype status. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
14:204–212. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Schnyder B, Lima C and Schnyder-Candrian
S: Interleukin-22 is a negative regulator of the allergic response.
Cytokine. 50:220–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qiao D, Yang BY, Li L, Ma JJ, Zhang XL,
Lao SH and Wu CY: ESAT-6- and CFP-10-specific Th1, Th22 and Th17
cells in tuberculous pleurisy may contribute to the local immune
response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Scand J
Immunol. 73:330–337. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang W, Chen Y, Wei H, Zheng C, Sun R,
Zhang J and Tian Z: Antiapoptotic activity of autocrine
interleukin-22 and therapeutic effects of interleukin-22-small
interfering RNA on human lung cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6432–6439. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dumoutier L, Lejeune D, Colau D and
Renauld JC: Cloning and characterization of IL-10 related T cell
derived inducible factor (IL-TIF), a novel cytokine structurally
related to IL-10 and inducible by IL-9. J Immunol. 164:1814–1819.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aujla SJ and Kolls JK: IL-22: a critical
mediator in mucosal host defense. J Mol Med1. 87:451–454. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dumoutier L, van Roost E, Colau D and
Renauld JC: Human interleukin-10-related T cell-derived inducible
factor: molecular cloning and functional characterization as a
hepatocyte-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:10144–10149. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kotenko SV, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko
OV, Esterova E, Dickensheets H, Donnelly RP and Pestka S:
Identification of the functional interleukin-22 (IL-22) receptor
complex: the IL-10R2 chain (IL-10Rbeta) is a common chain of both
the IL-10 and IL-22 (IL-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor,
IL-TIF) receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 276:2725–2732. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ikeuchi H, Kuroiwa T, Hiramatsu N, Kaneko
Y, Hiromura K, Ueki K and Nojima Y: Expression of interleukin-22 in
rheumatoid arthritis: potential role as a proinflammatory cytokine.
Arthritis Rheum. 52:1037–1046. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boucher D, Cournoyer D, Stanners CP and
Fuks A: Studies on the control of gene expression of the
carcinoembryonic antigen family in human tissue. Cancer Res.
49:847–852. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shi HZ, Liang QL, Jiang J, Qin XJ and Yang
HB: Diagnostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen in malignant
pleural effusion: a meta-analysis. Respirology. 13:518–527. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|