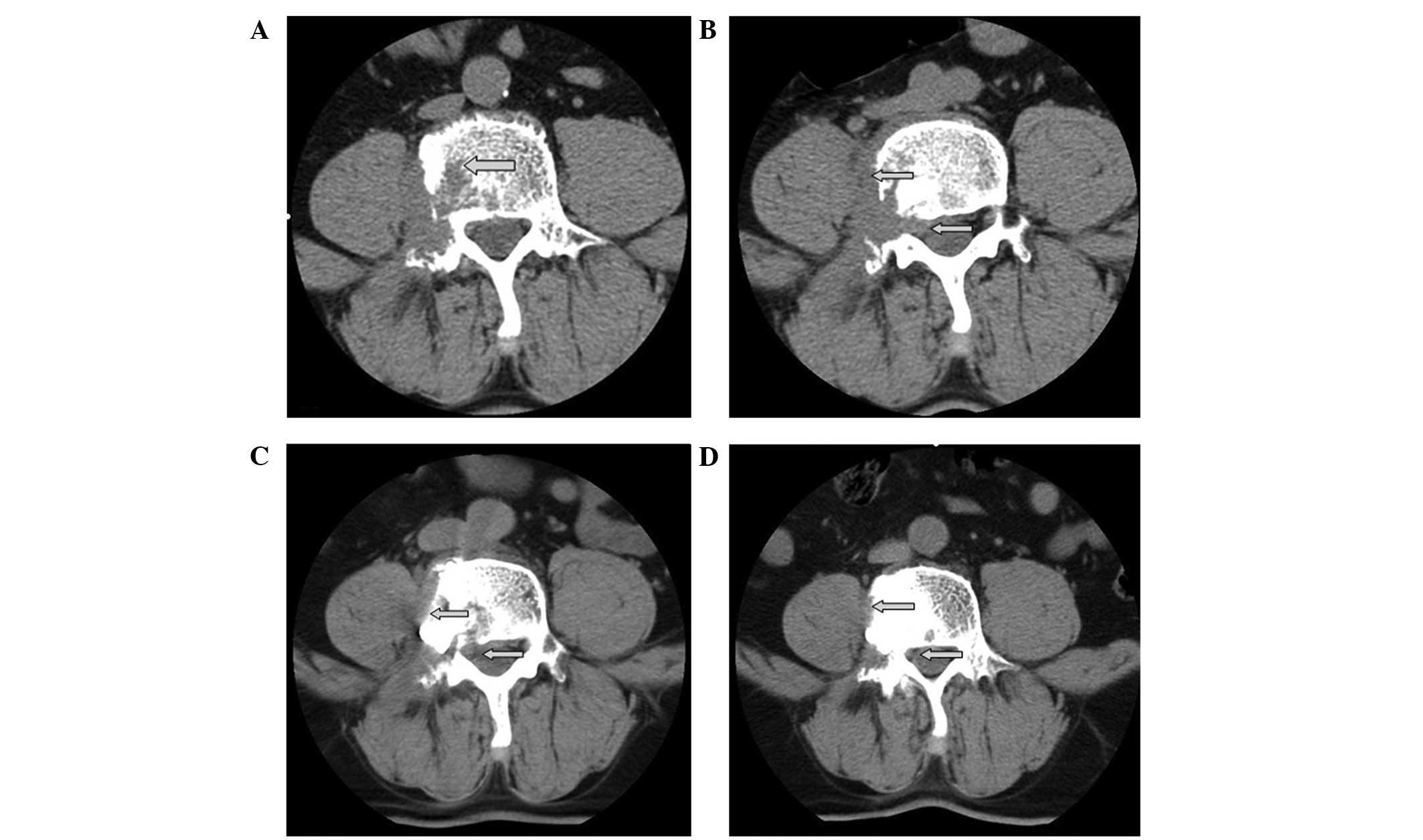
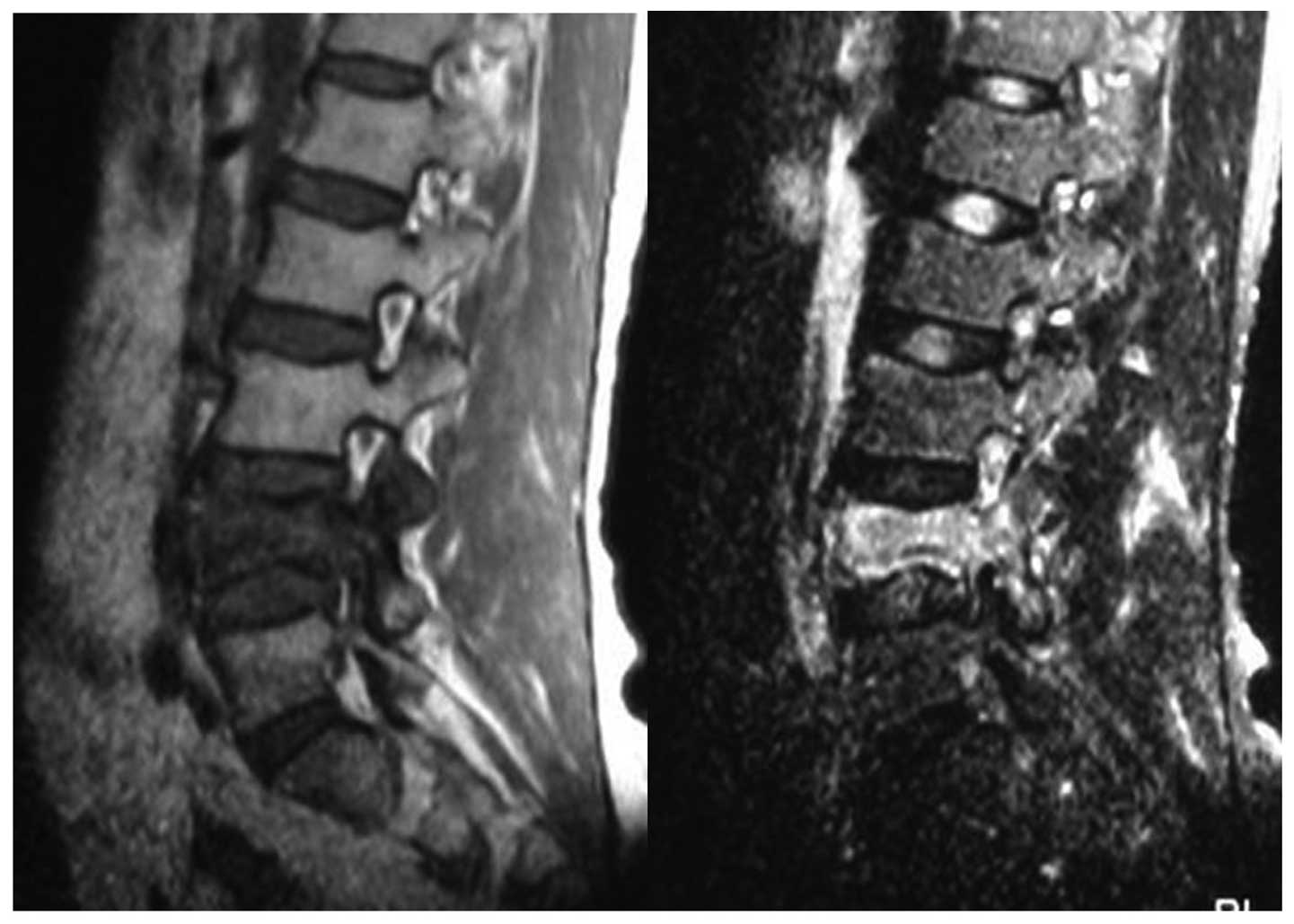
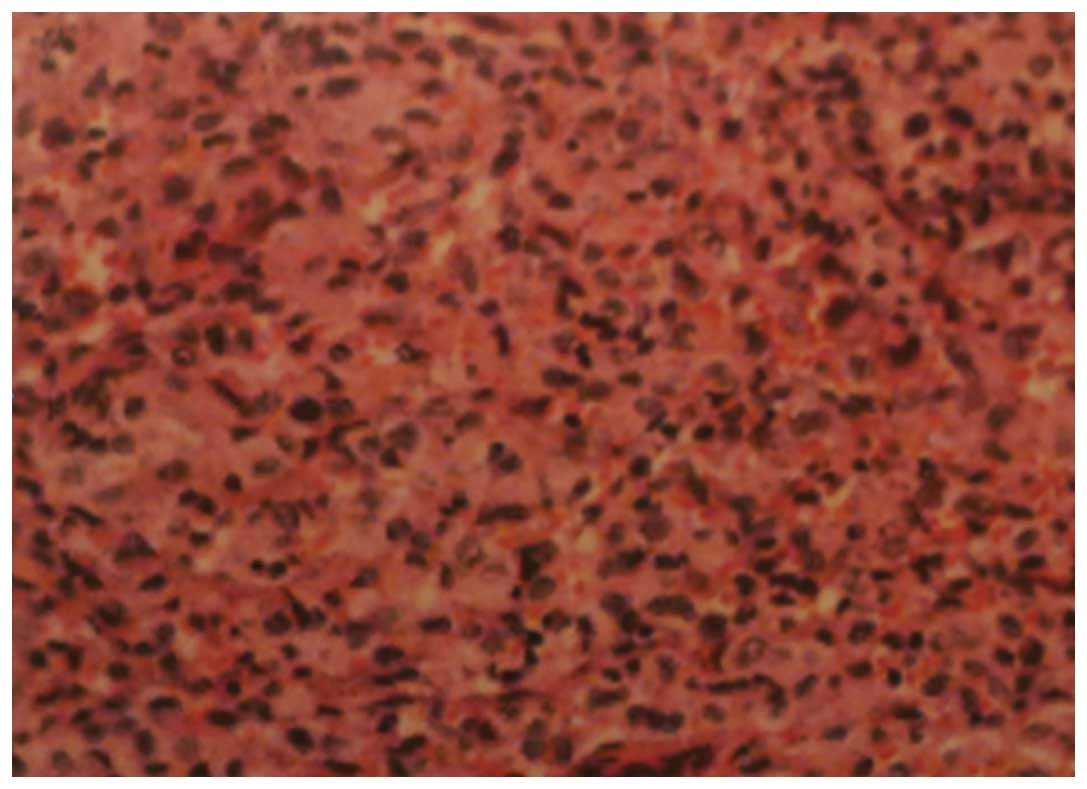
|
1
|
Aster J and Kumar V: White cells, lymph
nodes, spleen, and thymus. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease.
Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T and Robbins SL: Saunders;
Philadelphia, PA: pp. 644–686. 1999
|
|
2
|
Cheyne C: Histiocytosis X. J Bone Joint
Surg Br. 53:366–382. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhong WQ, Jiang L, Ma QJ, Liu ZJ, Liu XG,
Wei F, Yuan HS and Dang GT: Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the
atlas in an adult. Eur Spine J. 19:19–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weitzman S and Egeler RM: Histiocytic
Disorders of Children and Adults: Basic Science, Clinical Features
and Therapy. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Azouz EM, Saigal G, Rodriguez MM and Podda
A: Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis: pathology, imaging and treatment
of skeletal involvement. Pediatr Radiol. 35:103–115. 2005.
|
|
6
|
Peng XS, Pan T, Chen LY, Huang G and Wang
J: Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis of the spine in children with
soft tissue extension and chemotherapy. Int Orthop. 33:731–736.
2009.
|
|
7
|
Garg S, Mehta S and Dormans JP: Langerhans
cell histiocytosis of the spine in children. Long-term follow-up. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 86-A:1740–1750. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu XG, Zhong WQ, Liu ZJ, Yuan HS, Jiang
L, Ma QJ, Wei F and Dang GT: Diagnosis and treatment of Langerhans
cell histiocytosis of the cervical spine. Zhongguo Ji Zhu Ji Sui Za
Zhi. 19:431–436. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Tanaka N, Fujimoto Y, Okuda T, Nakanishi
K, Sumida T, Manabe H and Ochi M: Langerhans cell histiocytosis of
the atlas. A report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
87:2313–2317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aricó M, Girschikofsky M, Géneréau T, et
al: Langerhans cell histiocytosis in adults. Report from the
International Registry of the Histiocyte Society. Eur J Cancer.
39:2341–2348. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bertram C, Madert J and Eggers C:
Eosinophilic granuloma of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 27:1408–1413. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ngu BB, Khanna AJ, Pak SS, et al:
Eosinophilic granuloma of the atlas presenting as torticollis in a
child. Spine (Phila PA 1976). 29:E98–E100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeom JS, Lee CK, Shin HY, Lee CS, Han CS
and Chang H: Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis of the spine. Analysis
of twenty-three cases. Spine (Phila PA 1976). 24:1740–1749.
1999.
|
|
14
|
Levy El, Scarrow A, Hamilton RC, Wollman
MR, Fitz C and Pollack IF: Medical management of eosinophilic
granuloma of the cervical spine. Pediatr Neurosurg. 31:159–162.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Floman Y, Bar-On E, Mosheiff R, Mirovsky
Y, Robin GC and Ramu N: Eosinophilic granuloma of the spine. J
Pediatr Orthop B. 6:260–265. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Greenberger JS, Crocker AC, Vawter G,
Jaffe N and Cassady JR: Results of treatment of 127 patients with
systemic histiocytosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 60:311–338. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Stebut E, Schadmand-Fischer S,
Bräuninger W, Kreft A, Doberauer C and Steinbrink K: Successful
treatment of adult multisystemic Langerhans cell histiocytosis with
psoralen-UV-A, prednisolone, mercaptopurine, and vinblastine. Arch
Dermatol. 144:649–653. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levine SE, Dormans JP, Meyer JS and
Corcoran TA: Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis of the spine in
children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 323:288–293. 1996.
|
|
19
|
Ladisch S and Gadner H: Treatment of
Langerhans cell histiocytosis - evolution and current approaches.
Br J Cancer Suppl. 23:S41–S46. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McLelland J, Broadbent V, Yeomans E,
Malone M and Pritchard J: Langerhans cell histiocytosis: the case
for conservative treatment. Arch Dis Child. 65:301–303. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sessa S, Sommelet D, Lascombes P and
Prévot J: Treatment of Langerhans-cell histiocytosis in children:
experience at the Children’s Hospital of Nancy. J Bone Joint Surg
Am. 76:1513–1525. 1994.
|
|
22
|
Womer RB, Raney RB and D’Angio GJ: Healing
rates of treated and untreated bone lesions in histiocytosis X.
Pediatrics. 76:286–288. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P and Le
Gars D: Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by
percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 33:166–168.
1987.(In French).
|
|
24
|
Kobayashi K, Shimoyama K, Nakamura K and
Murata K: Percutaneous vertebroplasty immediately relieves pain of
osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and prevents prolonged
immobilization of patients. Eur Radiol. 15:360–367. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shimony JS, Gilula LA, Zeller AJ and Brown
DB: Percutaneous vertebroplasty for malignant compression fractures
with epidural involvement. Radiology. 232:846–853. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tan HQ, Li MH, Wu CG, Gu YF, Zhang H and
Fang C: Percutaneous vertebroplasty for eosinophilic granuloma of
the cervical spine in a child. Pediatr Radiol. 37:1053–1057. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cardon T, Hachulla E, Flipo RM, et al:
Percutaneous vertebroplasty with acrylic cement in the treatment of
a Langerhans cell vertebral histiocytosis. Clin Rheumatol.
13:518–521. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kevane B, Ryder DQ and Gilligan O:
Percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporosis, myeloma and
Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. Ir Med J. 102:212–215.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coumans JV, Reinhardt MK and Lieberman IH:
Kyphoplasty for vertebral compression fractures: 1-year clinical
outcomes from a prospective study. J Neurosurg. 99(1 Suppl): 44–50.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Erbe EM and Fenton
DC: Biomechanical evalution of a new bone cement for use in
vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:1061–1064. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cotten A, Boutry N, Cortet B, et al:
Percutaneous vertebroplasty: state of the art. Radiographics.
18:311–320. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, et al:
Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma:
effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of
methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiol. 200:525–530.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, et al: Spinal
metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection
of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology. 199:241–247. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, et al:
Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for
vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:373–81.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Radin EL, Rubin CT, Thrasher EL, et al:
Changes in the bone-cement interface after total hip replacement:
an in vivo animal study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 64:1188–1200.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|