Spandidos Publications style
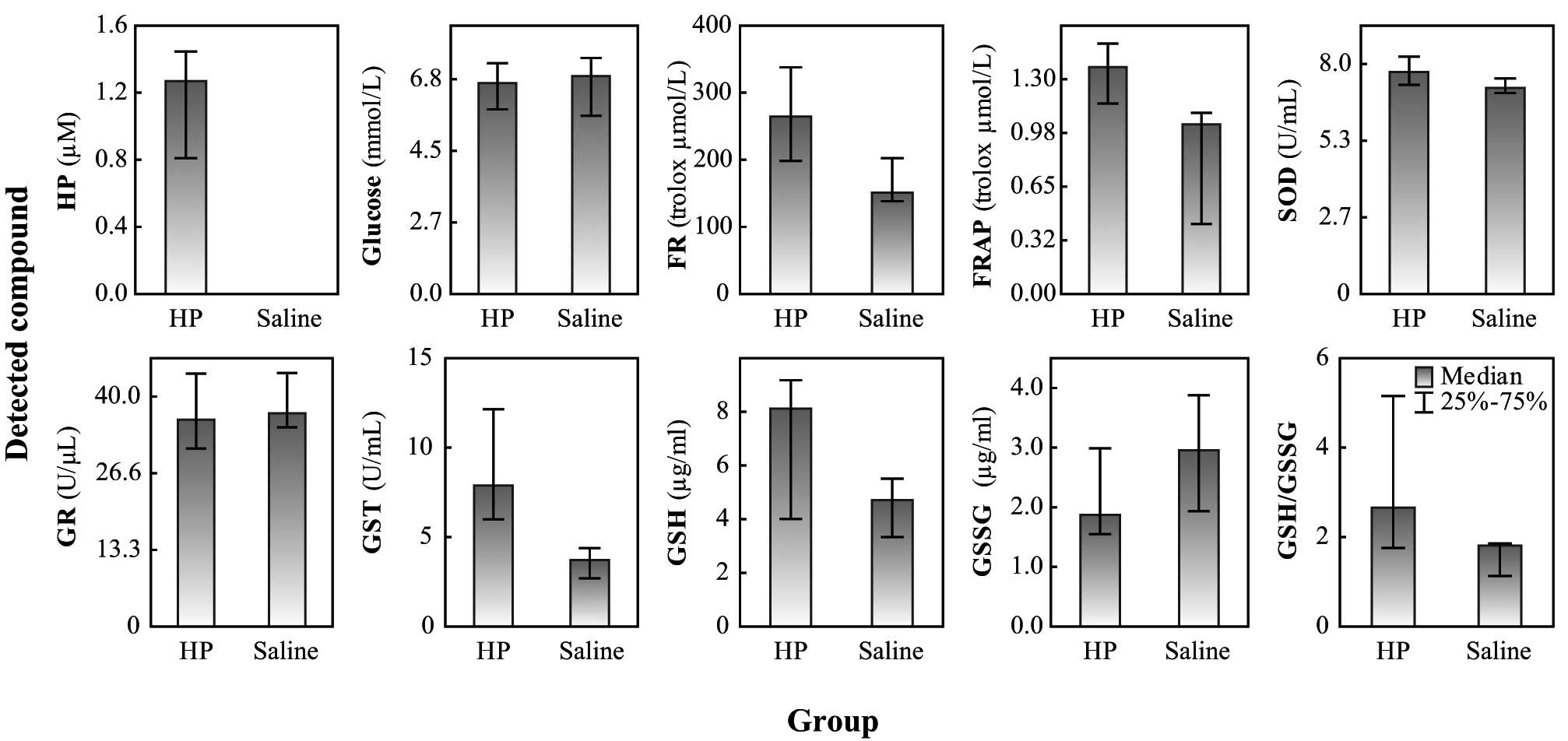
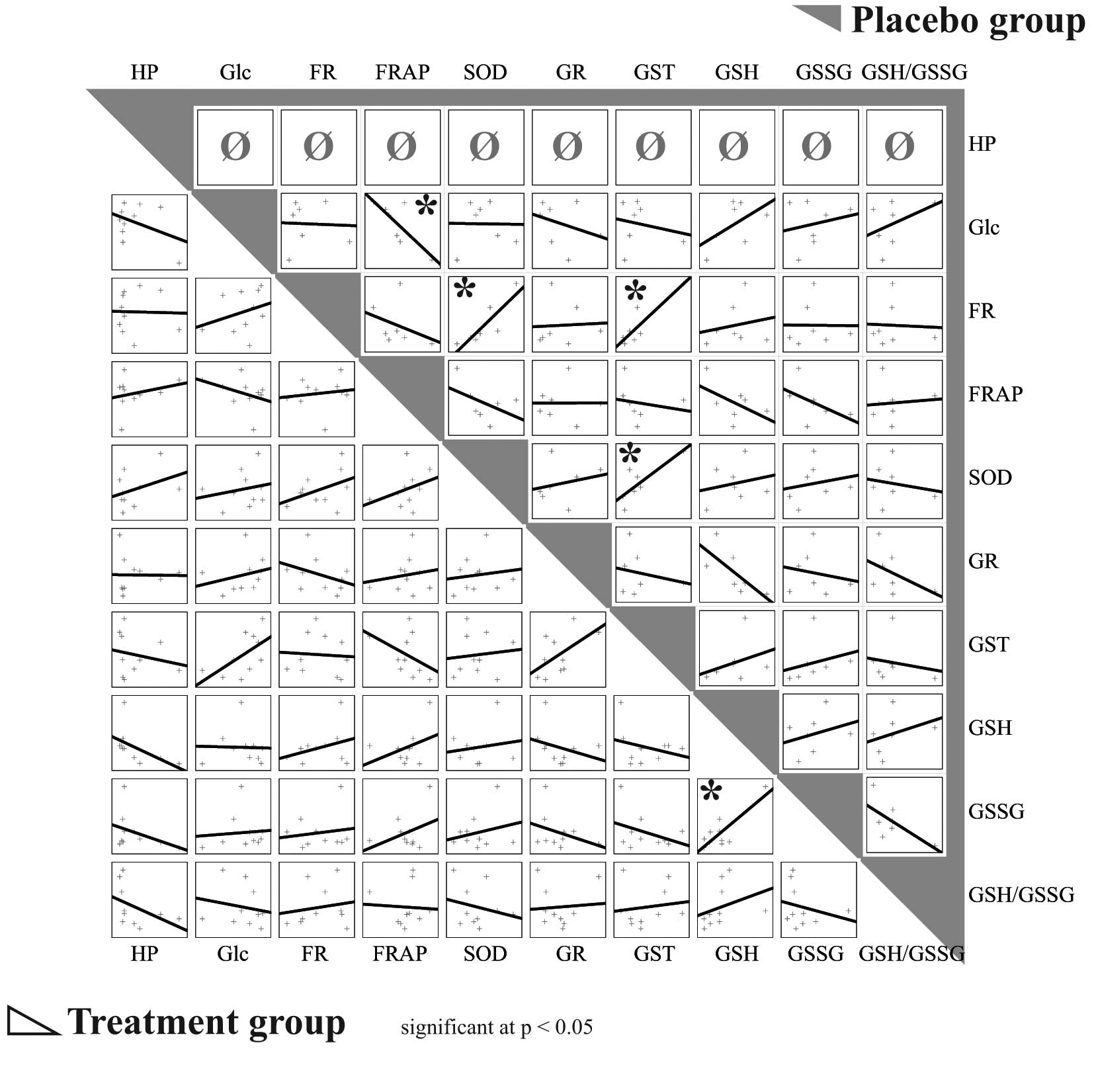
Gumulec J, Raudenska M, Hlavna M, Stracina T, Sztalmachova M, Tanhauserova V, Pacal L, Ruttkay‑Nedecky B, Sochor J, Zitka O, Zitka O, et al: Determination of oxidative stress and activities of antioxidant enzymes in guinea pigs treated with haloperidol. Exp Ther Med 5: 479-484, 2013.
APA
Gumulec, J., Raudenska, M., Hlavna, M., Stracina, T., Sztalmachova, M., Tanhauserova, V. ... Masarik, M. (2013). Determination of oxidative stress and activities of antioxidant enzymes in guinea pigs treated with haloperidol. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 5, 479-484. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2012.822
MLA
Gumulec, J., Raudenska, M., Hlavna, M., Stracina, T., Sztalmachova, M., Tanhauserova, V., Pacal, L., Ruttkay‑Nedecky, B., Sochor, J., Zitka, O., Babula, P., Adam, V., Kizek, R., Novakova, M., Masarik, M."Determination of oxidative stress and activities of antioxidant enzymes in guinea pigs treated with haloperidol". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 5.2 (2013): 479-484.
Chicago
Gumulec, J., Raudenska, M., Hlavna, M., Stracina, T., Sztalmachova, M., Tanhauserova, V., Pacal, L., Ruttkay‑Nedecky, B., Sochor, J., Zitka, O., Babula, P., Adam, V., Kizek, R., Novakova, M., Masarik, M."Determination of oxidative stress and activities of antioxidant enzymes in guinea pigs treated with haloperidol". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 5, no. 2 (2013): 479-484. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2012.822