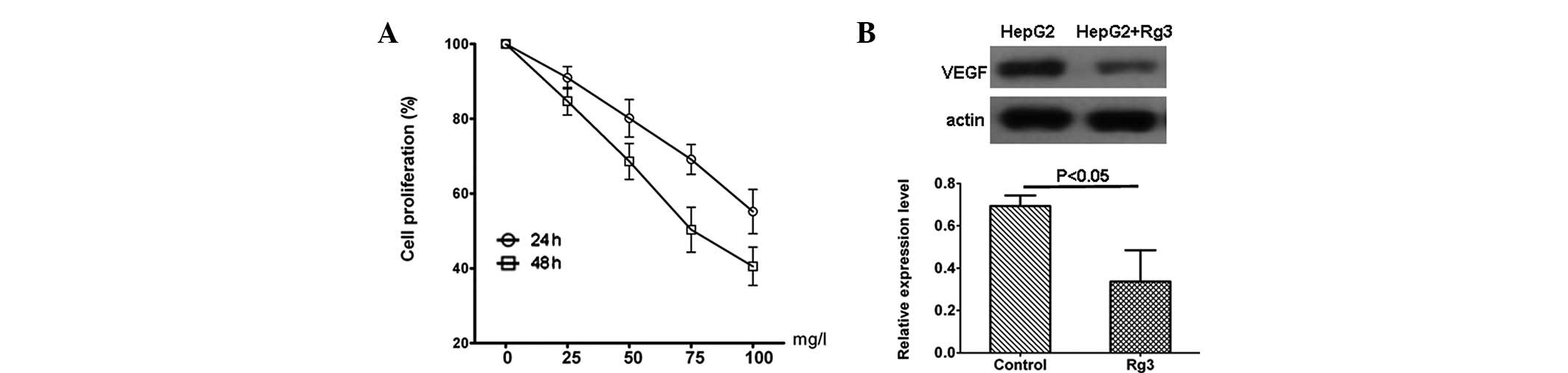
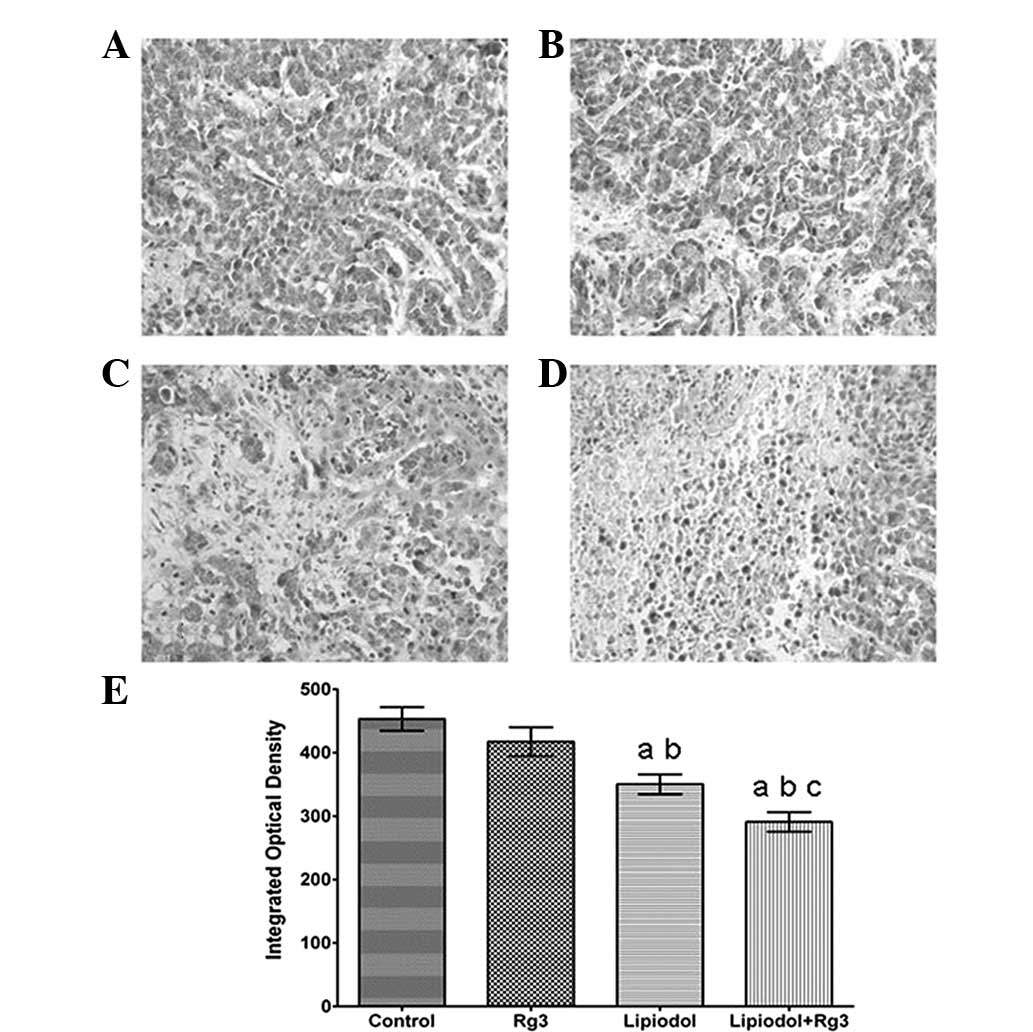
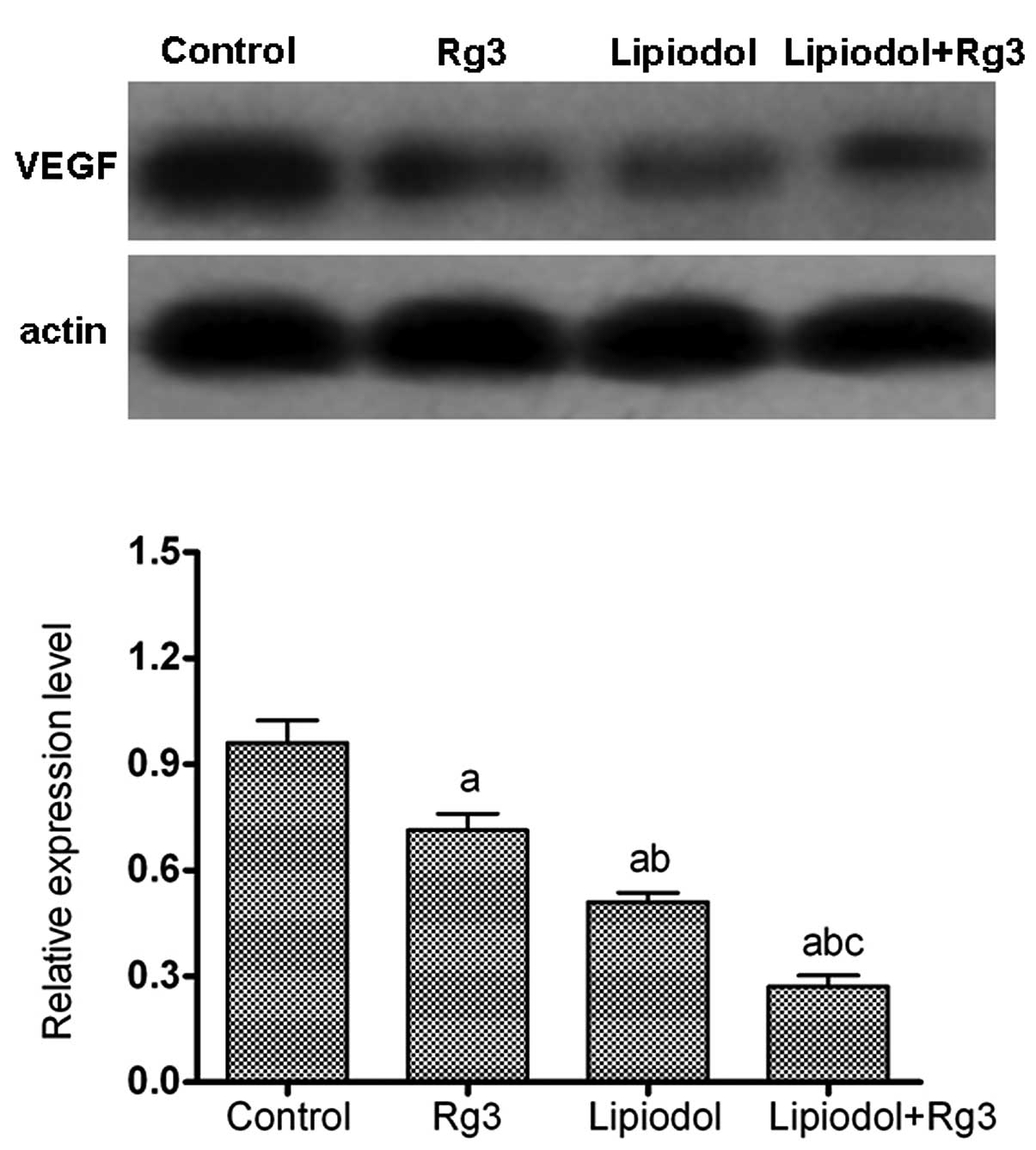
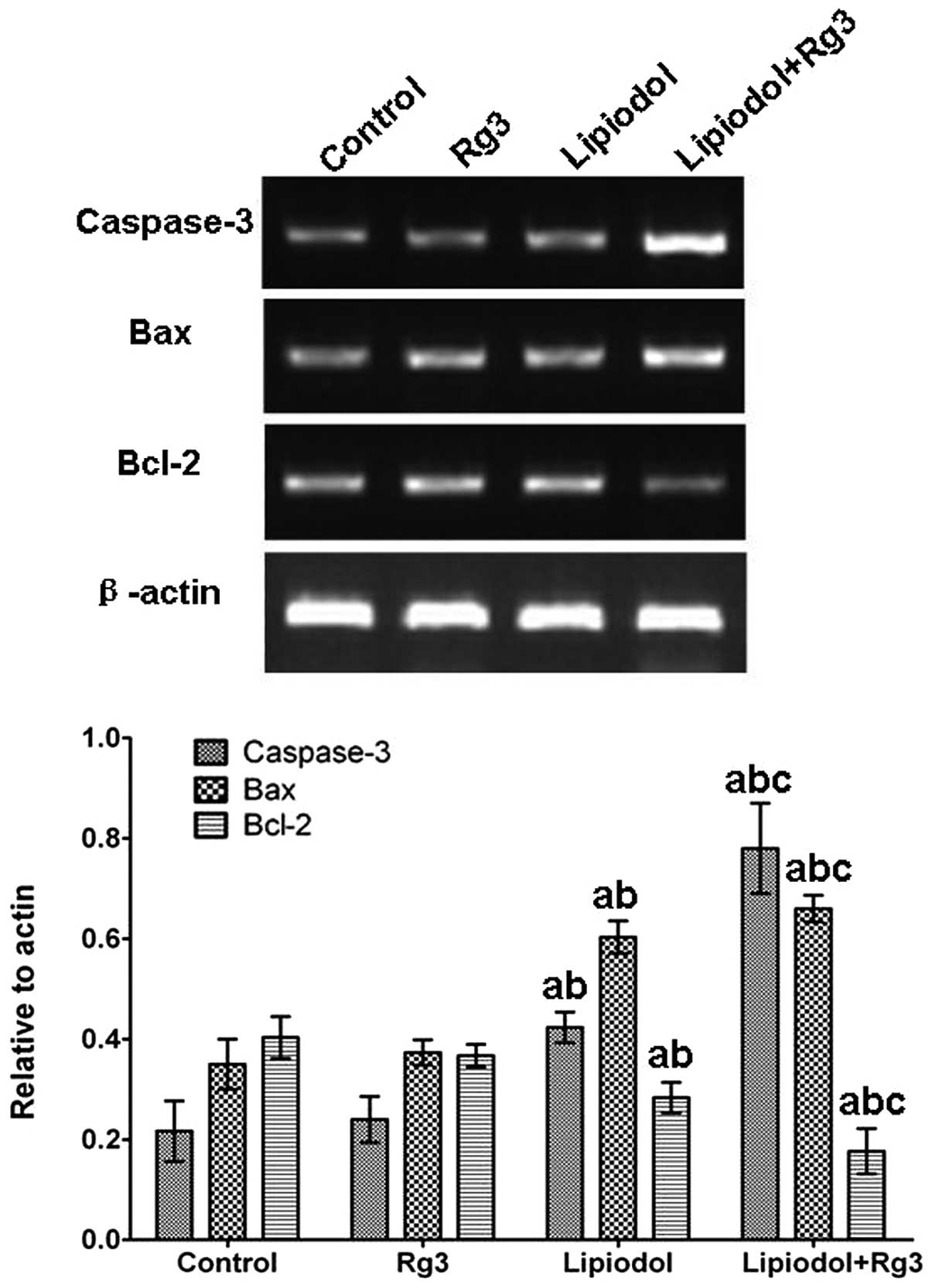
|
1.
|
Acunaş B and Rozanes I: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: treatment with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Eur J Radiol. 32:86–89. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lo CM, Ngan H, Tso WK, et al: Randomized
controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 35:1164–1171.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, et al:
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC): the role of angiogenesis and invasiveness. Am J
Gastroenterol. 103:914–921. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Kim KR, Moon HE and Kim KW:
Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Mol Med (Berl). 80:703–714. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
von Marschall Z, Cramer T, Höcker M, et
al: Dual mechanism of vascular endothelial growth factor
upregulation by hypoxia in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
48:87–96. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kaku T and Kawashima Y: Isolation and
characterization of ginsenoside-Rg2, 20R-prosapogenin,
20S-prosapogenin and delta 20-prosapogenin. Chemical studies on
saponins of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer, Third report.
Arzneimittelforschung. 30:936–943. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Kim HS, Lee EH, Ko SR, et al: Effects of
ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 on the proliferation of prostate cancer
cells. Arch Pharm Res. 27:429–435. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Wang CZ, Aung HH, Ni M, et al: Red
American ginseng: ginsenoside constituents and antiproliferative
activities of heat-processed Panax quinquefolius roots.
Planta Med. 73:669–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Yue PY, Wong DY, Wu PK, et al: The
angiosuppressive effects of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3. Biochem
Pharmacol. 72:437–445. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Rous P, Kidd JG and Smith WE: Experiments
on the cause of the rabbit carcinomas derived from virus-induced
papillomas. II. Loss by the Vx2 carcinoma of the power to immunize
hosts against the papilloma virus. J Exp Med. 96:159–174. 1952.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Khalil WK, Ahmed KA, Park MH, et al: The
inhibitory effects of garlic and Panax ginseng extract
standardized with ginsenoside Rg3 on the genotoxicity, biochemical,
and histological changes induced by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
in male rats. Arch Toxicol. 82:183–195. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Chen CF, Chiou WF and Zhang JT: Comparison
of the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng and Panax
quinquefolium. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:1103–1108. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Jia L, Zhao Y and Liang XJ: Current
evaluation of the millennium phytomedicine - ginseng (II):
Collected chemical entities, modern pharmacology, and clinical
applications emanated from traditional Chinese medicine. Curr Med
Chem. 16:2924–2942. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Keum YS, Han SS, Chun KS, et al:
Inhibitory effects of the ginsenoside Rg3 on phorbol ester-induced
cyclooxygenase-2 expression, NF-kappaB activation and tumor
promotion. Mutat Res. 523–524:75–85. 2003.
|
|
15.
|
Popovich DG and Kitts DD:
Structure-function relationship exists for ginsenosides in reducing
cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in the human leukemia
(THP-1) cell line. Arch Biochem Biophys. 406:1–8. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Yoon SR, Lee GD, Park JH, et al:
Ginsenoside composition and antiproliferative activities of
explosively puffed ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer). J
Food Sci. 75:378–382. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Liu WK, Xu SX and Che CT:
Anti-proliferative effect of ginseng saponins on human prostate
cancer cell line. Life Sci. 67:1297–1306. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kim SM, Lee SY, Yuk DY, et al: Inhibition
of NF-kappaB by ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the susceptibility of
colon cancer cells to docetaxel. Arch Pharm Res. 32:755–765. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Suzuki H, Mori M, Kawaguchi C, et al:
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor in the course of
transcatheter arterial embolization of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 14:1087–1090. 1999.
|
|
20.
|
Wu XZ, Xie GR and Chen D: Hypoxia and
hepatocellular carcinoma: The therapeutic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1178–1182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Burz C, Berindan-Neagoe I, Balacescu O and
Irimie A: Apoptosis in cancer: key molecular signaling pathways and
therapy targets. Acta Oncol. 48:811–821. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|