|
1
|
Swann JB and Smyth MJ: Immune surveillance
of tumors. J Clin Invest. 117:1137–1146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gross S and Walden P: Immunosuppressive
mechanisms in human tumors: why we still cannot cure cancer.
Immunol Lett. 116:7–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D and Sotomayor
EM: Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells.
Annu Rev Immunol. 25:267–296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Whiteside TL: Immune suppression in
cancer: effects on immune cells, mechanisms and future therapeutic
intervention. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:3–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shao BM, Dai H, Xu W, Lin ZB and Gao XM:
Immune receptors for polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 323:133–141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan WK, Cheung CC, Law HK, Lau YL and
Chan GC: Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides can induce human
monocytic leukemia cells into dendritic cells with
immunostimulatory function. J Hematol Oncol. 1:92008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Amarante MK, Watanabe MA, Conchon-Costa I,
Fiori LL, Oda JM, Búfalo MC and Sforcin JM: The effects of propolis
on CCL5 and IFN-γ expression by peripheral blood mononuclear cells
from leishmaniasis patients. J Pharm Pharmacol. 64:154–160.
2012.
|
|
8
|
Kour K, Sangwan PL, Khan I, Koul S, Sharma
SN, Kitchlu S and Bani S: Alcoholic extract of Cicer microphyllum
augments Th1 immune response in normal and chronically stressed
Swiss albino mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 63:267–277. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sliva D: Medicinal mushroom Phellinus
linteus as an alternative cancer therapy. Exp Ther Med.
1:407–411. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Vermorken AJ, Zhu J, Van de Ven WJ, Cui Y
and Fryns JP: Curcumin for the prevention of progression in
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: A word of
caution. Exp Ther Med. 1:265–269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li QQ, Wang G, Reed E, Huang L and Cuff
CF: Evaluation of cisplatin in combination with β-elemene as a
regimen for prostate cancer chemotherapy. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 107:868–876. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Mishra N, Tiwari S, Vaidya B, Agrawal GP
and Vyas SP: Lectin anchored PLGA nanoparticles for oral mucosal
immunization against hepatitis B. J Drug Target. 19:67–78. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhong Z, Dong Z, Yang L, Chen X and Gong
Z: Inhibition of proliferation of human lung cancer cells by green
tea catechins is mediated by upregulation of let-7. Exp Ther Med.
4:267–272. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Jin C, Li H, He Y, Liu Z, Bai L
and Dou K: Improved radiosensitizing effect of the combination of
etanidazole and paclitaxel for hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo.
Exp Ther Med. 3:299–303. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang X, Hu W, Zhang Q, Wang Y and Sun L:
Puerarin inhibits C-reactive protein expression via suppression of
nuclear factor kappaB activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced
peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with stable angina
pectoris. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 107:637–42. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lin ZB and Zhang HN: Anti-tumor and
immunoregulatory activities of Ganoderma lucidum and its
possible mechanisms. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:1387–1395.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
You YH and Lin ZB: Protective effects of
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides peptide on injury of
macrophages induced by reactive oxygen species. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
23:787–791. 2002.
|
|
18
|
Zhang GL, Wang YH, Ni W, Teng HL and Lin
ZB: Hepatoprotective role of Ganoderma lucidum
polysaccharide against BCG-induced immune liver injury in mice.
World J Gastroenterol. 8:728–733. 2002.
|
|
19
|
Zhang HN, He JH, Yuan L and Lin ZB: In
vitro and in vivo protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum
polysaccharides on alloxan-induced pancreatic islets damage. Life
Sci. 73:2307–2319. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu XL and Lin ZB: Modulation of cytokines
production, granzyme B and perforin in murine CIK cells by
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers.
63:188–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sun LX, Chen LH, Lin ZB, Qin Y, Zhang JQ,
Yang J, Ma J, Ye T and Li WD: Effects of Ganoderma lucidum
polysaccharides on IEC-6 cell proliferation, migration and
morphology of differentiation benefiting intestinal epithelium
healing in vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 63:1595–1603. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Sun LX, Lin ZB, Duan XS, Lu J, Ge ZH, Li
XJ, Li M, Xing EH, Jia J, Lan TF and Li WD: Ganoderma
lucidum polysaccharides antagonize the suppression on
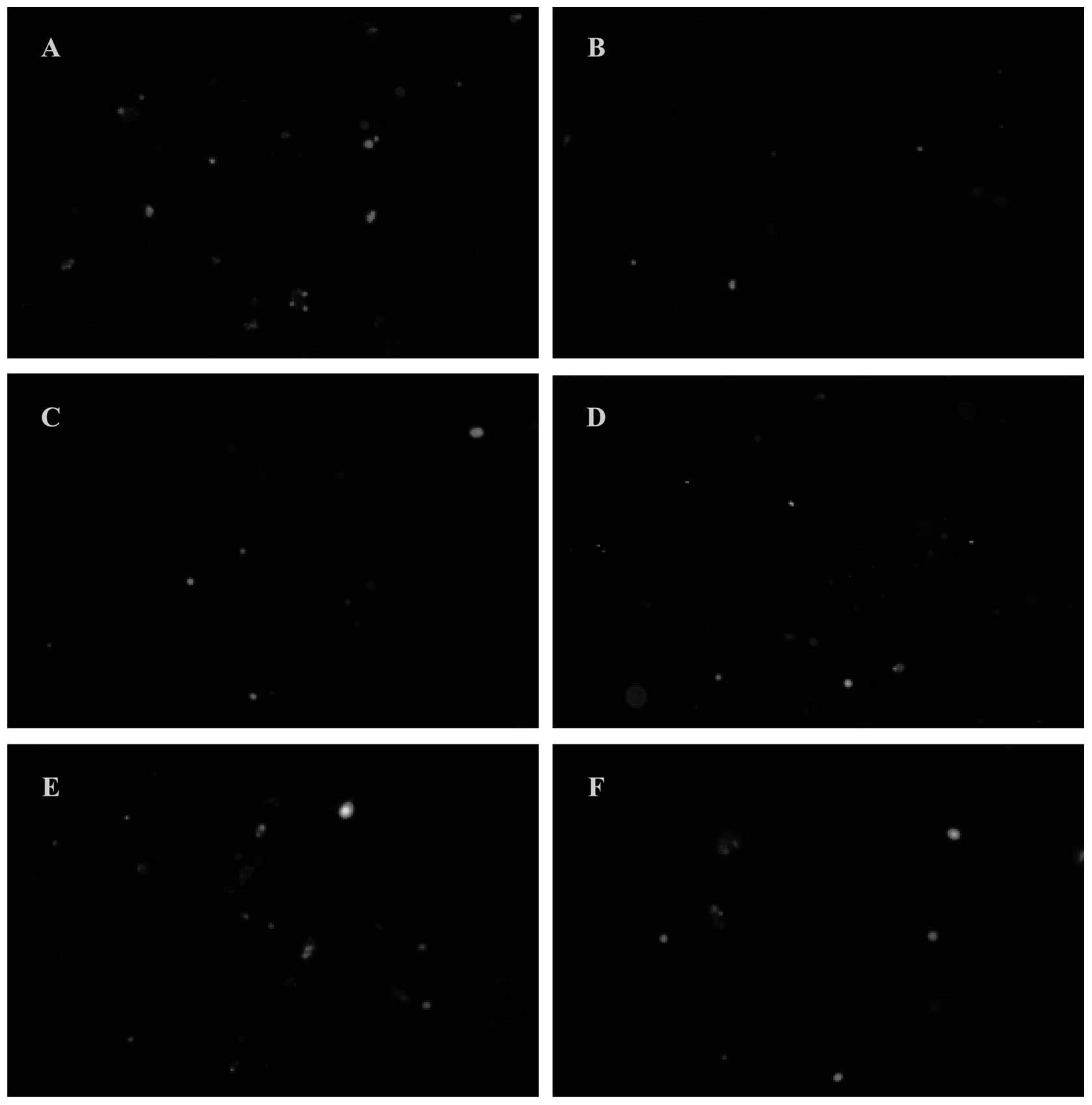
lymphocytes induced by culture supernatants of B16F10 melanoma
cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 63:725–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
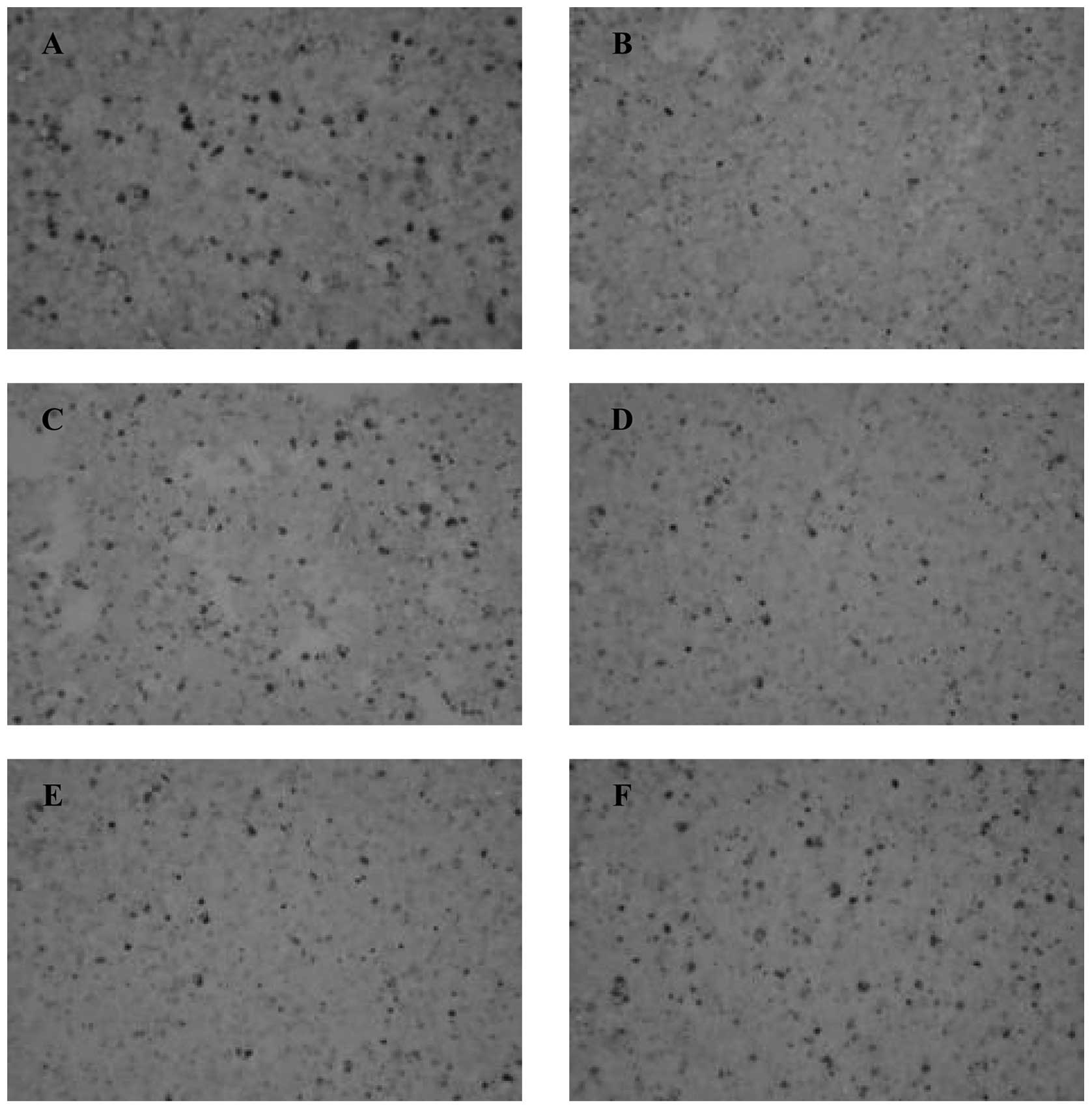
Sun LX, Lin ZB, Li XJ, Li M, Lu J, Duan
XS, Ge ZH, Song YX, Xing EH and Li WD: Promoting effects of
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on B16F10 cells to
activate lymphocytes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 108:149–154.
2011.
|
|
24
|
Sun LX, Lin ZB, Duan XS, Lu J, Ge ZH, Song
YX, Li XJ, Li M, Xing EH, Yang N and Li WD: Stronger cytotoxicity
in CTLs with granzyme B and porforin was induced by Ganoderma
lucidum polysaccharides acting on B16F10 cells. Biomed Prev
Nutr. 2:113–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
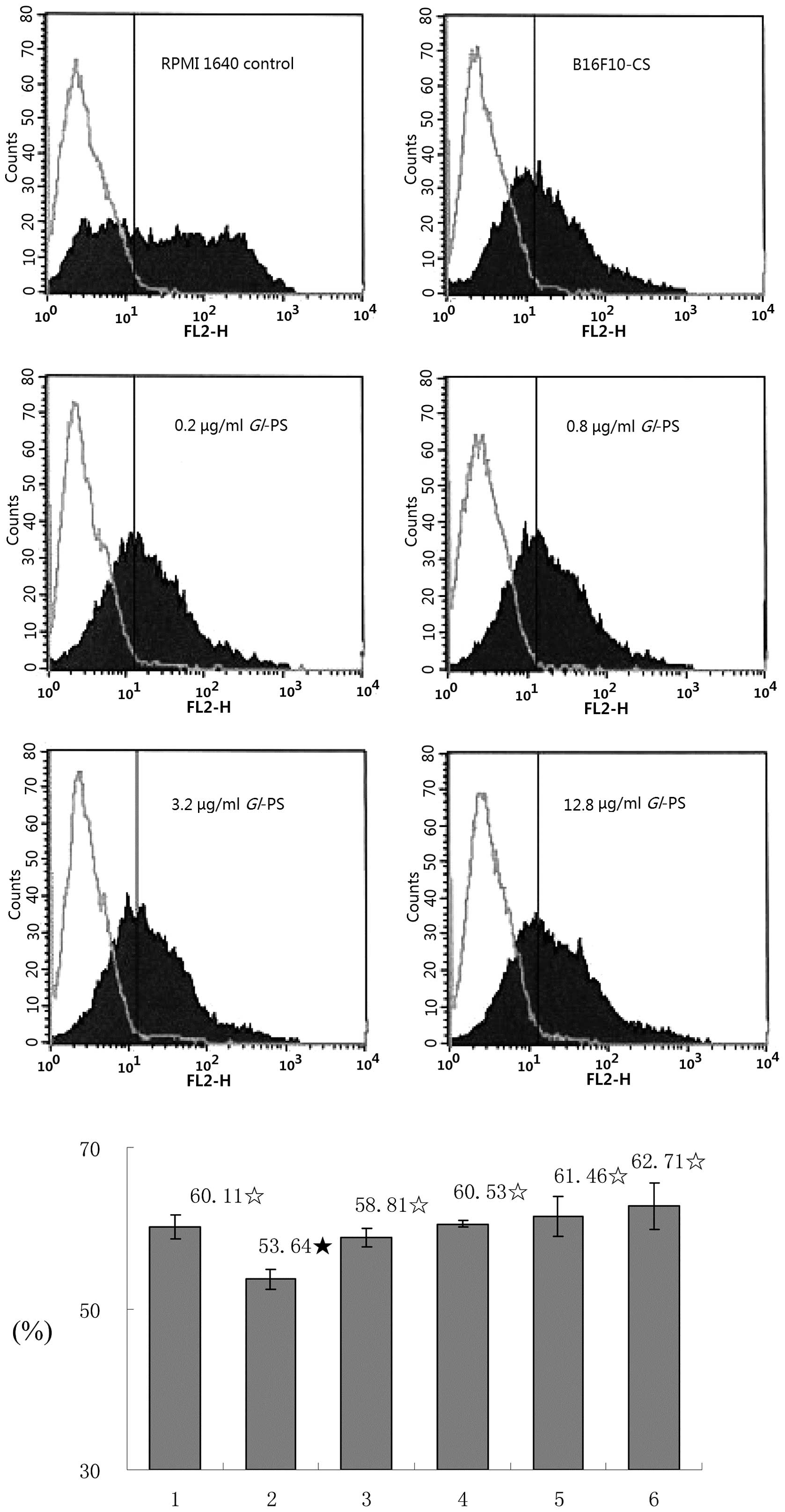
Sun LX, Lin ZB, Duan XS, Lu J, Ge ZH, Li
XF, Li XJ, Li M, Xing EH, Song YX, Jia J and Li WD: Enhanced MHC
class I and costimulatory molecules on B16F10 cells by Ganoderma
lucidum polysaccharides. J Drug Target. 20:582–592. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao LZ and Lin ZB: Regulation on
maturation and function of dendritic cells by Ganoderma
lucidum polysaccharides. Immunol Lett. 83:163–169. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang YY, Khoo KH, Chen ST, Lin CC, Wong CH
and Lin CH: Studies on the immuno-modulating and antitumor
activities of Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi) polysaccharides:
functional and proteomic analyses of a fucose-containing
glycoprotein fraction responsible for the activities. Bioorg Med
Chem. 10:1057–1062. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reddy M, Eirikis E, Davis C, Davis HM and
Prabhakar U: Comparative analysis of lymphocyte activation marker
expression and cytokine secretion profile in stimulated human
peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures: an in vitro model to
monitor cellular immune function. J Immunol Methods. 293:127–142.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Whiteside TL: Immune responses to
malignancies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125:S272–S283. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Whiteside TL, Mandapathil M, Szczepanski M
and Szajnik M: Mechanisms of tumor escape from the immune system:
adenosine-producing Treg, exosomes and tumor-associated TLRs. Bull
Cancer. 98:E25–E31. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wongkajornsilp A, Luankosolchai RA,
Huabprasert S, Chanyavanich V, Tisavipat N and Watanapa P: The
observation of immunosuppressor(s) derived from cultured tumor
cells and its partial neutralization with OK-432. J Med Assoc Thai.
84:212–122. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frumento G, Piazza T, Di Carlo E and
Ferrini S: Targeting tumor-related immunosuppression for cancer
immunotherapy. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 6:233–237.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cortés-Barberena E, González-Márquez H,
Gómez-Olivares JL and Ortiz-Muñiz R: Effects of moderate and severe
malnutrition in rats on splenic T lymphocyte subsets and activation
assessed by flow cytometry. Clin Exp Immunol. 152:585–592.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Testa U, Pelosi E and Peschle C: The
transferrin receptor. Crit Rev Oncog. 4:241–276. 1993.
|
|
35
|
Goral S: The three-signal hypothesis of
lymphocyte activation/targets for immunosuppression. Dial
Transplant. 40:14–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Reicher B and Barda-Saad M: Multiple
pathways leading from the T-cell antigen receptor to the actin
cytoskeleton network. FEBS Lett. 584:4858–4864. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chávez-Galán L, Arenas-Del Angel MC,
Zenteno E, Chávez R and Lascurain R: Cell death mechanisms induced
by cytotoxic lymphocytes. Cell Mol Immunol. 6:15–25. 2009.
|
|
38
|
Starling GC, Bajorath J, Emswiler J,
Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A and Kiener PA: Identification of amino acid
residues important for ligand binding to Fas. J Exp Med.
185:1487–1492. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun M, Ames KT, Suzuki I and Fink PJ: The
cytoplasmic domain of Fas ligand costimulates TCR signals. J
Immunol. 177:1481–1491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dzialo-Hatton R, Milbrandt J, Hockett RD
Jr and Weaver CT: Differential expression of Fas ligand in Th1 and
Th2 cells is regulated by early growth response gene and NF-AT
family members. J Immunol. 166:4534–4542. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gourley TS and Chang CH: Cutting edge: the
class II transactivator prevents activation-induced cell death by
inhibiting Fas ligand gene expression. J Immunol. 166:2917–2921.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carrington PE, Sandu C, Wei Y, Hill JM,
Morisawa G, Huang T, Gavathiotis E, Wei Y and Werner MH: The
structure of FADD and its mode of interaction with procaspase-8.
Mol Cell. 22:599–610. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Vries JF, von dem Borne PA, van
Luxemburg-Heijs SA, Heemskerk MH, Willemze R, Falkenburg JH and
Barge RM: Differential activation of the death receptor pathway in
human target cells induced by cytotoxic T lymphocytes showing
different kinetics of killing. Haematologica. 92:1671–1678.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|