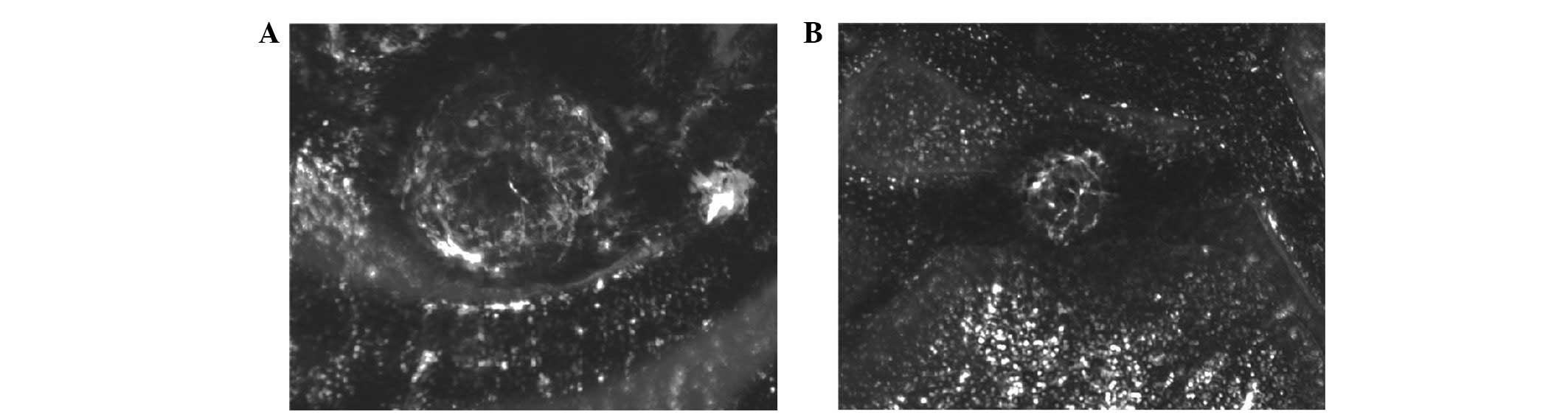
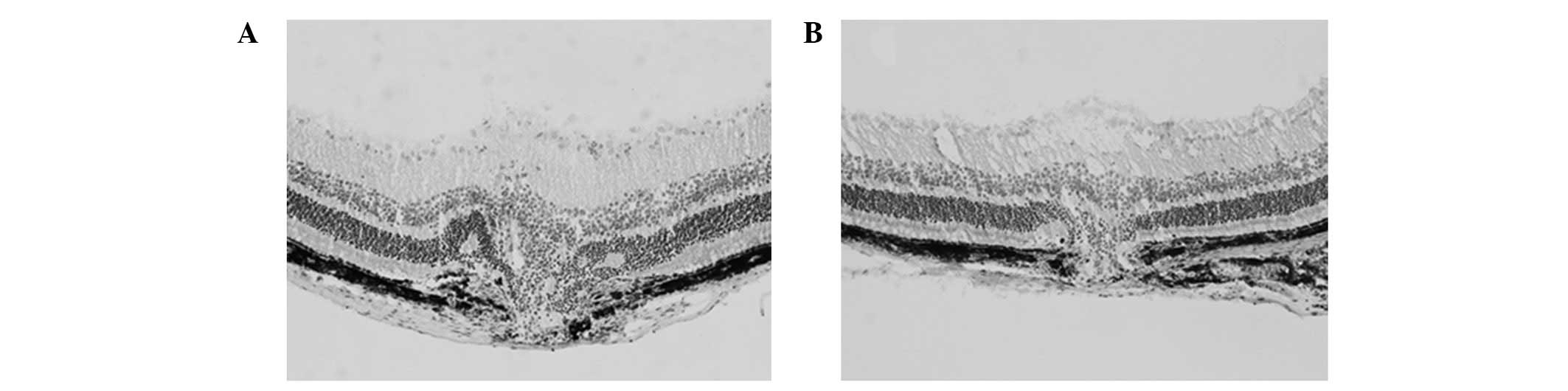
|
1
|
Héroult M, Schaffner F and Augustin HG:
Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during
angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res. 312:642–650.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kojima T, Chang JH and Azar DT:
Proangiogenic role of ephrinB1/EphB1 in basic fibroblast growth
factor-induced corneal angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 170:764–773.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen J, Hicks D, Brantley-Sieders D, et
al: Inhibition of retinal neovascularization by soluble EphA2
receptor. Exp Eye Res. 82:664–673. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zamora DO, Davies MH, Planck SR, et al:
Soluble forms of EphrinB2 and EphB4 reduce retinal
neovascularization in a model of proliferative retinopathy. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:2175–2182. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He S, Ding Y, Zhou J, et al: Soluble EphB4
regulates choroidal endothelial cell function and inhibits
laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 46:4772–4779. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Edelman JL and Castro MR: Quantitative
image analysis of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. Exp
Eye Res. 71:523–533. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang J and Hughes S: Role of the ephrin
and Eph receptor tyrosine kinase families in angiogenesis and
development of the cardiovascular system. J Pathol. 208:453–461.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davis S, Gale NW, Aldrich TH, et al:
Ligands for Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinases that require
membrane attachment or clustering for activity. Science.
266:816–819. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamada K, Oike Y, Ito Y, et al: Distinct
roles of ephrin-B2 forward and EphB4 reverse signaling in
endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:190–197. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Füller T, Korff T, Kilian A, Dandekar G
and Augustin HG: Forward EphB4 signaling in endothelial cells
controls cellular repulsion and segregation from ephrinB2 positive
cells. J Cell Sci. 116:2461–2470. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maekawa H, Oike Y, Kanda S, et al:
Ephrin-B2 induces migration of endothelial cells through the
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase pathway and promotes angiogenesis in
adult vasculature. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:2008–2014.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oike Y, Ito Y, Hamada K, et al: Regulation
of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis by EphB/ephrin-B2 signaling
between endothelial cells and surrounding mesenchymal cells. Blood.
100:1326–1333. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Helbling PM, Saulnier DM and Brändli AW:
The receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 and ephrin-B ligands restrict
angiogenic growth of embryonic veins in Xenopus laevis.
Development. 127:269–278. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang XQ, Takakura N, Oike Y, et al:
Stromal cells expressing ephrin-B2 promote the growth and sprouting
of ephrin-B2(+) endothelial cells. Blood. 98:1028–1037.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim I, Ryu YS, Kwak HJ, et al: EphB
ligand, ephrinB2, suppresses the VEGF- and angiopoietin 1-induced
Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in venous endothelial
cells. FASEB. 16:1126–1128. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Steinle JJ, Meininger CJ, Forough R, Wu G,
Wu MH and Granger HJ: Eph B4 receptor signaling mediates
endothelial cell migration and proliferation via the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Biol Chem.
277:43830–43835. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Steinle JJ, Meininger CJ, Chowdhury U, Wu
G and Granger HJ: Role of ephrinB2 in human retinal endothelial
cell proliferation and migration. Cell Signal. 15:1011–1017. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gale NW and Yancopoulos GD: Growth factors
acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases:
VEGFs, angiopoietins and ephrins in vascular development. Genes
Dev. 13:1055–1066. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Flanagan JG and Vanderhaeghen P: The
ephrins and Eph receptors in neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci.
21:309–345. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, et al:
Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular
development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular
morphogenesis and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 13:295–306.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hamada K, Oike Y, Ito Y, et al: Distinct
roles of ephrin-B2 forward and EphB4 reverse signaling in
endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:190–197. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Erber R, Eichelsbacher U, Powajbo V, et
al: EphB4 controls blood vascular morphogenesis during postnatal
angiogenesis. EMBO J. 25:628–641. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martiny-Baron G, Korff T, Schaffner F, et
al: Inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis by soluble EphB4.
Neoplasia. 6:248–257. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu Z, Jin H and Qian Q: Humanized
anti-EphB4 antibodies for the treatment of carcinomas and
vasculogenesis-related diseases. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
19:1035–1037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zamora DO, Babra B, Pan Y, Planck SR and
Rosenbaum JT: Human leukocytes express ephrinB2 which activates
microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Immunol. 242:99–109. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|