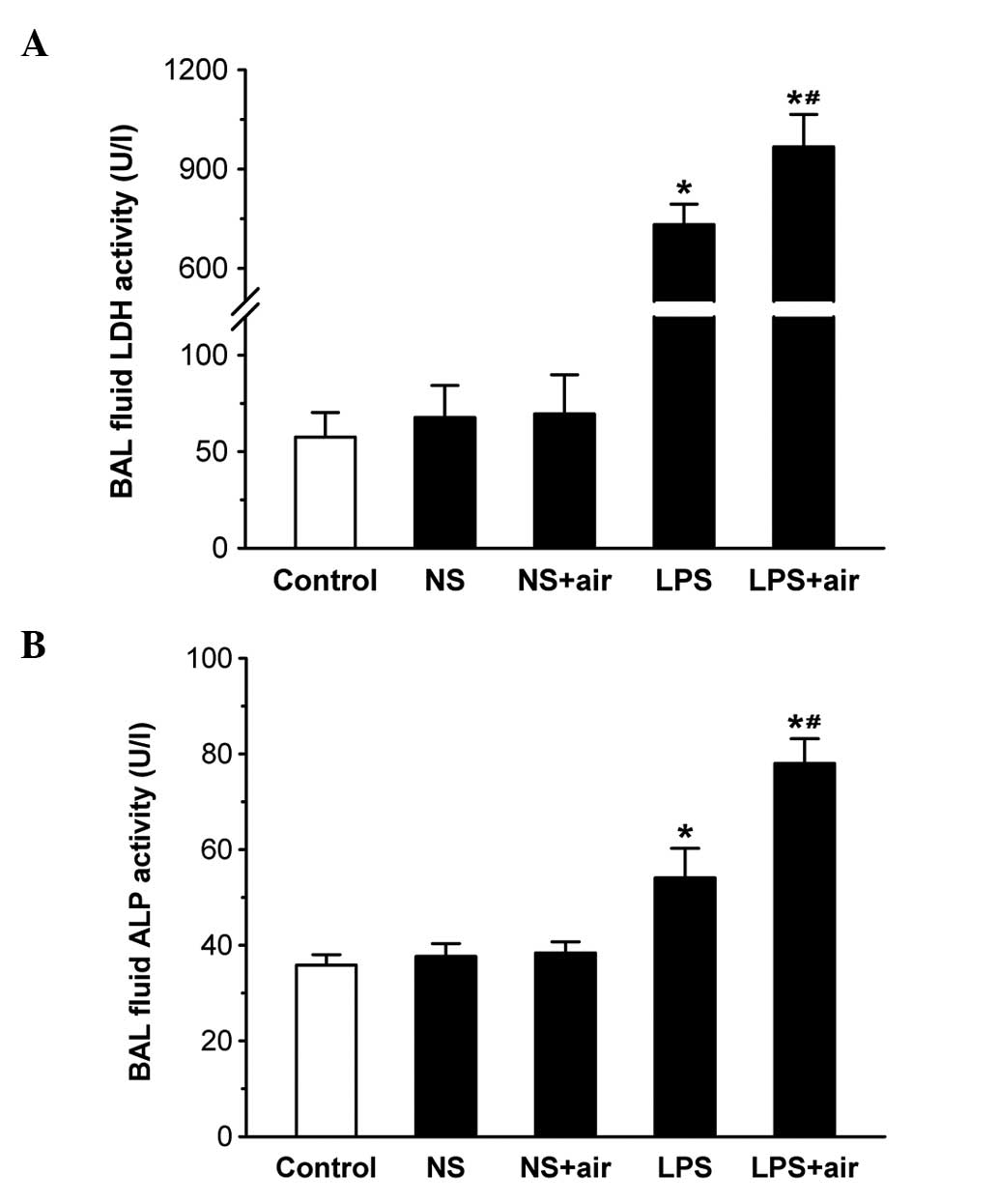
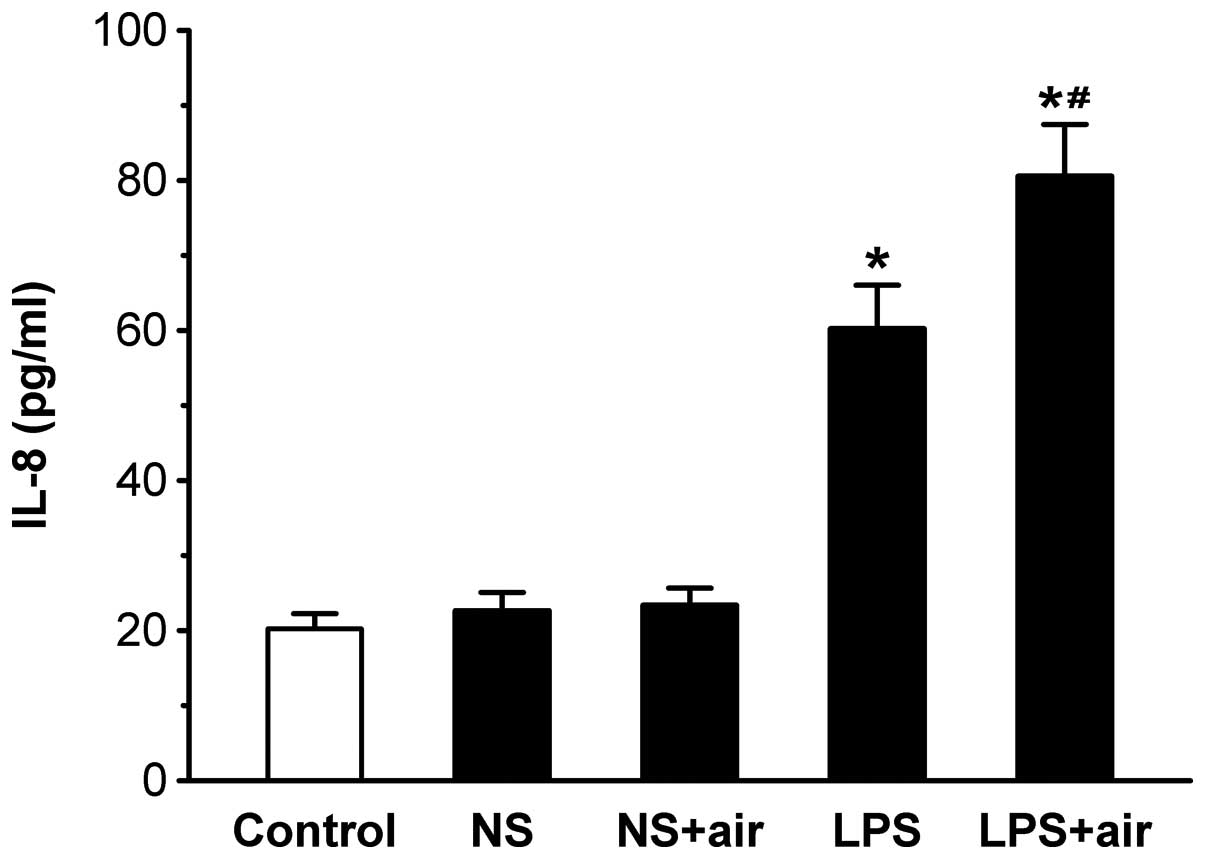
|
1
|
Matthay MA and Zemans RL: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome: pathogenesis and treatment. Annu Rev
Pathol. 6:147–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li B, Yang J, Huang Q, et al:
Biodistribution and pulmonary toxicity of intratracheally instilled
graphene oxide in mice. NPG Asia Materials. 5:e442013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Spragg RG, Bernard GR, Checkley W, et al:
Beyond mortality: future clinical research in acute lung injury. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 181:1121–1127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Phua J, Badia JR, Adhikari NK, et al: Has
mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over
time?: A systematic review. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 179:220–227.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, et
al: Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med.
353:1685–1693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muñoz NM, Meliton AY, Meliton LN, Dudek SM
and Leff AR: Secretory group V phospholipase A2 regulates acute
lung injury and neutrophilic inflammation caused by LPS in mice. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 296:L879–L887. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu XL, Xie QM, Shen YH, et al: Mannose
prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats.
Inflamm Res. 57:104–110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, Parker CH,
Liles WC and Stewart DJ: Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing
angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 4:e2692007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HA, Park JH, Lee S, Choi JS, Rhim T
and Lee M: Combined delivery of dexamethasone and plasmid DNA in an
animal model of LPS-induced acute lung injury. J Control Release.
156:60–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martin TR and Matute-Bello G: Experimental
models and emerging hypotheses for acute lung injury. Crit Care
Clin. 27:735–752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reiss LK, Uhlig U and Uhlig S: Models and
mechanisms of acute lung injury caused by direct insults. Eur J
Cell Biol. 91:590–601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu L, Gao Z, Xia C, et al: Comparative
study of trans-oral and trans-tracheal intratracheal instillations
in a murine model of acute lung injury. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
295:1513–1519. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lam CW, James JT, McCluskey R and Hunter
RL: Pulmonary toxicity of single-wall carbon nanotubes in mice 7
and 90 days after intratracheal instillation. Toxicol Sci.
77:126–134. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song YL, Fukuda N, Bai CX, Ma TH, Matthay
MA and Verkman AS: Role of aquaporins in alveolar fluid clearance
in neonatal and adult lung, and in oedema formation following acute
lung injury: studies in transgenic aquaporin null mice. J Physiol.
525:771–779. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su X, Bai CX, Hong QY, et al: Effect of
continuous hemofiltration on hemodynamics, lung inflammation and
pulmonary edema in a canine model of acute lung injury. Intensive
Care Med. 29:2034–2042. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li B, Dong C, Wang G, Zheng H, Wang X and
Bai C: Pulmonary epithelial CCR3 promotes LPS-induced lung
inflammation by mediating release of IL-8. J Cell Physiol.
226:2398–2405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bhatia M, Zemans RL and Jeyaseelan S: Role
of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 46:566–572. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thorley AJ, Ford PA, Giembycz MA,
Goldstraw P, Young A and Tetley TD: Differential regulation of
cytokine release and leukocyte migration by
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary human lung alveolar type II
epithelial cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 178:463–473. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Grommes J and Soehnlein O: Contribution of
neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol Med. 17:293–307. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kropski JA, Fremont RD, Calfee CS and Ware
LB: Clara cell protein (cc16), a marker of lung epithelial injury,
is decreased in plasma and pulmonary edema fluid from patients with
acute lung injury. Chest. 135:1440–1447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: Alveolar fluid
clearance is impaired in the majority of patients with acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 163:1376–1383. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pallister I, Dent C and Topley N:
Increased neutrophil migratory activity after major trauma: a
factor in the etiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome? Crit
Care Med. 30:1717–1721. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bao ZY, Ye QW, Gong WH, Xiang Y and Wan
HY: Humanized monoclonal antibody against the chemokine CXCL-8
(IL-8) effectively prevents acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol.
10:259–263. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Azoulay E, Darmon M, Delclaux C, et al:
Deterioration of previous acute lung injury during neutropenia
recovery. Crit Care Med. 30:781–786. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|