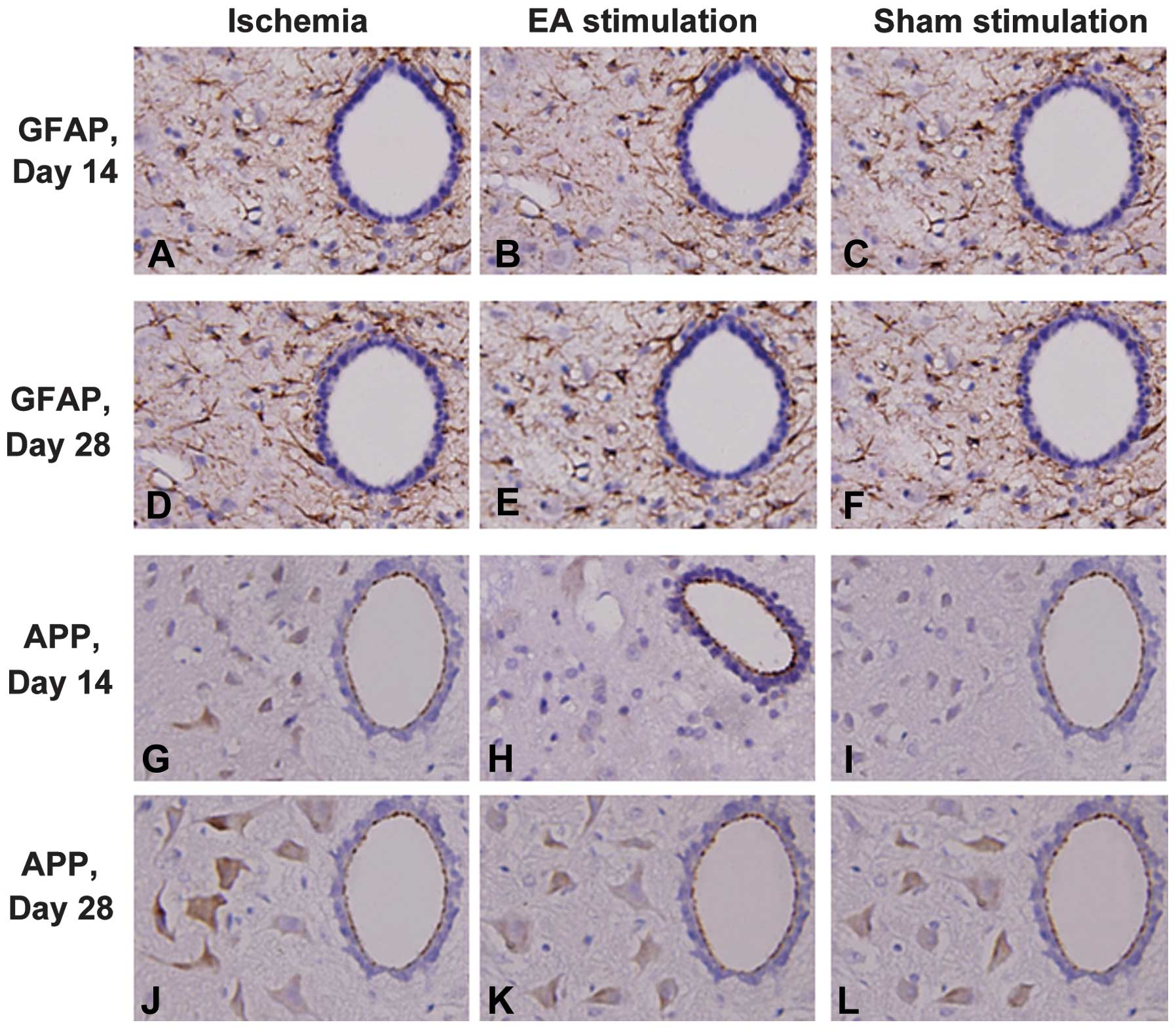
|
1
|
Rodriguez-Grande B, Blackabey V, Gittens
B, Pinteaux E and Denes A: Loss of substance P and inflammation
precede delayed neurodegeneration in the substantia nigra after
cerebral ischemia. Brain Behav Immun. 29:51–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siriphorn A, Dunham KA, Chompoopong S and
Floyd CL: Postinjury administration of 17β-estradiol induces
protection in the gray and white matter with associated functional
recovery after cervical spinal cord injury in male rats. J Comp
Neurol. 520:2630–2646. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Petrinovic MM, Hourez R, Aloy EM, et al:
Neuronal Nogo-A negatively regulates dendritic morphology and
synaptic transmission in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:1083–1088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang F, Xing S, He M, et al: Nogo-A is
associated with secondary degeneration of substantia nigra in
hypertensive rats with focal cortical infarction. Brain Res.
1469:153–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pernet V and Schwab ME: The role of Nogo-A
in axonal plasticity, regrowth and repair. Cell Tissue Res.
349:97–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu WW, Ma XL, Guo AL, Zhao HY and Luo HH:
Neuroprotective effects of NEP1-40 and fasudil on Nogo-A expression
in neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Genet Mol Res.
10:2987–2995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsai SY, Papadopoulos CM, Schwab ME and
Kartje GL: Delayed anti-Nogo-A therapy improves function after
chronic stroke in adult rats. Stroke. 42:186–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fukazawa Y, Maeda T and Kishioka S: The
pharmacological mechanisms of electroacupuncture. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 10:62–69. 2009.
|
|
9
|
Feng X, Yang S, Liu J, et al:
Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment through
inhibition of NF-κB-mediated neuronal cell apoptosis in cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med Rep. 7:1516–1522.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JH, Choi KH, Jang YJ, et al:
Electroacupuncture acutely improves cerebral blood flow and
attenuates moderate ischemic injury via an endothelial mechanism in
mice. PloS One. 8:e567362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim MW, Chung YC, Jung HC, et al:
Electroacupuncture enhances motor recovery performance with
brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rats with cerebral
infarction. Acupunct Med. 30:222–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan F, Wan S, Wu H, et al: Expression of
neurocan mRNA and ultrastructure of brain tissue after cerebral
ischemia and reperfusion in stroke-prone renovascular hypertensive
rats treated by electroacupuncture. Neural Regen Res. 6:2834–2838.
2011.
|
|
13
|
Liang YQ, Tan F and Chen J: Effects of
electroacupuncture on the ultrastructure and the Nogo-A expressions
in the cerebral cortex in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 32:209–213. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Liao SJ, Lin JW, Pei Z, Liu CL, Zeng JS
and Huang RX: Enhanced angiogenesis with dl-3n-butylphthalide
treatment after focal cerebral ischemia in RHRSP. Brain Res.
1289:69–78. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou J, Zhuang J, Li J, et al: Long-term
post-stroke changes include myelin loss, specific deficits in
sensory and motor behaviors and complex cognitive impairment
detected using active place avoidance. PloS One. 8:e575032013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xiong M, Zhang T, Zhang LM, et al: Caspase
inhibition attenuates accumulation of β-amyloid by reducing
β-secretase production and activity in rat brains after stroke.
Neurobiol Dis. 32:433–441. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Li W, Liu J, He P, et al: Hydroxysafflor
yellow A protects methylglyoxal-induced injury in the cultured
human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Neurosci Lett.
549:146–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dai H, Yu Z, Fan X, et al: Dysfunction of
annexin A2 contributes to hyperglycaemia-induced loss of human
endothelial cell surface fibrinolytic activity. Thromb Haemost.
109:1070–1078. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xie G, Yang S, Chen A, et al:
Electroacupuncture at Quchi and Zusanli treats cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of ERK signaling.
Exp Ther Med. 5:1593–1597. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao J, Xu H, Tian Y, Hu M and Xiao H:
Effect of electroacupuncture on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
mRNA expression in mouse hippocampus following cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:253–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huo ZJ, Die J and Xu JM: Influence of
electroacupuncture on spinal TNF-alpha and IL-6 contents in spinal
cord ischemia-reperfusion injury rabbits. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
37:308–311. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Zou LP, Du JB and Wong V:
Electro-acupuncture protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain-damaged
immature rat via hydrogen sulfide as a possible mediator. Neurosci
Lett. 485:74–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim JH, Choi KH, Jang YJ, et al:
Electroacupuncture preconditioning reduces cerebral ischemic injury
via BDNF and SDF-1α in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med.
13:222013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barreto G, White RE, Ouyang Y, Xu L and
Giffard RG: Astrocytes: targets for neuroprotection in stroke. Cent
Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 11:164–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Wegrzynowicz M,
Lee E, Bowman AB and Aschner M: Role of astrocytes in brain
function and disease. Toxicol Pathol. 39:115–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nawashiro H, Brenner M, Fukui S, Shima K
and Hallenbeck JM: High susceptibility to cerebral ischemia in
GFAP-null mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 20:1040–1044. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fournier AE, Gould GC, Liu BP and
Strittmatter SM: Truncated soluble Nogo receptor binds Nogo-66 and
blocks inhibition of axon growth by myelin. J Neurosci.
22:8876–8883. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wiessner C, Bareyre FM, Allegrini PR, et
al: Anti-Nogo-A antibody infusion 24 hours after experimental
stroke improved behavioral outcome and corticospinal plasticity in
normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 23:154–165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Huber AB, Weinmann O, Brösamle C, Oertle T
and Schwab ME: Patterns of Nogo mRNA and protein expression in the
developing and adult rat and after CNS lesions. J Neurosci.
22:3553–3567. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tseng CS, Shen WC, Cheng FC, Chen GW, Li
TC and Hsieh CL: Dynamic change in energy metabolism by
electroacupuncture stimulation in rats. Am J Chin Med. 33:767–778.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|