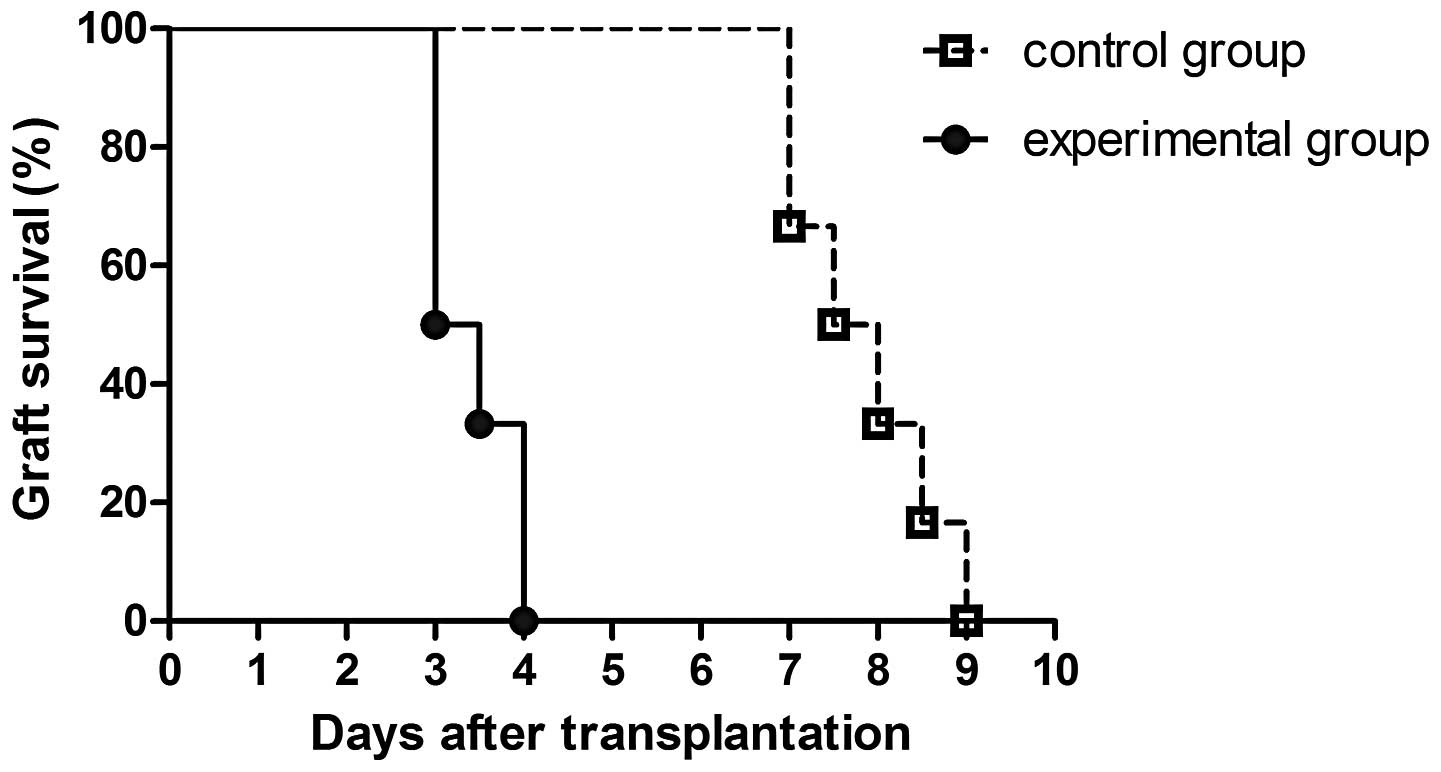
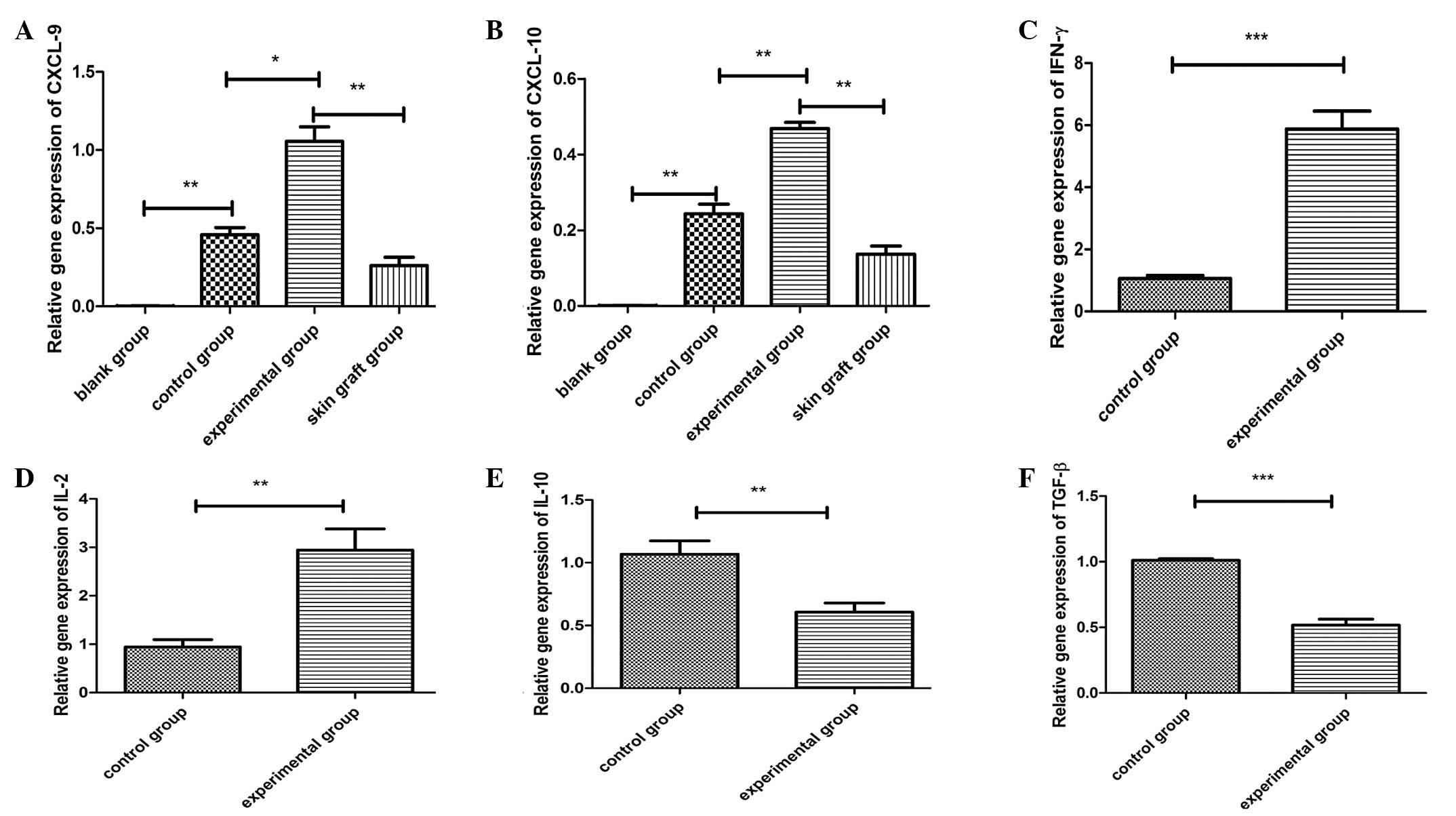
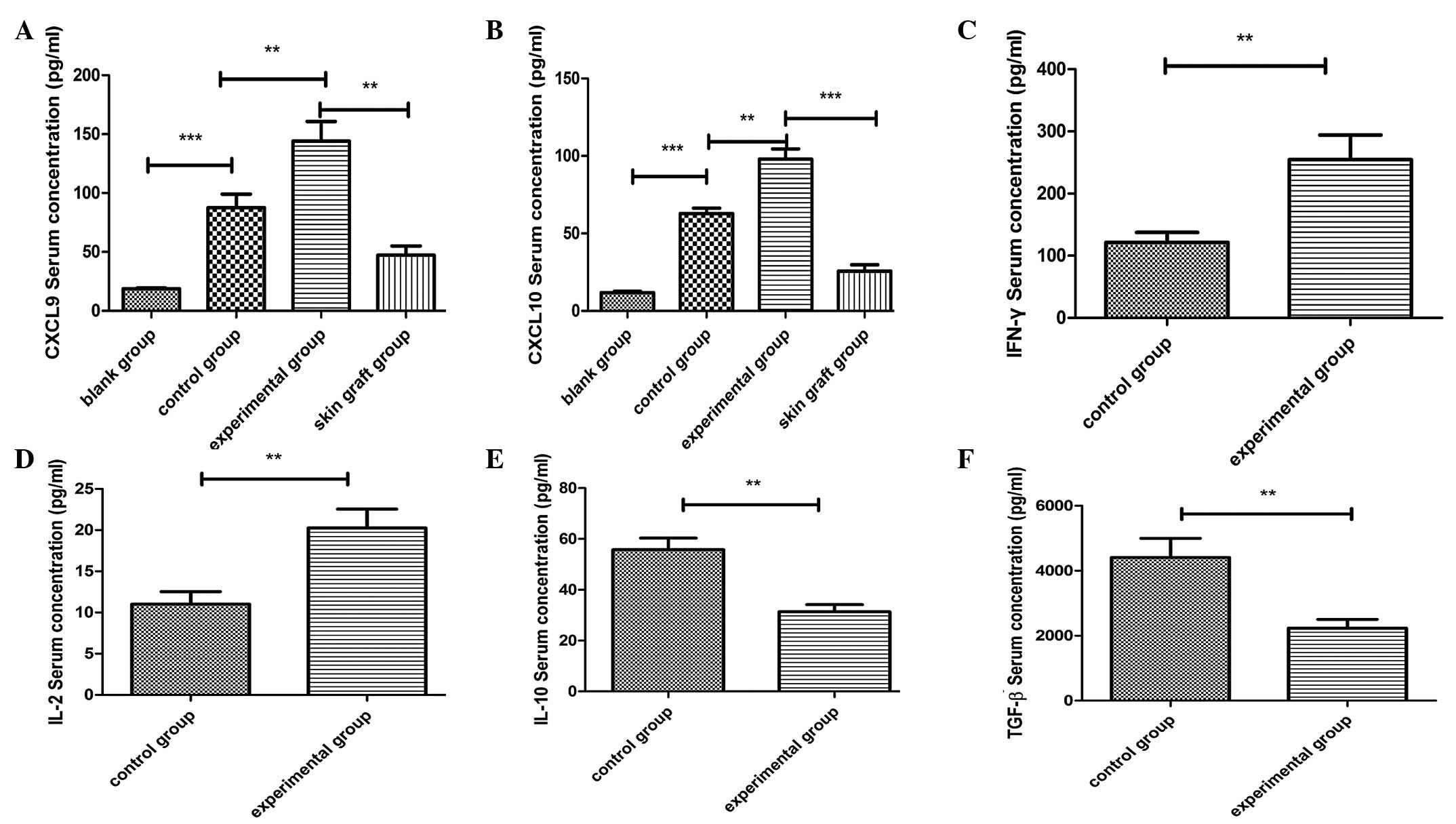
|
1
|
Luo L, Li C, Wu W, Lu J, et al: Functional
analysis of alloreactive memory CD4+ T cells derived
from skin transplantation recipient and naïve CD4+ T
cells derived from untreated mice. J Surg Res. 176:649–656.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McFarland RD, Douek DC, Koup RA and Picker
LJ: Identification of a human recent thymic emigrant phenotype.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4215–4220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Douek DC, McFarland RD, Keiser PH, et al:
Changes in thymic function with age and during the treatment of HIV
infection. Nature. 396:690–695. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Arendonk KJ, Garonzik Wang JM,
Deshpande NA, James NT, Smith JM, Montgomery RA, Colombani PM and
Segev DL: Practice patterns and outcomes in retransplantation among
pediatric kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation.
95:1360–1368. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnson MR, Aaronson KD, Canter CE,
Kirklin JK, Mancini DM, Mehra MR, Radovancevic B, Taylor DO and
Webber SA: Heart retransplantation. Am J Transplant. 7:2075–2081.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Saito A, Novick RJ, Kiaii B, McKenzie FN,
Quantz M, Pflugfelder P, Fisher G and Chu MW: Early and late
outcomes after cardiac retransplantation. Can J Surg. 56:21–26.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Richters CD, Hoekstra MJ, et al:
Immunology of skin transplantation. Clin Dermatol. 23:338–342.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Game DS and Lechler RI: Pathways of
allorecognition: implications for transplantation tolerance.
Transpl Immunol. 10:101–108. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sánchez Lázaro IJ, Almenar Bonet L, Moro
López J, Sánchez Lacuesta E, Martínez-Dolz L, Agüero Ramón-Llín J,
et al: Influence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors in the
recipient on the development of cardiac allograft vasculopathy
after heart transplantation. Transplant Proc. 40:3056–3057.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Springer TA: Traffic signals on
endothelium for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration.
Annu Rev Physiol. 57:827–872. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flach R, Speidel N, Flohé S, Börgermann J,
Dresen IG, Erhard J and Schade FU: Analysis of intragraft cytokine
expression during early reperfusion after liver transplantation
using semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Cytokine. 10:445–451. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rosenblum JM, Shimoda N, Schenk AD, Zhang
H, Kish DD, Keslar K, Farber JM and Fairchild RL: CXC chemokine
ligand (CXCL) 9 and CXCL10 are antagonistic costimulation molecules
during the priming of alloreactive T cell effectors. J Immunol.
184:3450–3460. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Matsuura A, Abe T and Yasuura K:
Simplified mouse cervical heart transplantation using a cuff
technique. Transplantation. 51:896–898. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Billingham ME, Cary NR, Hammond ME,
Kemnitz J, Marboe C, McCallister HA, et al: A working formulation
for the standardization of nomenclature in the diagnosis of heart
and lung rejection: Heart Rejection Study Group. The International
Society for Heart Transplantation. J Heart Transplant. 9:587–593.
1990.
|
|
15
|
Winters GL, Marboe CC and Billingham ME:
The International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation
grading system for heart transplant biopsy specimens: clarification
and commentary. J Heart Lung Transplant. 17:754–760.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koga S, Auerbach MB, Engeman TM, Novick
AC, Toma H and Fairchild RL: T cell infiltration into class II
MHC-disparate allografts and acute rejection is dependent on the
IFN-gamma-induced chemokine Mig. J Immunol. 163:4878–4885.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watarai Y, Koga S, Paolone DR, Engeman TM,
Tannenbaum C, Hamilton TA and Fairchild RL: Intraallograft
chemokine RNA and protein during rejection of MHC-matched/multiple
minor histocompatibility-disparate skin grafts. J Immunol.
164:6027–6033. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Miura M, Morita K, Kobayashi H, Hamilton
TA, Burdick MD, Strieter RM and Fairchild RL: Monokine induced by
IFN-gamma is a dominant factor directing T cells into murine
cardiac allografts during acute rejection. J Immunol.
167:3494–3504. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hancock WW, Gao W, Csizmadia V, Faia KL,
Shemmeri N and Luster AD: Donor-derived IP-10 initiates development
of acute allograft rejection. J Exp Med. 193:975–980. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liang H, Zhao Y, San Z, Liao C, Sha C, Xie
B, Chen J, Xia J, Wang Y and Qi Z: The recall alloresponse
following retransplantation is more intense compared with the T
cell memory-transfer model. Immunol Invest. 39:39–53. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou X, Shan Z, Liang H, et al: Role of
regulated upon activation normal T-cell expressed and secreted in a
model of retransplantation acute rejection mediated by alloreactive
memory CD4+ T cells. Transplant Proc. 45:546–551. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roedder S, Vitalone M, Khatri P and Sarwal
MM: Biomarkers in solid organ transplantation: establishing
personalized transplantation medicine. Genome Med. 3:372011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Romagnani P and Crescioli C: CXCL10: a
candidate biomarker in transplantation. Clin Chim Acta.
413:1364–1373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang H, Liao C, Qi Z, et al: Rapamycin or
tacrolimus alone fails to resist cardiac allograft accelerated
rejection mediated by alloreactive CD4(+) memory T cells in mice.
Transpl Immunol. 22:128–136. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Agostini C, Calabrese F, Rea F, et al:
Cxcr3 and its ligand CXCL10 are expressed by inflammatory cells
infiltrating lung allografts and mediate chemotaxis of T cells at
sites of rejection. Am J Pathol. 158:1703–1711. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Burdick MD, et al:
Role of CXCL9/CXCR3 chemokine biology during pathogenesis of acute
lung allograft rejection. J Immunol. 171:4844–4852. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|