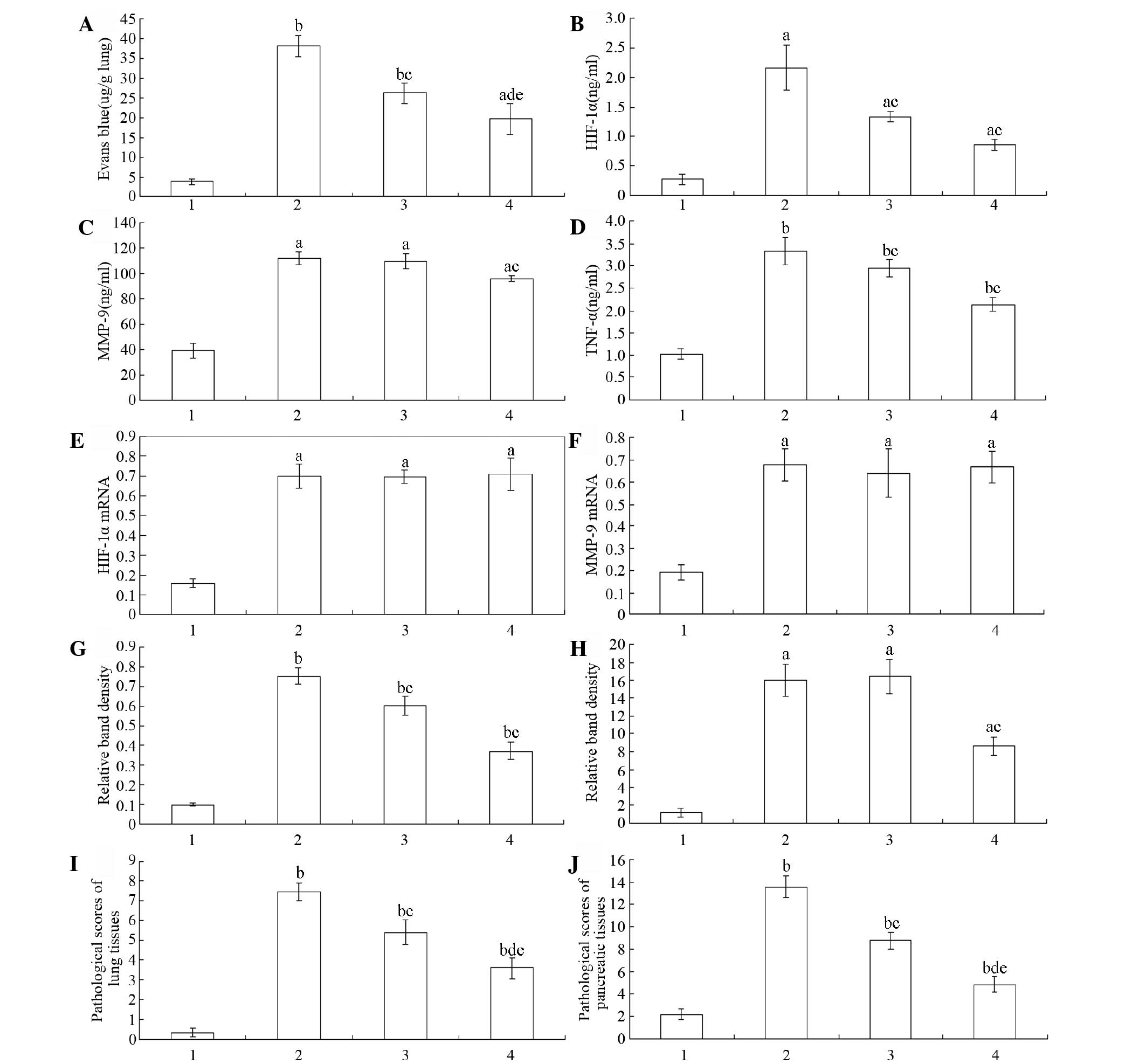
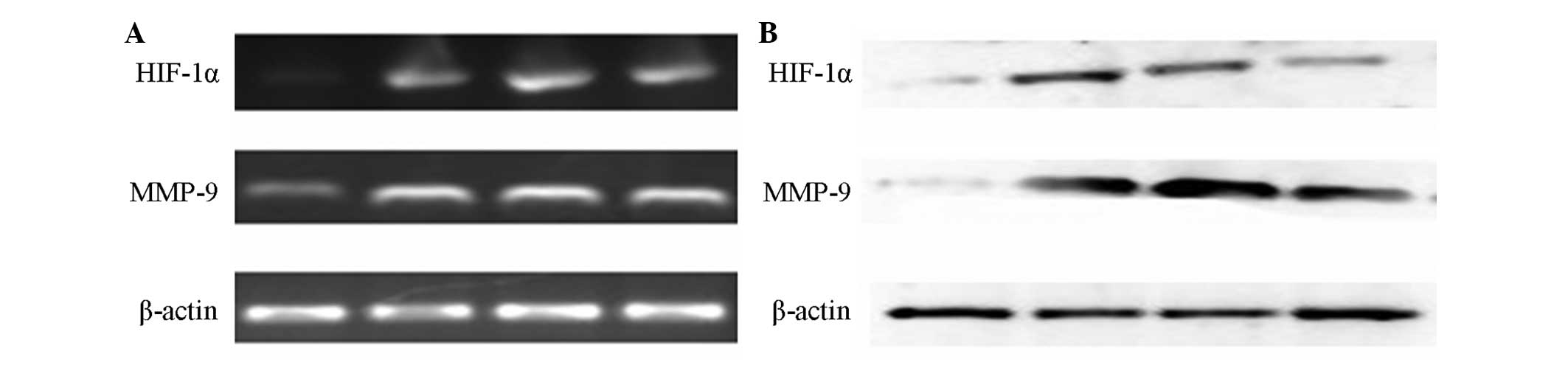
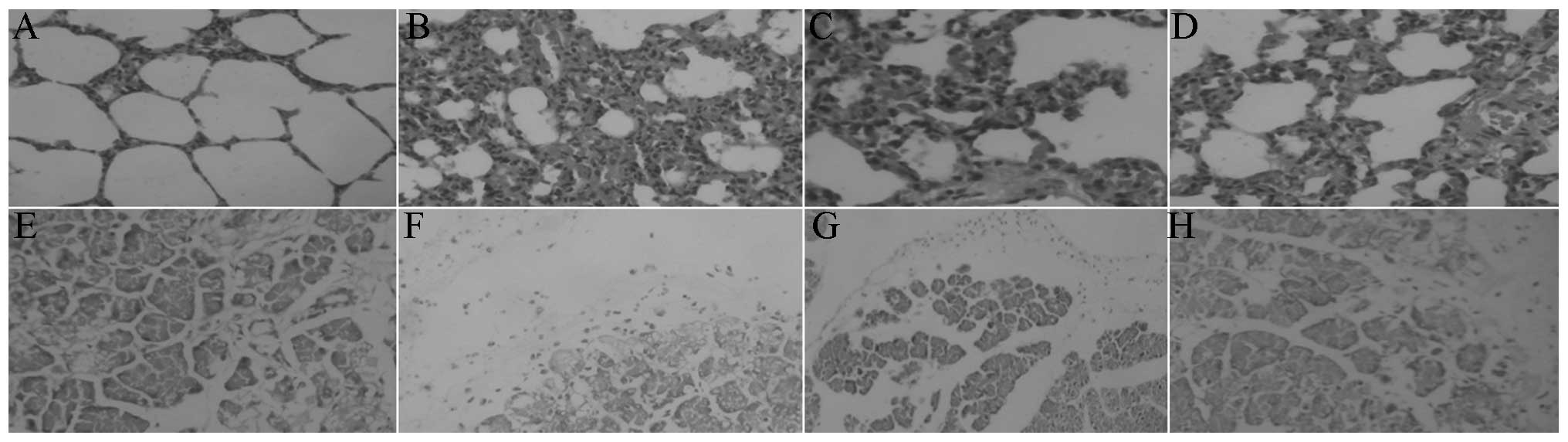
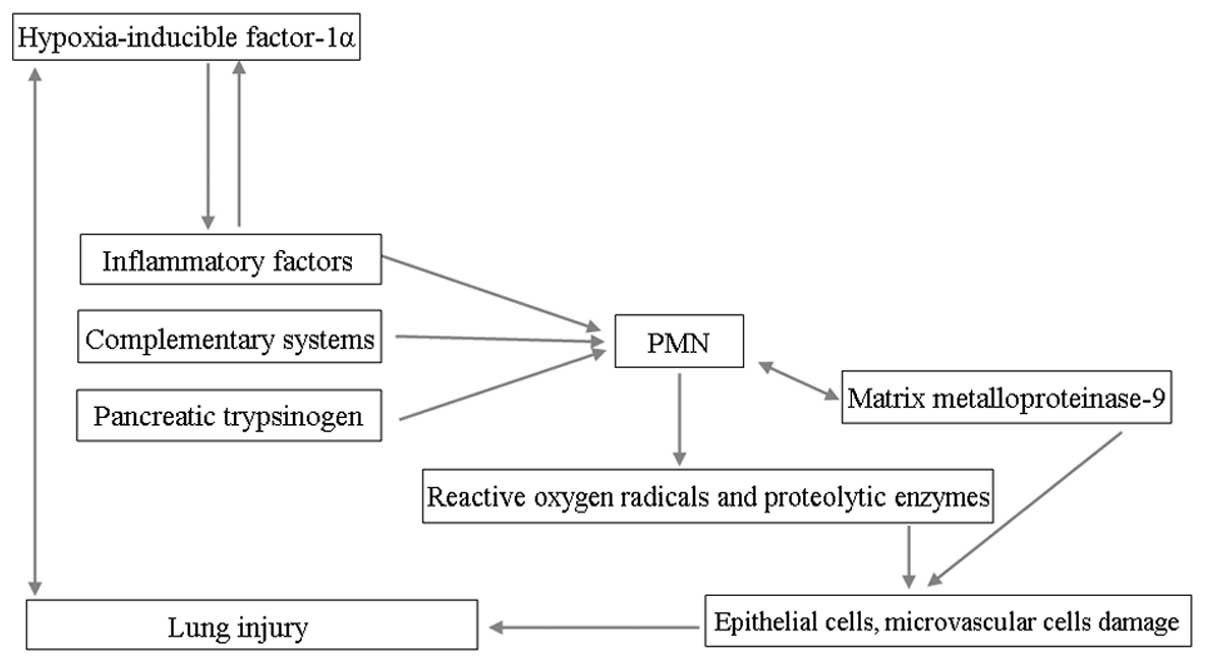
|
1
|
Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, et al:
Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 5:132–144.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bhatia M: Novel therapeutic targets for
acute pancreatitis and associated multiple organ dysfunction
syndrome. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 1:343–351. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang G, Chen HL, Ren F, Li J and Li YQ:
Expression of Cav-1, AQP1 and AQP5 in lung of acute
pancreatitis-associated lung injury rats and the therapeutic role
of Qingyitang. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 90:2564–2569. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Higashida T, Kreipke CW, Rafols JA, et al:
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, aquaporin-4, and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in blood brain barrier disruption and brain
edema after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 114:92–101.
2011.
|
|
5
|
Gao ZM, Chen HL and Liu XD: Expression and
function of aquaporin-1 in acute lung injury induced by severe
acute pancreatitis in rats. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi.
15:453–457. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Renzulli P, Jakob SM, Täuber M, Candinas D
and Gloor B: Severe acute pancreatitis: Case-oriented discussion of
interdisciplinary management. Pancreatology. 5:145–156. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen P, Huang L, Sun Y and Yuan Y:
Upregulation of PIAS1 protects against sodium taurocholate-induced
severe acute pancreatitis associated with acute lung injury.
Cytokine. 54:305–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sochor M, Richter S, Schmidt A, Hempel S,
Hopt UT and Keck T: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 with
doxycycline reduces pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Digestion.
80:65–73. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eckle T, Faigle M, Grenz A, Laucher S,
Thompson LF and Eltzschig HK: A2B adenosine receptor dampens
hypoxia-induced vascular leak. Blood. 111:2024–2035. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pirrone F, Pastore C, Mazzola S and
Albertini M: In vivo study of the behaviour of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) in mechanical, hypoxic and
septic-induced acute lung injury. Vet Res Commun. 33(Suppl 1):
121–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kobayashi Y, Matsumoto M, Kotani M and
Makino T: Possible involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in
Langerhans cell migration and maturation. J Immunol. 163:5989–5993.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martinez-Hernandez A and Amenta PS: The
basement membrane in pathology. Lab Invest. 48:656–677. 1983.
|
|
13
|
Keck T, Balcom JH 4th, Fernández-del
Castillo C, Antoniu BA and Warshaw AL: Matrix metalloproteinase-9
promotes neutrophil migration and alveolar capillary leakage in
pancreatitis-associated lung injury in the rat. Gastroenterology.
122:188–201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimoda LA and Semenza GL: HIF and the
lung: role of hypoxia-inducible fctors in pulmonary development and
disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:152–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Semenza G: Signal transduction to
hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Pharmacol. 64:993–998. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai X, Sun B, Pan S, et al:
Down-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by hyperbaric
oxygen attenuates the severity of acute pancreatitis in rats.
Pancreas. 38:515–522. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gomez G, Englander EW, Wang G and Greeley
GH Jr: Increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha,
p48, and the Notch signaling cascade during acute pancreatitis in
mice. Pancreas. 28:58–64. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Becker PM, Alcasabas A, Yu AY, Semenza GL
and Bunton TE: Oxygen-independent upregulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor and vascular barrier dysfunction during
ventilated pulmonary ischemia in isolated ferret lungs. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 22:272–279. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Standiford TJ, Kunkel SL, Lukacs NW, et
al: Macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha mediates lung leukocyte
recruitment, lung capillary leak, and early mortality in murine
endotoxemia. J Immunol. 155:1515–1524. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, et
al: A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy.
Ann Surg. 215:44–56. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Liu JW, Li ZL, et al: Development
of a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis associated lung injury.
Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi. 21:211–219. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Chen C, Ostrowski RP, Zhou C, Tang J and
Zhang JH: Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and its
downstream genes reduces acute hyperglycemia-enhanced hemorrhagic
transformation in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res.
88:2046–2055. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Koeppen M, Eckle T and Eltzschig HK: The
hypoxia-inflammation link and potential drug targets. Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 24:363–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hartmann G, Tschöp M, Fischer R, et al:
High altitude increases circulating interleukin-6, interleukin-1
receptor antagonist and C-reactive protein. Cytokine. 12:246–252.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rosenberger P, Schwab JM, Mirakaj V, et
al: Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent induction of netrin-1
dampens inflammation caused by hypoxia. Nat Immunol. 10:195–202.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hartwig W, Werner J, Jimenez RE, et al:
Trypsin and activation of circulating trypsinogen contribute to
pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Am J Physiol. 277:G1008–G1016.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou H, Chen X, Zhang WM, Zhu LP and Cheng
L: HIF-1α inhibition reduces nasal inflammation in a murine
allergic rhinitis model. Plos One. 7:e486182012.
|
|
28
|
Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM, et al:
2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting
microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell. 3:363–375. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Salama SA, Kamel MW, Botting S, et al:
Catechol-o-methyltransferase expression and 2-methoxyestradiol
affect microtubule dynamics and modify steroid receptor signaling
in leiomyoma cells. PLoS One. 4:e73562009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pastor CM, Matthay MA and Frossard JL:
Pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury: new insights. Chest.
124:2341–2351. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|