Spandidos Publications style
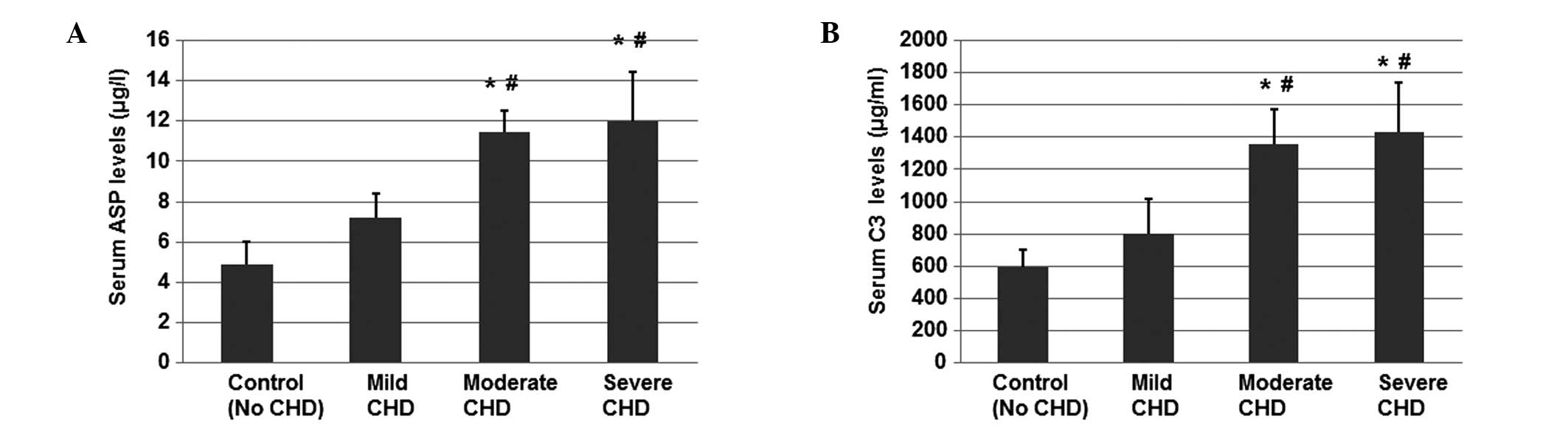
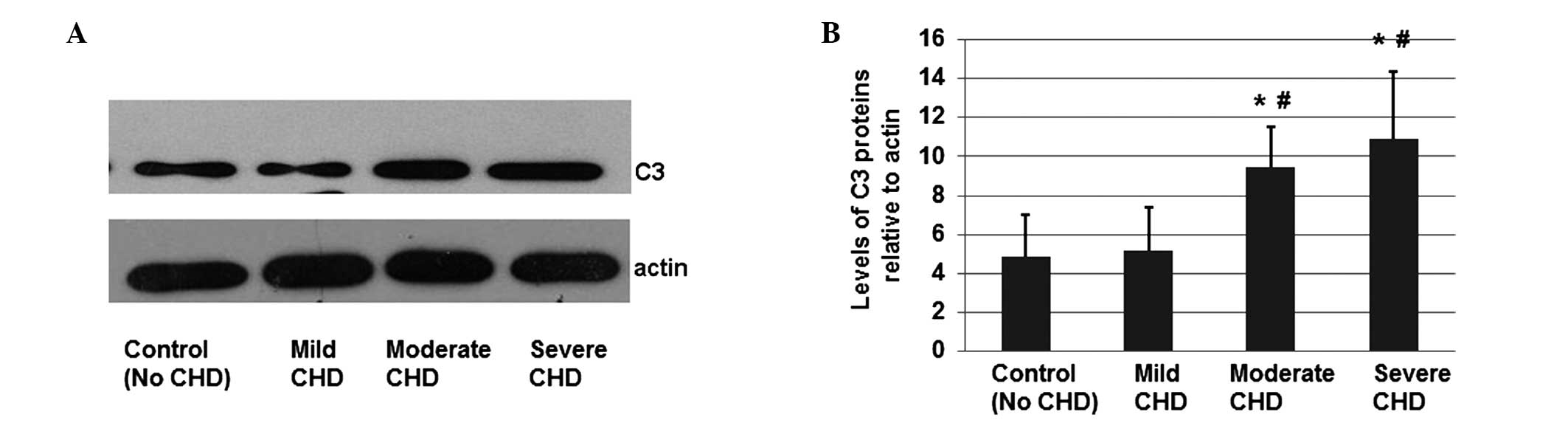
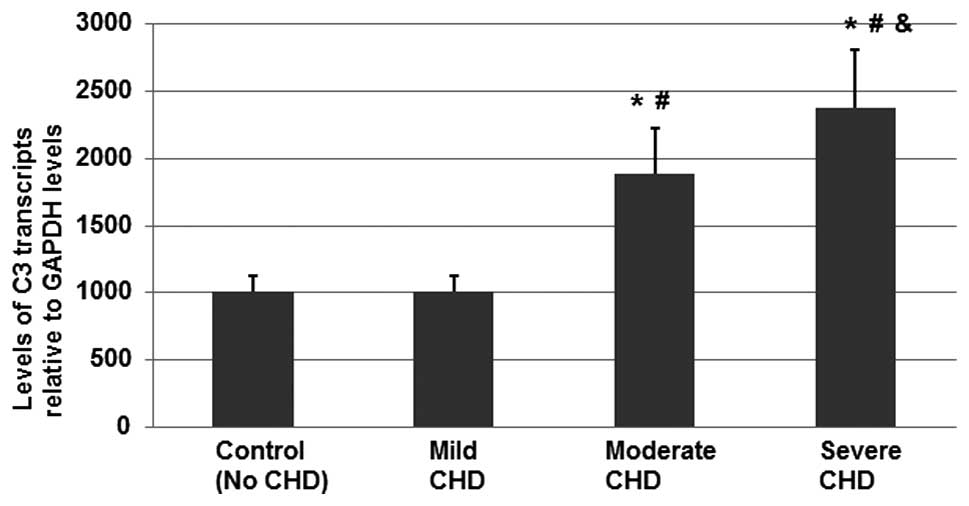
Jiang H, Guo M, Dong L, Cao C, Wang D, Liang X, Guo F, Xing Z, Bu P, Liu J, Liu J, et al: Levels of acylation stimulating protein and the complement component 3 precursor are associated with the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease. Exp Ther Med 8: 1861-1866, 2014.
APA
Jiang, H., Guo, M., Dong, L., Cao, C., Wang, D., Liang, X. ... Liu, J. (2014). Levels of acylation stimulating protein and the complement component 3 precursor are associated with the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 8, 1861-1866. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.2018
MLA
Jiang, H., Guo, M., Dong, L., Cao, C., Wang, D., Liang, X., Guo, F., Xing, Z., Bu, P., Liu, J."Levels of acylation stimulating protein and the complement component 3 precursor are associated with the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 8.6 (2014): 1861-1866.
Chicago
Jiang, H., Guo, M., Dong, L., Cao, C., Wang, D., Liang, X., Guo, F., Xing, Z., Bu, P., Liu, J."Levels of acylation stimulating protein and the complement component 3 precursor are associated with the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 8, no. 6 (2014): 1861-1866. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.2018