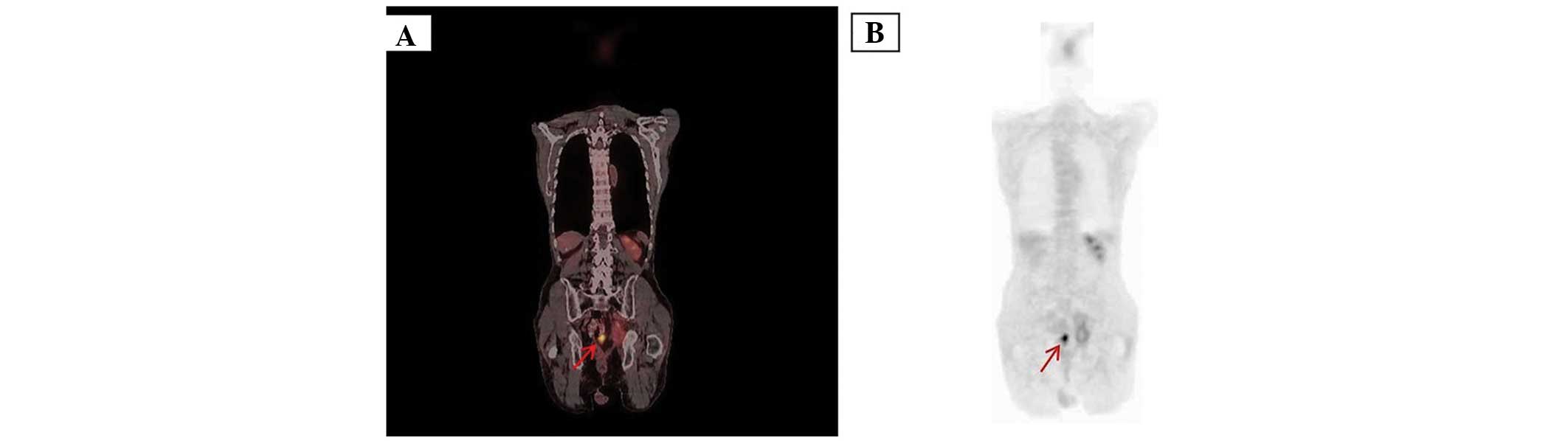
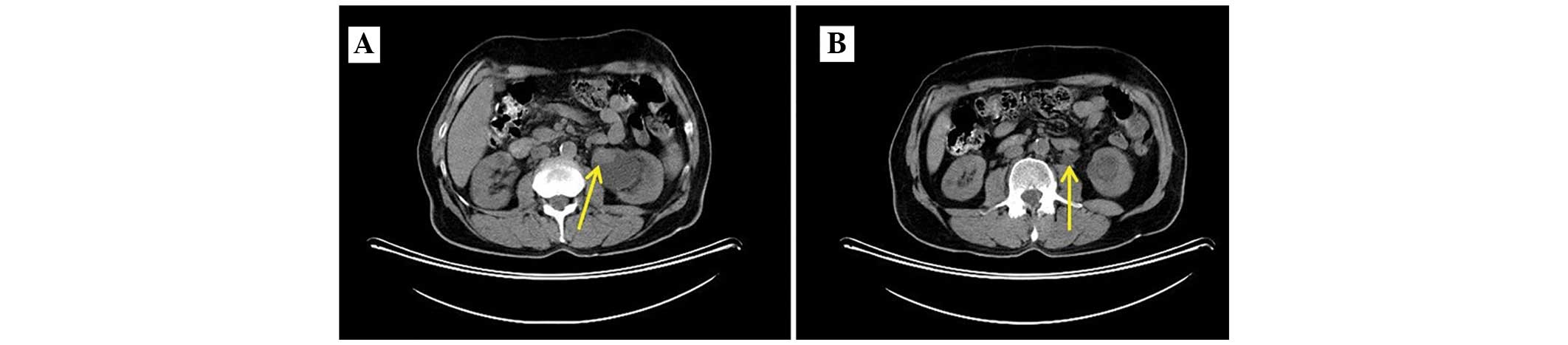
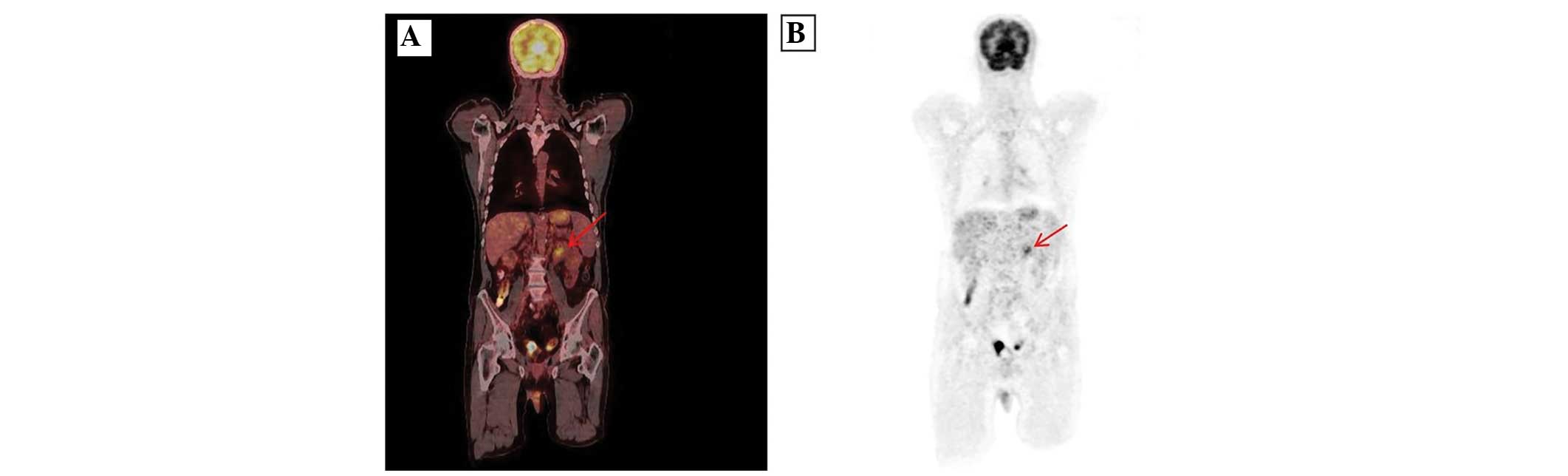
|
1
|
Ploeg M, Aben KK and Kiemeney LA: The
present and future burden of urinary bladder cancer in the world.
World J Urol. 27:289–293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abdollah F, Gandaglia G, Thuret R, et al:
Incidence, survival and mortality rates of stage-specific bladder
cancer in United States: a trend analysis. Cancer Epidemiol.
37:219–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaidya A, Soloway MS, Hawke C, et al: De
novo muscle invasive bladder cancer: is there a change in trend? J
Urol. 165:47–50. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, et al:
Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer:
long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 19:666–675.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simone G, Papalia R, Ferriero M, et al:
Stage-specific impact of extended versus standard pelvic lymph node
dissection in radical cystectomy. Int J Urol. 20:390–397. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Barentsz JO, Jager GJ, Witjes JA and Ruijs
JH: Primary staging of urinary bladder carcinoma: the role of MR
imaging and a comparison with CT. Eur Radiol. 6:129–133. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kundra V and Silverman PM: Imaging in
oncology from the University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Imaging in the diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of cancer of the
urinary bladder. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 180:1045–1054. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barentsz JO, Engelbrecht MR, Witjes JA, et
al: MRI of the male pelvis. Eur Radiol. 9:1722–1736. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Palapattu GS,
et al: Outcomes of radical cystectomy for transitional cell
carcinoma of the bladder: a contemporary series from the Bladder
Cancer Research Consortium. J Urol. 176:2414–2422. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gillies RJ, Robey I and Gatenby RA: Causes
and consequences of increased glucose metabolism of cancers. J Nucl
Med. 49(Suppl 2): 24S–42S. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smith TA: Mammalian hexokinases and their
abnormal expression in cancer. Br J Biomed Sci. 57:170–178.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harney JV, Wahl RL, Liebert M, Kuhl DE,
Hutchins GD, Wedemeyer G and Grossman HB: Uptake of 2-deoxy,
2-(18F) fluoro-D-glucose in bladder cancer: animal
localization and initial patient positron emission tomography. J
Urol. 145:279–283. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Drieskens O, Oyen R, Van Poppel H, Vankan
Y, Flamen P and Mortelmans L: FDG-PET for preoperative staging of
bladder cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 32:1412–1417. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Apolo AB, Riches J, Schöder H, Akin O,
Trout A, Milowsky MI and Bajurin DF: Clinical value of fluorine-18
2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed
tomography in bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:3973–3978. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kibel AS, Dehdashti F, Katz MD, Klim AP,
Grubb RL, Humphrey PA, et al: Prospective study of [18F]
fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
for staging of muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
27:4314–4320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu YY, Chen JH, Liang JA, Wang HY, Lin CC,
Lin WY and Kao CH: Clinical value of FDG PET or PET/CT in urinary
bladder cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Radiol.
81:2411–2416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gallagher BM, Fowler JS, Gutterson NI,
MacGregor RR, Wan CN and Wolf AP: Metabolic trapping as a principle
of radiopharmaceutical design: some factors responsible for the
biodistribution of [18F] 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose. J
Nucl Med. 19:1154–1161. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar R, Zhuang H and Alavi A: PET in the
management of urologic malignancies. Radiol Clin North Am.
42:1141–1153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caracó C, Aloj L, Chen LY, Chou JY and
Eckelman WC: Cellular release of
[18F]2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose as a function of the
glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme system. J Biol Chem. 275:18489–18494.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin EC and Alavi A: Urologic tumors. PET
and PET/CT: A Clinical Guide. 2nd edition. Thieme; New York, NY:
pp. 204–211. 2009
|
|
22
|
Kosuda S, Kison PV, Greenough R, Grossman
HB and Wahl RL: Preliminary assessment of fluorine-18
fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with
bladder cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 24:615–620. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
López-Gandul S, Pérez-Moure G,
García-Garzón JR, et al: Intravenous furosemide injection during
18F-FDG PET acquisition. J Nucl Med Technol. 34:228–231.
2006.
|
|
24
|
Anjos DA, Etchebehere EC, Ramos CD, Santos
AO, Albertotti C and Camargo EE: 18F-FDG PET/CT delayed
images after diuretic for restaging invasive bladder cancer. J Nucl
Med. 48:764–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harkirat S, Anand S and Jacob M: Forced
diuresis and dual-phase F-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT scan for
restaging of urinary bladder cancers. Indian J Radiol Imaging.
20:13–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lodde M, Lacombe L, Friede J, Morin F,
Saourine A and Fradet Y: Evaluation of fluorodeoxyglucose
positron-emission tomography with computed tomography for staging
of urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int. 106:658–663. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Swinnen G, Maes A, Pottel H, Vanneste A,
Billiet I, et al: FDG-PET/CT for the preoperative lymph node
staging of invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 57:641–647. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bouchelouche K, Turkbey B and Choyke PL:
PET/CT and MRI in bladder cancer. J Cancer Sci Ther. (Suppl
14)30:76922012.
|
|
29
|
Jadvar H, Quan V, Henderson RW and Conti
PS: [F-18]-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and PET-CT in diagnostic imaging
evaluation of locally recurrent and metastatic bladder transitional
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 13:42–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goodfellow H, Viney Z, Hughes P, Rankin S,
Rottenberg G, Hughes S, et al: Role of fluorodeoxyglucose positron
emission tomography (FDG PET)-computed tomography (CT) in the
staging of bladder cancer. BJU Int. 114:389–395. 2014.
|
|
31
|
Mertens LS, Mir MC, Scott AM, Lee ST,
Fioole-Bruining A, Vegt E, et al:
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose--positron emission
tomography/computed tomography aids staging and predicts mortality
in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Urology.
83:393–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jana S and Blaufox MD: Nuclear medicine
studies of the prostate, testes, and bladder. Semin Nucl Med.
36:51–72. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Maurer T, Souvatzoglou M, Kübler H,
Opercan K, Schmidt S, et al: Diagnostic efficacy of
[11C]choline positron emission tomography/computed
tomography compared with conventional computed tomography in lymph
node staging of patients with bladder cancer prior to radical
cystectomy. Eur Urol. 61:1031–1038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Golan S, Sopov V, Baniel J and Groshar D:
Comparison of 11C-choline with 18F-FDG in
positron emission tomography/computerized tomography for staging
urothelial carcinoma: a prospective study. J Urol. 186:436–441.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ahlström H, Malmström PU, Letocha H,
Andersson J, Långström B and Nilsson S: Positron emission
tomography in the diagnosis and staging of urinary bladder cancer.
Acta Radiol. 37:180–185. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schoder H, Ong SC, Reuter VE, Cai S,
Burnazi E, et al: Initial Results with [11]C-acetate
positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in the
staging of urinary bladder cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 14:245–251.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
El Fakhri G, Surti S, Trott CM, et al:
Improvement in lesion detection with whole-body oncologic
time-of-flight PET. J Nucl Med. 52:347–353. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|