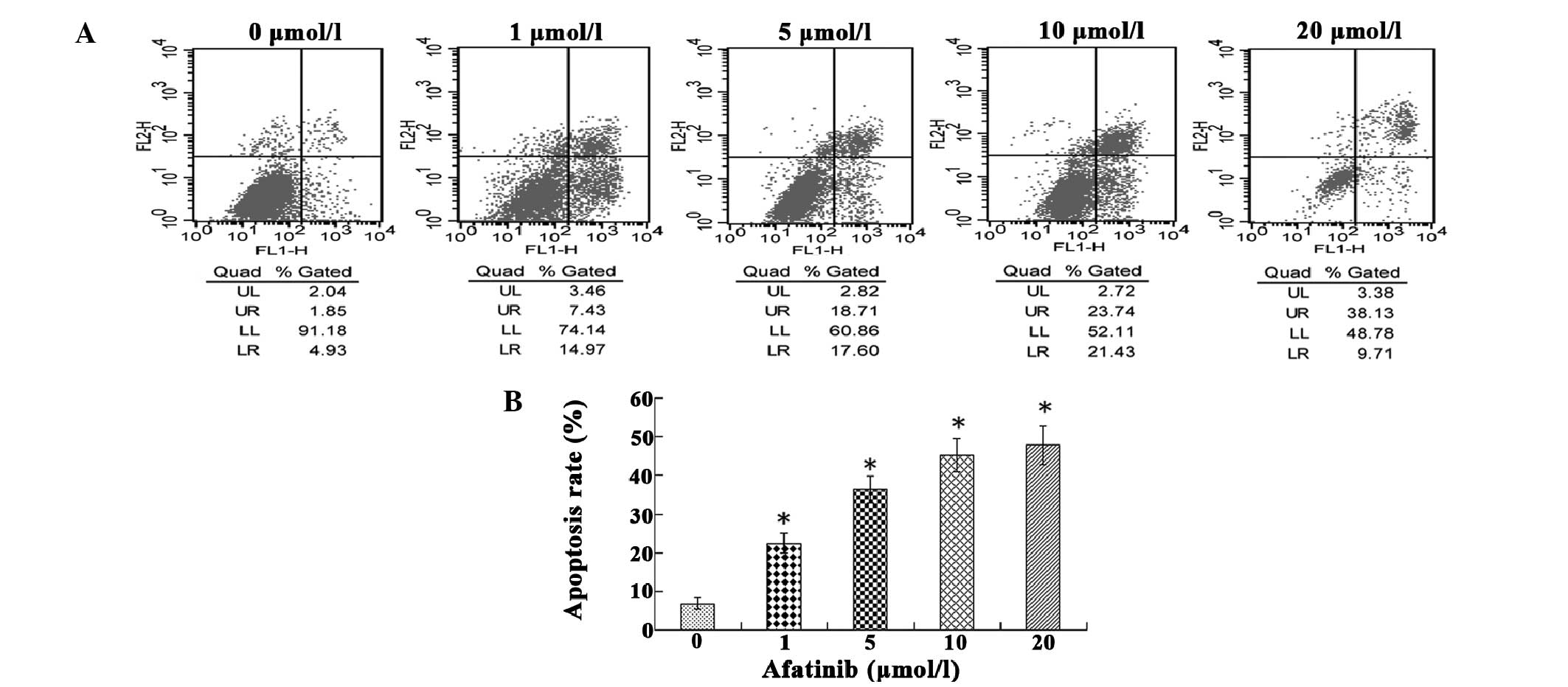
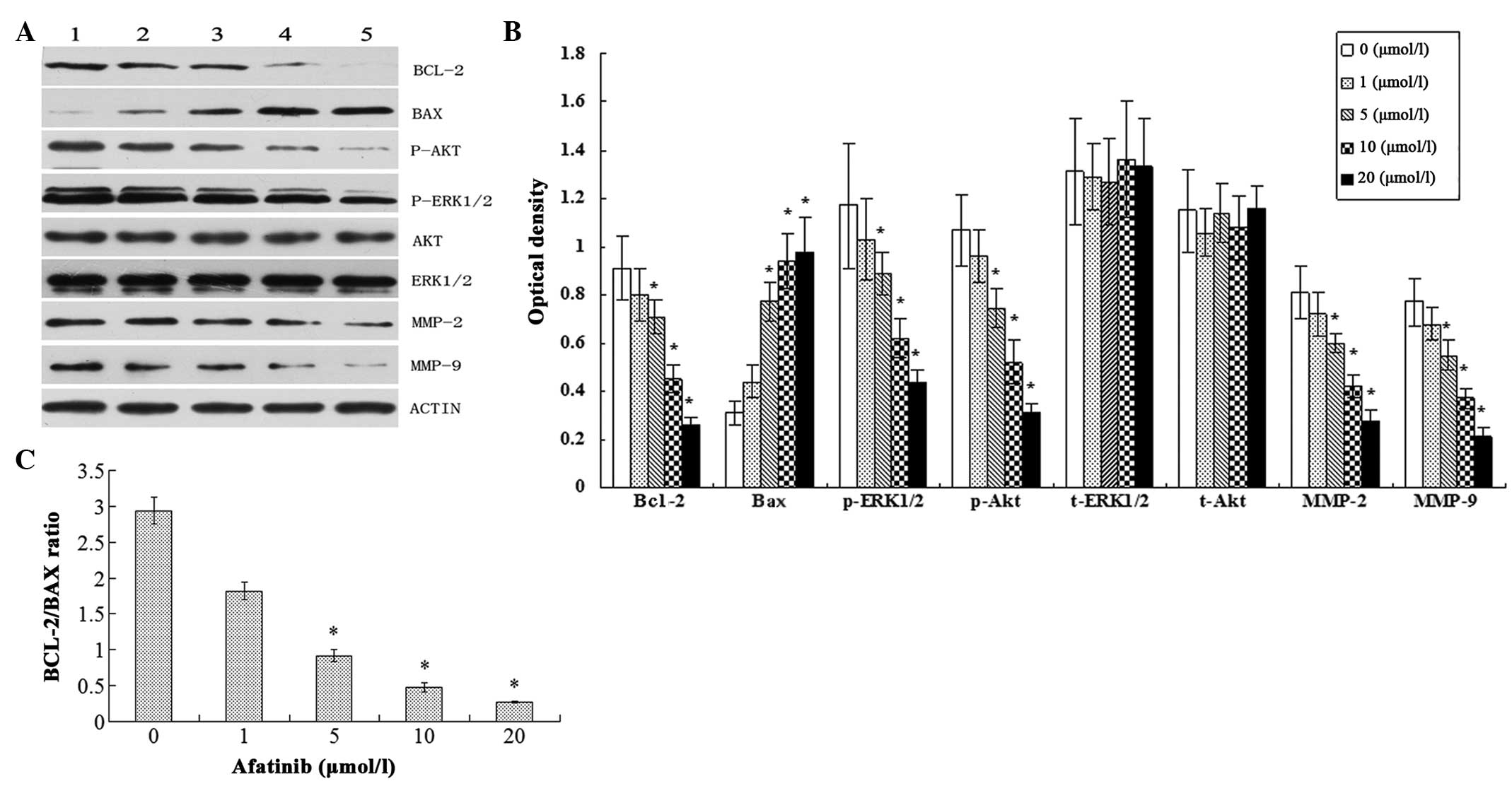
|
1
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kwak C, Ku JH, Park JY, Lee E, Lee SE and
Lee C: Initial tumor stage and grade as a predictive factor for
recurrence in patients with stage T1 grade 3 bladder cancer. J
Urol. 171:149–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D,
Jain M, Ganti AK and Batra SK: Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway
in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:15–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, Berezov A, Wang Q, et al: ErbB
receptors: from oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies. J Clin
Invest. 117:2051–2058. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, et al:
BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in
preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 27:4702–4711. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harbeck N, Solca F and Gauler TC:
Preclinical and clinical development of afatinib: a focus on breast
cancer and squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Future
Oncol. 10:21–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai YC, Yeh CH, Tzen KY, Ho PY, Tuan TF,
Pu YS, Cheng AL and Cheng JC: Targeting epidermal growth factor
receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 signalling
pathway by a dual receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor afatinib for
radiosensitisation in murine bladder carcinoma. Eur J Cancer.
49:1458–1466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Quesnelle KM and Grandis JR: Dual kinase
inhibition of EGFR and HER2 overcomes resistance to cetuximab in a
novel in vivo model of acquired cetuximab resistance. Clinical
cancer research. 17:5935–5944. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Greulich H, Kaplan B, Mertins P, Chen TH,
Tanaka KE, Yun CH, Zhang X, Lee SH, Cho J, Ambrogio L, et al:
Functional analysis of receptor tyrosine kinase mutations in lung
cancer identifies oncogenic extracellular domain mutations of
ERBB2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:14476–14481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cardillo MR, Castagna G, Memeo L, De
Bernardinis E and Di Silverio F: Epidermal growth factor receptor,
MUC-1 and MUC-2 in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
19:225–233. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Caner V, Turk NS, Duzcan F, et al: No
strong association between HER-2/neu protein overexpression and
gene amplification in high-grade invasive urothelial carcinomas.
Pathol Oncol Res. 14:261–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kiyoshima K, Oda Y, Kinukawa N, Naito S
and Tsuneyoshi M: Overexpression of laminin-5 gamma2 chain and its
prognostic significance in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder:
association with expression of cyclooxygenase 2, epidermal growth
factor receptor [corrected] and human epidermal growth factor
receptor [corrected] 2. Hum Pathol. 36:522–530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al: Prevention
of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
blocked. Science. 275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee DH, Ha JH, Kim Y, et al: A conserved
mechanism for binding of p53 DNA-binding domain and anti-apoptotic
Bcl-2 family proteins. Mol Cells. 37:264–269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi YD, Cho NH, Ahn HS, Cho KS, Cho SY
and Yang WJ: Matrix metalloproteinase expression in the recurrence
of superficial low grade bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J
Urol. 177:1174–1178. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Di Carlo A, Terracciano D, Mariano A and
Macchia V: Urinary gelatinase activities (matrix metalloproteinases
2 and 9) in human bladder tumors. Oncol Rep. 15:1321–1326.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chambers AF and Matrisian LM: Changing
views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1260–1270. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stamenkovic I: Matrix metalloproteinases
in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 10:415–433.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanayama H, Yokota K, Kurokawa Y, Murakami
Y, Nishitani M and Kagawa S: Prognostic values of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2
expression in bladder cancer. Cancer. 82:1359–1366. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Davies B, Waxman J, Wasan H, et al: Levels
of matrix metalloproteases in bladder cancer correlate with tumor
grade and invasion. Cancer Res. 53:5365–5369. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanayama H: Matrix metalloproteinases and
bladder cancer. J Med Invest. 48:31–43. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brzezianska E and Pastuszak-Lewandoska D:
A minireview: the role of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in thyroid
follicular cell-derived neoplasm. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
16:422–439. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nicholson RI, Gee JM and Harper ME: EGFR
and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 37 (Suppl 4):S9–S15. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu X, Obata T, Khan Q, Highshaw RA, De
Vere White R and Sweeney C: The phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
pathway regulates bladder cancer cell invasion. BJU Int.
93:143–150. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Akinleye A, Furqan M, Mukhi N, Ravella P
and Liu D: MEK and the inhibitors: From bench to bedside. J Hematol
Oncol. 6:272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friday BB and Adjei AA: Advances in
targeting the Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase
cascade with MEK inhibitors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
14:342–346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, et
al: Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascade inhibitors: how
mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome
resistance. Oncotarget. 3:1068–1111. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|