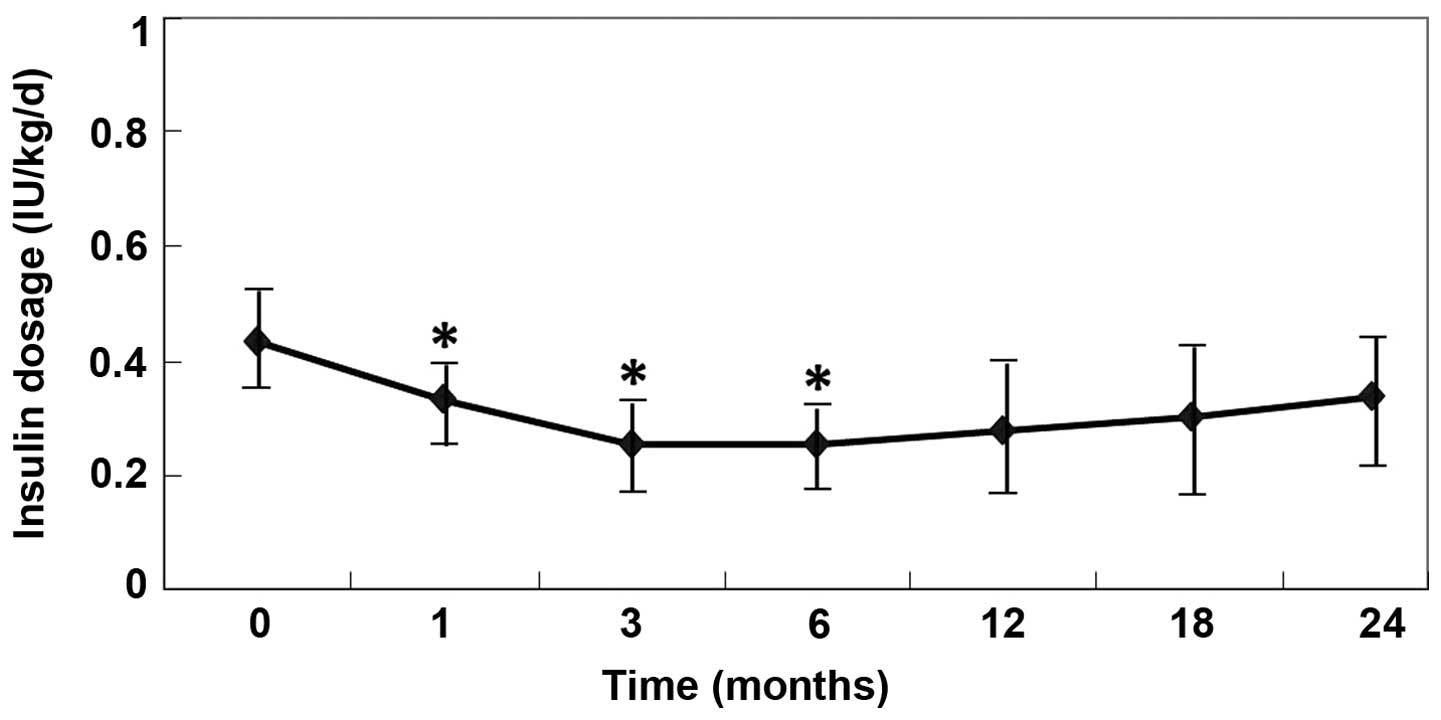
|
1
|
Jung KY, Kim KM and Lim S: Therapeutic
approaches for preserving or restoring pancreatic β-cell function
and mass. Diabetes Metab J. 36:426–436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Larsen JL: Pancreas transplantation:
indications and consequences. Endocr Rev. 25:919–946. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, et al:
Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes
mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N
Engl J Med. 343:230–238. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ryan EA, Lakey JR, Rajotte RV, et al:
Clinical outcomes and insulin secretion after islet transplantation
with the Edmonton protocol. Diabetes. 50:710–719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamaoka T: Regeneration therapy of
pancreatic beta cells: towards a cure for diabetes? Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 296:1039–1043. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al:
Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.
Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sekiya I, Vuoristo JT, Larson BL and
Prockop DJ: In vitro cartilage formation by human adult stem cells
from bone marrow stroma defines the sequence of cellular and
molecular events during chondrogenesis. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99. pp. 4397–4402. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et
al: Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte
proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli.
Blood. 99:3838–3843. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sharma RR, Pollock K, Hubel A, et al:
Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: a review of clinical
applications and manufacturing practices. Transfusion.
54:1418–1437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Domínguez-Bendala J, Lanzoni G, Inverardi
L and Ricordi C: Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells for
diabetes. Stem Cells Transl Med. 1:59–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bianco P and Robey PG: Stem cells in
tissue engineering. Nature. 414:118–121. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et
al: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult
marrow. Nature. 418:41–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T, et al:
Regeneration of human infarcted heart muscle by intracoronary
autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in chronic coronary
artery disease: The IACT Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 46:1651–1658.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schächinger V, Erbs S, Elsässer A, et al:
REPAIR-AMI Investigators: Intracoronary bone marrow-derived
progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med.
355:1210–1221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chopp M and Li Y: Treatment of neural
injury with marrow stromal cells. Lancet Neurol. 1:92–100. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park JH, Kim DY, Sung IY, et al: Long-term
results of spinal cord injury therapy using mesenchymal stem cells
derived from bone marrow in humans. Neurosurgery. 70:1238–1247.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang ZX, Guan LX, Zhang K, et al: A
combined procedure to deliver autologous mesenchymal stromal cells
to patients with traumatic brain injury. Cytotherapy. 10:134–139.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun L, Akiyama K, Zhang H, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation reverses multiorgan
dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus mice and humans. Stem
Cells. 27:1421–1432. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang J, Zhang H, Hua B, et al: Allogenic
mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in refractory systemic lupus
erythematosus: a pilot clinical study. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:1423–1429.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun L, Wang D, Liang J, et al: Umbilical
cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory
systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 62:2467–2475. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng L, Xie DY, Lin BL, et al: Autologous
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in liver failure
patients caused by hepatitis B: short-term and long-term outcomes.
Hepatology. 54:820–828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with bone marrow cells in therapy
of diabetes. Stem Cells. 26:244–253. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong QY, Chen L, Gao GQ, et al: Allogeneic
diabetic mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Clin Invest Med. 31:E328–E337.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Le Blanc K and Ringdén O: Immunomodulation
by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience. J Intern Med.
262:509–525. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, et al:
Developmental Committee of the European Group for Blood and Marrow
Transplantation: Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of
steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase
II study. Lancet. 371:1579–1586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carlin R, Davis D, Weiss M, et al:
Expression of early transcription factors Oct-4, Sox-2 and Nanog by
porcine umbilical cord (PUC) matrix cells. Reprod Biol Endocrinol.
4:82006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Torrente Y and Polli E: Mesenchymal stem
cell transplantation for neurodegenerative diseases. Cell
Transplant. 17:1103–1113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton's jelly of the human
umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 22:1330–1337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yagi H, Soto-Gutierrez A, Parekkadan B, et
al: Mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms of immunomodulation and
homing. Cell Transplant. 19:667–679. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Joyce N, Annett G, Wirthlin L, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of neurodegenerative
disease. Regen Med. 5:933–946. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao YM: Medical ethics: unavoidable issue
in medical research. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 85:424–426.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moniri MR, Sun XY, Rayat J, et al:
TRAIL-engineered pancreas-derived mesenchymal stem cells:
characterization and cytotoxic effects on pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Gene Ther. 19:652–658. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Haffner SM, Stern MP, Hazuda HP, et al:
Hyperinsulinemia in a population at high risk for
non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 315:220–224.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alberti KG and Zimmet PZ: Definition,
diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes
mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med.
15:539–553. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Majore I, Moretti P, Stahl F, et al:
Growth and differentiation properties of mesenchymal stromal cell
populations derived from whole human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev.
7:17–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tong CK, Vellasamy S, Tan BC, et al:
Generation of mesenchymal stem cell from human umbilical cord
tissue using a combination enzymatic and mechanical disassociation
method. Cell Biol Int. 35:221–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ley SH, Hamdy O, Mohan V and Hu FB:
Prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: dietary components
and nutritional strategies. Lancet. 383:1999–2007. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Halban PA, Polonsky KS, Bowden DW, et al:
β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Postulated mechanisms and
prospects for prevention and treatment. Diabetes Care.
37:1751–1758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Harrison LB, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P and
Lingvay I: β-cell function preservation after 3.5 years of
intensive diabetes therapy. Diabetes Care. 35:1406–1412. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hess D, Li L, Martin M, et al: Bone
marrow-derived stem cells initiate pancreatic regeneration. Nat
Biotechnol. 21:763–770. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nir T and Dor Y: How to make pancreatic
beta cells-prospects for cell therapy in diabetes. Curr Opin
Biotechnol. 16:524–529. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ahlqvist E, Ahluwalia TS and Groop L:
Genetics of type 2 diabetes. Clin Chem. 57:241–254. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Voltarelli JC, Couri CE, Stracieri AB, et
al: Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for type 1
diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1150:220–229. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tang DQ, Cao LZ, Burkhardt BR, et al: In
vivo and in vitro characterization of insulin-producing cells
obtained from murine bone marrow. Diabetes. 53:1721–1732. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Oh SH, Muzzonigro TM, Bae SH, et al: Adult
bone marrow-derived cells trans-differentiating into
insulin-producing cells for the treatment of type I diabetes. Lab
Invest. 84:607–617. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Banerjee M, Kumar A and Bhonde RR:
Reversal of experimental diabetes by multiple bone marrow
transplantation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 328:318–325. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL, et al:
Multipotent stromal cells from human marrow home to and promote
repair of pancreatic islets and renal glomeruli in diabetic
NOD/scid mice. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103. pp. 17438–17443.
2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Shyr YM, et al:
Transplantation of insulin-producing cells from umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. J Biomed Sci. 19:472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Trivedi HL, Vanikar AV, Thakker U, et al:
Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation synthesize insulin.
Transplant Proc. 40:1135–1139. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Moore KA and Lemischka IR: Stem cells and
their niches. Science. 311:1880–1885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cutler AJ, Limbani V, Girdlestone J and
Navarrete CV: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells
modulate monocyte function to suppress T cell proliferation. J
Immunol. 185:6617–6623. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liang J, Gu F, Wang H, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cell transplantation for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in SLE.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 6:486–489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shi M, Zhang Z, Xu R, et al: Human
mesenchymal stem cell transfusion is safe and improves liver
function in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Stem Cells
Transl Med. 1:725–731. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lv YT, Zhang Y, Liu M, et al:
Transplantation of human cord blood mononuclear cells and umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in autism. J Transl Med.
11:1962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|