|
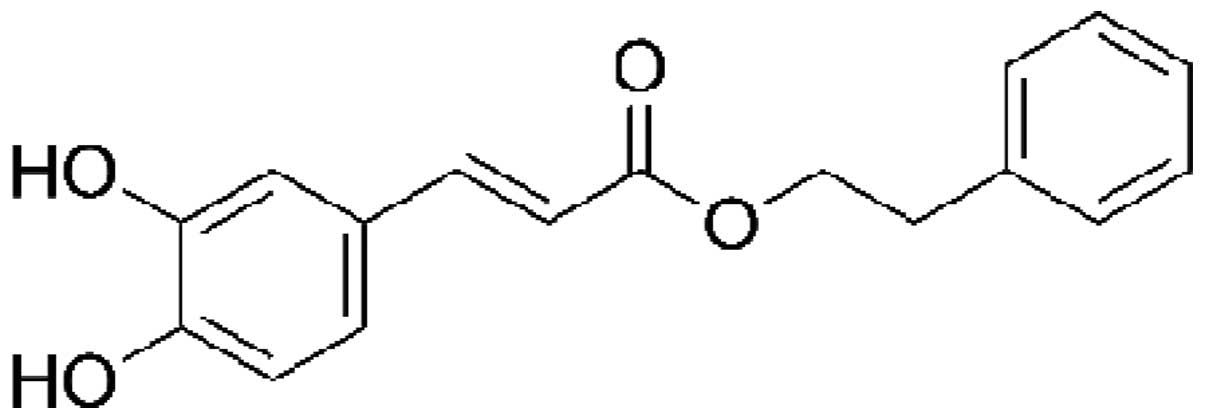
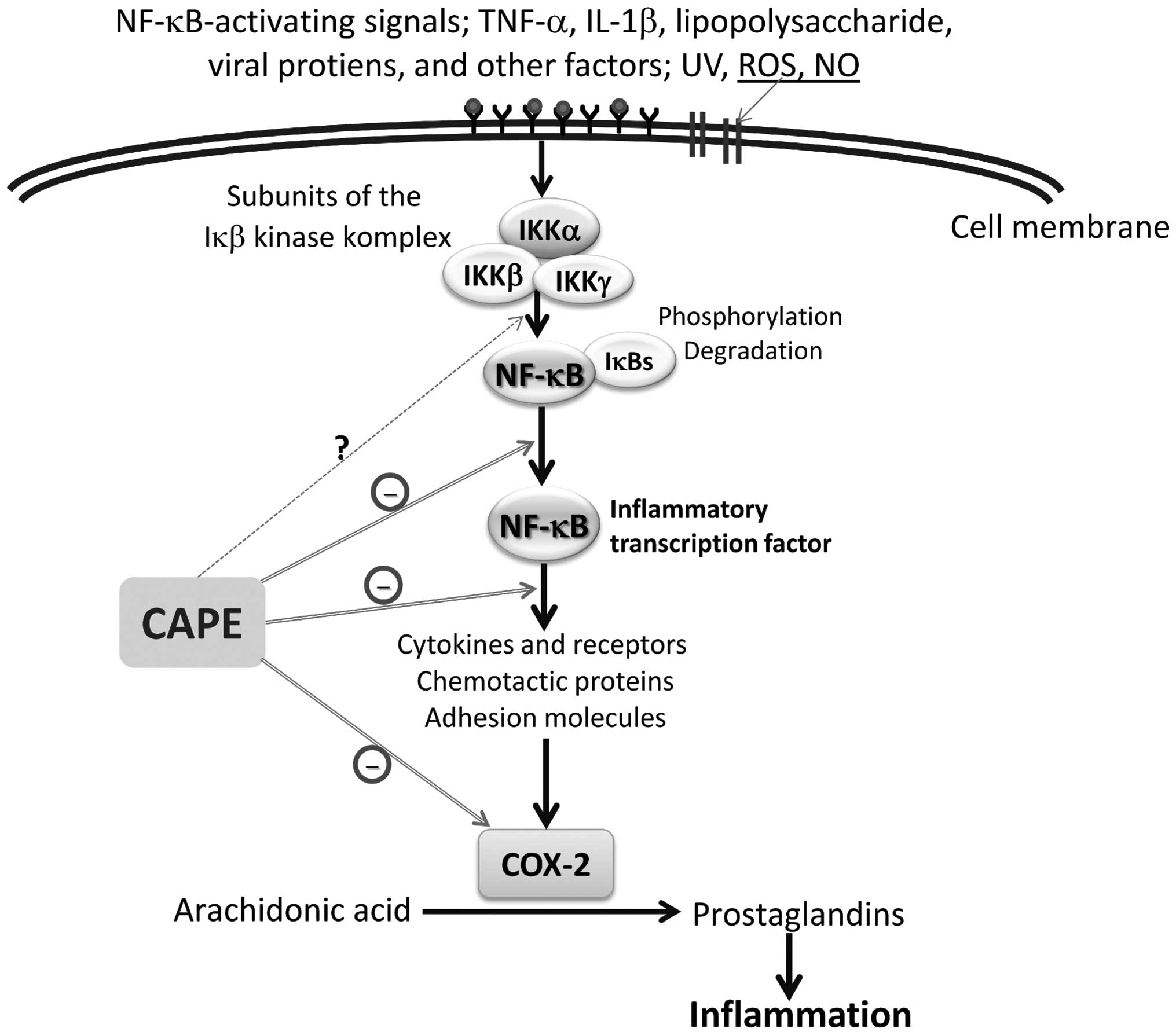
1
|
Sud'ina GF, Mirzoeva OK, Pushkareva MA,
Korshunova GA, Sumbatyan NV and Varfolomeev SD: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester as a lipoxygenase inhibitor with antioxidant
properties. FEBS Lett. 329:21–24. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR Jr,
Grunberger D and Aggarwal BB: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a
potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear
transcription factor NF-kappa B. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93.
pp. 9090–9095. 1996; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koltuksuz U, Mutuş HM, Kutlu R, Ozyurt H,
Cetin S, Karaman A, Gürbüz N, Akyol O and Aydin NE: Effects of
caffeic acid phenethyl ester and epidermal growth factor on the
development of caustic esophageal stricture in rats. J Pediatr
Surg. 36:1504–1509. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Akyol S, Ozturk G, Ginis Z, Armutcu F,
Yigitoglu MR and Akyol O: In vivo and in vitro antineoplastic
actions of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE): Therapeutic
perspectives. Nutr Cancer. 65:515–526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Czermak BJ, Friedl HP and Ward PA:
Complement, cytokines, and adhesion molecule expression in
inflammatory reactions. In: Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 110. pp.
306–312. 1998; PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI and
Nourshargh S: Getting to the site of inflammation: The leukocyte
adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:678–689. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Pang J, Maffucci JA, Pade DS,
Newman RA, Kerwin SM, Bowman PD and Stavchansky S: Pharmacokinetics
of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its catechol-ring fluorinated
derivative following intravenous administration to rats. Biopharm
Drug Dispos. 30:221–228. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eming SA, Krieg T and Davidson JM:
Inflammation in wound repair: Molecular and cellular mechanisms. J
Invest Dermatol. 127:514–525. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leder C, Ziegler M and Gawaz M: Modulating
immune responses and inflammation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 36:219–222.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stow JL and Murray RZ: Intracellular
trafficking and secretion of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 24:227–239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dinarello CA: Proinflammatory cytokines.
Chest. 118:503–508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sabio G and Davis RJ: TNF and MAP kinase
signalling pathways. Semin Immunol. 26:237–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Janes KA, Gaudet S, Albeck JG, Nielsen UB,
Lauffenburger DA and Sorger PK: The response of human epithelial
cells to TNF involves an inducible autocrine cascade. Cell.
124:1225–1239. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB: NF-kappa B
and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:225–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X and Demers LM:
New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB, a ubiquitous
transcription factor in the initiation of diseases. Clin Chem.
45:7–17. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tak PP and Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: A key
role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 107:7–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muller DN, Dechend R, Mervaala EM, Park
JK, Schmidt F, Fiebeler A, Theuer J, Breu V, Ganten D, Haller H and
Luft FC: NF-kappaB inhibition ameliorates angiotensin II-induced
inflammatory damage in rats. Hypertension. 35:193–201. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jura J, Wegrzyn P, Korostyński M, Guzik K,
Oczko-Wojciechowska M, Jarzab M, Kowalska M, Piechota M, Przewlocki
R and Koj A: Identification of interleukin-1 and
interleukin-6-responsive genes in human monocyte-derived
macrophages using microarrays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1779:383–389.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bonizzi G and Karin M: The two NF-kappaB
activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity.
Trends Immunol. 25:280–288. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song YS, Park EH, Hur GM, Ryu YS, Lee YS,
Lee JY, Kim YM and Jin C: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits
nitric oxide synthase gene expression and enzyme activity. Cancer
Lett. 175:53–61. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ilhan A, Akyol O, Gurel A, Armutcu F, Iraz
M and Oztas E: Protective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester
against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis-induced oxidative
stress in rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 37:386–394. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Takasu S, Shi L,
Hirano N, Ban H, Kumagai T and Tatematsu M: Anti-inflammatory
effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a nuclear
factor-kappaB inhibitor, on Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis
in Mongolian gerbils. Int J Cancer. 125:1786–1795. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Naito Y and Yoshikawa T: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced
inflammation and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:323–336.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Keates S, Hitti YS, Upton M and Kelly CP:
Helicobacter pylori infection activates NF-kappa B in gastric
epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 113:1099–1109. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aihara M, Tsuchimoto D, Takizawa H, Azuma
A, Wakebe H, Ohmoto Y, Imagawa K, Kikuchi M, Mukaida N and
Matsushima K: Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced
interleukin-8 production by a gastric cancer cell line, MKN45.
Infect Immun. 65:3218–3224. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orban Z, Mitsiades N, Burke TR Jr..Tsokos
M and Chrousos GP: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces leukocyte
apoptosis, modulates nuclear factor-kappa B and suppresses acute
inflammation. Neuroimmunomodulation. 7:99–105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hoşnuter M, Gürel A, Babucçu O, Armutcu F,
Kargı E and Işikdemir A: The effect of CAPE on lipid peroxidation
and nitric oxide levels in the plasma of rats following thermal
injury. Burns. 30:121–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Armutcu F, Gürel A, Hoşnuter M, Pabuçcu O
and Altnyazar C: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester improves oxidative
erythrocyte damage in a rat model of thermal injury. J Burn Care
Rehabil. 25:171–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
dos Santos JS and Monte-Alto-Costa A:
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester improves burn healing in rats through
anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. J Burn Care Res.
34:682–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khan M, Elango C, Ansari MA, Singh I and
Singh AK: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester reduces neurovascular
inflammation and protects rat brain following transient focal
cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 102:365–377. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jung WK, Choi I, Lee DY, et al: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock and
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible
nitric oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via the
p38/ERK and NF-kappaB pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
40:2572–2582. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee KW, Chun KS, Lee JS, Kang KS, Surh YJ
and Lee HJ: Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and
restoration of gap junction intercellular communication in
H-ras-transformed rat liver epithelial cells by caffeic acid
phenethyl ester. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1030:501–507. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen YC, Yen JC and Liou KT: Ameliorative
effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on an eccentric
exercise-induced skeletal muscle injury by down-regulating NF-κb
mediated inflammation. Pharmacology. 91:219–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Juman S, Yasui N, Ikeda K, Ueda A,
Sakanaka M, Negishi H and Miki T: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in
hypertrophic adipocytes through lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:1941–1946. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kassim M, Mansor M, Kamalden TA,
Shariffuddin II, Hasan MS, Ong G, Sekaran SD, Suhaimi A, Al-Abd N
and Yusoff KM: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE): Scavenger of
peroxynitrite in vitro and in sepsis models. Shock. 42:154–160.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Carrasco-Legleu CE, Márquez-Rosado L,
Fattel-Fazenda S, Arce-Popoca E, Pérez-Carreón JI and Villa-Treviño
S: Chemoprotective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on
promotion in a medium-term rat hepatocarcinogenesis assay. Int J
Cancer. 108:488–492. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cao Q, Kaur C, Wu CY, Lu J and Ling EA:
Nuclear factor-kappa B regulates Notch signaling in production of
proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide in murine BV-2
microglial cells. Neuroscience. 192:140–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Omene CO, Wu J and Frenkel K: Caffeic Acid
Phenethyl Ester (CAPE) derived from propolis, a honeybee product,
inhibits growth of breast cancer stem cells. Invest New Drugs.
30:1279–1288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Coimbra M, Crielaard BJ, Storm G and
Schiffelers RM: Critical factors in the development of
tumor-targeted anti-inflammatory nanomedicines. J Control Release.
160:232–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen YJ, Shiao MS and Wang SY: The
antioxidant caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces apoptosis
associated with selective scavenging of hydrogen peroxide in human
leukemic HL-60 cells. Anticancer Drugs. 12:143–149. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Watabe M, Hishikawa K, Takayanagi A,
Shimizu N and Nakaki T: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces
apoptosis by inhibition of NFkappaB and activation of Fas in human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 279:6017–6026. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee YT, Don MJ, Hung PS, Shen YC, Lo YS,
Chang KW, Chen CF and Ho LK: Cytotoxicity of phenolic acid
phenethyl esters on oral cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 223:19–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park MH, Kang DW, Jung Y, Choi KY and Min
S: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester downregulates phospholipase D1 via
direct binding and inhibition of NFκB transactivation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 442:1–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yilmaz A, Yildirim O, Tamer L, et al:
Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on endotoxin-induced
uveitis in rats. Curr Eye Res. 30:755–762. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shvarzbeyn J and Huleihel M: Effect of
propolis and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on NFκB activation
by HTLV-1 Tax. Antiviral Res. 90:108–115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee Y, Shin DH, Kim JH, et al: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester-mediated Nrf2 activation and IkappaB kinase
inhibition are involved in NFkappaB inhibitory effect: Structural
analysis for NFkappa B inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 643:21–28.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bezerra RM, Veiga LF, Caetano AC, Rosalen
PL, Amaral ME, Palanch AC and de Alencar SM: Caffeic acid phenethyl
ester reduces the activation of the nuclear factor κB pathway by
high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Metabolism. 61:1606–1614.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang LC, Lin YL, Liang YC, et al: The
effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on the functions of human
monocyte-derived dendritic cells. BMC Immunol. 10:392009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Márquez N, Sancho R, Macho A, Calzado MA,
Fiebich BL and Muñoz E: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits
T-cell activation by targeting both nuclear factor of activated
T-cells and NF-kappaB transcription factors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
308:993–1001. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mirzoeva OK and Calder PC: The effect of
propolis and its components on eicosanoid production during the
inflammatory response. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
55:441–449. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hart LA, Krishnan VL, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ
and Chung KF: Activation and localization of transcription factor,
nuclear factor-kappaB, in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
158:1585–1592. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jung WK, Lee DY, Choi YH, Yea SS, Choi I,
Park SG, Seo SK, Lee SW, Lee CM, Kim SK, et al: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester attenuates allergic airway inflammation and
hyperresponsiveness in murine model of ovalbumin-induced asthma.
Life Sci. 82:797–805. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Choi IW, Kim DK, Ko HM and Lee HK:
Administration of antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide to the
p65 subunit of NF-kappaB inhibits established asthmatic reaction in
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:1817–1828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Park JH, Lee JK, Kim HS, Chung ST, Eom JH,
Kim KA, Chung SJ, Paik SY and Oh HY: Immunomodulatory effect of
caffeic acid phenethyl ester in Balb/c mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
4:429–436. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Park SG, Lee DY, Seo SK, Lee SW, Kim SK,
Jung WK, Kang MS, Choi YH, Yea SS, Choi I and Choi IW: Evaluation
of anti-allergic properties of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in a
murine model of systemic anaphylaxis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
226:22–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nader MA: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
attenuates IgE-induced immediate allergic reaction.
Inflammopharmacology. 21:169–176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: Therapeutic
potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment
of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 107:135–142. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|