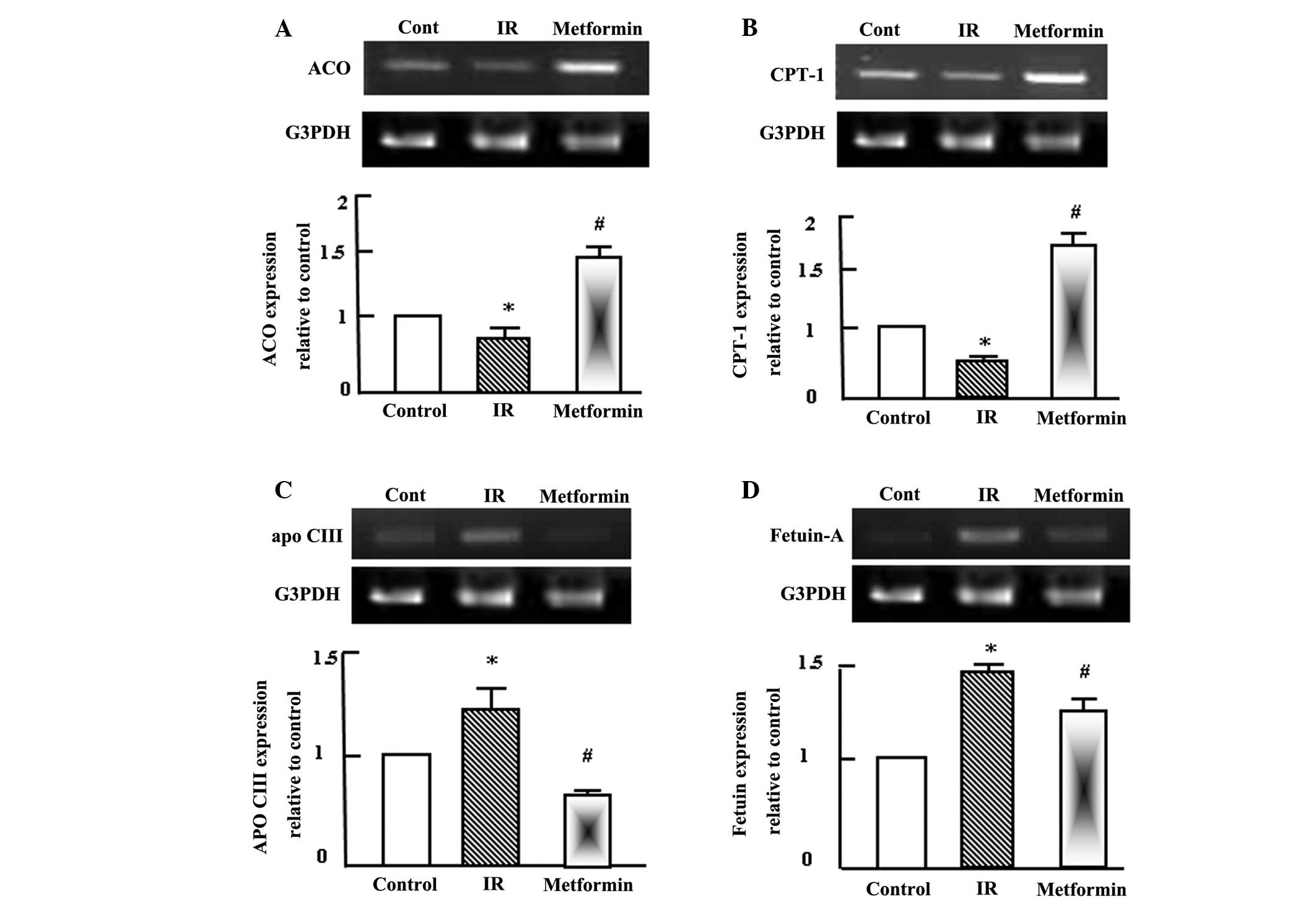
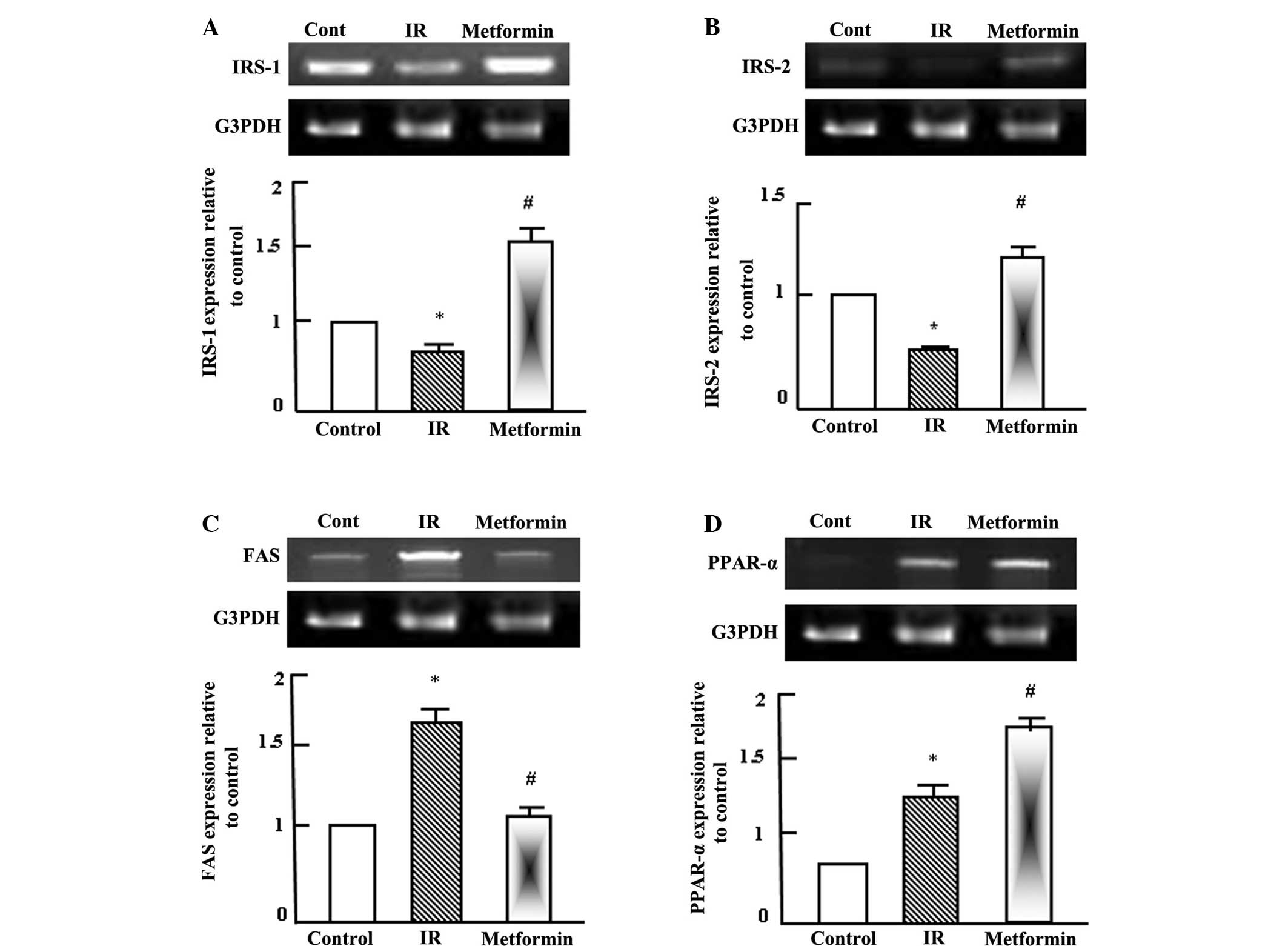
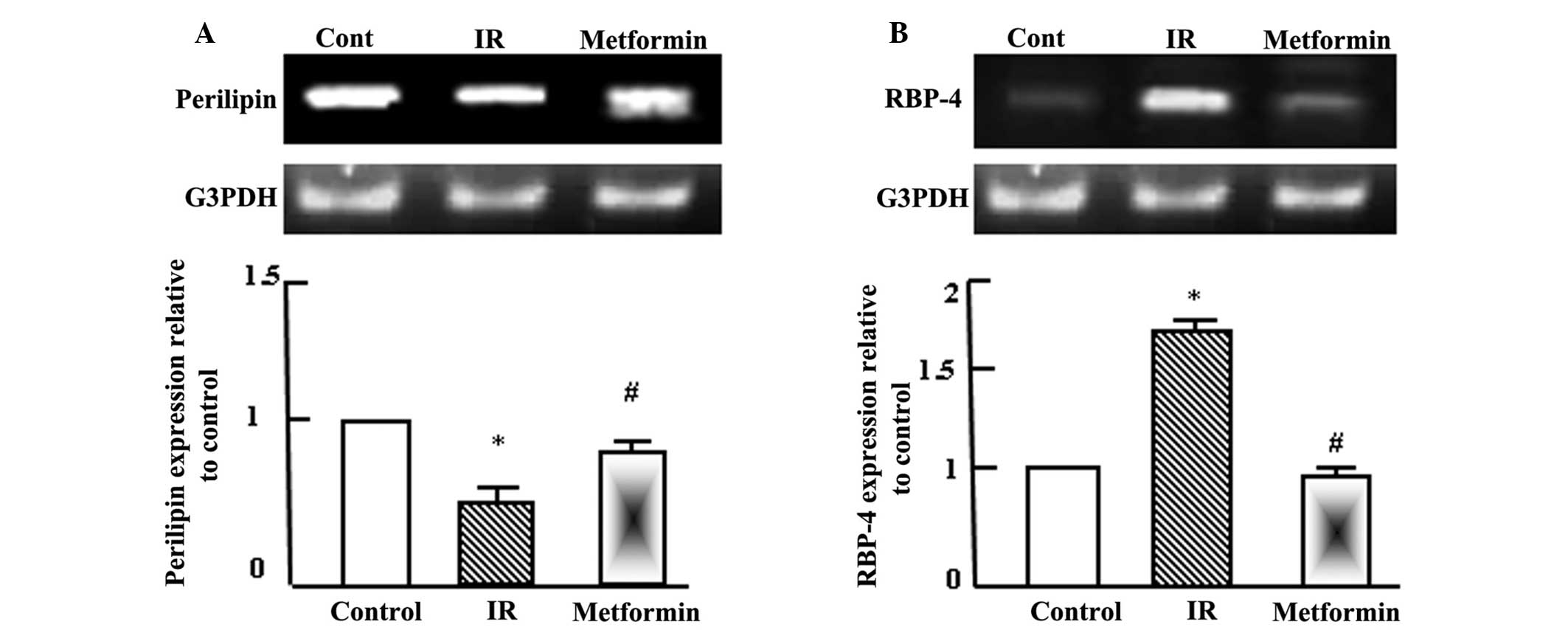
|
1
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roglic G and Unwin N: Mortality
attributable to diabetes: Estimates for the year 2010. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 87:15–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ and van Haeften
TW: Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy.
Lancet. 365:1333–1346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rewers M, Zaccaro D, D'Agostino R, Haffner
S, Saad MF, Selby JV, Bergman R and Savage P: Insulin Resistance
Atherosclerosis Study Investigators: Insulin sensitivity,
insulinemia and coronary artery disease: the Insulin Resistance
Atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care. 27:781–787. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Myers MG Jr and Olson DP: Central nervous
system control of metabolism. Nature. 491:357–363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reaven GM: The insulin resistance
syndrome: Definition and dietary approaches to treatment. Annu Rev
Nutr. 25:391–406. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bouche C, Lopez X, Fleischman A, Cypess
AM, O'Shea S, Stefanovski D, Bergman RN, Rogatsky E, Stein DT, Kahn
CR, et al: Insulin enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in
healthy humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:4770–4775. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rhodes CJ, White MF, Leahy JL and Kahn SE:
Direct autocrine action of insulin on β-cells: Does it make
physiological sense? Diabetes. 62:2157–2163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jung TW, Youn BS, Choi HY, Lee SY, Hong
HC, Yang SJ, Yoo HJ, Kim BH, Baik SH and Choi KM: Salsalate and
adiponectin ameliorate hepatic steatosis by inhibition of the
hepatokine fetuin-A. Biochem Pharmacol. 86:960–969. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mori K, Emoto M and Inaba M: Fetuin-A: a
multifunctional protein. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug
Discov. 5:124–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Syed Ikmal SI, Zaman Huri H, Vethakkan SR
and Wan Ahmad WA: Potential biomarkers of insulin resistance and
atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with coronary
artery disease. Int J Endocrinol. 2013:6985672013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sztalryd C and Kimmel AR: Perilipins:
lipid droplet coat proteins adapted for tissue-specific energy
storage and utilization and lipid cytoprotection. Biochimie.
96:96–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, et al: Role
of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Woods YL, Petrie JR and Sutherland C:
Dissecting insulin signaling pathways: Individualised therapeutic
targets for diagnosis and treatment of insulin resistant states.
Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 9:187–198. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Radziuk J, Zhang Z, Wiernsperger N and Pye
S: Effects of metformin on lactate uptake and gluconeogenesis in
the perfused rat liver. Diabetes. 46:1406–1413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB,
Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R and Zinman B: American Diabetes
Association, European Association for Study of Diabetes: Medical
management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: A consensus
algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: A consensus
statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European
Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 32:193–203.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Christakou CD,
Kandaraki E and Economou FN: Metformin: an old medication of new
fashion: evolving new molecular mechanisms and clinical
implications in polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol.
162:193–212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hundal RS and Inzucchi SE: Metformin: new
understandings, new uses. Drugs. 63:1879–1894. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bancroft JD and Gamble M: Theory and
Practice of Histological Techniques6th. Churchill Livingstone
Elsevier; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 126–127. 2008
|
|
21
|
Werner ED, Lee J, Hansen L, Yuan M and
Shoelson SE: Insulin resistance due to phosphorylation of insulin
receptor substrate-1 at serine 302. J Biol Chem. 279:35298–35305.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Elmadhun NY, Lassaletta AD, Chu LM and
Sellke FW: Metformin alters the insulin signaling pathway in
ischemic cardiac tissue in a swine model of metabolic syndrome. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 145:258–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sykiotis GP and Papavassiliou AG: Serine
phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1: A novel target for
the reversal of insulin resistance. Mol Endocrinol. 15:1864–1869.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yogalakshmi B, Bhuvaneswari S, Sreeja S
and Anuradha CV: Grape seed proanthocyanidins and metformin act by
different mechanisms to promote insulin signaling in rats fed high
calorie diet. J Cell Commun Signal. 8:13–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grisouard J, Timper K, Radimerski TM, Frey
DM, Peterli R, Kola B, Korbonits M, Herrmann P, Krähenbühl S,
Zulewski H, et al: Mechanisms of metformin action on glucose
transport and metabolism in human adipocytes. Biochem Pharmacol.
80:1736–1745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shepherd PR and Kahn BB: Glucose
transporters and insulin action - implications for insulin
resistance and diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 341:248–257. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye JM, Doyle PJ, Iglesias MA, Watson DG,
Cooney GJ and Kraegen EW: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor (PPAR)-α activation lowers muscle lipids and improves
insulin sensitivity in high fat-fed rats: Comparison with PPAR-γ
activation. Diabetes. 50:411–417. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Escher P and Wahli W: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors: Insight into multiple cellular
functions. Mutat Res. 448:121–138. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schoonjans K, Peinado-Onsurbe J, Lefebvre
AM, Heyman RA, Briggs M, Deeb S, Staels B and Auwerx J: PPARα and
PPARγ activators direct a distinct tissue-specific transcriptional
response via a PPRE in the lipoprotein lipase gene. EMBO J.
15:5336–5348. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kliewer SA, Umesono K, Noonan DJ, Heyman
RA and Evans RM: Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome
proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of
their receptors. Nature. 358:771–774. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schoonjans K, Watanabe M, Suzuki H,
Mahfoudi A, Krey G, Wahli W, Grimaldi P, Staels B, Yamamoto T and
Auwerx J: Induction of the acyl-coenzyme A synthetase gene by
fibrates and fatty acids is mediated by a peroxisome proliferator
response element in the C promoter. J Biol Chem. 270:19269–19276.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Louet JF, Chatelain F, Decaux JF, Park EA,
Kohl C, Pineau T, Girard J and Pegorier JP: Long-chain fatty acids
regulate liver carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 gene (L-CPT I)
expression through a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α
(PPARα)-independent pathway. Biochem J. 354:189–197. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hertz R, Bishara-Shieban J and Bar-Tana J:
Mode of action of peroxisome proliferators as hypolipidemic drugs.
Suppression of apolipoprotein C-III. J Biol Chem. 270:13470–13475.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen WL, Wei HW, Chiu WZ, Kang CH, Lin TH,
Hung CC, Chen MC, Shieh MS, Lee CC and Lee HM: Metformin regulates
hepatic lipid metabolism through activating AMP-activated protein
kinase and inducing ATGL in laying hens. Eur J Pharmacol.
671:107–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Musi N, Hirshman MF, Nygren J, Svanfeldt
M, Bavenholm P, Rooyackers O, Zhou G, Williamson JM, Ljunqvist O,
Efendic S, et al: Metformin increases AMP-activated protein kinase
activity in skeletal muscle of subjects with type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes. 51:2074–2081. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schreurs M, Kuipers F and van der Leij FR:
Regulatory enzymes of mitochondrial beta-oxidation as targets for
treatment of the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev. 11:380–388. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Clarke SD and Jump DB: Regulation of gene
transcription by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prog Lipid Res.
32:139–149. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lingvay I, Raskin P and Szczepaniak LS:
Effect of insulin-metformin combination on hepatic steatosis in
patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications.
21:137–142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bhalla K, Hwang BJ, Dewi RE, Twaddel W,
Goloubeva OG, Wong KK, Saxena NK, Biswal S and Girnun GD: Metformin
prevents liver tumorigenesis by inhibiting pathways driving hepatic
lipogenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 5:544–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roden M: Mechanisms of disease: Hepatic
steatosis in type 2 diabetes - pathogenesis and clinical relevance.
Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2:335–348. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He J, Jiang H, Tansey JT, Tang C, Pu S and
Xu G: Calyculin and okadaic acid promote perilipin phosphorylation
and increase lipolysis in primary rat adipocytes. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1761:247–255. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sztalryd C, Xu G, Dorward H, Tansey JT,
Contreras JA, Kimmel AR and Londos C: Perilipin A is essential for
the translocation of hormone-sensitive lipase during lipolytic
activation. J Cell Biol. 161:1093–1103. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ren T, He J, Jiang H, Zu L, Pu S, Guo X
and Xu G: Metformin reduces lipolysis in primary rat adipocytes
stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-α or isoproterenol. J Mol
Endocrinol. 37:175–183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F,
Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L and Kahn BB: Serum
retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 436:356–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fischer CP, Perstrup LB, Berntsen A,
Eskildsen P and Pedersen BK: Elevated plasma interleukin-18 is a
marker of insulin-resistance in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic
humans. Clin Immunol. 117:152–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cho YM, Youn BS, Lee H, Lee N, Min SS,
Kwak SH, Lee HK and Park KS: Plasma retinol-binding protein-4
concentrations are elevated in human subjects with impaired glucose
tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 29:2457–2461. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gavi S, Stuart LM, Kelly P, Melendez MM,
Mynarcik DC, Gelato MC and McNurlan MA: Retinol-binding protein 4
is associated with insulin resistance and body fat distribution in
nonobese subjects without type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
92:1886–1890. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tajtáková M, Semanová Z, Ivancová G,
Petrovicová J, Donicová V and Zemberová E: Serum level of
retinol-binding protein 4 in obese patients with insulin resistance
and in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin. Vnitr
Lek. 53:960–963. 2007.[(In Slovak)]. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fang P, Shi M, Yu M, Guo L, Bo P and Zhang
Z: Endogenous peptides as risk markers to assess the development of
insulin resistance. Peptides. 51:9–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Stoffers DA: The development of beta-cell
mass: Recent progress and potential role of GLP-1. Horm Metab Res.
36:811–821. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel
R, Rizza RA and Butler PC: Beta-cell deficit and increased
beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.
52:102–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cozar-Castellano I, Fiaschi-Taesch N,
Bigatel TA, Takane KK, Garcia-Ocaña A, Vasavada R and Stewart AF:
Molecular control of cell cycle progression in the pancreatic
beta-cell. Endocr Rev. 27:356–370. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kahn SE, Hull RL and Utzschneider KM:
Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2
diabetes. Nature. 444:840–846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Marselli L,
Lupi R, Masini M, Pollera M, Bugliani M, Boggi U, Vistoli F, Mosca
F and Del Prato S: Pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic patients
have functional defects and increased apoptosis that are
ameliorated by metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:5535–5541.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kral JG, Thung SN, Biron S, Hould FS,
Lebel S, Marceau S, Simard S and Marceau P: Effects of surgical
treatment of the metabolic syndrome on liver fibrosis and
cirrhosis. Surgery. 135:48–58. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kirpichnikov D, McFarlane SI and Sowers
JR: Metformin: An update. Ann Intern Med. 137:25–33. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|