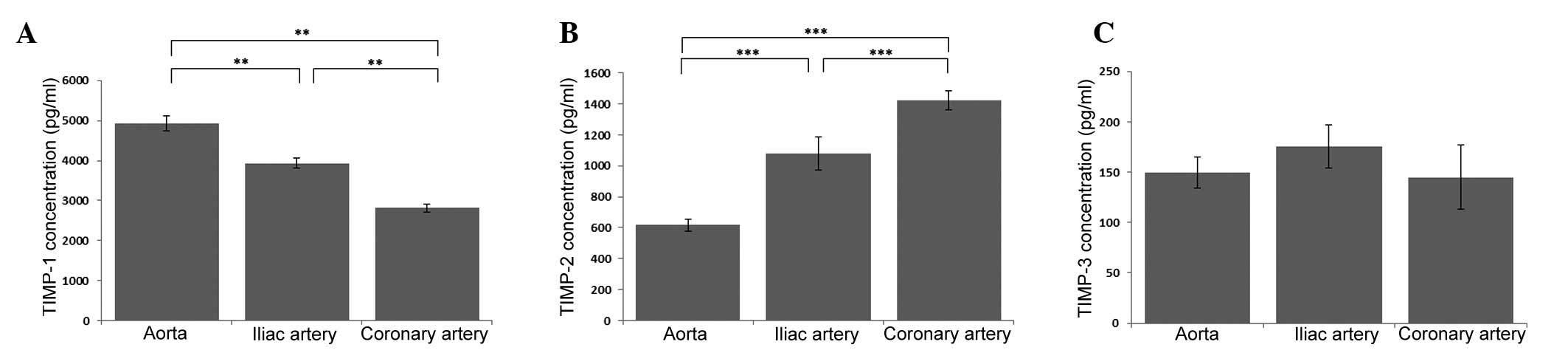
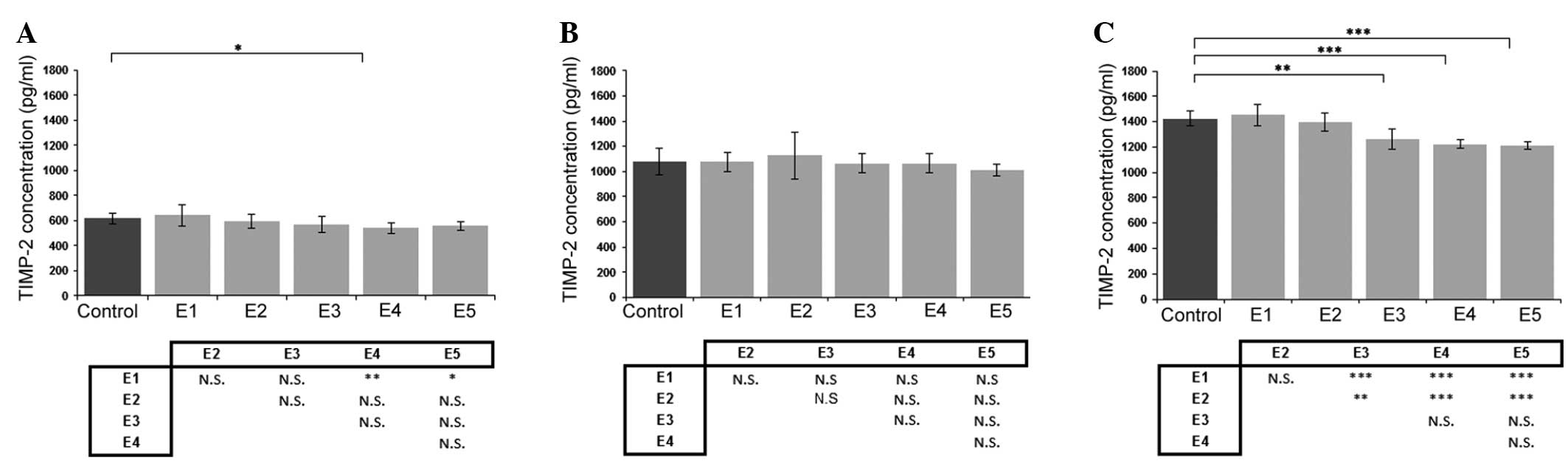
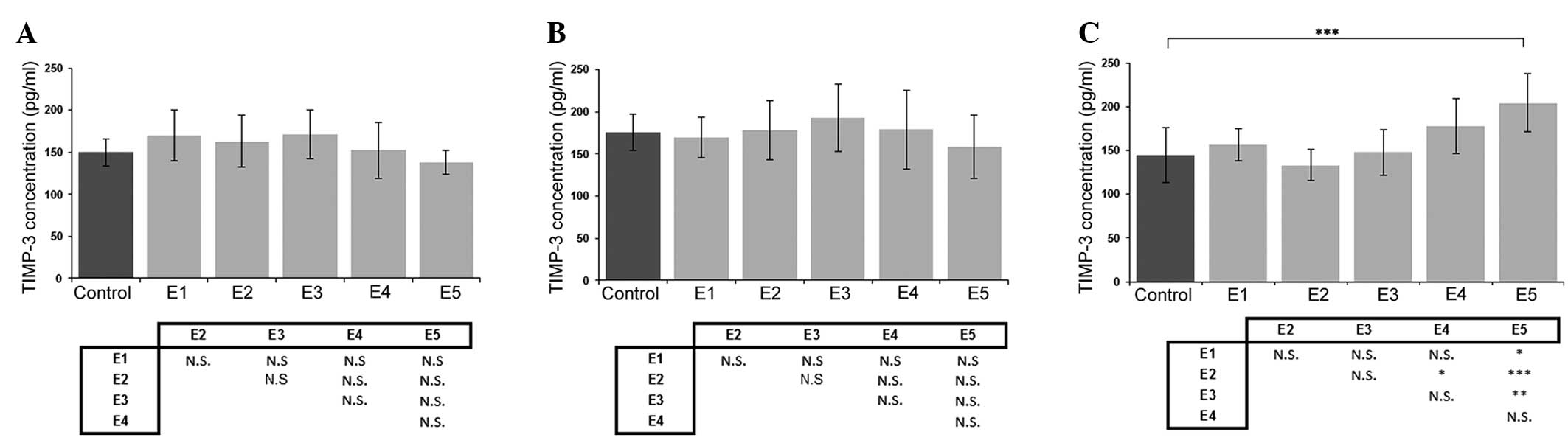
|
1
|
Ganea E, Trifan M, Laslo AC, Putina G and
Cristescu C: Matrix metalloproteinases: useful and deleterious.
Biochem Soc Trans. 35:689–691. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raffetto JD and Khalil RA: Matrix
metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and
vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:346–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Troeberg L and Nagase H: Analysis of TIMP
expression and activity. Methods Mol Med. 135:251–267. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: The tumor
microenvironment: regulation by MMP-independent effects of tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:57–66.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shen Q, Lee ES, Pitts RL, Wu MH and Yuan
SY: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 regulates matrix
metalloproteinase-2-mediated endothelial barrier dysfunction and
breast cancer cell transmigration through lung microvascular
endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 8:939–951. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seo DW, Li H, Guedez L, Wingfield PT, et
al: TIMP-2 mediated inhibition of angiogenesis: an MMP-independent
mechanism. Cell. 114:171–180. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kallio JP, Hopkins-Donaldson S, Baker AH
and Kahari VM: TIMP-3 promotes apoptosis in nonadherent small cell
lung carcinoma cells lacking functional death receptor pathway. Int
J Cancer. 128:991–996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grundy SM: National Cholesterol Education
Program (NCEP) - The National Cholesterol Guidelines in 2001, Adult
Treatment Panel (ATP) III: Approach to lipoprotein management in
2001 National Cholesterol Guidelines. Am J Cardiol. 90:11i–21i.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis - an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hornebeck W and Robert L: Elastase-like
enzymes in aortas and human breast carcinomas: quantitative
variations with age and pathology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 79:145–164.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gayral S, Garnotel R, Castaing-Berthou A,
et al: Elastin-derived peptides potentiate atherosclerosis through
the immune Neu1-PI3K൧ pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 102:118–127. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gminski J and Drozdz M: Succinyl
trialanine p-nitroanilide hydrolytic activities in plasma and the
aorta of rabbits experimentally immunized with soluble elastin. Exp
Pathol. 43:37–40. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Faury G, Ristori MT, Verdetti J, Jacob MP
and Robert L: Effect of elastin peptides on vascular tone. J Vasc
Res. 32:112–119. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Faury G, Garnier S, Weiss AS, et al:
Action of tropoelastin and synthetic elastin sequences on vascular
tone and on free Ca2+ level in human vascular
endothelial cells. Circ Res. 82:328–336. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Robert L, Labat-Robert J and Robert AM:
Genetic, epigenetic and posttranslational mechanisms of aging.
Biogerontology. 11:387–399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Siemianowicz K, Gminski J, Goss M, Francuz
T, Likus W, Jurczak T and Garczorz W: Influence of elastin-derived
peptides on metalloprotease production in endothelial cells. Exp
Ther Med. 1:1057–1060. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Robinet A, Fahem A, Cauchard J-H, et al:
Elastin-derived peptides enhance angiogenesis by promoting
endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis through upregulation
of MT1-MMP. J Cell Sci. 118:343–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mieczkowska J, Mosiewicz J, Barud W and
Kwasniewski W: Changes in the activity of connective tissue matrix
enzymes in the metabolic syndrome. Arch Med Sci. 7:634–641. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
de la Sierra A and Larrousse M:
Endothelial dysfunction is associated with increased levels of
biomarkers in essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 24:373–379.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ragino IuI, Cherniavskiĭ AM, Polonskaia
IaV, Volkov AM, Kashtanova EV, Tsymbal SIu and Polovnikova EM:
Inflammatory-destructive biomarkers of atherosclerotic plaques
instability. Study of arterial wall and blood. Kardiologiia.
52:37412012.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zou Y, Qi Y, Roztocil E and Davies MG:
Patterns of gelatinase activation induced by injury in the murine
femoral artery. J Surg Res. 154:135–142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zou Y, Fu Y and Davies MG: Role for Gᵝᵧ
G-proteins in protease regulation during remodeling of the murine
femoral artery. J Surg Res. 178:40–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Moore R, Hawley A, Sigler R, Farris D,
Wrobleski S, Ramacciotti E and Myers D: Tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 is an early marker of acute endothelial
dysfunction in a rodent model of venous oxidative injury. Ann Vasc
Surg. 23:498–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Misra S, Fu AA, Misra KD, Shergill UM,
Leof EB and Mukhopadhyay D: Hypoxia-induced phenotypic switch of
fibroblasts to myofibroblasts through a matrix metalloproteinase
2/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-mediated pathway:
implications for venous neointimal hyperplasia in hemodialysis
access. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 21:896–902. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mammi C, la Sala A, Volterrani M, et al:
Exercise training reduces serum capacity to induce endothelial cell
death in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail.
13:642–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ramirez Correa GA, Zacchigna S, Arsic N,
Zentilin L, Salvi A, Sinagra G and Giacca M: Potent inhibition of
arterial intimal hyperplasia by TIMP1 gene transfer using AAV
vectors. Mol Ther. 9:876–884. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Seo DW, Saxinger WC, Guedez L, Cantelmo
AR, Albini A and Stetler-Stevenson WG: An integrin-binding
N-terminal peptide region of TIMP-2 retains potent angio-inhibitory
and anti-tumorigenic activity in vivo. Peptides. 32:1840–1848.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qi JH, Ebrahem Q, Ali M, et al: Tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 peptides inhibit angiogenesis and
choroidal neovascularization in mice. PLoS One. 8:e556672013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vacek TP, Gillespie W, Tyagi N, Vacek JC
and Tyagi SC: Hydrogen sulfide protects against vascular remodeling
from endothelial damage. Amino Acids. 39:1161–1169. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Basu P, Qipshidze N, Sen U, Givvimani S,
Munjal C, Mishra PK and Tyagi SC: Chronic hyperhomocysteinemia
causes vascular remodelling by instigating vein phenotype in
artery. Arch Physiol Biochem. 117:270–282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lemaitre V, Dabo AJ and D'Armiento J:
Cigarette smoke components induce matrix metalloproteinases-1 in
aortic endothelial cells through inhibition of mTOR signaling.
Toxicol Sci. 123:542–549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
George SJ, Wan S, Hu J, MacDonald R,
Johnson JL and Baker AH: Sustained reduction of vein graft
neointima formation by ex vivo TIMP-3 gene therapy. Circulation.
124:(Suppl). S135–S142. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|