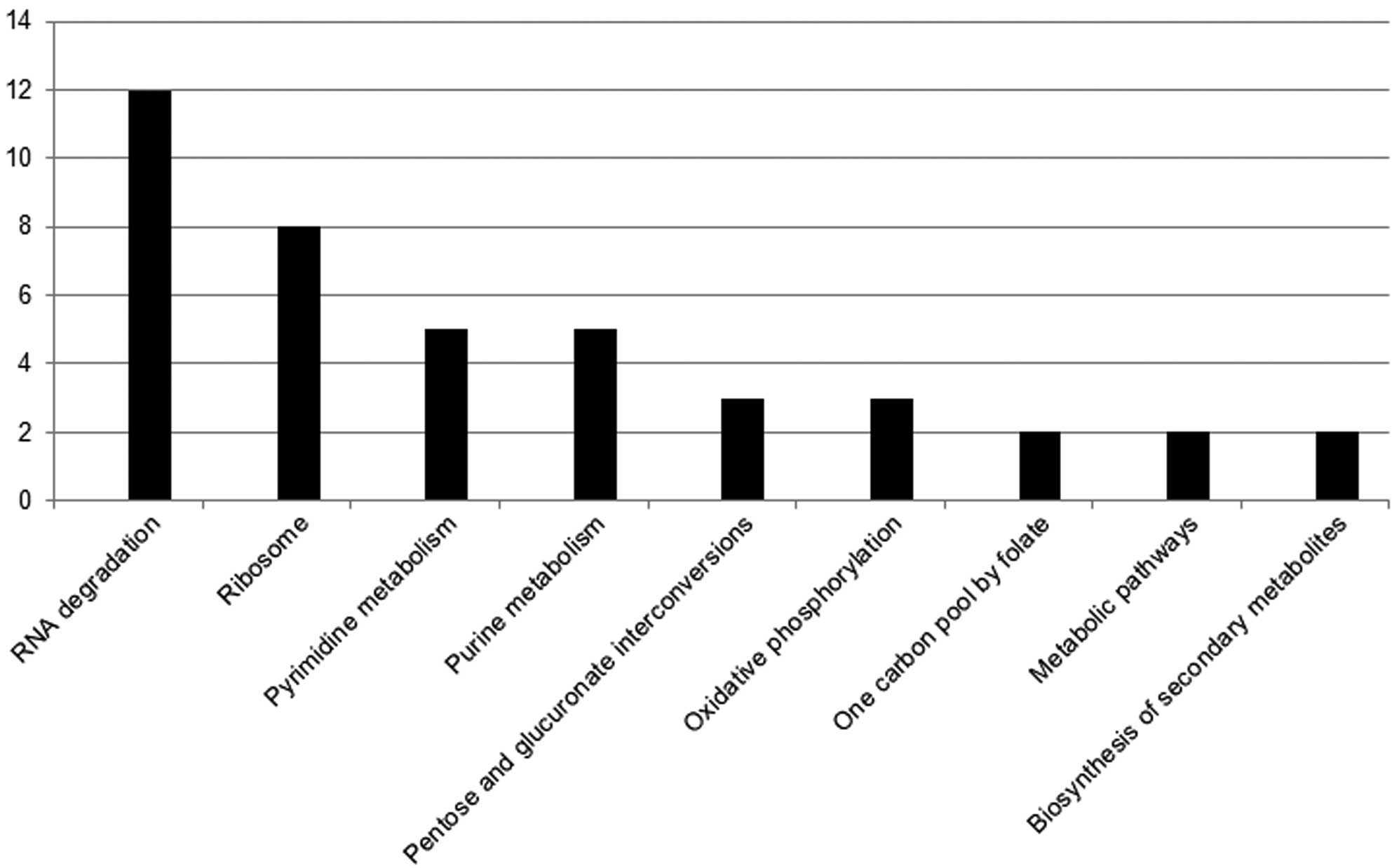
|
1
|
Staats JJ, Feder I, Okwumabua O and
Chengappa MM: Streptococcus suis: Past and present. Vet Res Commun.
21:381–407. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Busque P, Higgins R, Caya F and Quessy S:
Immunization of pigs against Streptococcus suis serotype 2
infection using a live avirulent strain. Can J Vet Res. 61:275–279.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vecht U, Stockhofe-Zurwieden N, Tetenburg
BJ, Wisselink HJ and Smith HE: Virulence of Streptococcus suis type
2 for mice and pigs appeared host-specific. Vet Microbiol.
58:53–60. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gottschalk M, Xu J, Calzas C and Segura M:
Streptococcus suis: A new emerging or an old neglected zoonotic
pathogen? Future Microbiol. 5:371–391. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sanchez S and Demain AL: Metabolic
regulation and overproduction of primary metabolites. Microb
Biotechnol. 1:283–319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Willenborg J, de Greeff A, Jarek M,
Valentin-Weigand P and Goethe R: The CcpA regulon of Streptococcus
suis reveals novel insights into the regulation of the
streptococcal central carbon metabolism by binding of CcpA to two
distinct binding motifs. Mol Microbiol. 92:61–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaufman GE and Yother J: CcpA-dependent
and -independent control of beta-galactosidase expression in
Streptococcus pneumoniae occurs via regulation of an upstream
phosphotransferase system-encoding operon. J Bacteriol.
189:5183–5192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sumby P, Barbian KD, Gardner DJ, et al:
Extracellular deoxyribonuclease made by group A Streptococcus
assists pathogenesis by enhancing evasion of the innate immune
response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:1679–1684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Willenborg J, Fulde M, de Greeff A, et al:
Role of glucose and CcpA in capsule expression and virulence of
Streptococcus suis. Microbiology. 157:1823–1833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seidl K, Stucki M, Ruegg M, et al:
Staphylococcus aureus CcpA affects virulence determinant production
and antibiotic resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
50:1183–1194. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iyer R, Baliga NS and Camilli A:
Catabolite control protein A (CcpA) contributes to virulence and
regulation of sugar metabolism in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J
Bacteriol. 187:8340–8349. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Varga J, Stirewalt VL and Melville SB: The
CcpA protein is necessary for efficient sporulation and enterotoxin
gene (cpe) regulation in Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol.
186:5221–5229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Warner JB and Lolkema JS: CcpA-dependent
carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
67:475–490. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van der Voort M, Kuipers OP, Buist G, de
Vos WM and Abee T: Assessment of CcpA-mediated catabolite control
of gene expression in Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579. BMC Microbiol.
8:622008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jankovic I, Egeter O and Brückner R:
Analysis of catabolite control protein A-dependent repression in
Staphylococcus xylosus by a genomic reporter gene system. J
Bacteriol. 183:580–586. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zomer AL, Buist G, Larsen R, Kok J and
Kuipers OP: Time-resolved determination of the CcpA regulon of
Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris MG1363. J Bacteriol.
189:1366–1381. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abranches J, Nascimento MM, Zeng L, et al:
CcpA regulates central metabolism and virulence gene expression in
Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 190:2340–2349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Behari J and Youngman P: A homolog of CcpA
mediates catabolite control in Listeria monocytogenes but not
carbon source regulation of virulence genes. J Bacteriol.
180:6316–6324. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen C, Tang J, Dong W, et al: A glimpse
of streptococcal toxic shock syndrome from comparative genomics of
S. suis 2 Chinese isolates. PLoS One. 2:e3152007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lang X, Wan Z, Bu Z and Wang X and Wang X,
Zhu L, Wan J, Sun Y and Wang X: Catabolite control protein A is an
important regulator of metabolism in Streptococcus suis type 2.
Biomed Rep. 2:709–712. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang J, Wang C, Feng Y, et al:
Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis
serotype 2. PLoS Med. 3:e1512006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sriskandan S and Slater JD: Invasive
disease and toxic shock due to zoonotic Streptococcus suis: An
emerging infection in the East? PLoS Med. 3:e1872006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ren C, Gu Y, Wu Y, Zhang W, Yang C, Yang S
and Jiang W: Pleiotropic functions of catabolite control protein
CcpA in Butanol-producing Clostridium acetobutylicum. BMC Genomics.
13:3492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Poncet S, Milohanic E, Mazé A, et al:
Correlations between carbon metabolism and virulence in bacteria.
Contrib Microbiol. 16:88–102. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Dang Y, Wang X, et al: Comparative
proteomic analyses of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 cell
wall-associated proteins. Curr Microbiol. 62:578–588. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deutscher J, Herro R, Bourand A, Mijakovic
I and Poncet S: P-Ser-HPr - A link between carbon metabolism and
the virulence of some pathogenic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1754:118–125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Seidel G, Diel M, Fuchsbauer N and Hillen
W: Quantitative interdependence of coeffectors, CcpA and cre in
carbon catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J.
272:2566–2577. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Blencke HM, Homuth G, Ludwig H, et al:
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose
in Bacillus subtilis: Regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng. 5:133–149. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kraus A, Hueck C, Gärtner D and Hillen W:
Catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis xyl operon involves
a cis element functional in the context of an unrelated sequence
and glucose exerts additional xylR-dependent repression. J
Bacteriol. 176:1738–1745. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoshida K, Kobayashi K, Miwa Y, et al:
Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis as a powerful approach
to study genes under glucose repression in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res. 29:683–692. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lulko AT, Buist G, Kok J and Kuipers OP:
Transcriptome analysis of temporal regulation of carbon metabolism
by CcpA in Bacillus subtilis reveals additional target genes. J Mol
Microbiol Biotechnol. 12:82–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang Y, Wu W, Zhang X, Lu Z, Chen J and
Fang W: Catabolite control protein A of Streptococcus suis type 2
contributes to sugar metabolism and virulence. J Microbiol.
50:994–1002. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|