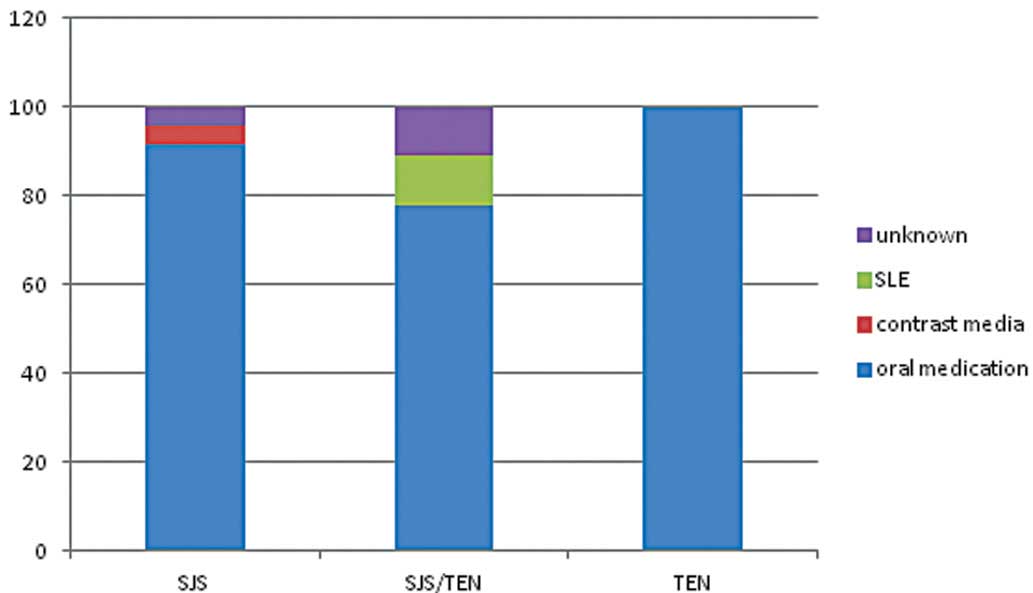
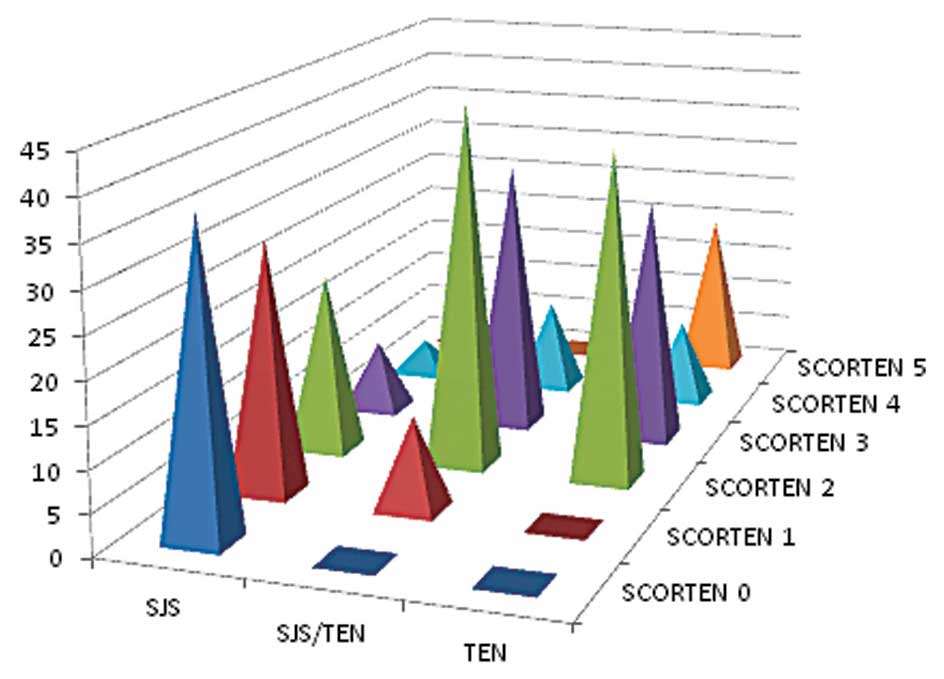
|
1
|
Mockenhaupt M: The current understanding
of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Expert
Rev Clin Immunol. 7:803–813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gerull R, Nelle M and Schaible T: Toxic
epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A review. Crit
Care Med. 39:1521–1532. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mays SR, Bogle MA and Bodey GP: Cutaneous
fungal infections in the oncology patient: Recognition and
management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 7:31–43. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bodey GP: Dermatologic manifestations of
infections in neutropenic patients. Infect Dis Clin North Am.
8:655–675. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fournier S, Bastuji-Garin S, Mentec H,
Revuz J and Roujeau JC: Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect
Dis. 14:558–559. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka A, Nakano M, Tani M, Kira M,
Katayama I, Nakagawa J, et al: Adult case of Stevens-Johnson
syndrome possibly induced by Chlamydophila pneumoniae
infection with severe involvement of bronchial epithelium resulting
in constructive respiratory disorder. J Dermatol. 40:492–494. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khalaf D, Toema B, Dabbour N and Jehani F:
Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with severe cytomegalovirus
infection in a patient on regular hemodialysis. Mediterr J Hematol
Infect Dis. 3:e20110042011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kannenberg SM, Jordaan HF, Koegelenberg
CF, Von Groote-Bidlingmaier F and Visser WI: Toxic epidermal
necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome in South Africa: A 3-year
prospective study. QJM. 105:839–846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pavlos R, Mallal S, Ostrov D, Pompeu Y and
Phillips E: Fever, rash and systemic symptoms: Understanding the
role of virus and HLA in severe cutaneous drug allergy. J Allergy
Clin Immunol Pract. 2:21–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Badia M, Trujillano J, Gascó E, Casanova
JM, Alvarez M and León M: Skin lesions in the ICU. Intensive Care
Med. 25:1271–1276. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Neff P, Meuli-Simmen C, Kempf W, Gaspert
T, Meyer VE and Künzi W: Lyell syndrome revisited: Analysis of 18
cases of severe bullous skin disease in a burns unit. Br J Plast
Surg. 58:73–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rzany B, Mockenhaupt M, Baur S, Schröder
W, Stocker U, Mueller J, et al: Epidemiology of erythema
exsudativum multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic
epidermal necrolysis in Germany (1990–1992): Structure and results
of a population-based registry. J Clin Epidemiol. 49:769–773. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schneck J, Fagot JP, Sekula P, Sassolas B,
Roujeau JC and Mockenhaupt M: Effects of treatments on the
mortality of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal
necrolysis: A retrospective study on patients included in the
prospective EuroSCAR study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 58:33–40. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M,
Roujeau JC, Revuz J and Wolkenstein P: SCORTEN: A
severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest
Dermatol. 115:149–153. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chung WH and Hung SI: Recent advances in
the genetics and immunology of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic
epidermal necrosis. J Dermatol Sci. 66:190–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Perkins JR, Ayuso P, Cornejo-Garcia JA and
Ranea JA: The study of severe cutaneous drug hypersensitivity
reactions from a systems biology perspective. Curr Opin Allergy
Clin Immunol. 14:301–306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mockenhaupt M, Viboud C, Dunant A, Naldi
L, Halevy S, Bouwes Bavinck JN, et al: Stevens-Johnson syndrome and
toxic epidermal necrolysis: assessment of medication risks with
emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSCAR-study. J Invest
Dermatol. 128:35–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen P, Lin JJ, Lu CS, Ong CT, Hsieh PF,
Yang CC, et al: Carbamazepine-induced toxic effects and HLA-B*1502
screening in Taiwan. N Engl J Med. 364:1126–1133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mallal S, Phillips E, Carosi G, Molina JM,
Workman C, Tomazic J, et al: HLA-B*5701 screening for
hypersensitivity to abacavir. N Engl J Med. 358:568–579. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hershfield MS, Callaghan JT, Tassaneeyakul
W, Mushiroda T, Thorn CF, Klein TE, et al: Clinical
Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for human
leukocyte antigen-B genotype and allopurinol dosing. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 93:153–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tassaneeyakul W, Jantararoungtong T, Chen
P, Lin PY, Tiamkao S, Khunarkornsiri U, et al: Strong association
between HLA-B*5801 and allopurinol-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome
and toxic epidermal necrolysis in a Thai population. Pharmacogenet
Genomics. 19:704–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mockenhaupt M: Severe drug-induced skin
reactions: clinical pattern, diagnostics and therapy. J Dtsch
Dermatol Ges. 7:142–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Araki Y, Sotozono C, Inatomi T, Ueta M,
Yokoi N, Ueda E, et al: Successful treatment of Stevens-Johnson
syndrome with steroid pulse therapy at disease onset. Am J
Ophthalmol. 147:1004–1011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
López-Garcia JS, Rivas Jara L,
Garcia-Lozano CI, Conesa E, de Juan IE and Murube del Castillo J:
Ocular features and histopathologic changes during follow-up of
toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ophthalmology. 118:265–271. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De Rojas MV, Dart JK and Saw VP: The
natural history of Stevens Johnson syndrome: patterns of chronic
ocular disease and the role of systemic immunosuppressive therapy.
Br J Ophthalmol. 91:1048–1053. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Prabhasawat P, Tesavibul N,
Karnchanachetanee C and Kasemson S: Efficacy of cyclosporine 0.05%
eye drops in Stevens Johnson syndrome with chronic dry eye. J Ocul
Pharmacol Ther. 29:372–377. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hague JS, Goulding JM, Long TM and Gee BC:
Respiratory involvement in toxic epidermal necrolysis portends a
poor prognosis that may not be reflected in SCORTEN. Br J Dermatol.
157:1294–1296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thong BY: Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic
epidermal necrolysis: An Asia-pacific perspective. Asia Pac
Allergy. 3:215–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
von Wild T, Stollwerck PL, Namdar T, Stang
FH, Mailänder P and Siemers F: Are multimorbidities underestimated
in scoring systems of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal
necrolysis like in SCORTEN. Eplasty. 12:e352012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee HY, Dunant A, Sekula P, Mockenhaupt M,
Wolkenstein P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al: The role of prior
corticosteroid use on the clinical course of Stevens-Johnson
syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a case-control analysis of
patients selected from the multinational EuroSCAR and RegiSCAR
studies. Br J Dermatol. 167:555–562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|