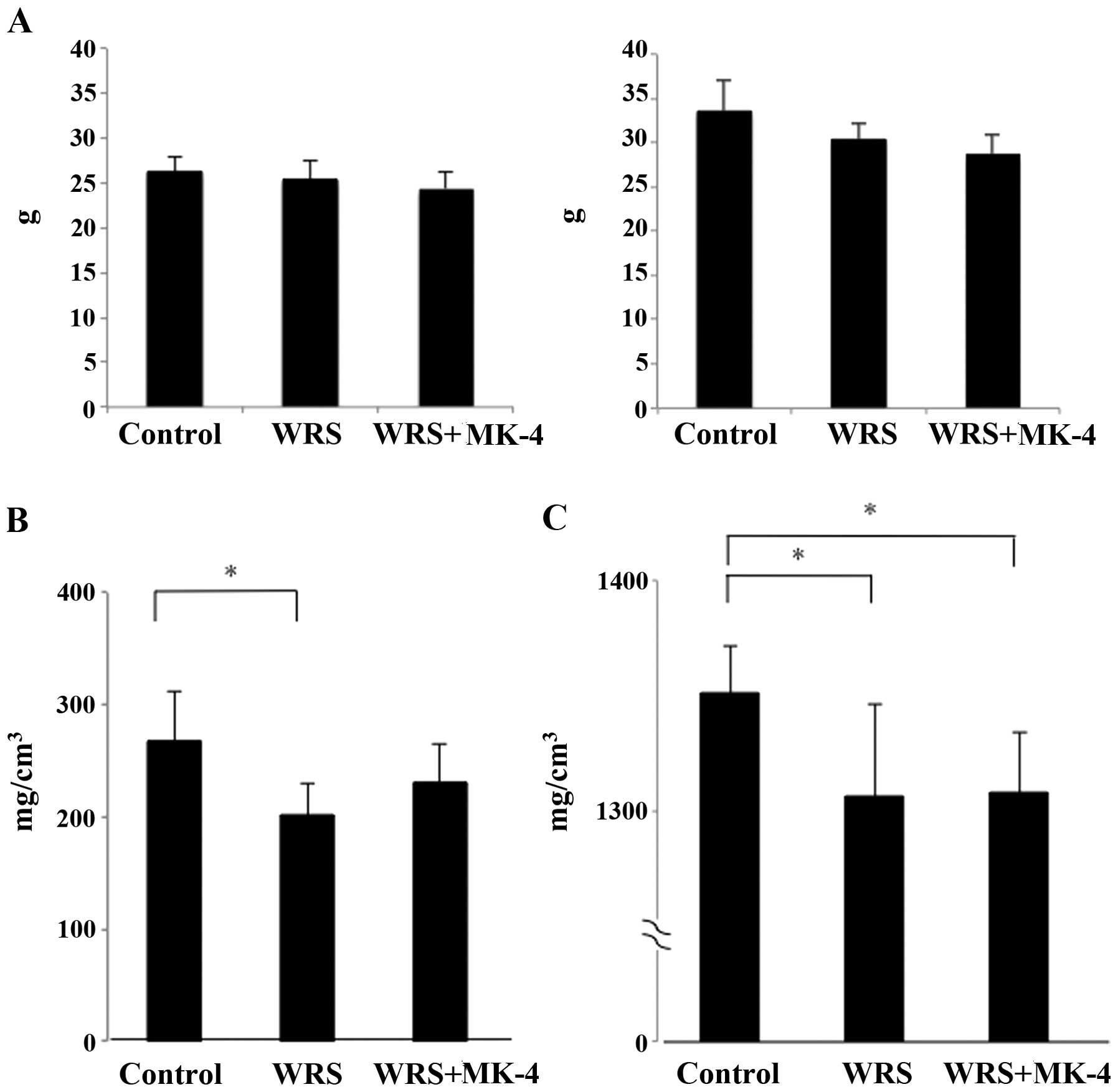
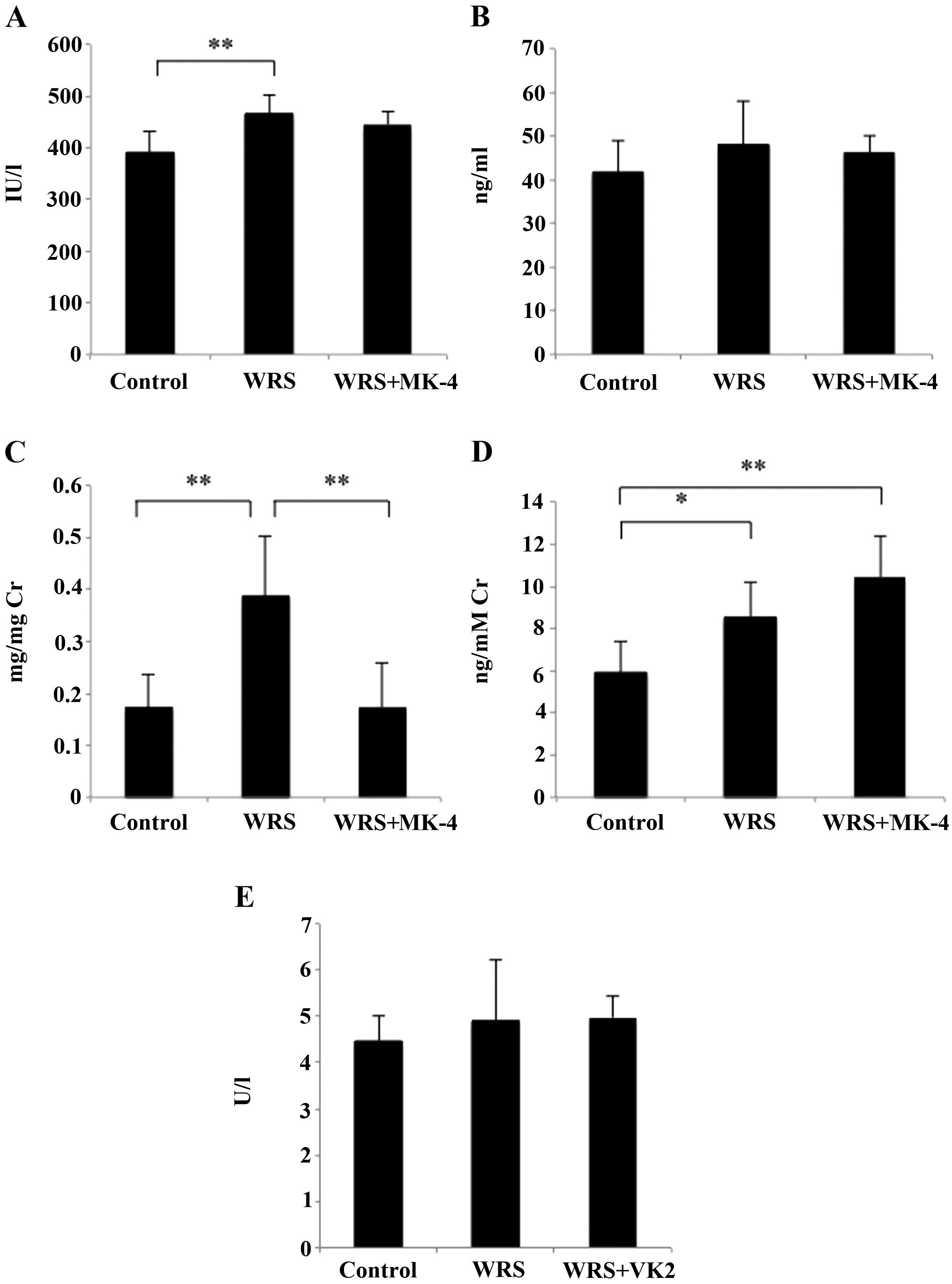
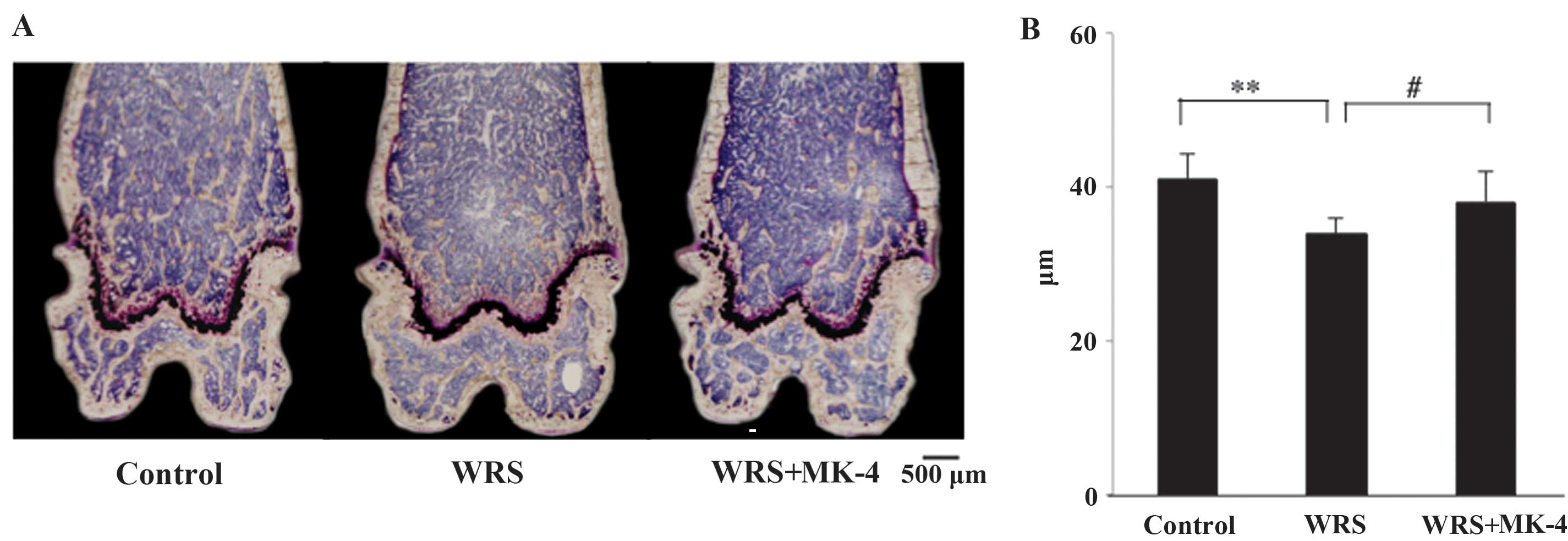
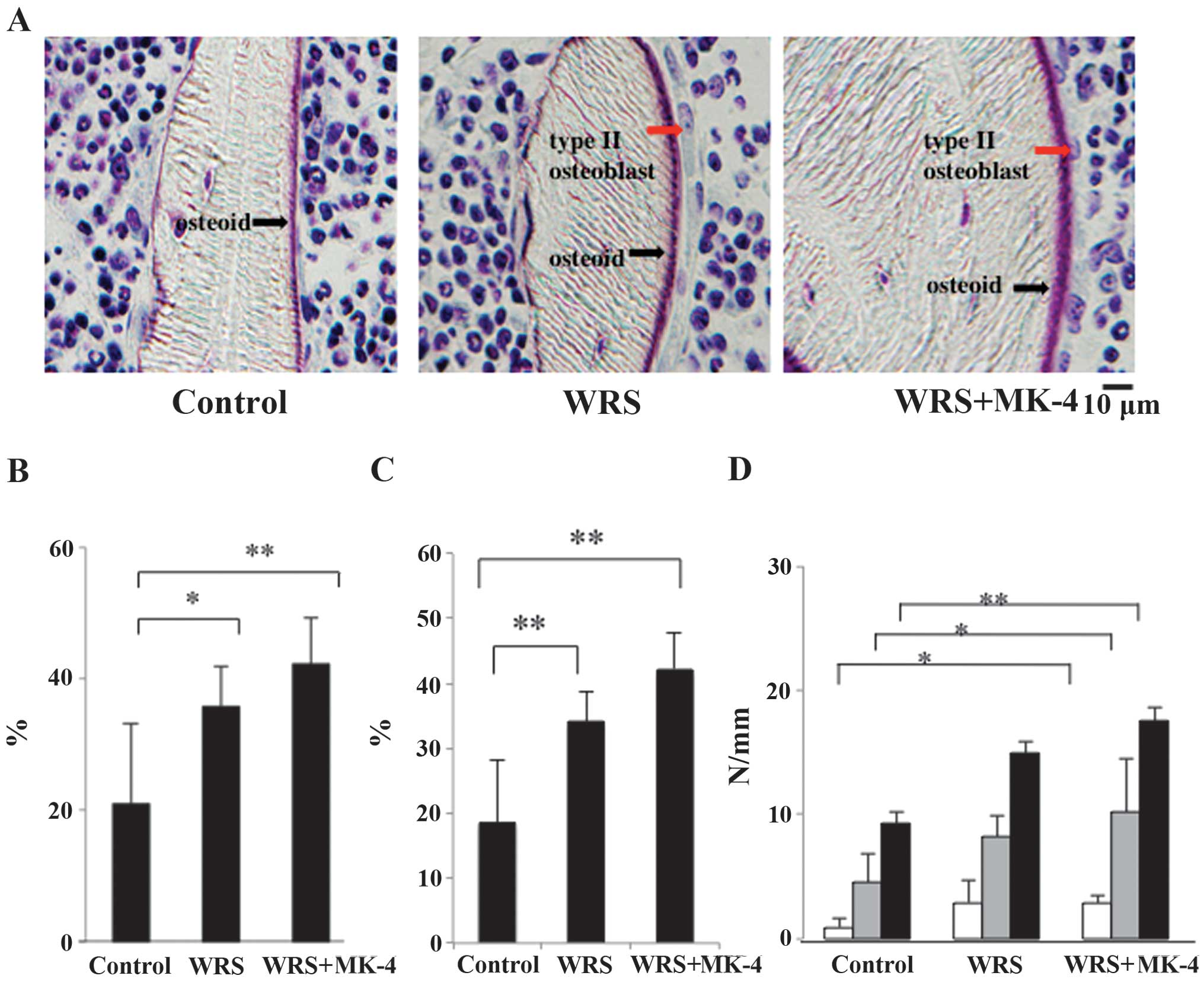
|
1
|
Knapen MH, Drummen NE, Smit E, Vermeer C
and Theuwissen E: Three-year low-dose menaquinone-7 supplementation
helps decrease bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women.
Osteoporos Int. 24:2499–2507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koshihara Y, Hoshi K, Ishibashi H and
Shiraki M: Vitamin K2 promotes 1alpha,25(OH)2 vitamin D3-induced
mineralization in human periosteal osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int.
59:466–473. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iwamoto J, Matsumoto H and Takeda T:
Efficacy of menatetrenone (vitamin K2) against non-vertebral and
hip fractures in patients with neurological diseases: Meta-analysis
of three randomized, controlled trials. Clin Drug Investig.
29:471–479. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cockayne S, Adamson J, Lanham-New S,
Shearer MJ, Gilbody S and Torgerson DJ: Vitamin K and the
prevention of fractures: Systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 166:1256–1261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Akiyama Y, Hara K, Kobayashi M, Tomiuga T
and Nakamura T: Inhibitory effect of vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) on
bone resorption in ovariectomized rats: A histomorphometric and
dual energy X-ray absorptiometric study. Jpn J Pharmacol. 80:67–74.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Azuma K, Casey SC, Ito M, Urano T, Horie
K, Ouchi Y, Kirchner S, Blumberg B and Inoue S: Pregnane X receptor
knockout mice display osteopenia with reduced bone formation and
enhanced bone resorption. J Endocrinol. 207:257–263. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu X, Moreines J and Booth SL: Vitamin K
supplementation does not prevent bone loss in ovariectomized Norway
rats. Nutr Metab (Lond). 9:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Landeira-Fernandez J: Analysis of the
cold-water restraint procedure in gastric ulceration and body
temperature. Physiol Behav. 82:827–833. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang P, Zhou ZR, Zheng MQ and Shi FX:
Effect of the IGF-1/PTEN/Akt/FoxO signaling pathway in the duodenal
mucosa of rats subjected to water immersion and restraint stress.
Genet Mol Res 11 (AOP). 4775–4788. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Szlachcic A, Sliwowski Z, Krzysiek-Maczka
G, Majka J, Surmiak M, Pajdo R, Drozdowicz D, Konturek SJ and
Brzozowski T: New satiety hormone nesfatin-1 protects gastric
mucosa against stress-induced injury: Mechanistic roles of
prostaglandins, nitric oxide, sensory nerves and vanilloid
receptors. Peptides. 49:9–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nur Azlina MF, Kamisah Y, Chua KH and
Qodriyah HM: Tocotrienol attenuates stress-induced gastric lesions
via activation of prostaglandin and upregulation of COX-1 mRNA.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:8047962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Magierowski M, Jasnos K, Pawlik M,
Krzysiek-Maczka G, Ptak-Belowska A, Olszanecki R, Kwiecien S,
Korbut R and Brzozowski T: Role of angiotensin-(1–7) in
gastroprotection against stress-induced ulcerogenesis. The
involvement of mas receptor, nitric oxide, prostaglandins and
sensory neuropeptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 347:717–726. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ohta Y, Yashiro K, Ohashi K and Imai Y:
Disruption of non-enzymatic antioxidant defense systems in the
brain of rats with water-immersion restraint stress. J Clin Biochem
Nutr. 51:136–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takeda T, Hosokawa M, Takeshita S, Irino
M, Higuchi K, Matsushita T, Tomita Y, Yasuhira K, Hamamoto H and
Shimizu K: A new murine model of accelerated senescence. Mech
Ageing Dev. 17:183–194. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsushita M, Tsuboyama T, Kasai R,
Okumura H, Yamamuro T, Higuchi K, Higuchi K, Kohno A, Yonezu T,
Utani A, et al: Age-related changes in bone mass in the
senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). SAM-R/3 and SAM-P/6 as new
murine models for senile osteoporosis. Am J Pathol. 125:276–283.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ohnishi K, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Seriu
N, Kawamata T, Nakamura S, Kimura J, Nishio T, Higuchi K and
Hosokawa M: Age-related decrease of nerve growth factor-like
immunoreactivity in the basal forebrain of senescence-accelerated
mice. Acta Neuropathol. 90:11–16. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takeda T, Hosokawa M and Higuchi K:
Senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM): A novel murine model of
senescence. Exp Gerontol. 32:105–109. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Washimi Y, Chen H, Ito A, Takao R, Uzawa
T, Yamamoto Y, Yamada H and Shoumura S: Effect of intermittent
treatment with human parathyroid hormone 1–34 in SAMP6
senescence-accelerated mice. J Encocrinol Invest. 33:395–400. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Takagi K and Okabe S: The effects of drugs
on the production and recovery processes of the stress ulcer. Jpn J
Pharmacol. 18:9–18. 1968. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parfitt AM: The cellular basis of bone
remodeling: The quantum concept reexamined in light of recent
advances in the cell biology of bone. Calcif Tissue Int 36. (Suppl
1):37–45. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kawamori Y, Katayama Y, Asada N, Minagawa
K, Sato M, Okamura A, Shimoyama M, Nakagawa K, Okano T, Tanimoto M,
et al: Role for vitamin D receptor in the neuronal control of the
hematopoietic stem cell niche. Blood. 116:5528–5535. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dempster DW, Compston JE, Drezner MK,
Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR
and Parfitt AM: Standardized nomenclature, symbols and units for
bone histomorphometry: A 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR
Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res. 28:2–17.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duque G, Macoritto M, Dion N, Ste-Marie LG
and Kremer R: 1,25(OH)2D3 acts as a bone-forming agent in the
hormone-independent senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM-P/6). Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 288:E723–E730. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tomita M, Katsuyama H, Okuyama T, Watanabe
Y, Hidaka K, Otsuki T and Nata M: The effect of CAG repeat
polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor on stress responses of
mice exposed to water-immersion restraint stress. Int J Mol Med.
25:415–420. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sasaki H, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Maekawa
S, Noguchi H, Kamo K and Shimada Y: Effects of combination
treatment with alendronate and vitamin K2 on bone mineral density
and strength in ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Metab.
28:403–409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tomimori Y, Mori K, Koide M, Nakamichi Y,
Ninomiya T, Udagawa N and Yasuda H: Evaluation of pharmaceuticals
with a novel 50-hour animal model of bone loss. J Bone Miner Res.
24:1194–1205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sakata T, Sakai A, Tsurukami H, Okimoto N,
Okazaki Y, Ikeda S, Norimura T and Nakamura T: Trabecular bone
turnover and bone marrow cell development in tail-suspended mice. J
Bone Miner Res. 14:1596–1604. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ohsaki Y, Shirakawa H, Miura A, Giriwono
PE, Sato S, Ohashi A, Iribe M, Goto T and Komai M: Vitamin K
suppresses the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of
inflammatory cytokines in cultured macrophage-like cells via the
inhibition of the activation of nuclear factor κB through the
repression of IKKα/β phosphorylation. J Nutr Biochem. 21:1120–1126.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ichikawa T, Horie-Inoue K, Ikeda K,
Blumberg B and Inoue S: Vitamin K2 induces phosphorylation of
protein kinase A and expression of novel target genes in
osteoblastic cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 39:239–247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Iwamoto J, Matsumoto H, Tadeda T, Sato Y
and Yeh JK: Comparison of the effect of vitamin K(2) and
residronate on trabecular bone in glucocorticoid-treated rats: A
bone histomorphometry study. Yonsei Med J. 50:189–194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Katsuyama H, Saijoh K, Otsuki T, Tomita M,
Fukunaga M and Sunami S: Menaquinone-7 regulates gene expression in
osteoblastic MC3T3E1 cells. Int J Mol Med. 19:279–284.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Atkins GJ, Welldon KJ, Wijenayaka AR,
Bonewald LF and Findlay DM: Vitamin K promotes mineralization,
osteoblast-to-osteocyte transition and an anticatabolic phenotype
by {gamma}-carboxylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 297:C1358–C1367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koshihara Y, Hoshi K, Okawara R, Ishibashi
H and Yamamoto S: Vitamin K stimulates osteoblastogenesis and
inhibits osteoclastogenesis in human bone marrow cell culture. J
Endocrinol. 176:339–348. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|